Complex stratum large-section tunnel over-break and under-break control device and method
A technology of complex strata and control devices, applied in tunnels, earth-moving mining, mining equipment, etc., can solve problems such as the increased probability of tunnel excavation over-under-excavation, the inclination of the blasting range of blasting parts, and the easy inclination of hole paths. The effect of working stability, improving stability, and reducing the probability of over-under-digging
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0044] Attached to the following Figure 1-4 This application will be described in further detail.
[0045] The embodiments of the present application disclose a device for controlling over-under-excavation of large-section tunnels in complex strata.
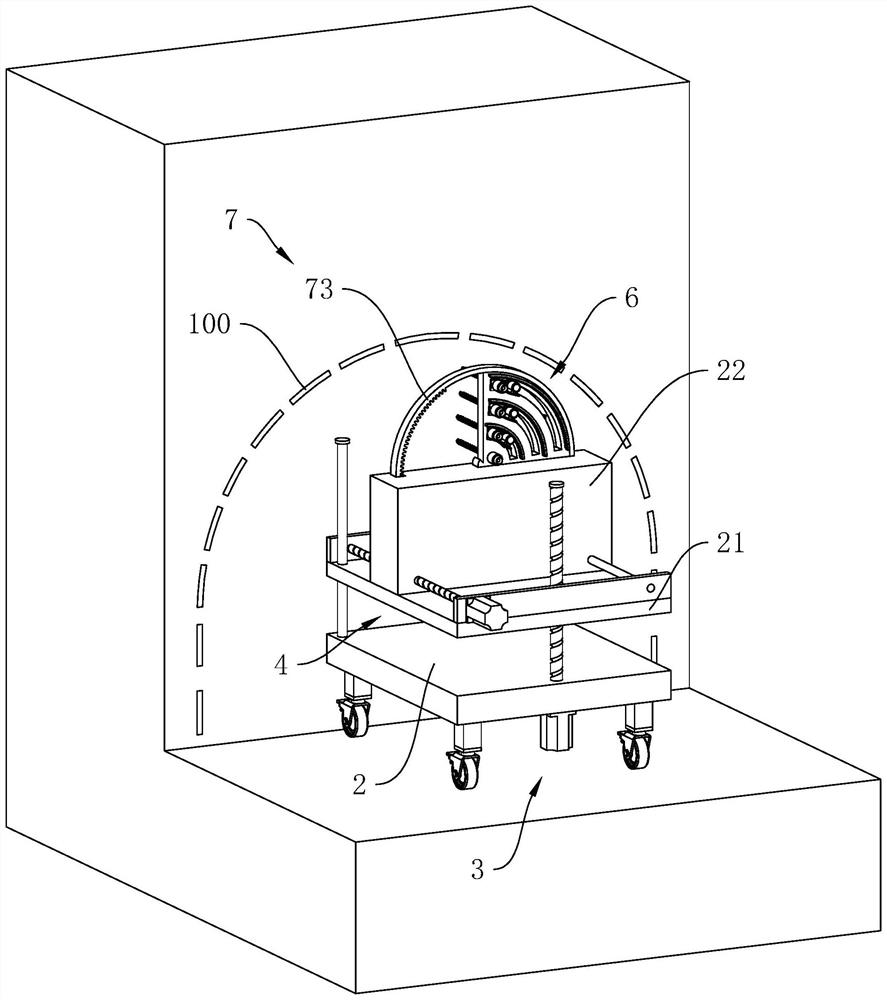
