Peptide vaccines
A technology of polypeptide antigens and amino acids, applied in the field of polypeptides and vaccines
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0587] Example 1 HLA epitope binding prediction method and verification
[0588] Prediction of binding between specific HLAs and epitopes (9mer peptides) was based on the ImmunoEpitope Database tool for epitope prediction (www.iedb.org).
[0589] The HLA I epitope binding prediction process was validated by comparison with HLA I epitope pairs determined by laboratory experiments. Datasets of HLA I epitope pairs reported in peer-reviewed publications or public immunology databases were compiled.
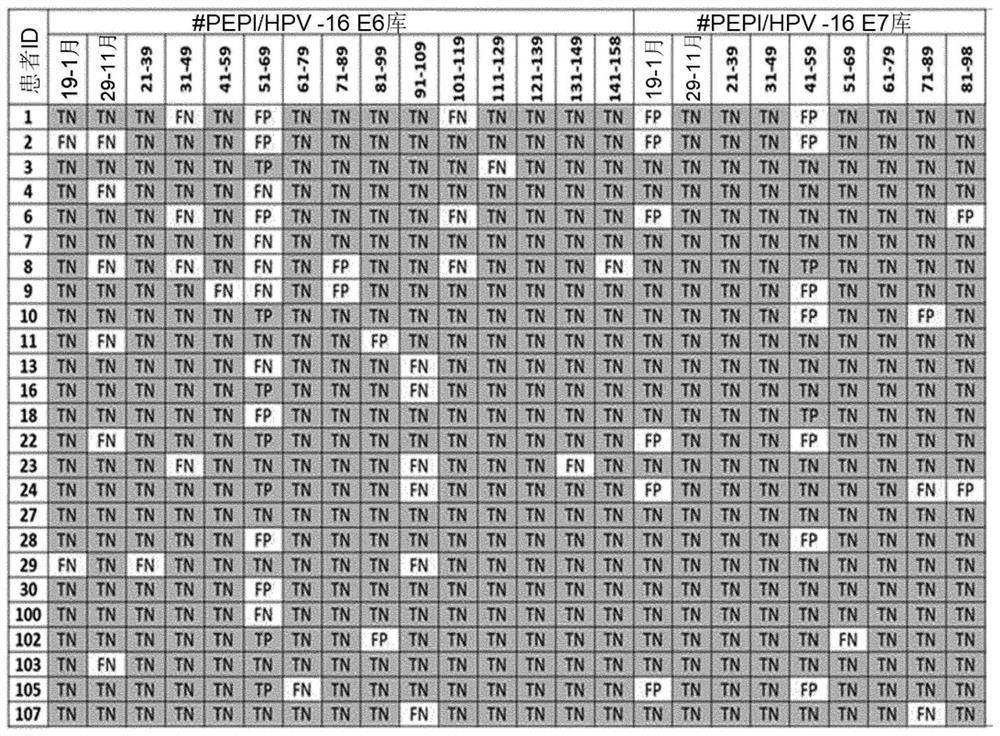
[0590] The rate of agreement with the experimentally determined data set (Table 2) was determined. Binding HLA I epitope pairs for the dataset were correctly predicted with 93% probability. Coincidentally, non-binding HLA I epitope pairs were also predicted correctly with a probability of 93%.
[0591] Table 2 Analytical specificity and sensitivity of HLA epitope binding prediction methods
[0592]
[0593] The accuracy of predicting multiple HLA binding epitopes was also det...
example 2
[0597] Example 2 Epitope Presentation of Multiple HLAs Predicts Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte (CTL) Response
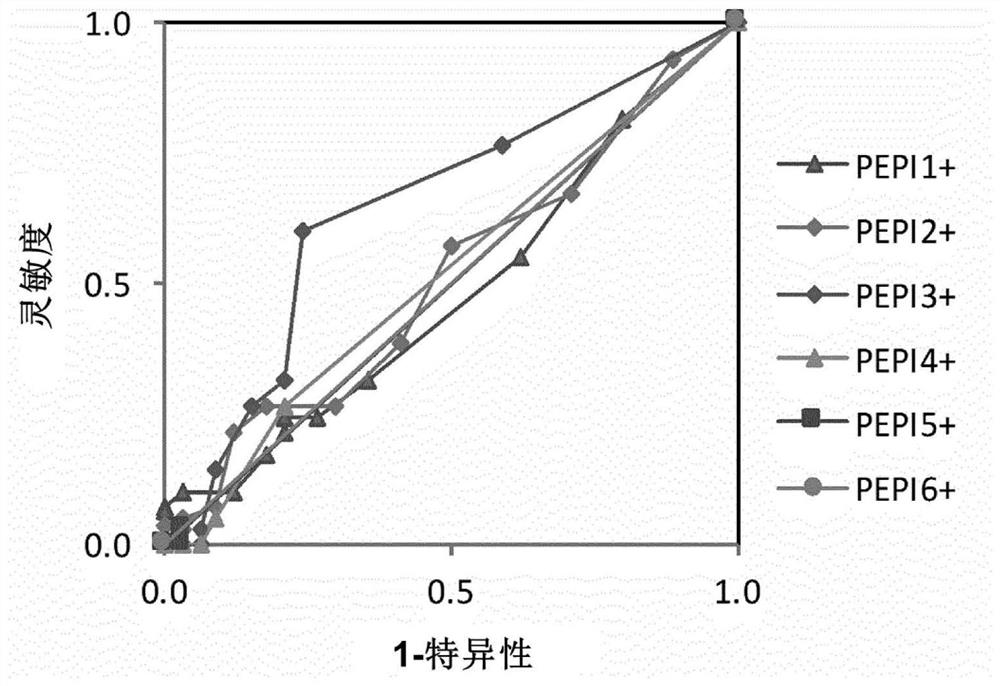
[0598] This study investigated whether an individual's presentation of one or more epitopes of a polypeptide antigen by one or more HLA class I molecules is predictive of a CTL response.
