Patents
Literature
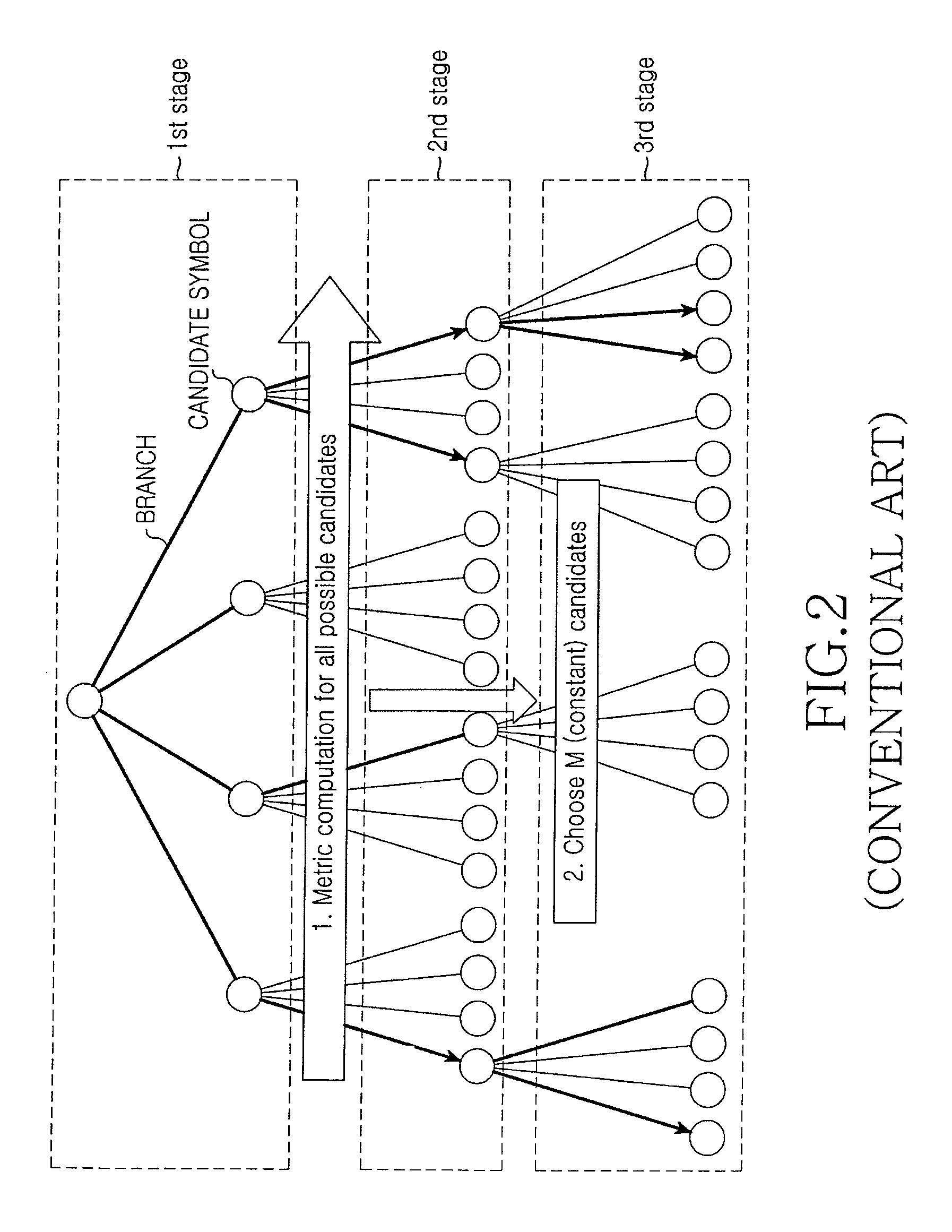
