Foam-metal current collector of secondary battery using zinc as negative electrode and its preparing process
A foam metal and secondary battery technology, applied in the direction of electrode manufacturing, electrode carrier/collector, etc., can solve the problems of expensive, restricting the popularization and use of zinc-nickel batteries, and unable to replace silver, etc., achieve low cost, and inhibit the growth of dendrites , the effect of excellent performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
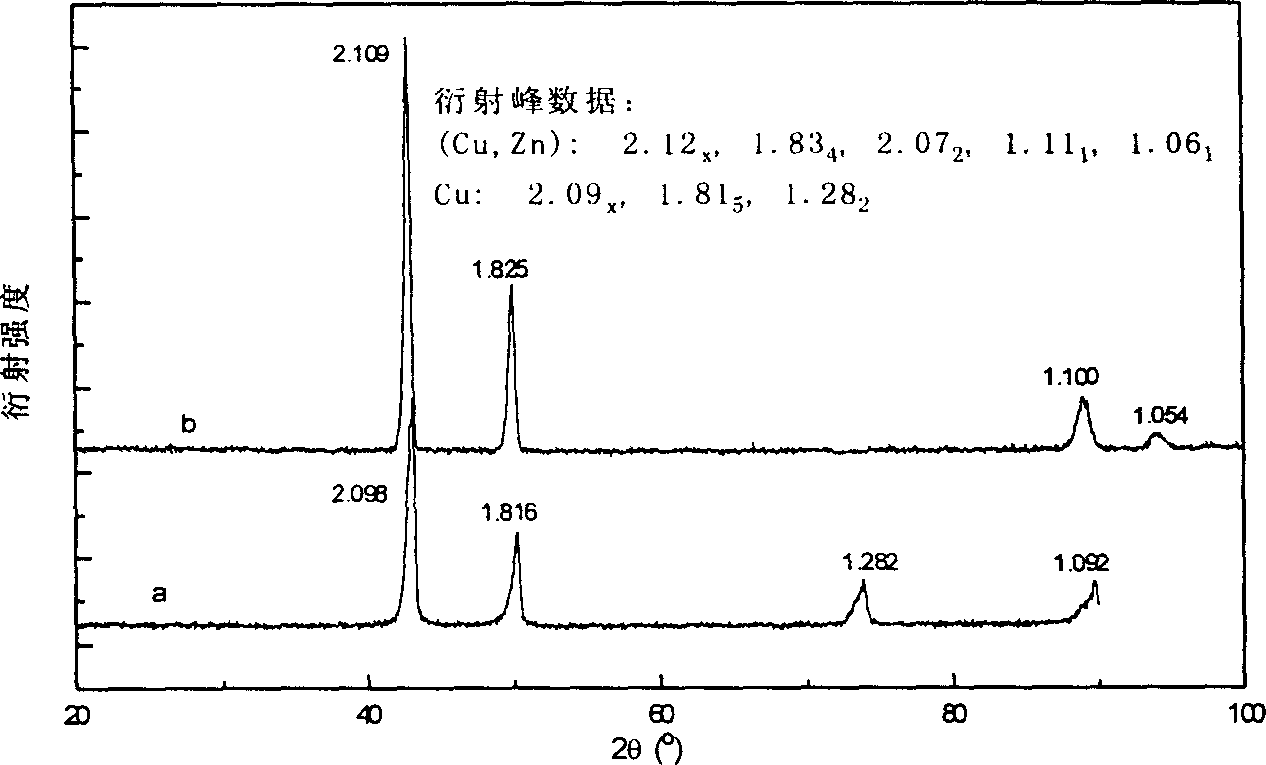
[0018] Embodiment 1 The foamed plastic sheet of thick 2mm is about 10cm 2 SnCl 2 Sensitization, silver ammonia complex solution activation, put 250ml10g / lCuSO 4 .5H 2 O + 30g / l EDTA (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid) + 5ml / l methanol, pH value of 12.5 solution, constant temperature to 35 ℃, under the stirring condition of about 200 rpm, dropwise add 1.5gNiCl 2 .6H 2 O solution and 5ml formaldehyde, react for about 1 hour, take out the foamed plastic sheet through electroless copper plating, clean, dry. The electroless copper-plated foam plastic sheet was placed in a tube resistance furnace and heated with Ar+H 2 Protected by mixed gas, the temperature was raised to 750°C and cooled to obtain foamed copper. Use foamed copper as the cathode, placed in 225g / lCuSO 4 .5H 2 O+60g / lH 2 SO 4 In the electroplating solution of +35g / l glucose, the copper sheet is used as the anode, stirred at a speed of about 80 rpm, and the cathode current density is 60mA / cm 2 (for apparent are...