[0599] The study was performed by a retrospective analysis of 6 clinical trials conducted in 71 cancer patients and 9 HIV-infected patients (Table 4)1-7. Patients from these studies were treated with HPV vaccines, three different NY-ESO-1-specific cancer vaccines, an HIV-1 vaccine, and a CTLA-4-specific monoclonal antibody (ipilimmab), the Antibodies shown to reactivate CTLs against NY-ESO-1 antigen in melanoma patients. All of these clinical trials measure antigen-specific CD8+ CTL responses (immunogenicity) in study subjects after vaccination. In some cases, a correlation between CTL response and clinical response was reported.
[0600] No patients were excluded from the retrospecti...
example 3
[0612] Example 3 Retrospective Validation of ≥1 PEPI3+ Threshold as a New Biomarker for PEPI Test
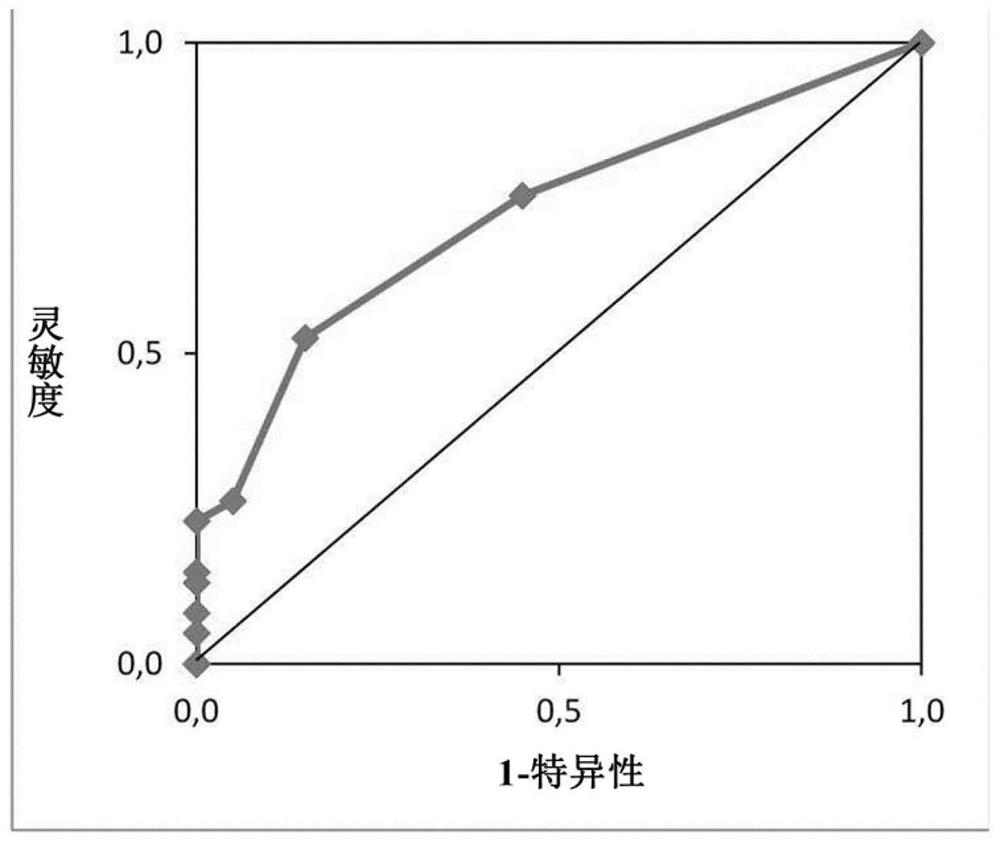
[0613] In a retrospective analysis, a test cohort of 81 datasets from 51 patients was used to validate a ≥1 PEPI3+ threshold to predict antigen-specific CD8+ T cell or CTL responses. For each data set in the test cohort, it was determined whether a > 1 PEPI3+ threshold (at least one antigen-derived epitope presented by at least three class I HLAs of the individual) was met. This was compared to experimentally measured CD8+ T cell responses (CTL responses) reported in clinical trials (Table 7).
[0614] A retrospective validation demonstrated that the PEPI3+ peptide induces a CD8+ T cell response (CTL response) in an individual with a probability of 84%. 84% is the same value as determined in the analytical validation of the PEPI3+ prediction that the epitope is bound to at least 3 HLAs of the individual (Table 3). These data provide strong evidence that PEPI induces an immun...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com