Optical fiber welding machine and welding method
An optical fiber and butt joint technology, which is applied in the field of optical fiber fusion splicing machine and fusion splicing connection, can solve the problems of complicated operation and inability to be simple.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
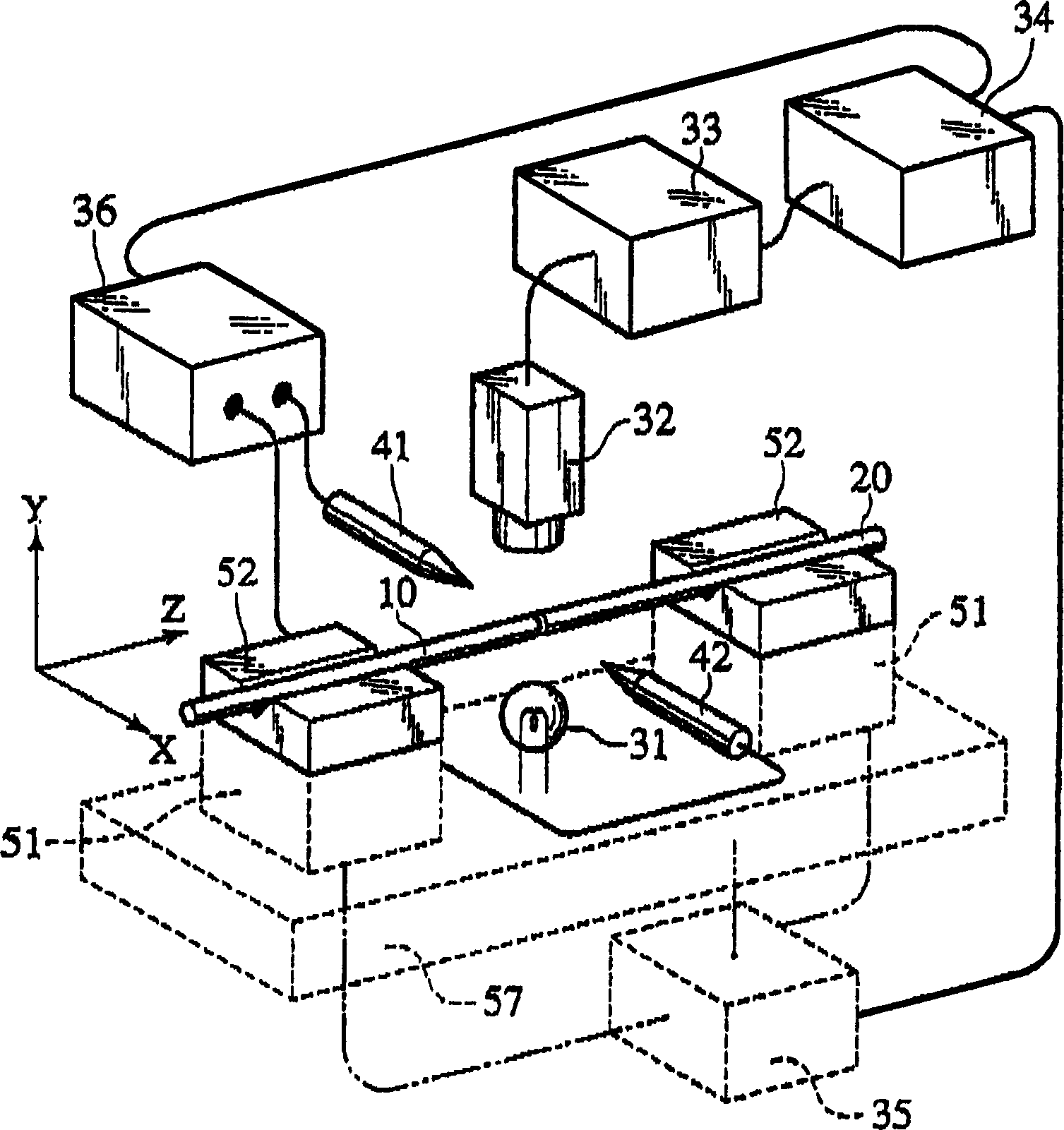
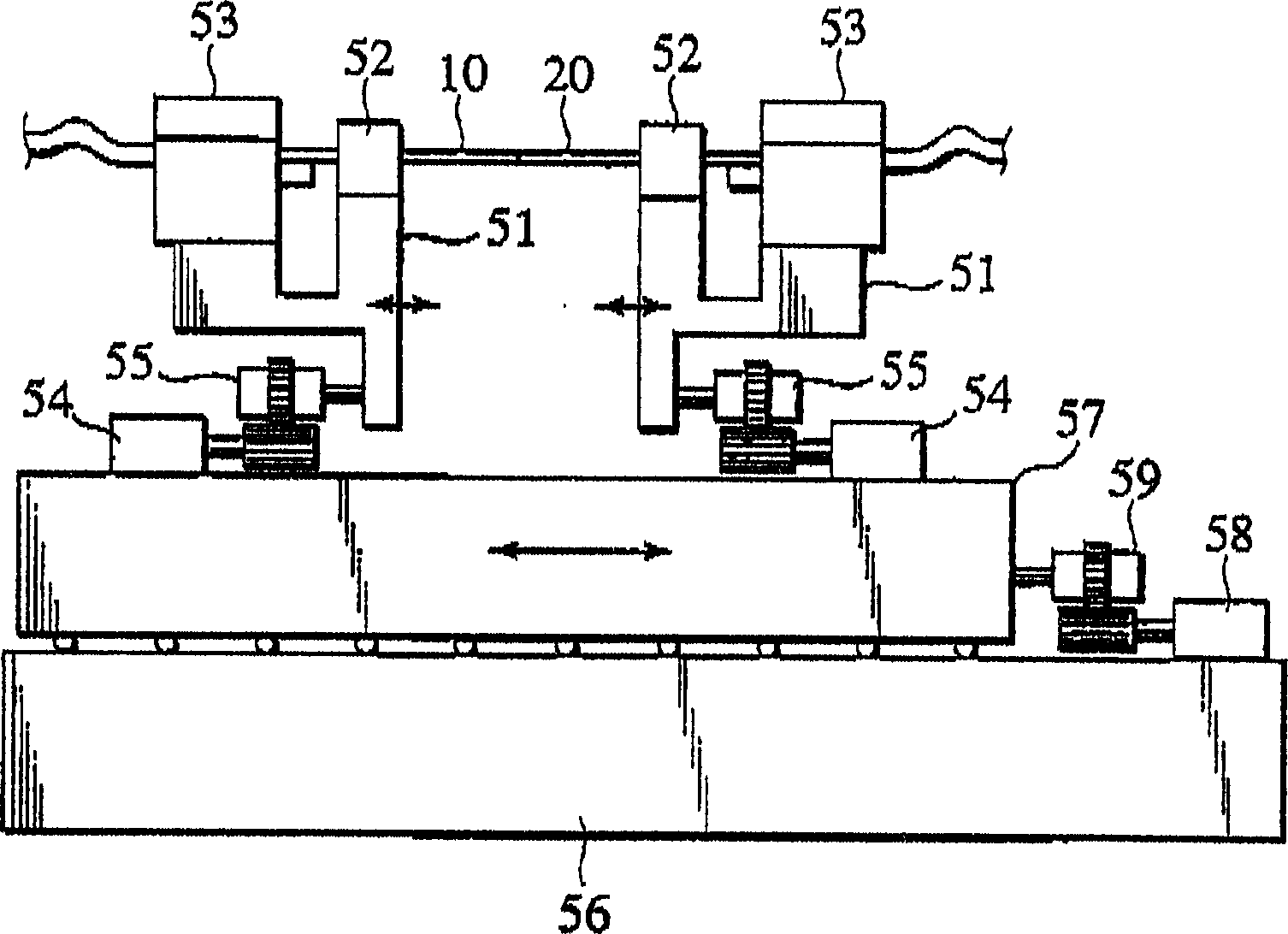
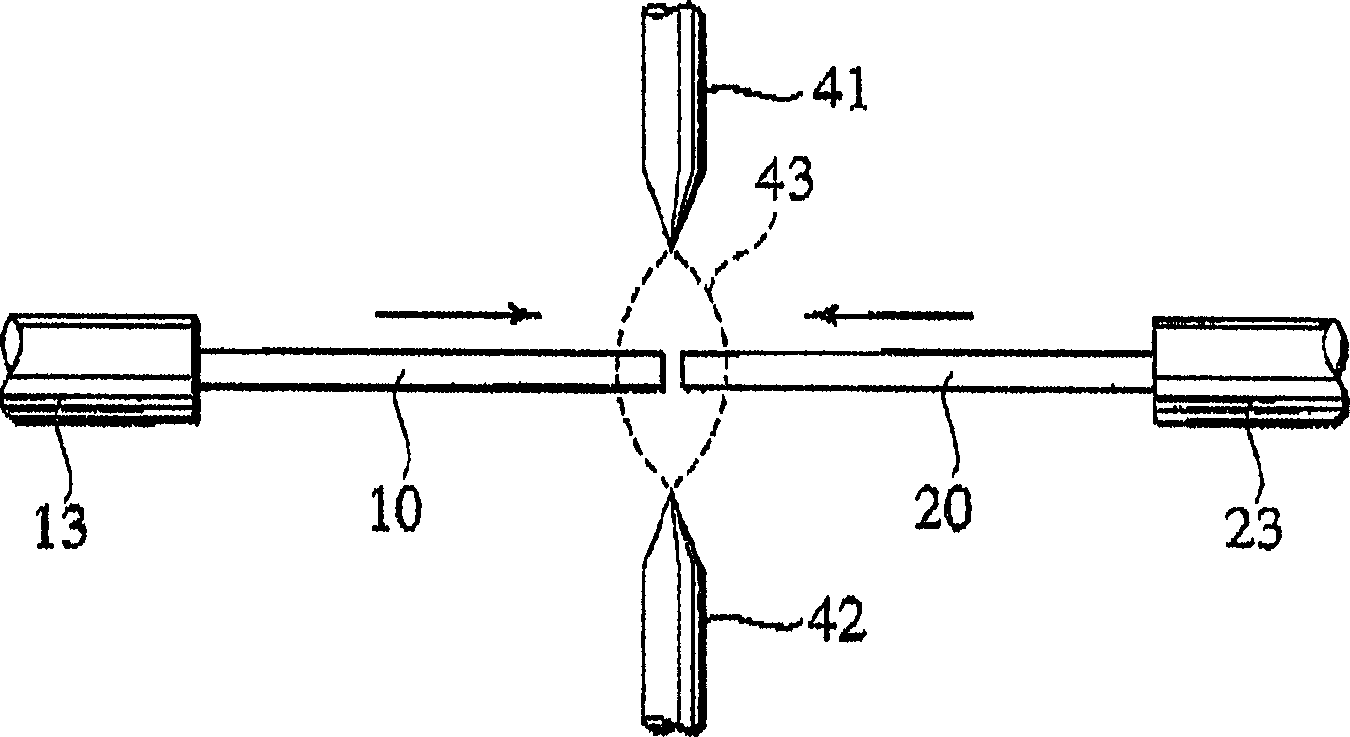
[0036] Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings. figure 1 It is a schematic diagram conceptually showing an optical fiber fusion splicing machine according to an embodiment of the present invention. in the figure 1 Among them, the V-groove bases 52, 52 are used to respectively set the two optical fibers 10, 20 to be connected and place them on the moving bases 51, 51. These moving bases 51, 51 can move along the directions of X, Y, and Z axes. Here, the axial direction (horizontal direction) of the optical fibers 10, 20 is defined as the Z-axis, the horizontal direction at right angles to the axes of the optical fibers 10, 20 is defined as the X-axis, and the vertical direction at right angles to the axes of the optical fibers 10, 20 is defined as the X-axis. The direction is taken as the Y axis. These moving seats 51, 51 are placed on the movable base 57, and the movable base 57 moves along the Z axis, so ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com