Dynamic train tracking interval calculation method
A train and dynamic technology, applied in railway car body parts, railway signal and safety, transportation center control system, etc., can solve the problems of inability to meet the timeliness of scheduling adjustment, unfavorable rapid relief of backlog traffic, and limited manual scheduling operations. , to reduce train delay time, meet refinement requirements, and improve comfort
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
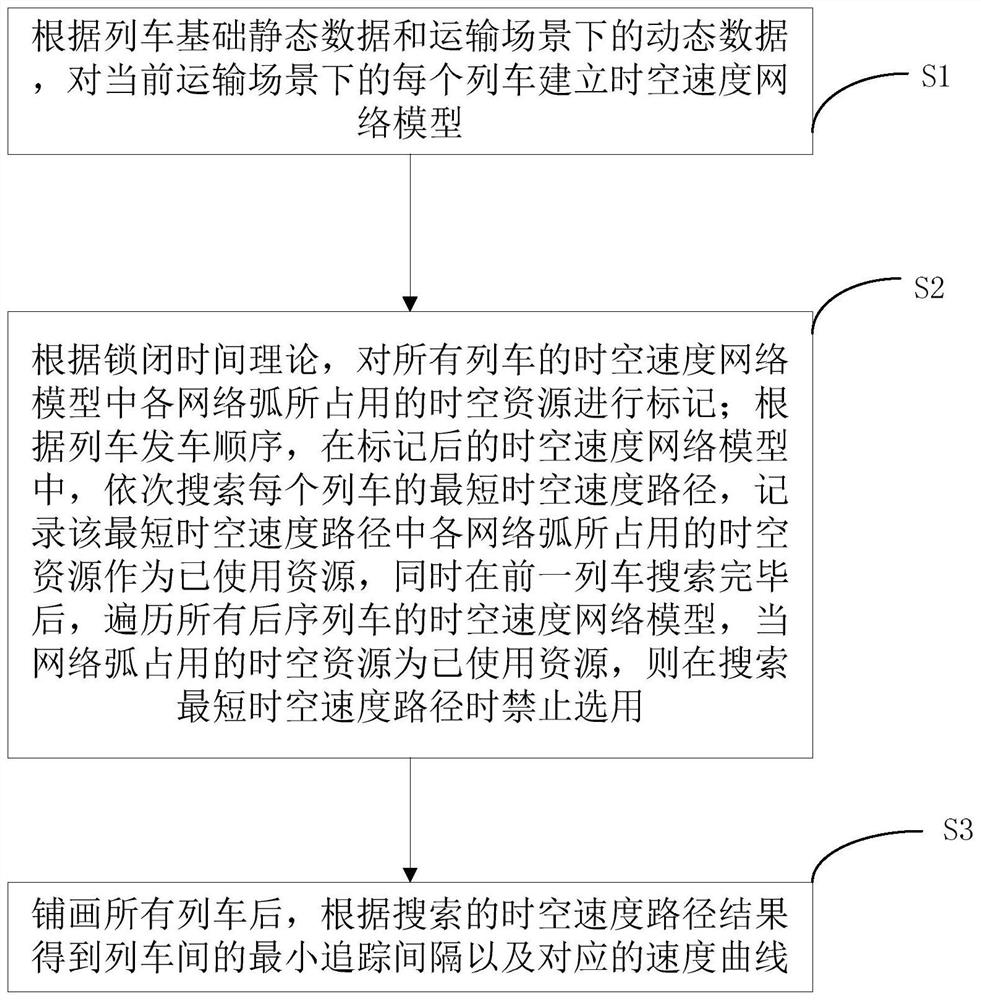
[0056] figure 1 For the flow chart of the dynamic train tracking interval calculation method of the present embodiment, refer to figure 1 , the method includes:
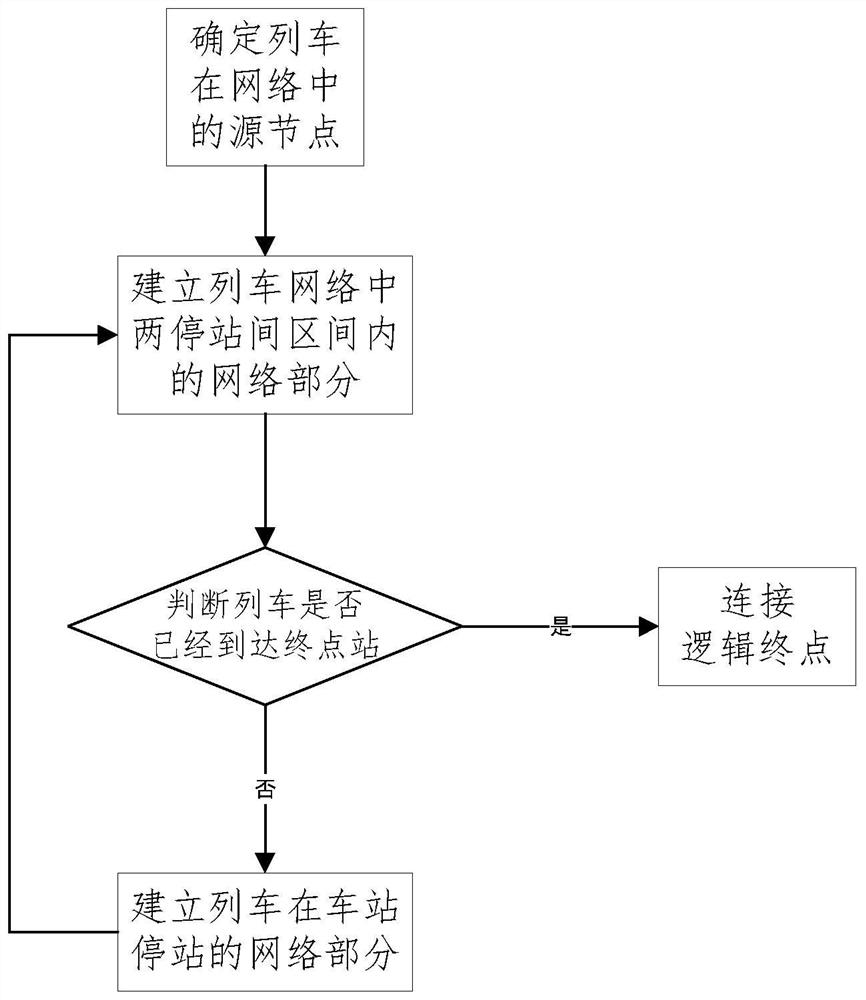
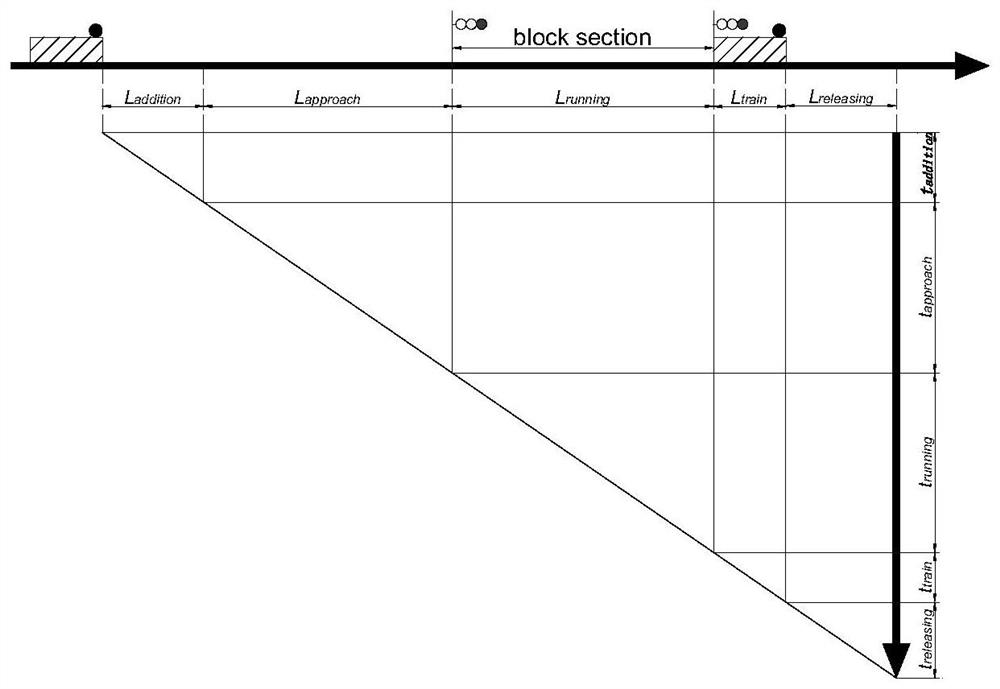
[0057] S1 establishes a space-time velocity network model for each train in the current transportation scenario based on the basic static data of the train and the dynamic data in the transportation scenario.
[0058] Basic static data of trains include: connection relationship of high-speed railway stations, engineering data information of incoming and outgoing routes at stations, basic speed limit of railway lines, engineering data information of blocked sections, length of each train, minimum and maximum acceleration of each train, braking curve of each train Calculation formulas and formula parameters;
[0059] The dynamic data in the transportation scene include: the spatial position and speed of each train collected by the signal system when the network is established, the range of the temporary speed limit t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com