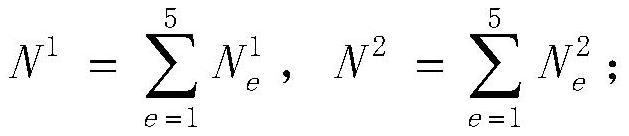Monogenic disease name recommendation method and system
A single-gene disease name technology, applied in the field of digital medicine, can solve the problems of single-gene disease coverage limitation, misdiagnosis and missed diagnosis, high cost, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
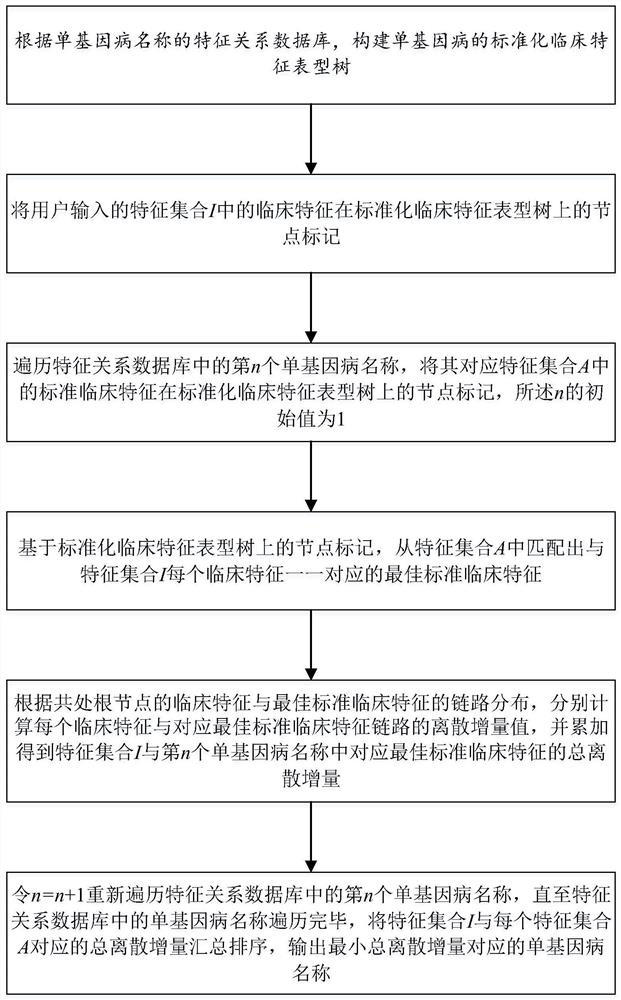
[0062] see figure 1 , this example provides a method for recommending the name of a monogenic disease, including:
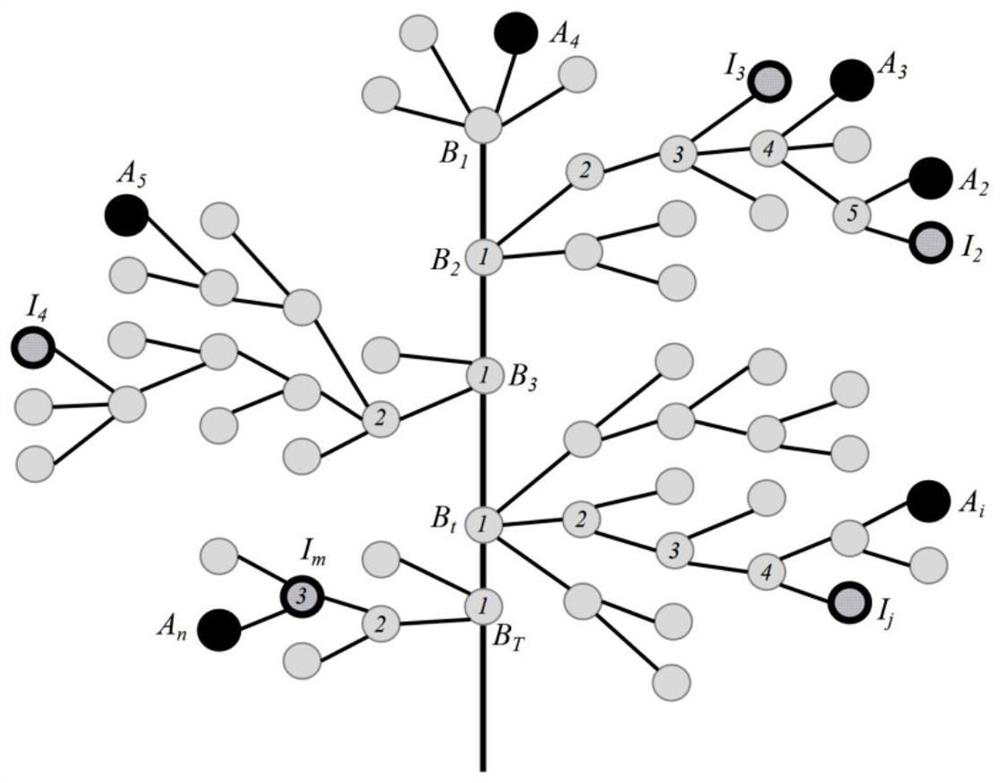
[0063] According to the feature relationship database of the name of the monogenic disease, construct a standardized clinical feature phenotype tree of the monogenic disease; mark the clinical features in the feature set I input by the user on the node mark on the standardized clinical feature phenotype tree; traverse the feature relationship database The name of the n-th monogenic disease, the node mark of the standard clinical features in the corresponding feature set A on the standardized clinical feature phenotype tree, the initial value of n is 1; based on the standardized clinical feature phenotype tree Node labeling, from the feature set A, match the best standard clinical features corresponding to each clinical feature of the feature set I; according to the link distribution of the clinical features of the co-located root node and the best standard clinic...
Embodiment 2
[0118] This embodiment provides a recommendation system for monogenic disease names, including:
[0119]The data acquisition unit is used to construct a standardized clinical characteristic phenotype tree of the monogenic disease according to the characteristic relational database of the monogenic disease name;
[0120] The input marking unit is used to mark the nodes of the clinical features in the feature set I input by the user on the standardized clinical feature phenotype tree;
[0121] The traversal marking unit is used to traverse the nth monogenic disease name in the feature relational database, and mark the node of the standard clinical feature in the corresponding feature set A on the standardized clinical feature phenotype tree, and the initial value of n is 1;
[0122] The retrieval unit, based on the node marks on the standardized clinical feature phenotype tree, matches the best standard clinical feature from the feature set A with one-to-one correspondence with...
Embodiment 3
[0132] This embodiment provides a computer-readable storage medium, on which a computer program is stored, and when the computer program is run by a processor, the steps of the method for recommending the name of a single-gene disease are executed.
[0133] Compared with the prior art, the beneficial effect of the computer-readable storage medium provided by this embodiment is the same as that of the method for recommending the name of a single-gene disease provided by the above-mentioned technical solution, and details are not repeated here.
[0134] Those of ordinary skill in the art can understand that all or part of the steps in the above-mentioned inventive method can be completed by instructing related hardware through a program. The above-mentioned program can be stored in a computer-readable storage medium. When the program is executed, it includes: For each step of the method in the above embodiments, the storage medium may be: ROM / RAM, magnetic disk, optical disk, mem...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com