354 results about "Branch Metrics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
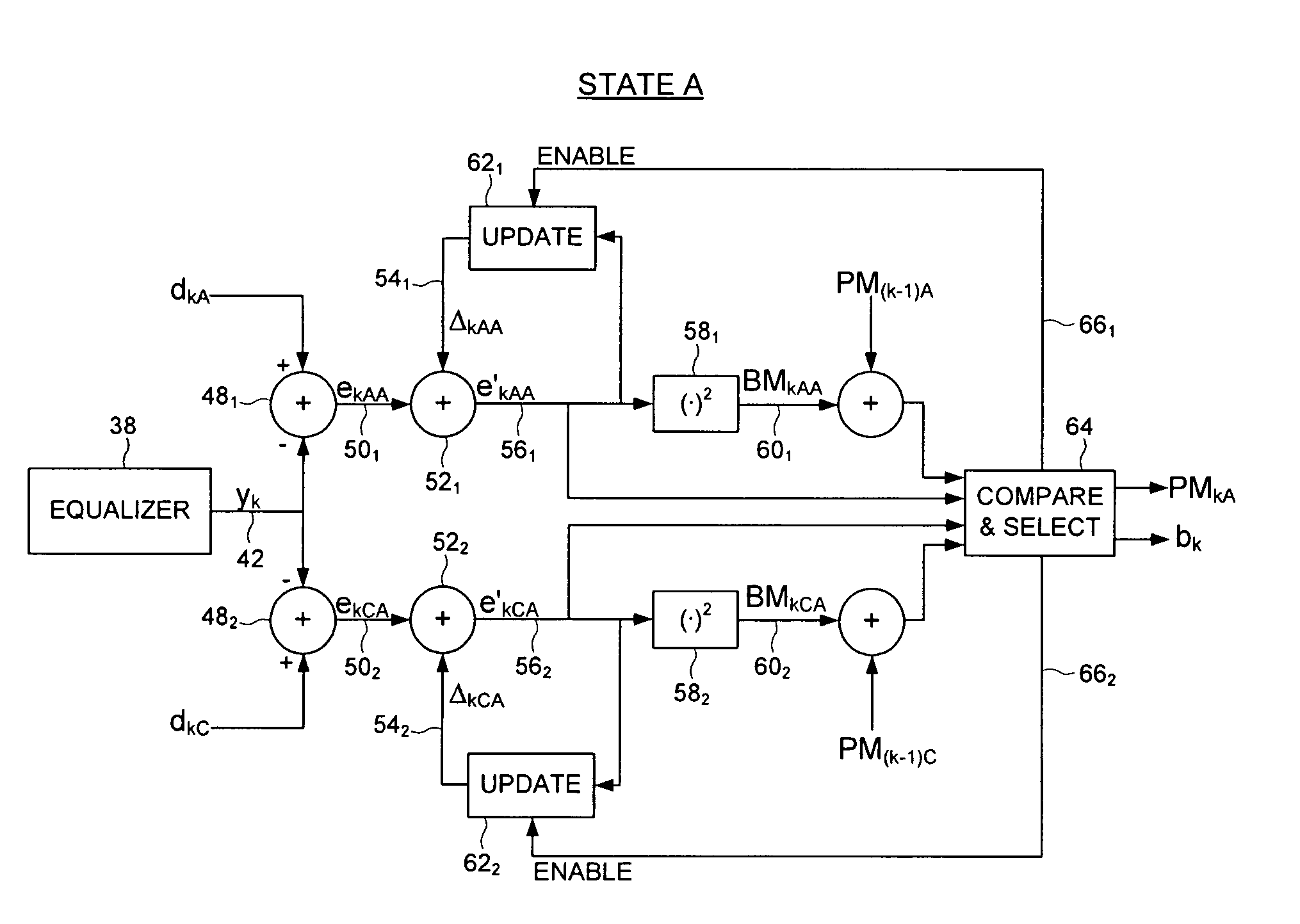
