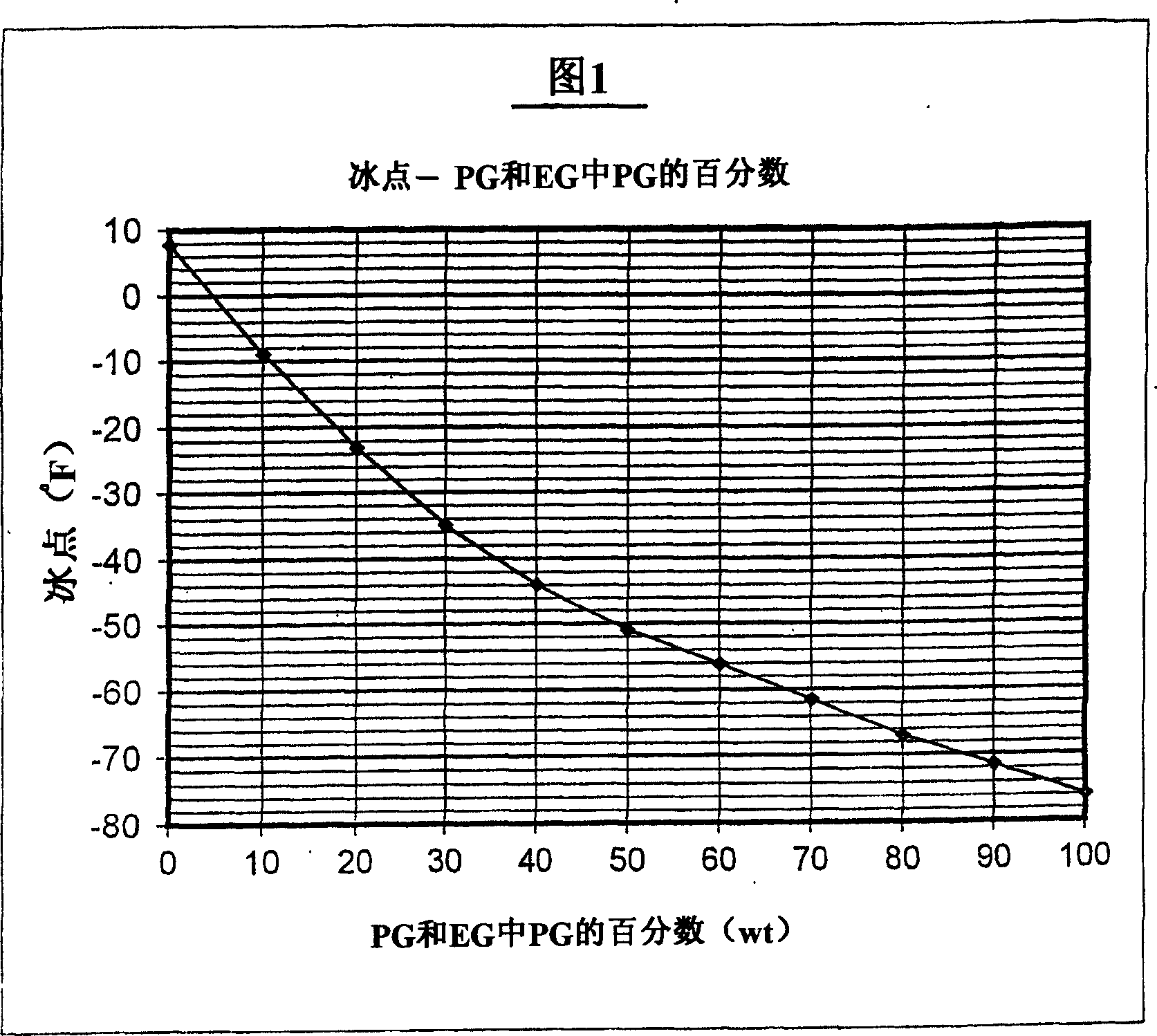
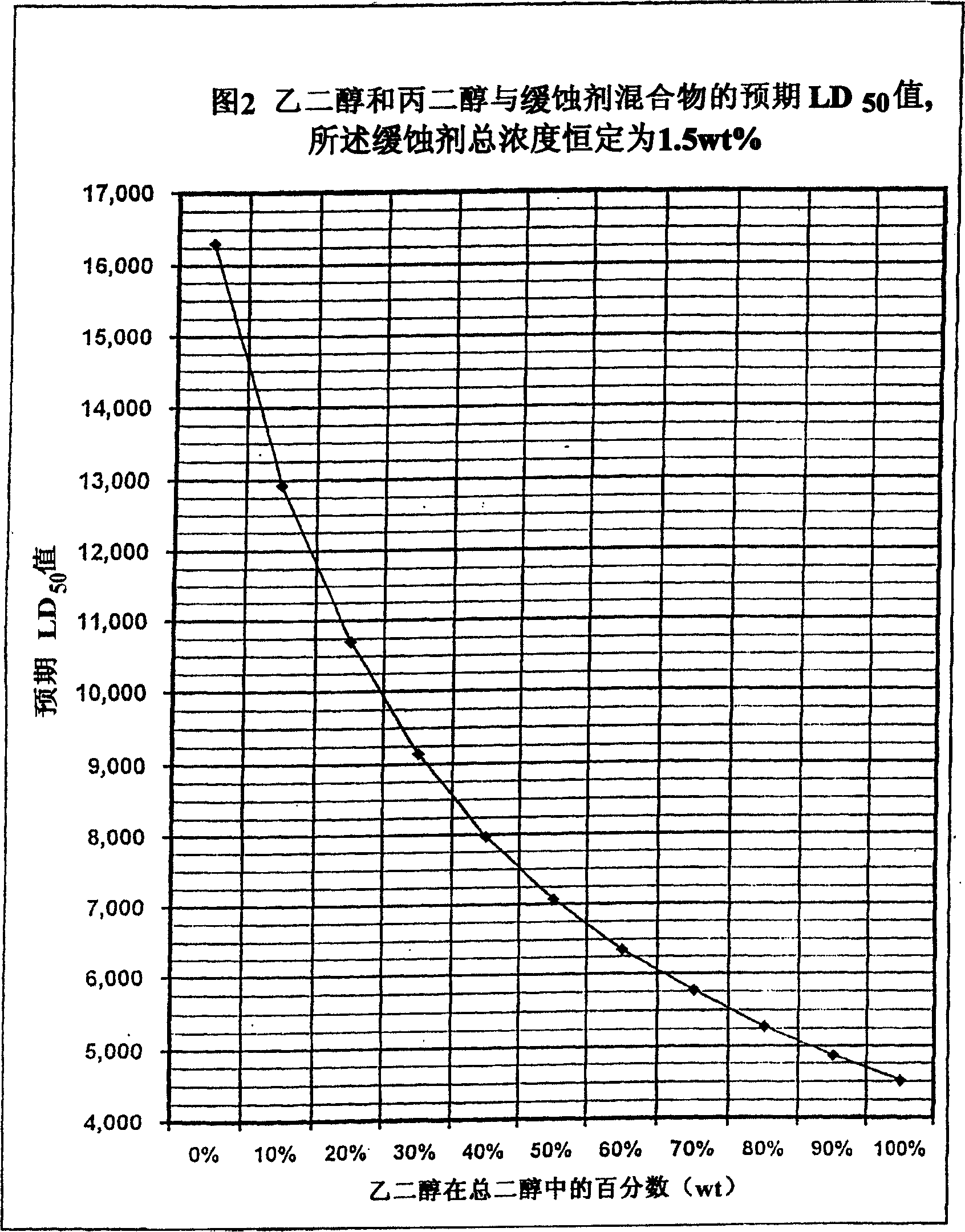
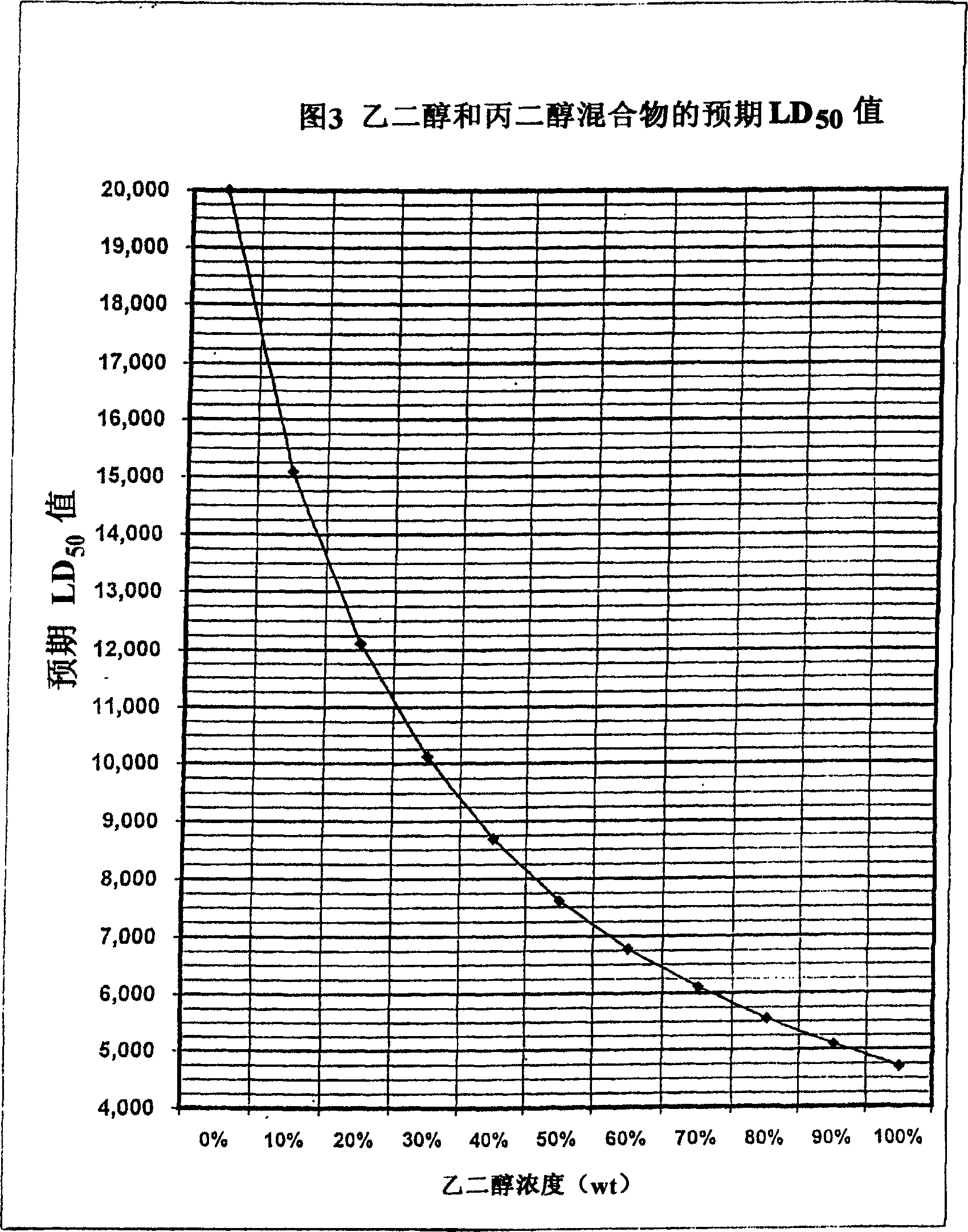
Non-aqueous heat transfer fluid and use thereof
A technology of heat transfer fluid and heat exchange system, which is applied in the field of low-toxic fluid preparation, can solve the problems of toxicity and additive toxicity, and achieve the effects of reducing overheating, preventing cavitation corrosion, and reducing losses
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0122] This corrosion test was performed using the test procedure described in ASTM #D-1384 (Revised Edition). Six substances, which are typical metals found in engine coolant systems, were completely immersed in the test coolant contained in glass vessels. Coolant "A" is a non-aqueous heat transfer fluid of the present invention in which the proportion of polyol is 100% PG. Coolant "B" is a conventional engine coolant formulation consisting of EG-based antifreeze concentrate mixed with water.
