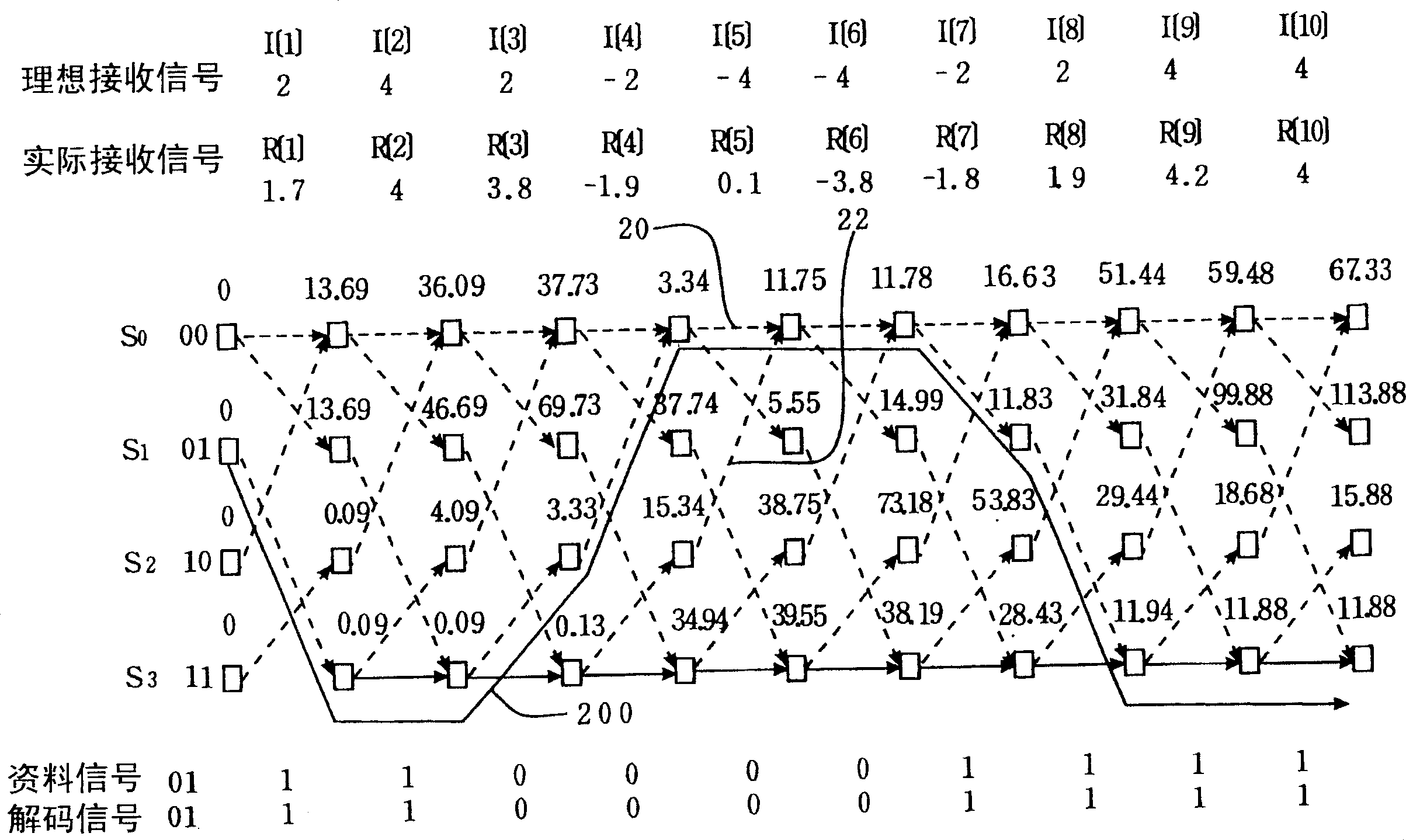Method and system for regulating maximum probability detection
A possibility and maximum technology, applied in the field of dynamically changing the branch metric weight of the maximum possibility detector, which can solve the problems of decoding influence and insoluble detection results.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
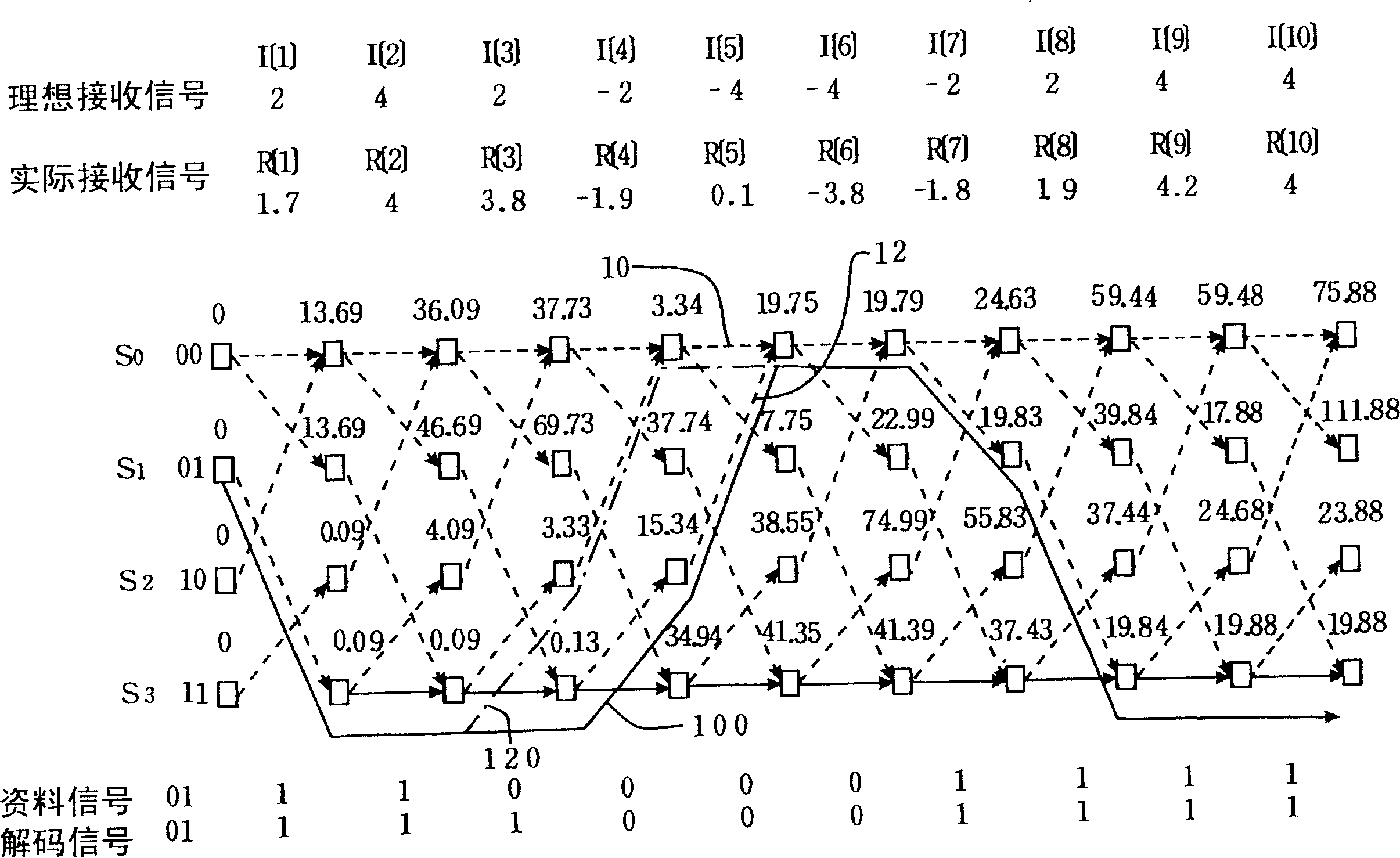
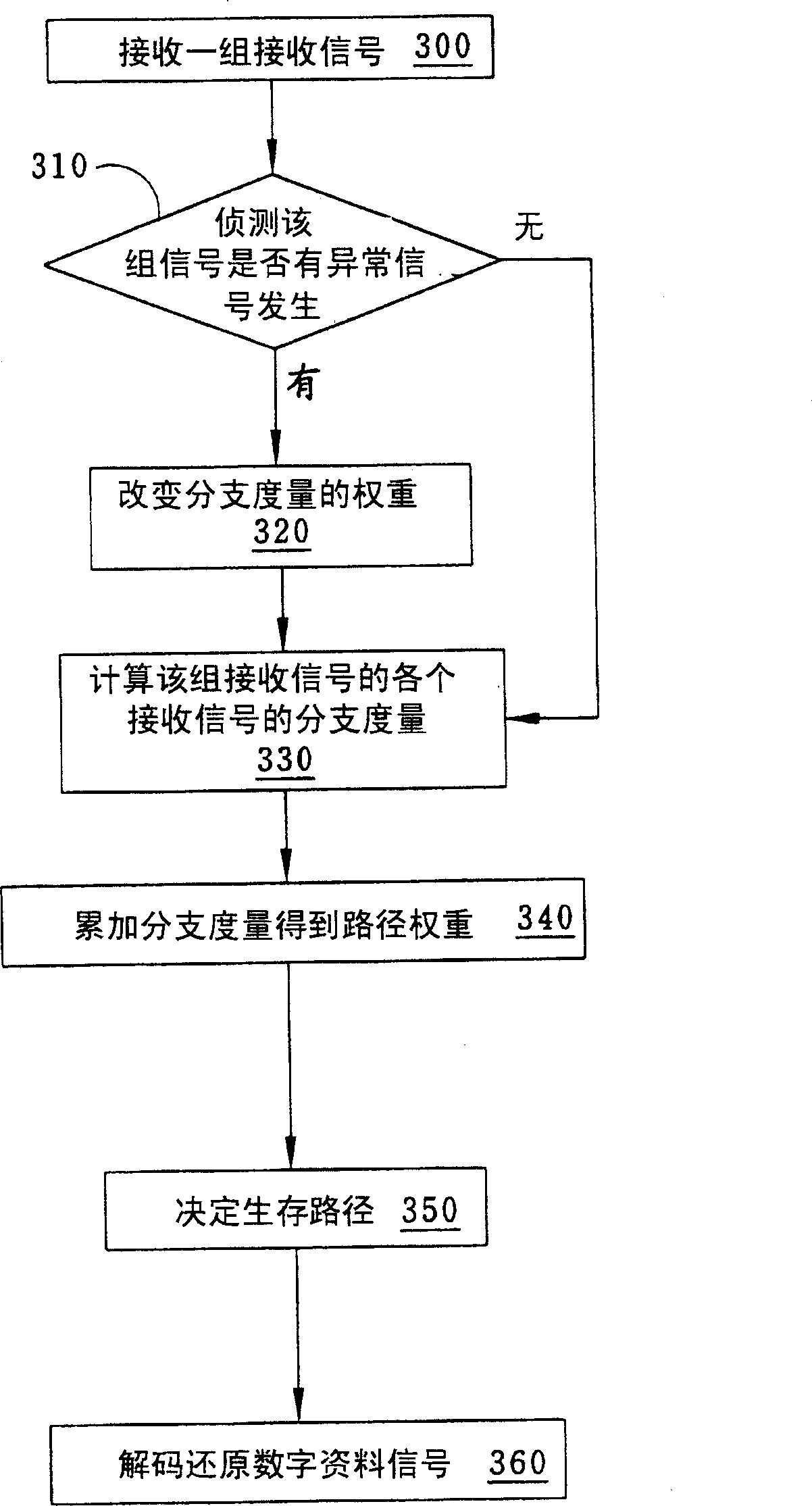
[0027] From the foregoing, one of the features of the present invention is to use detected anomalies to adjust maximum likelihood detection before decoding a received signal. Therefore, when the receiver receives a certain signal pattern (Pattern), it can determine whether the signal is an abnormal signal or an error is generated due to excessive noise.
[0028] If we encode the original digital data signal in RLL(2,10) (Run Length Limited) format, when this signal passes through a part of the response channel PR(1,2,1), the ideal signal level is (4,2, -2, -4) four, while receiving signals will not have (2, -2, 2), (-2, 2, -2), (-2, 4, -2), or (2, -4 , 2) This type of (+, -, +) or (-, +, -) signal pattern, and the situation that the level difference of two consecutive received signals exceeds 6 occurs. Therefore, if the signal received by the receiving end has the above situation, it can be determined that the signal is abnormal.
[0029] figure 2 Schematic diagram of maki...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com