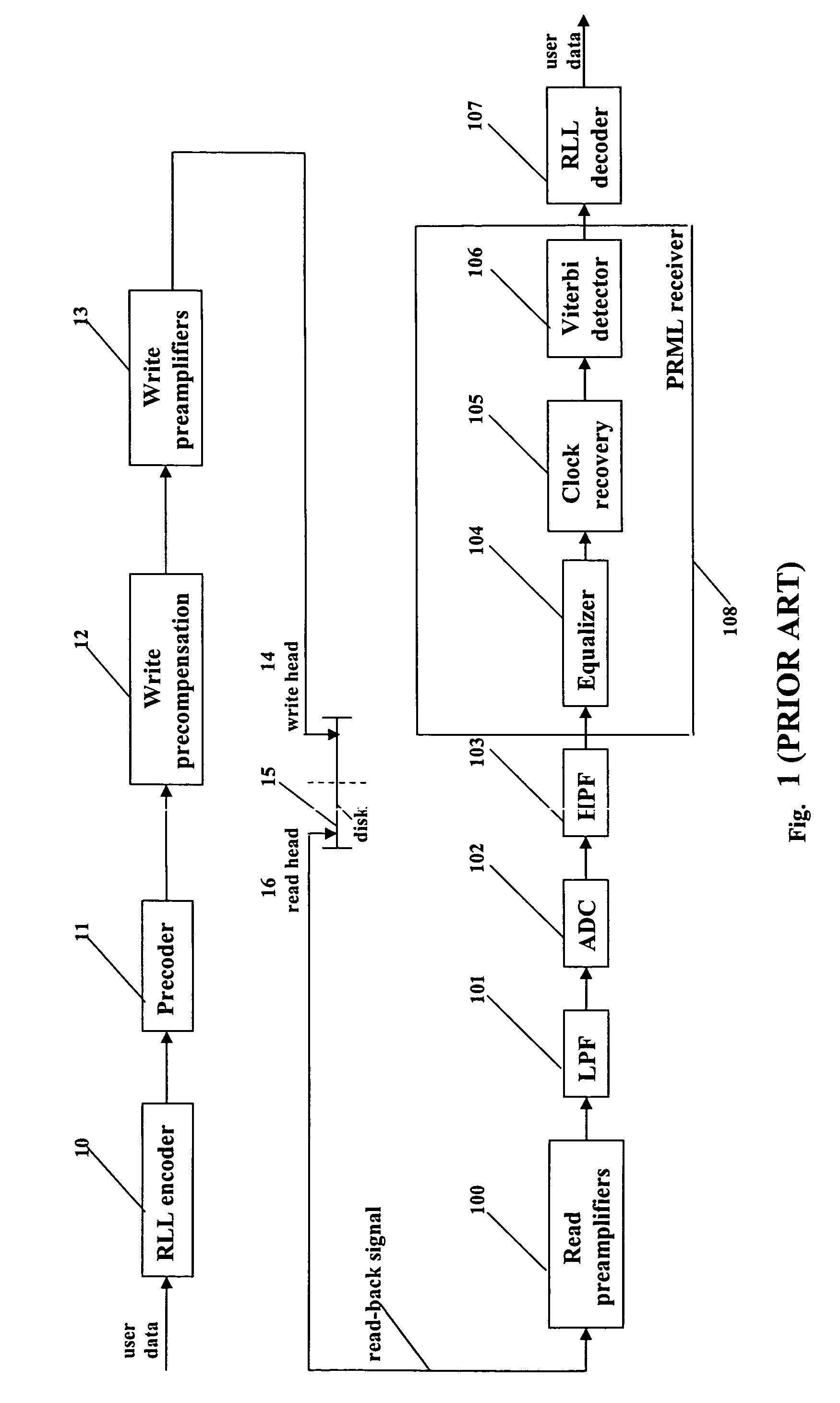
