Saccharomyces cerevisiae for industrial production with high organic acid tolerance and construction method thereof
A technology of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains, which is applied in the field of Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains for industrial production and its construction, can solve the problems of product quality reduction, harm to Saccharomyces cerevisiae physiology and metabolism, and affect the quality of fermentation products, and achieve the goal of improving tolerance Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
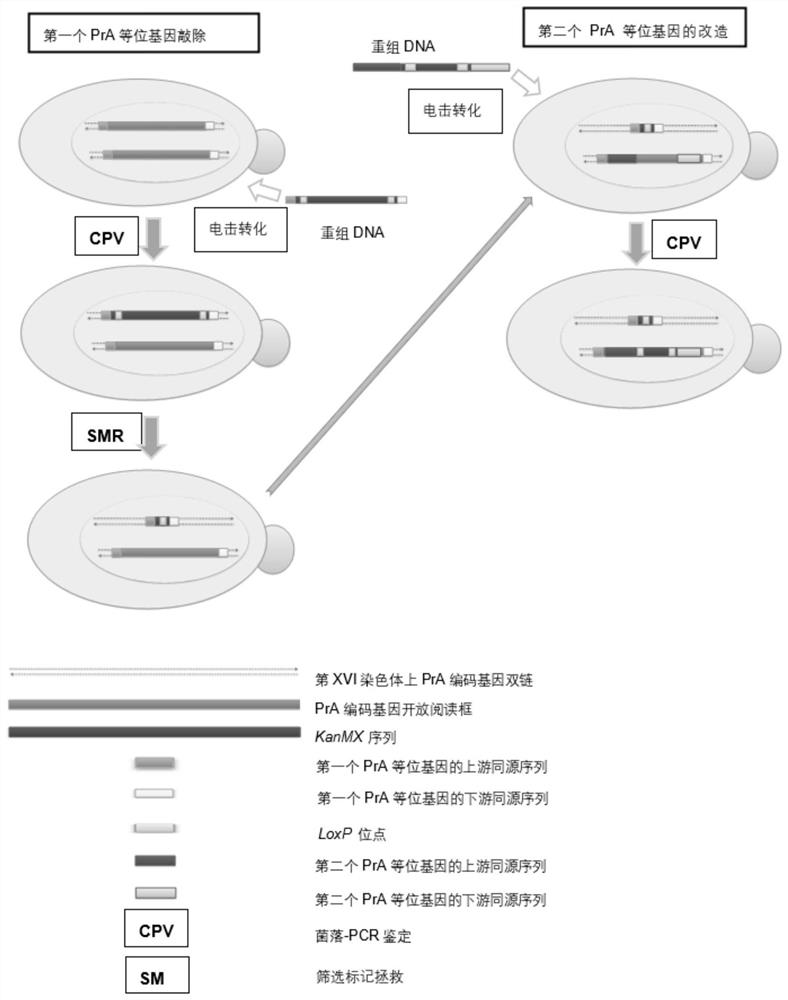
[0067] Construction of a PrA-encoding allele knockout and a PrA-encoding allele-modified strain
[0068] (1) Knockout of PrA encoding allele
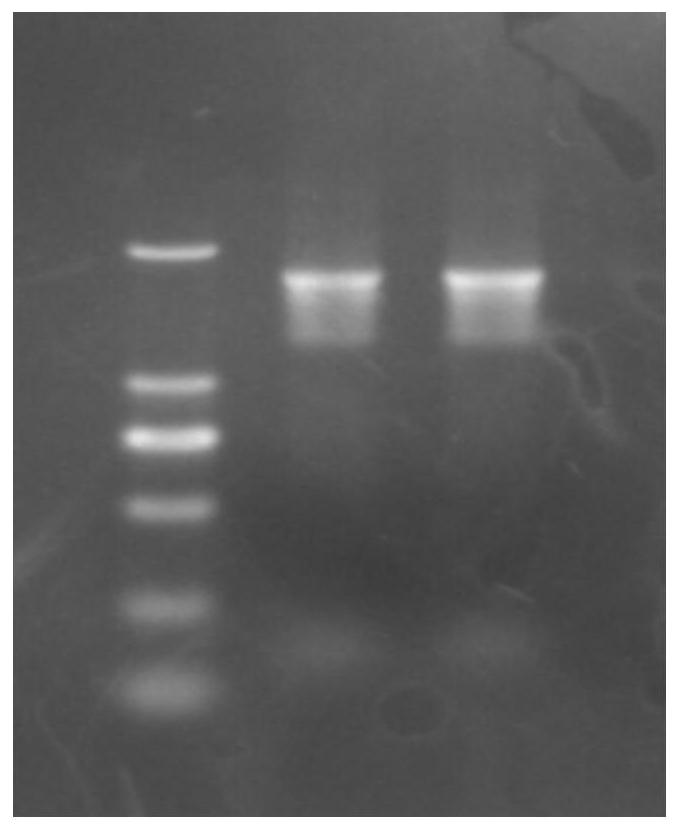
[0069] ① Using the plasmid pUG6 as the template, PCR amplify the kanamycin-resistant fragment, add homology arms before and after the sequence, for the PrA coding allele PEP4 (the full-length sequence in the genome is SEQ ID NO: 1 , including the knockout of the original 1kb promoter coding region and the original 1kb terminator coding region), the amplified DNA fragment is "REC-Kan";
[0070] Upstream primer Rec-F:
[0071] 5'-GTATTTAATCCAAATAAAATTCAAACAAAAACCAAAACTAACATGCAGCTGAAGCTTCGTACGC-3', SEQ ID NO: 3;
[0072] Downstream primer Rec-R:
[0073] 5'-ATGGCAGAAAAGGATAGGGCGGAGAAGTAAGAAAAGTTTAGCTCGCATAGGCCACTAGTGGATCTG-3', SEQ ID NO: 4
[0074] Bold parts are homology arms
[0075] The PCR reaction conditions were: 94°C for 5 minutes, 94°C for 30 seconds, 58°C for 40 seconds, 72°C for 1 minute and 50 seconds (30 cycles), and 72°C ...
