Base station rapid decoding method based on polarization code SCL algorithm
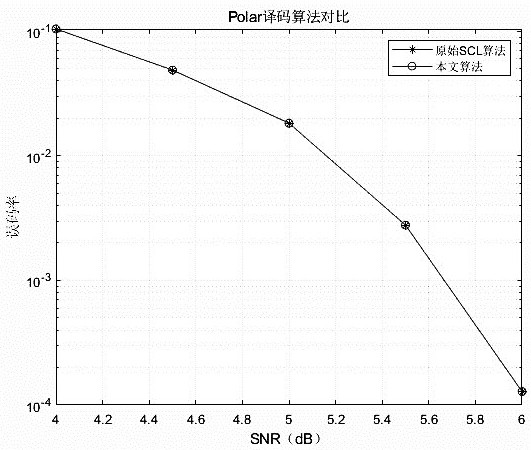
A fast decoding and polar code technology, applied in the field of channel coding, can solve the problems of large path duplication delay and reduce decoding delay, so as to improve communication efficiency, speed up decoding speed, and avoid invalid path duplication. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
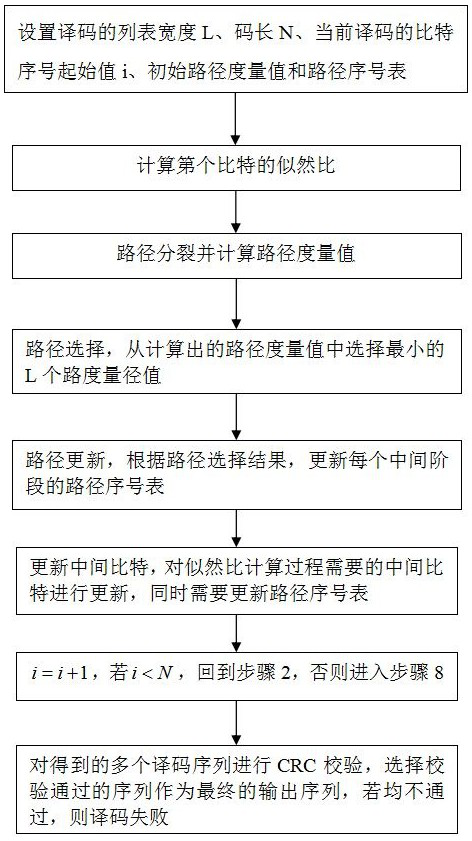
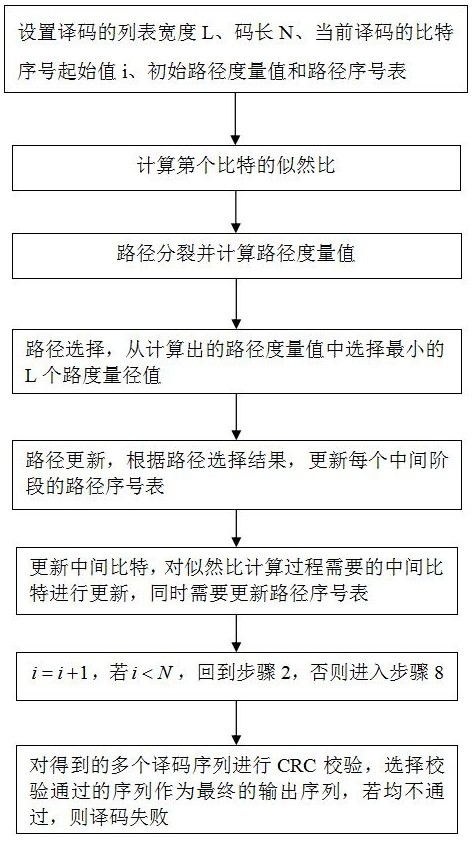
[0041] In this example, if figure 1 As shown, in view of the problem of long path duplication delay, a fast base station decoding method based on the polar code SCL algorithm is proposed to reduce the decoding delay, which can be applied to 5G communication between base stations, or between other devices 5G network communication. The methods specifically include:
[0042] Step 1: Set the basic parameters of decoding, including the list width L and the code length N, then all the likelihood ratios and the dimensions of the intermediate bits are L N (log N+1), and set the bit sequence number of the current decoding The starting value is i=0, the initial path metric value is 0, and a path sequence number table is set to record which path each path is copied from, and the dimension is L·(log N+1).
[0043] Step 2: Calculate the likelihood ratio of the i-th bit. When calculating the likelihood ratio for the middle bit, it is necessary to copy the path according to the path number...
Embodiment 2
[0051] In this embodiment, on the basis of the first embodiment, the implementation process of each step of the method is further disclosed.
[0052] In this embodiment, regarding the process of setting the basic parameters of decoding in step 1, the code length is set to N in this embodiment, and the total number of intermediate stages is S=log(N)+1.
[0053] The dimension of the likelihood ratio is L·N·S, the l-th path is translating the i-th information bit and the likelihood ratio in the s-th stage is denoted as LLR l (i,s).
[0054] The dimension of the intermediate bit is L·N·S, the l-th path is translating the i-th information bit and the intermediate bit in the s-th stage is denoted as b l (i,s).
[0055] The dimension of the path number table is L·S, and the path number value of the lth path at the sth stage is recorded as p l (s), indicating that the lth path at the current moment adopts the pth path l Likelihood ratios and intermediate bits for (s) paths.
[00...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com