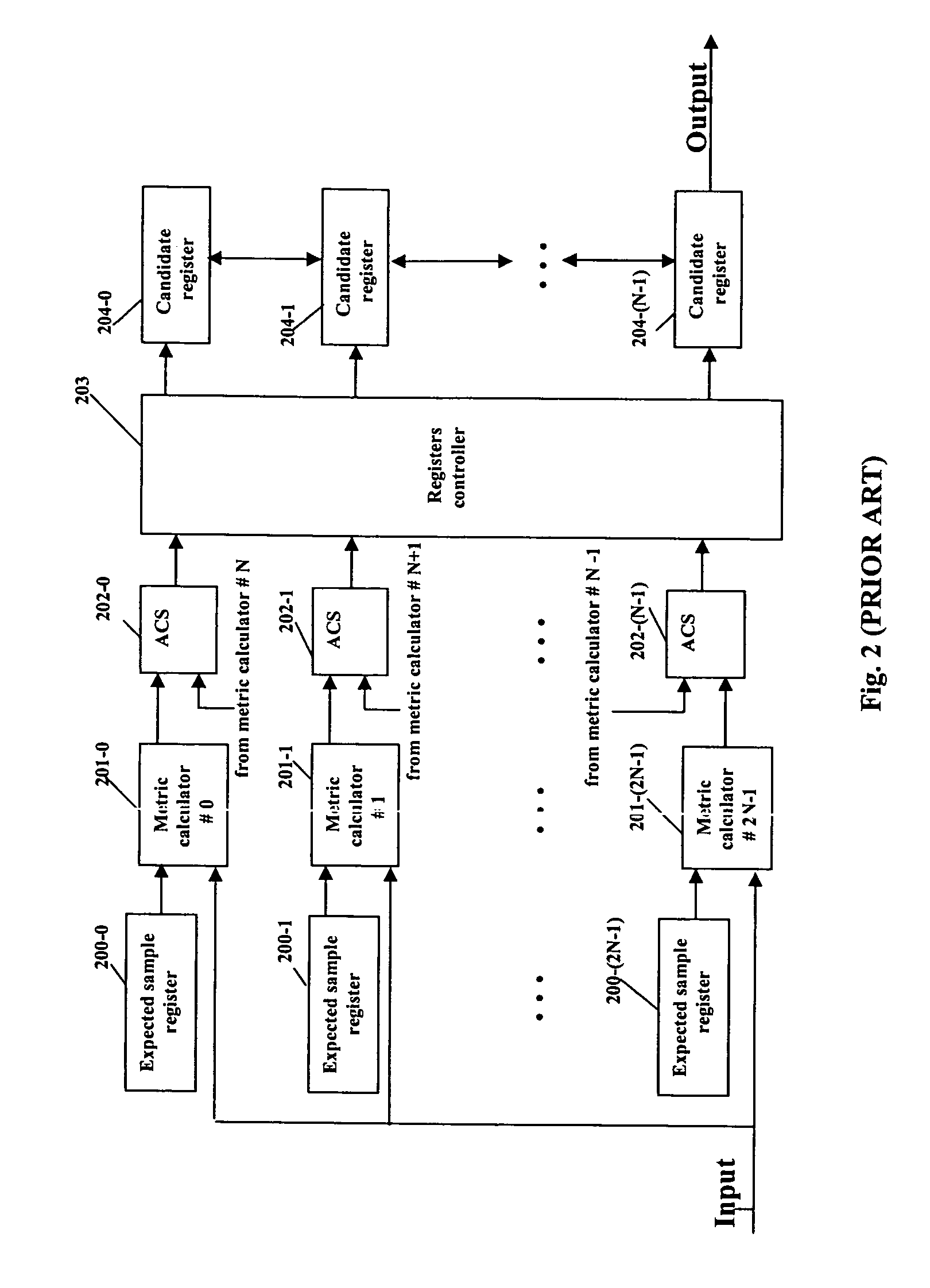
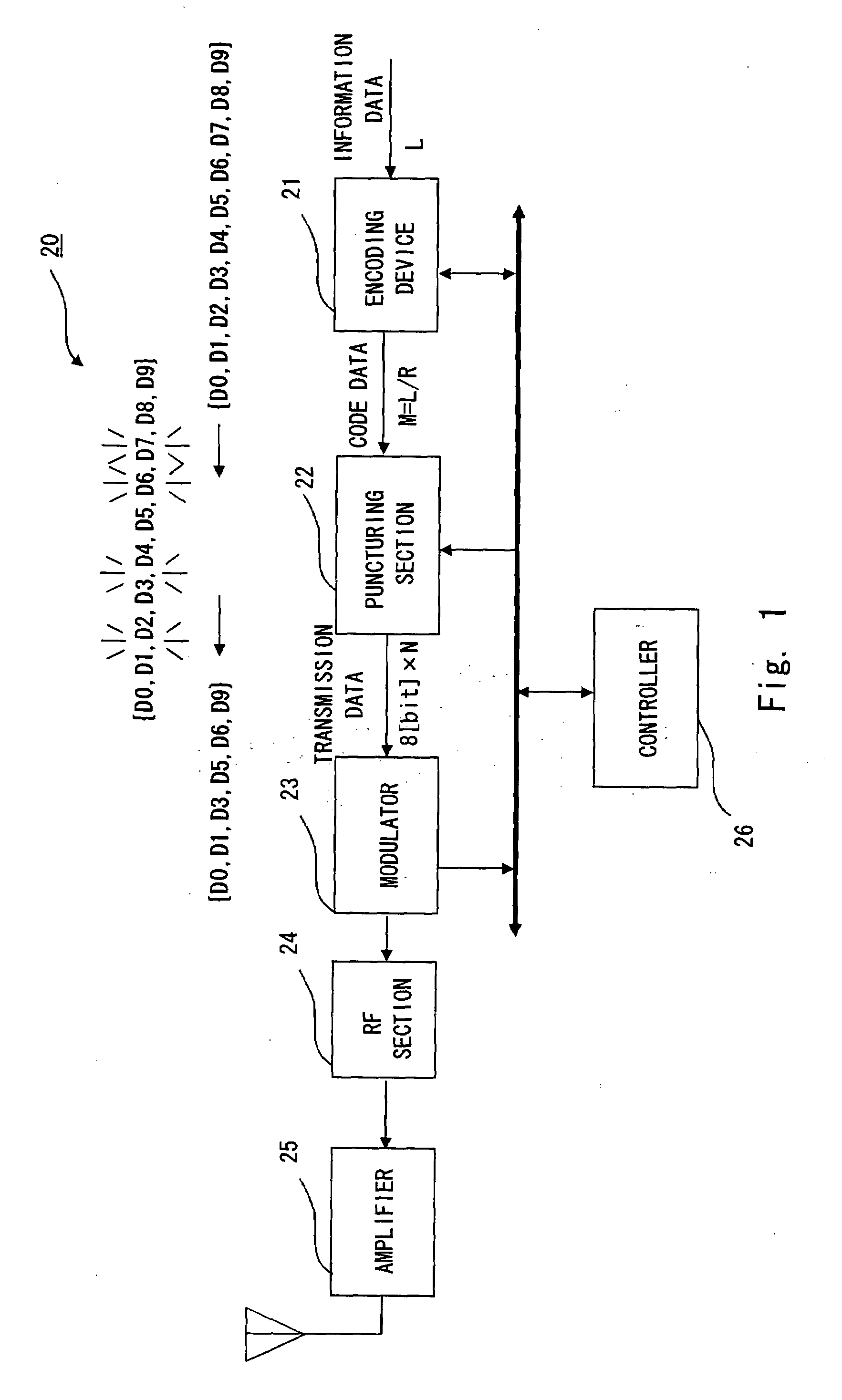