Embodiment 2
[0131] Comparison of organic acid tolerance in liquid culture
[0132] Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains SWY85, SWY85F and SWY-ZH were activated and cultured in YPD liquid medium with natural acidity, and the culture conditions were 30°C and 160rpm for 48 hours. YPD medium and synthetic nitrogen-limited medium (SD medium) were adjusted to pH 30 and 27 with citric acid, tartaric acid, and malic acid, respectively, and the strains that had been previously activated with natural acidity YPD liquid medium were inoculated at 01% inoculum size Cells were cultured in YPD liquid medium with natural acidity and in liquid YPD medium with pH adjusted to 30 and 27 using organic acid, and cultured at 30°C and 160rpm to the middle and late logarithmic growth period, and the cell growth amount (OD) was determined. 600 value), and the amount of cell growth (OD) in YPD medium with natural acidity for the same time period 600 value) is the control, and the calculation of the cell growth inhibit...
Embodiment 3
[0134] Comparison of organic acid tolerance in solid culture
[0135] Preparation of medium: Refer to the liquid culture acid tolerance part of the experiment to prepare the medium. The solid medium needs to add 2% agar to the liquid medium for solidification. After adjusting the pH of the solid YPD medium to 30 and 27 with citric acid, tartaric acid and malic acid, respectively, the plate was poured out for use.
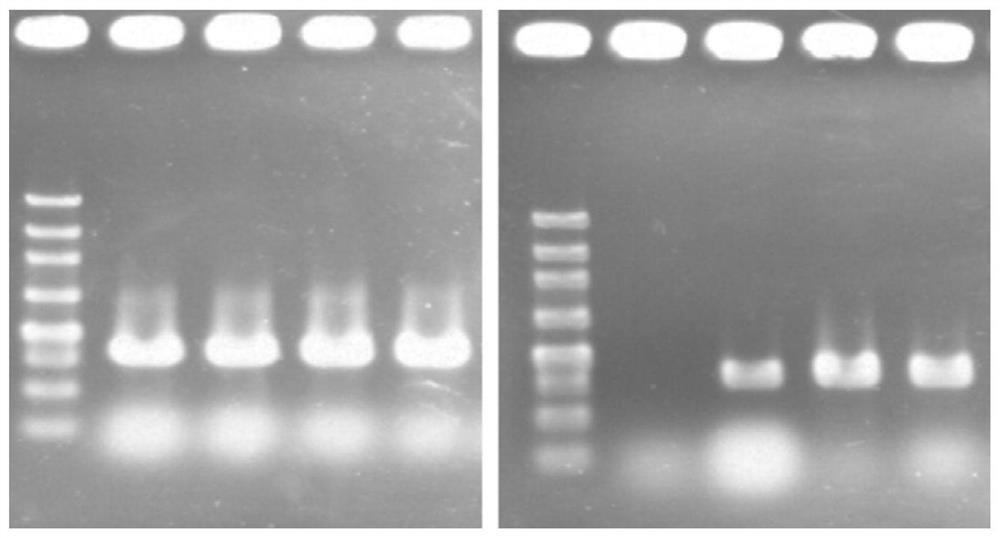
[0136]Centrifuge at 5000rpm to collect the cell culture medium that was cultured in liquid YPD medium at 28°C-30°C and 160rpm for 48 hours, wash the bacterial cells twice with sterile water and suspend them to the same cell concentration, press After the multiples of 10 were diluted by gradient concentration, 3 microliters were inoculated on the pre-prepared organic acidified solid medium, and after static culture at 28°C-30°C for 48-72 hours, the colony formation was observed, and after constructing strains and wild comparison between strains, such as Figure 13 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com