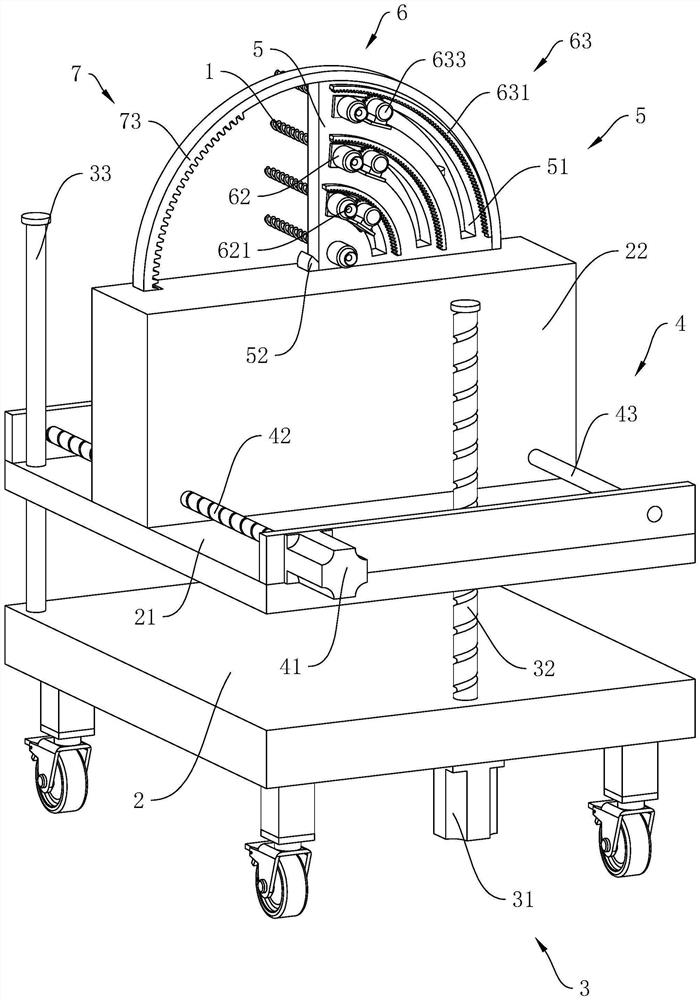
[0046] refer to figure 1 and figure 2 , a large-section tunnel over-under-excavation control device in complex strata includes a base 2 arranged on the ground, a horizontally arranged lifting plate 21 is arranged on the base 2, and a lifting assembly for driving the lifting plate 21 to vertically lift is arranged on the base 2 3. An adjustment block 22 is provided on the upper surface of the lifting plate 21 to slide, and a power assembly 4 for driving the adjustment block 22 to slide horizontally is arranged between the lifting plate 21 and the adjustment block 22 .
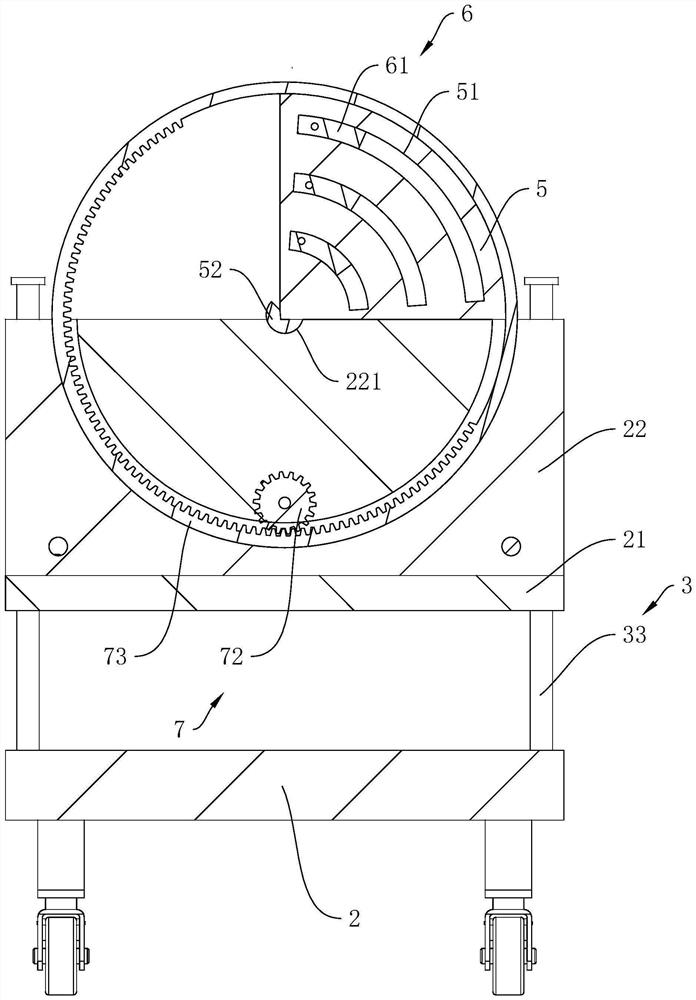
[0047] refer to figure 2 , the adjusting block 22 is rotatably connected with the protective plate 5, between the adjusting block 22 and the protective plat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com