Brain function network classification method based on conditional mutual information and kernel density estimation
A brain function network and kernel density estimation technology, which is applied in the field of brain function network classification based on conditional mutual information and kernel density estimation, can solve the problems of insufficient performance of TML method and poor interpretability of DL method, and achieve excellent classification performance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
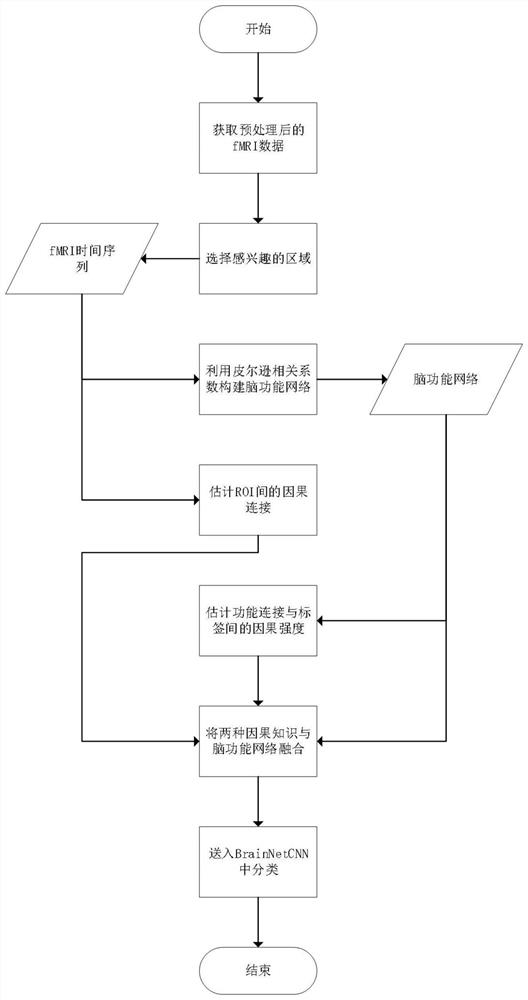
[0022] Set forth below the specific embodiment of the present invention and detailed steps, the flow process of the concrete realization of the present invention is as follows figure 1 shown, including:
[0023] (Step 1) Data Acquisition.
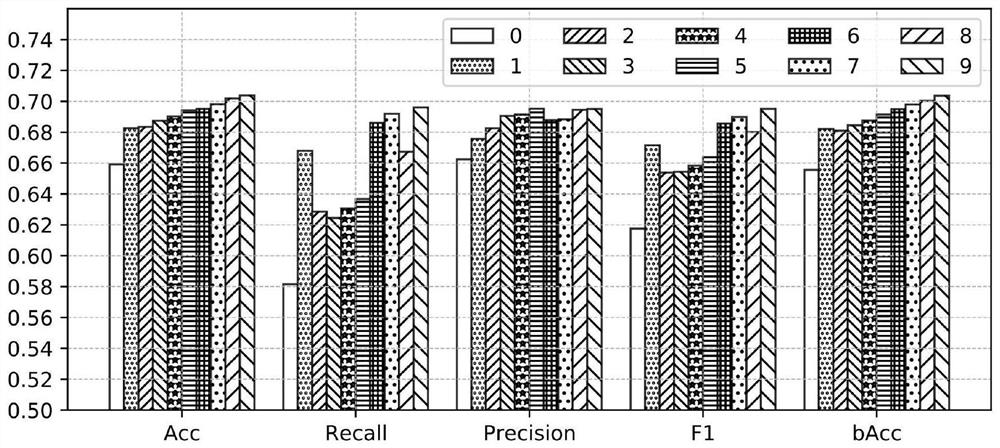
[0024] In order to verify the effectiveness of the model proposed in the present invention, we will conduct experiments on the ABIDE I data set to evaluate the classification performance of the model. ABIDE I has functional and structural brain imaging data from 17 different sites around the world. Because fMRI data processing is very flexible, the Preprocessed Connectomes Project (http: / / preprocessed-connectomesproject.org / abide / ) provides five preprocessed data by different groups using their preferred strategies. We chose the version of DPARSF, which included 505 ASD patients and 530 normal subjects after removing subjects with incomplete phenotype information.
[0025] (Step 2) Select a region of interest (ROI).
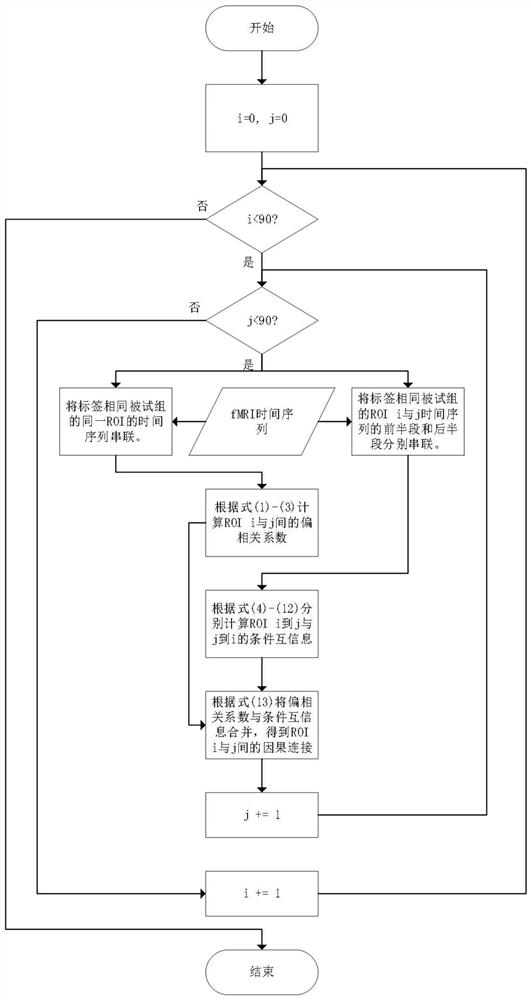
[0026] The presen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com