Passive tactile scheme for multiple virtual targets in VR large space
A virtual target and large space technology, applied in the field of passive haptic solutions for multiple virtual targets in a large VR space, can solve the problems of no haptic feedback, errors, difficulty in providing haptic feedback, etc., and achieve the effect of accurate haptic feedback
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] The treatment process of this embodiment includes the following steps:
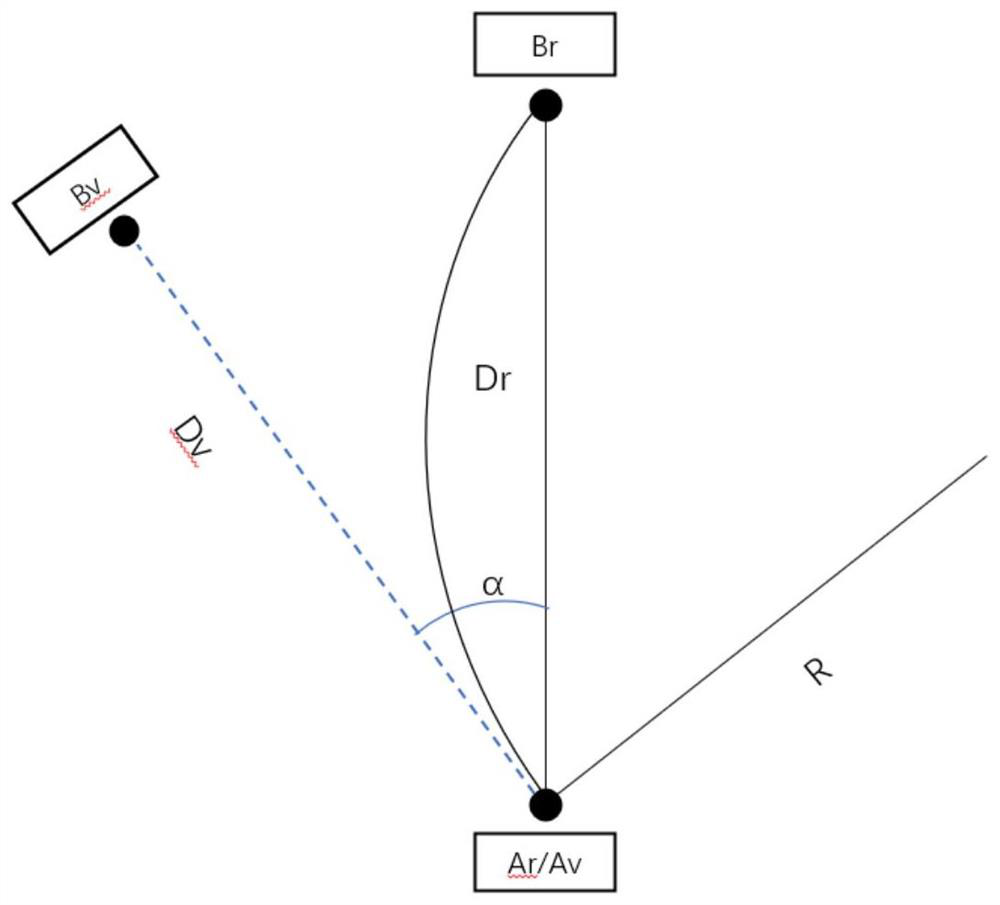
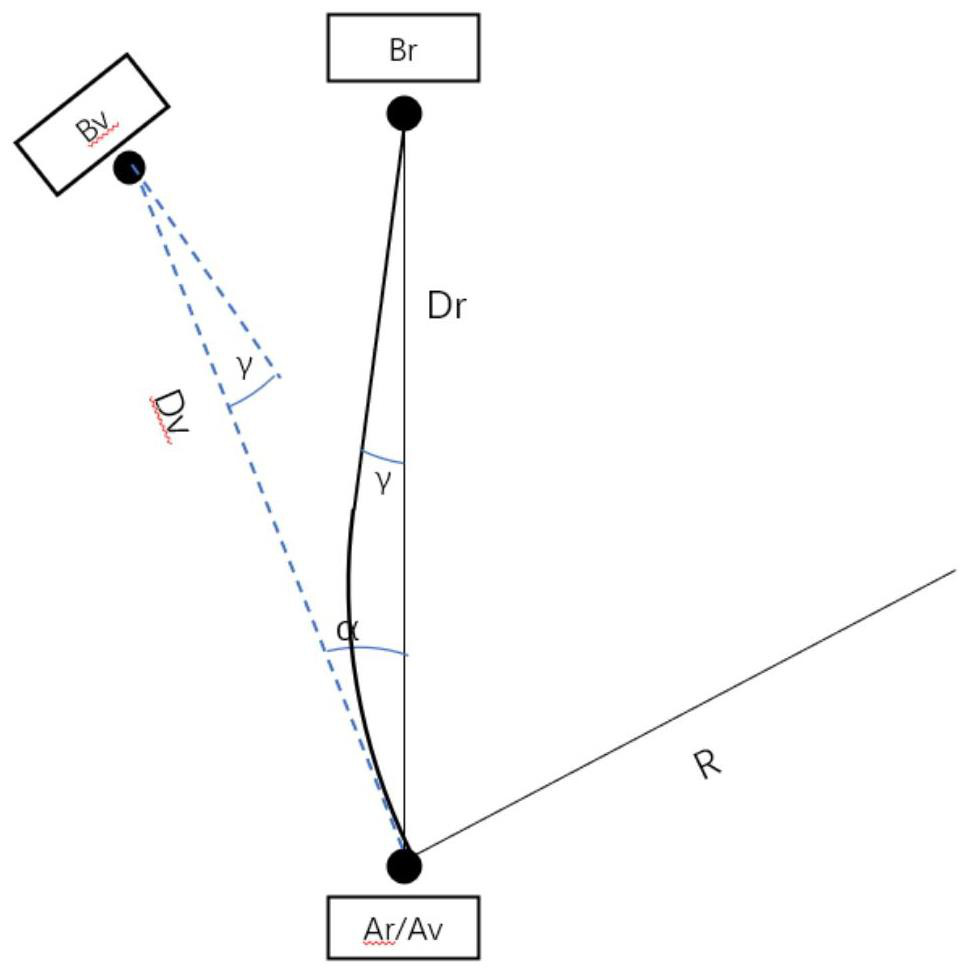
[0039] S1. First, pre-design the path, that is, the user's route in the virtual environment. In this method, the user's route adopts a "polyline", so that the route between the source virtual target Av and the destination virtual target Bv AvBv and the source physical agent Ar The included angle of the connection line ArBr to the destination physical agent Br is α, then the range of α is determined by the physical distance between ArBr. When the user moves towards the virtual object Bv, the redirection algorithm only applies the curvature gain and the translation gain, so the ideal In this case, when the user moves directly toward the virtual object, the real trajectory is an arc, and the connection line ArBr of the two physical agents is exactly the chord corresponding to the arc, so that the radius corresponding to the arc applying the curvature gain is R, Then when the distance of ArBr is Dr, α ...
Embodiment 2
[0078] The difference with the first embodiment is:
[0079] The treatment process of this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0080] S1, first spatial positioning
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com