Training machine-learned models for perceptual tasks using biometric data
A technology of biostatistics and machine learning, applied in biometric identification patterns based on physiological signals, computer components, biometric identification, etc., can solve problems such as insufficient model performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0029] Overview
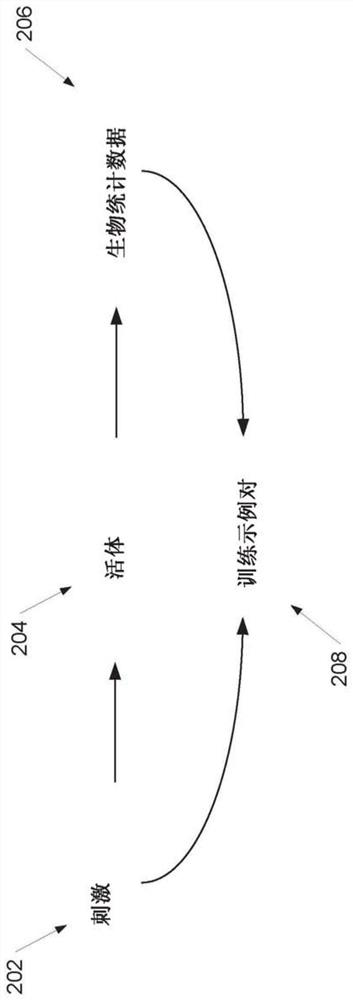
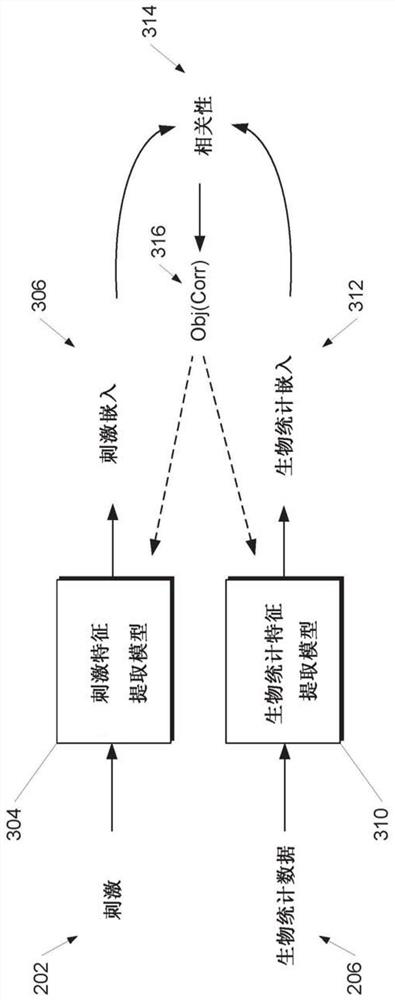
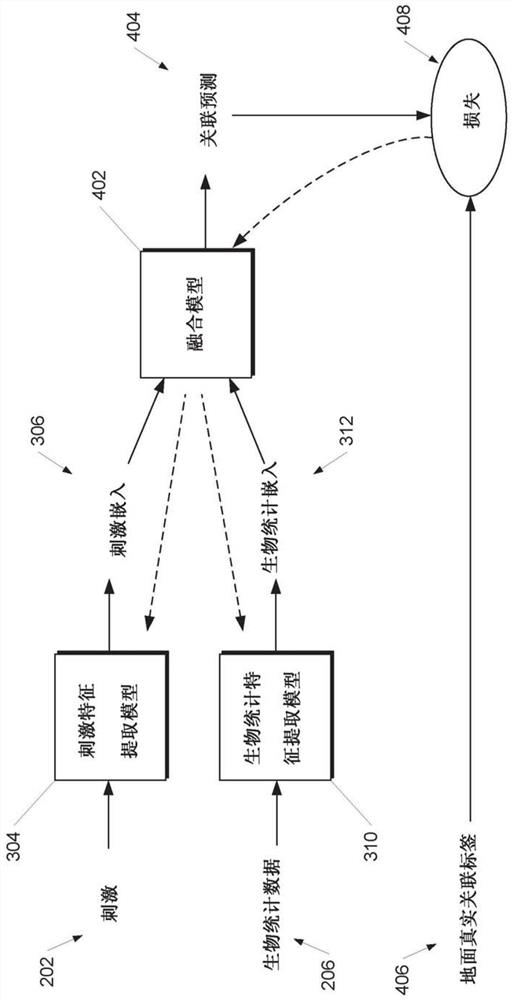
[0030] Generally, the present disclosure relates to training a machine learning model (eg, an artificial neural network) to perform perception or recognition based on biometric data (eg, brain wave recordings) collected from a living body while the living body is performing a sensory or cognitive task Systems and methods for knowledge tasks. In particular, aspects of the present disclosure relate to a new paradigm of supervision by which the use of the Example stimuli paired with companion biometric data (eg, EEG data, EEG data, and / or magnetoencephalography data) collected by humans participating in data collection efforts, such as neural activity recordings, to train machine learning features Extract the model. In this way, implicit but learnable markers encoded within the biometric data can simply be obtained by collecting the biometric data while exposing the labeled organism to the stimulus, which is easier than (eg, via manual data input to a comput...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com