[0123] In the ASTM test procedure, the coolant is aerated with air bubbling through a glass vessel and maintained at a test temperature of 190°F (88°C) for 336 hours. This procedure was changed to more accurately reflect the conditions experienced by metals in engine coolant systems in service. Tests were conducted at a control temperature of 215°F (101.6°C) to simulate heavy-duty use. Coolant "A" was tested without an air charge in order to more closely approximate operation in non...
Embodiment 2
[0144] Corrosion testing is performed to determine the amount of corrosion of cast aluminum or magnesium alloys in engine coolants under heat rejection conditions. A sample of cast aluminum alloy typically used in an engine cylinder head or cylinder block is contacted with a test engine coolant solution. Coolant "A" is a non-aqueous coolant of the present invention consisting of 100% PG. To simulate the operating conditions of coolant systems using coolants other than water, tests using Coolant "A" were conducted at a temperature of 275°F (135°C) and a pressure of 2 psig (13.79kPa), which is slightly higher than Atmospheric pressure. Test coolant "B" contained corrosive water as specified by ASTM and was used to make up the water portion of a 50 / 50 PG / EG water coolant. The test conditions for Coolant B were to simulate the conditions in an aqueous coolant engine cooling system, a temperature of 275°F (135°C) and a pressure of 28 psig (193 kPa).
[0145] For each test, the h...
Embodiment 3-
[0150] Embodiment 3-field test
[0151]Operate a 3.8L V-6 engine on the road for a test period of 55,000 miles (88,511.5 kilometers). The engine cooling system of a vehicle is constructed as described in US Patent 5,031,579. Coolant "A" was the same non-aqueous coolant described in Example 1 above. During the test period, the coolant was not drained or replaced. The metal sample pack was placed in the full flow of the engine coolant flow (lower hose) and kept submerged in the coolant at all times. The ability of the test coolant to inhibit metal corrosion was evaluated by comparing the weight loss (in milligrams) of the specimens at the end of the test period to the ASTM test standard. The result looks like this:
[0152] Δweight (mg)
[0153] Metal Coolant "A" ASTM Standard
[0154] Cast iron -2.8 -10
[0155] Aluminum +0.2 -30
[0156] Steel -1.1 -10
[0157] Copper -1.3 -10
[0158] Solder -3.7 -30
[0159] Brass -0.9 -10
[0160] Starting pH +7.1 NA
...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com