Ipilimumab variants with enhanced specificity for binding at low ph
A technology of ipilimumab and antibodies, which is applied in the direction of antibodies, antibody medical components, and medical preparations containing active ingredients, etc., which can solve the problems of toxicity and dose limitation of ipilimumab
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0125] Lead selection of ipilimumab heavy chain CDR sequence variants with enhanced low pH binding preference
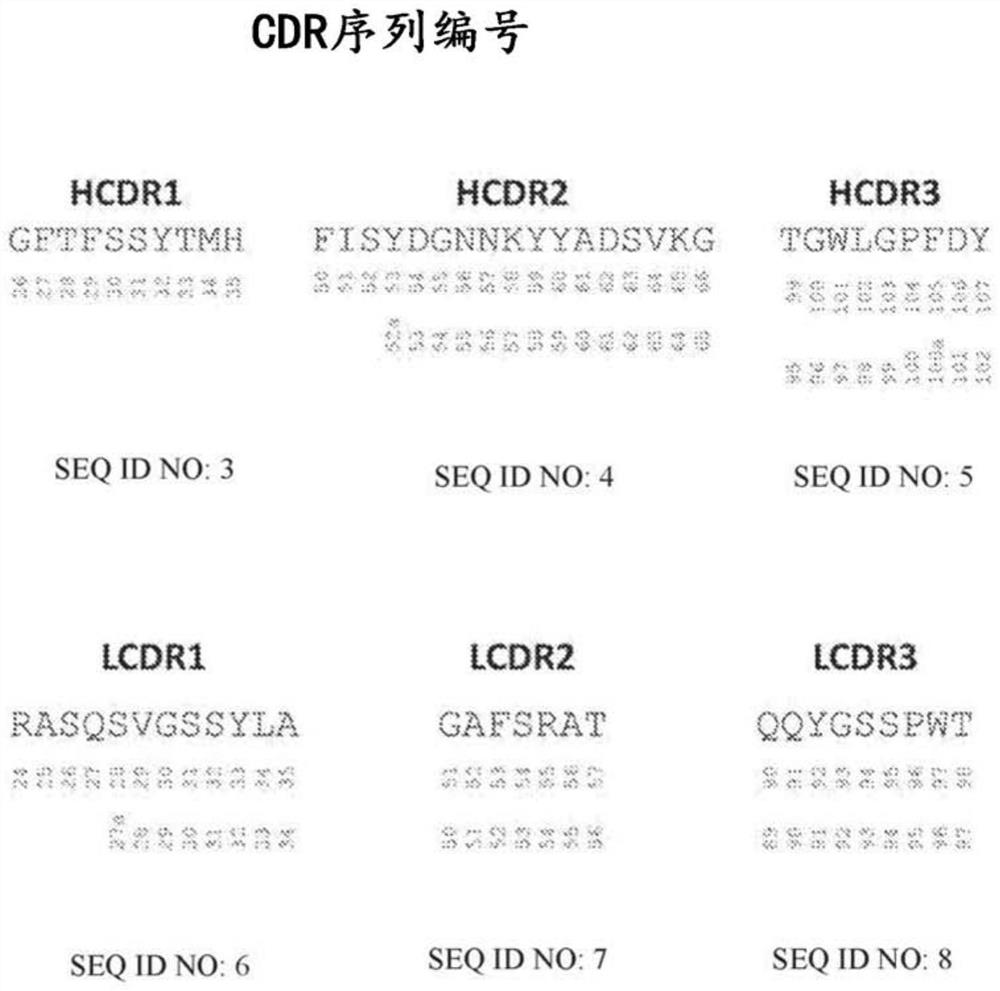
[0126] To test the process for selecting pH-optimized sequence variants, one mutation was introduced in each CDR of the ipilimumab heavy chain for a total of three amino acid substitutions per heavy chain. The CDRs are modified at positions 28, 30, 31, 32, and 33 in HCDR1; at positions 52, 52a, 53, 54, 55, and 56 in HCDR2; and at positions 95, 97, 98 in HCDR3 (all Numbering all have histidine (H) according to Kabat). See Figure 1. The light chain was unchanged.
[0127] Selection for sequence variants with enhanced binding preference at low / acidic pH was performed essentially as described in Hornsby et al. (2015) Mol. Cell. Proteomics 14:2833. Briefly, ipilimumab light and heavy chain variable domain sequences containing one or more sequence alterations were cloned into an M13 phagemid vector and phage were generated such that the cloned scFv fragment was on the s...
Embodiment 2
[0138] Combinatorial library of ipilimumab CDR sequence variants with enhanced low pH binding preference
[0139] Following the lead heavy chain variable screen (Example 1), a full combinatorial approach was designed to account for modifications in all six CDRs. To obtain ipilimumab sequence variants with enhanced binding preference at pH 6.0 compared to binding at pH 7.4, mutations were introduced at selected positions in the heavy and light chain CDRs. CDRs are modified at the following positions: T28, S30, S31, Y32, T33 in HCDR1; F50, S52, Y52a, D53, G54, N55, N56, Y58 in HCDR2; T95, W97, L98 in HCDR3; and Q27, S27a, S30, S31, Y32 in LCDR1; F52, S53, T56 in LCDR2; Q90, Y91, W96 in LCDR3. Each position of LCDR1 is replaced by H (His) and D (Asp) or E (Glu), where each CDR has one to three mutations, each chain has one to three mutations, and each scFv has a total of two to three mutations. Six mutations. All residues are numbered according to Kabat, as shown in Figure 1. ...
Embodiment 3
[0157] Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) Spectroscopic Determination of Binding Parameters of the Antibodies of the Invention
[0158] Surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy (SPR) was used to determine the binding parameters of various ipilimumab sequence variants of the invention to human CTLA-4 essentially as follows. Unless otherwise specified, use The SPR surface plasmon resonance spectrometer (Biacore AB, Uppsala, Sweden) was used for the experiments. Antibodies are tested as monovalent Fab fragments to simplify analysis. Data can be provided in the form of sensorgrams, as in Figures 5A, 5B, 7A, and 7B, or summarized as binding parameters, such as equilibrium dissociation binding constants (K D ), association (association / on) rate constant (k a , k on ), dissociation (dissociation / off) rate constant (k d , k off ) and / or half-life (t 1 / 2 ).
[0159] Briefly, the ipilimumab variants of the present invention were produced as Fab fragments and produced in the presence...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com