Embodiment 2
[0020] The foamed brass prepared in Example 1 was used as a current collector (matrix), and electroplated with zinc in a saturated zincate solution to prepare a zinc electrode. First degrease in acetone for 5min, then at 20mA / cm 2 Under current density, cathodic polarization was performed in 5M KOH solution for 1 min. Finally, in a saturated zincate solution with a current density of I = 100mA / cm 2 , electroplating time t = 10min, electroplating temperature T = 40 ℃ conditions electroplating zinc. The current collectors of Cu, Ni, In, Ag, and Zn were galvanized by the same method, and compared with electrochemical performance tests. The obtained data are listed in Table 1, as can be seen from Table 1:
[0021] Collector (base
quality)
E. corr (base
quality) / V
E. corr / V
i corr / mA / cm 2
b a / mV
E. p / V
Ni
-0.960
-1.362
5.976
40.7
-1.281
Zn
-1.374
...
Embodiment 3
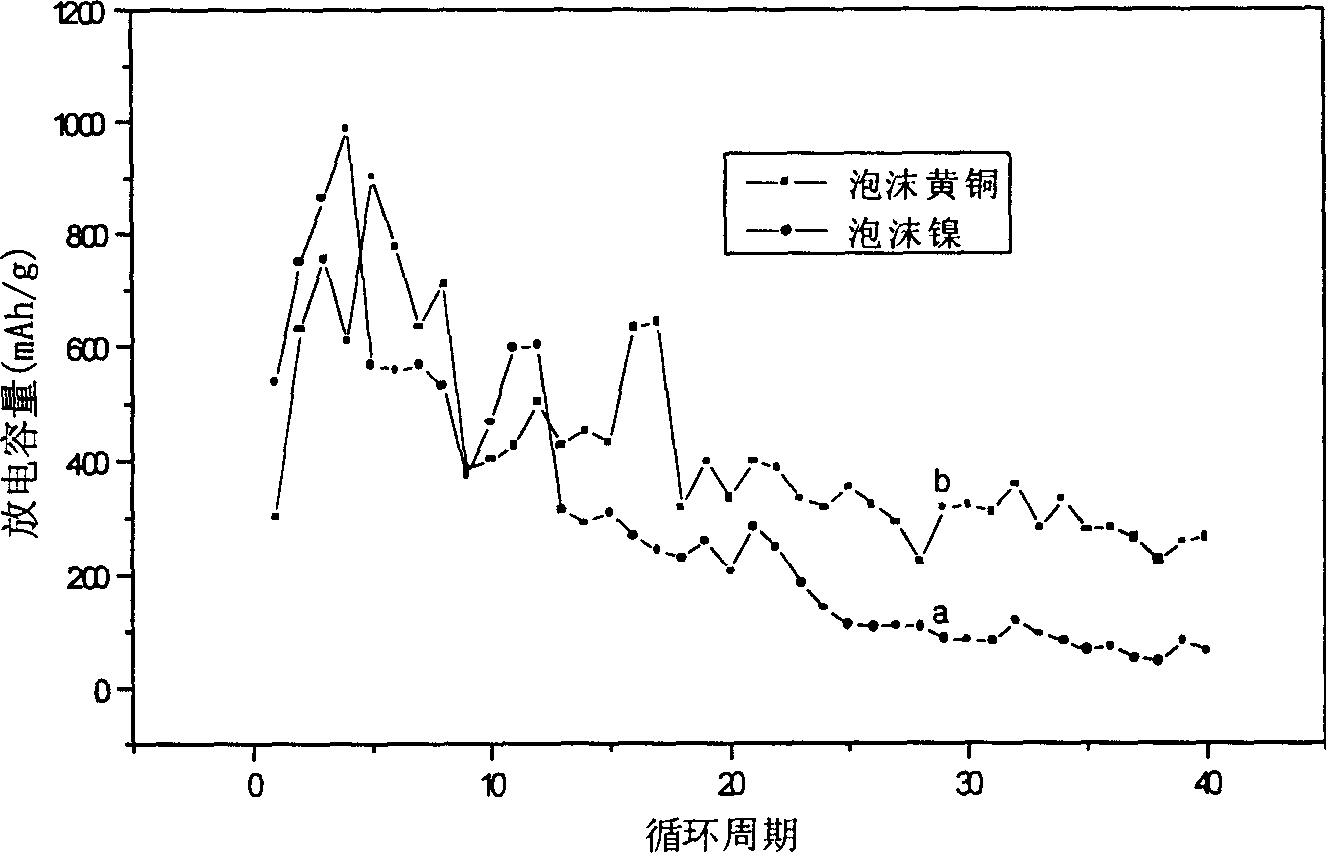
[0029] The brass foam prepared in Example 1 and the brass mesh and nickel foam commonly used in secondary batteries (matrix) were compared to study the dendrite growth of zinc electrodes using them as current collectors (matrix). In a saturated zincate solution, an overpotential of -100mV was applied to three current collectors (substrates) of foamed brass, brass mesh and foamed nickel, and the constant potential was polarized for 4500 seconds. When dendrites grow, the surface area of the zinc electrode will be greatly increased, thereby increasing the total current of the zinc electrode. The growth of zinc dendrites on the current collector (substrate) is judged according to the growth rate of the total current. The total current increase and growth rate of the zinc electrode of the three current collectors (substrates) are shown in Table 2.
[0030] foam brass
[0031] Zinc electrodes will produce dendrites during the charging process, and the growth of dendri...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| current density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com