Method for producing microalbumin-positive nerve cells, cells, and differentiation-inducing agent
A differentiation inducing agent and technology of manufacturing method, which can be applied to nervous system cells, cell culture active agents, animal cells, etc., can solve the problem of low induction efficiency of parvalbumin-positive nerve cells, and achieve the advantages of less differentiation induction process, high efficiency, and high efficiency. high-manufacturing effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
experiment example 1
[0092] (Maintenance culture of iPS cells)
[0093] For iPS cells (strain 1210B2), the seeding density of iPS cells at the time of cell passage was set to 1.5×10 in a 6-well plate 4 1.5 ml / well of undifferentiated cell medium Stem Fit (AK02N, manufactured by Ajinomoto Co., Ltd.) was injected into a 6-well plate immediately before cell seeding without the need for pre-plating at the time of cell passage. ), the medium contained 1.5 mL of 10 μg / ml ROCK inhibitor Y27632 (manufactured by Fuji Film Wako Pure Chemical Co., Ltd.) and 1.5 μg / ml iMatrix-511 (manufactured by Nippi Co., Ltd.), and the cells were directly Inoculation, other than the above, was cultured according to a known cell culture method disclosed by the iPS Research Institute of Kyoto University.
experiment example 2
[0095] (Introduction of Ascl1 and Dlx2 genes into iPS cells)
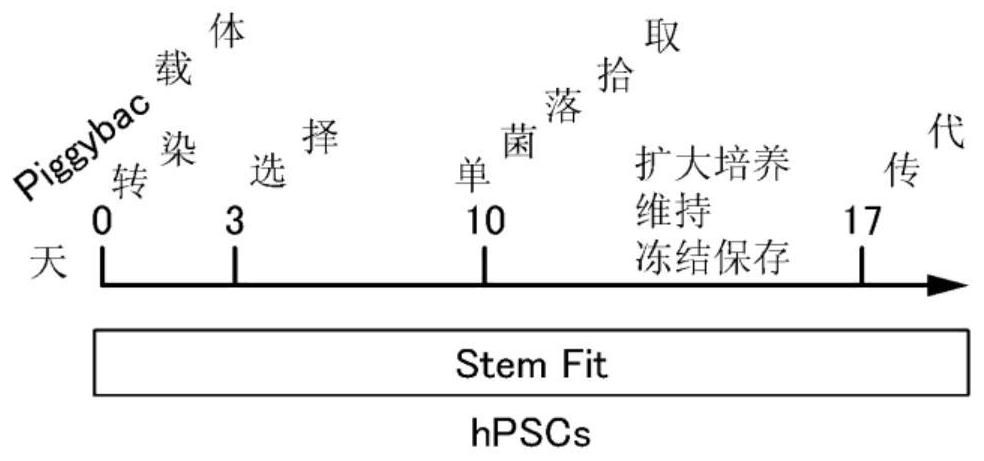
[0096] The protocol for introducing Ascl1 and Dlx2 genes into iPS cells is shown in Figure 1A . Specifically, the Ascl1 gene and the Dlx2 gene were introduced into iPS cells in the following manner.
[0097] (1) Preparation of medium and preparation for coating of plate for cell seeding after gene transfer operation
[0098] To Stem Fit (AK02N, manufactured by Ajinomoto Co., Ltd.), 20 μg / ml of Y27632 (manufactured by Fuji Film WakoPure Chemical Co., Ltd.) and 2.5 μg / ml of iMatrix-511 (manufactured by Nippi Co., Ltd.) were added at 6 Put it into 6 wells (1 plate) at 2ml / well in a well plate, and heat it at 37°C, 5% CO. 2 Incubation.
[0099] (2) Monocellularization of iPS cells
[0100] will be approximately 1.5 x 10 in a 6-well plate 4 The iPS cells seeded in 1 cell / well were cultured with Stem Fit (AK02N, manufactured by Ajinomoto Co., Ltd.) for about 1 week. After removing the medium with an aspirator, the ...
experiment example 3
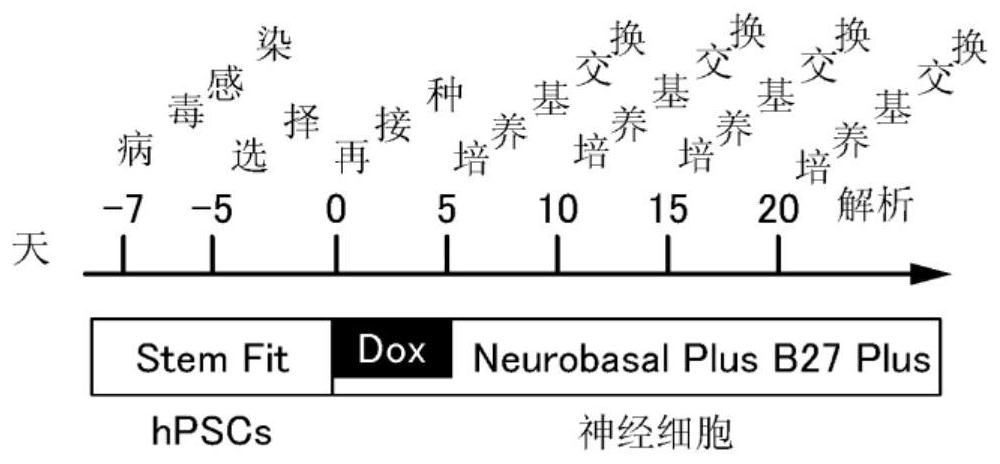
[0113] (Introduction of MEF2C gene, miRNA-9 / 9 to iPS cells *, miRNA-124 and BclxL genes)
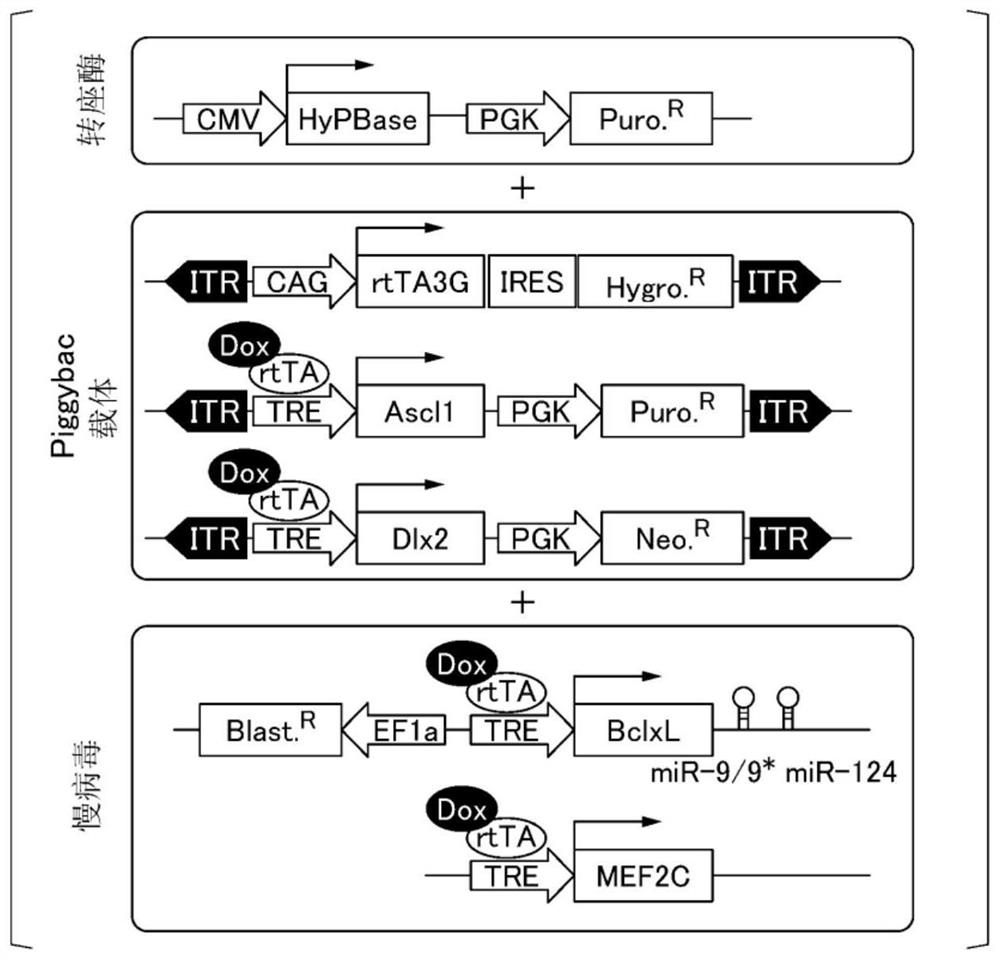
[0114] MEF2C gene, miRNA-9 / 9 will be introduced into iPS cells * , miRNA-124 and BclxL gene protocols are shown in Figure 1B . Specifically, the MEF2C gene and miRNA-9 / 9 were introduced into iPS cells in the following manner. * , miRNA-124 and BclxL genes.
[0115] (1) MEF2C gene, miRNA-9 / 9 were introduced * , miRNA-124 and BclxL gene purification of lentivirus
[0116] According to conventional methods, purification such as Figure 1C MEF2C gene, miRNA-9 / 9 were introduced as shown in the lower paragraph * , miRNA-124 and BclxL genes lentivirus. Specifically, the MEF2C gene and miRNA-9 / 9 were purified and introduced in the following manner. * , miRNA-124 and BclxL genes lentivirus.
[0117] A 0.01% poly-L-lysine solution (0.01%, #P4832, manufactured by Sigma) was mixed with PBS(-) to 1:100 to obtain a solution, which was used for coating cells and tissue culture After washing...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com