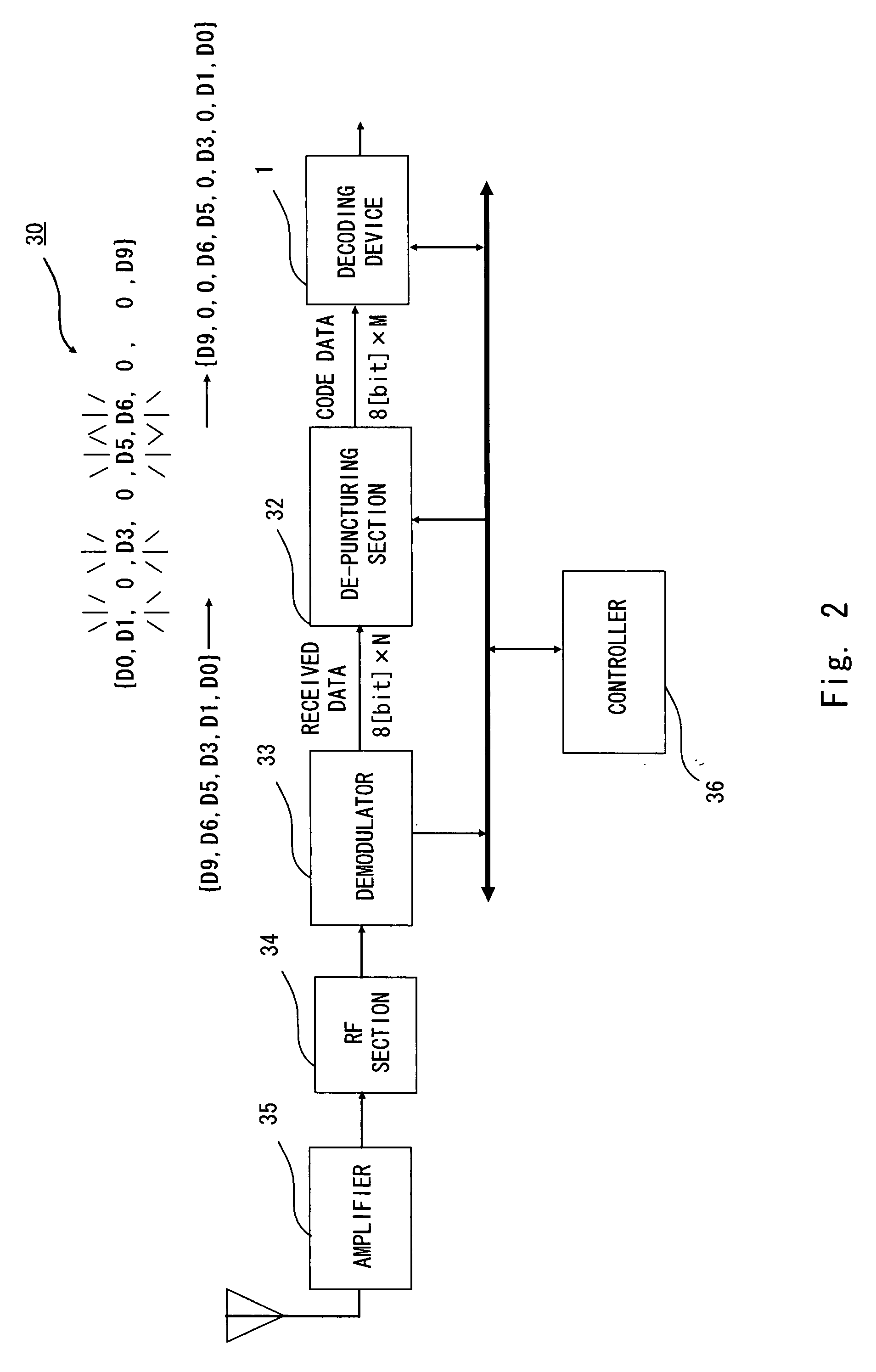
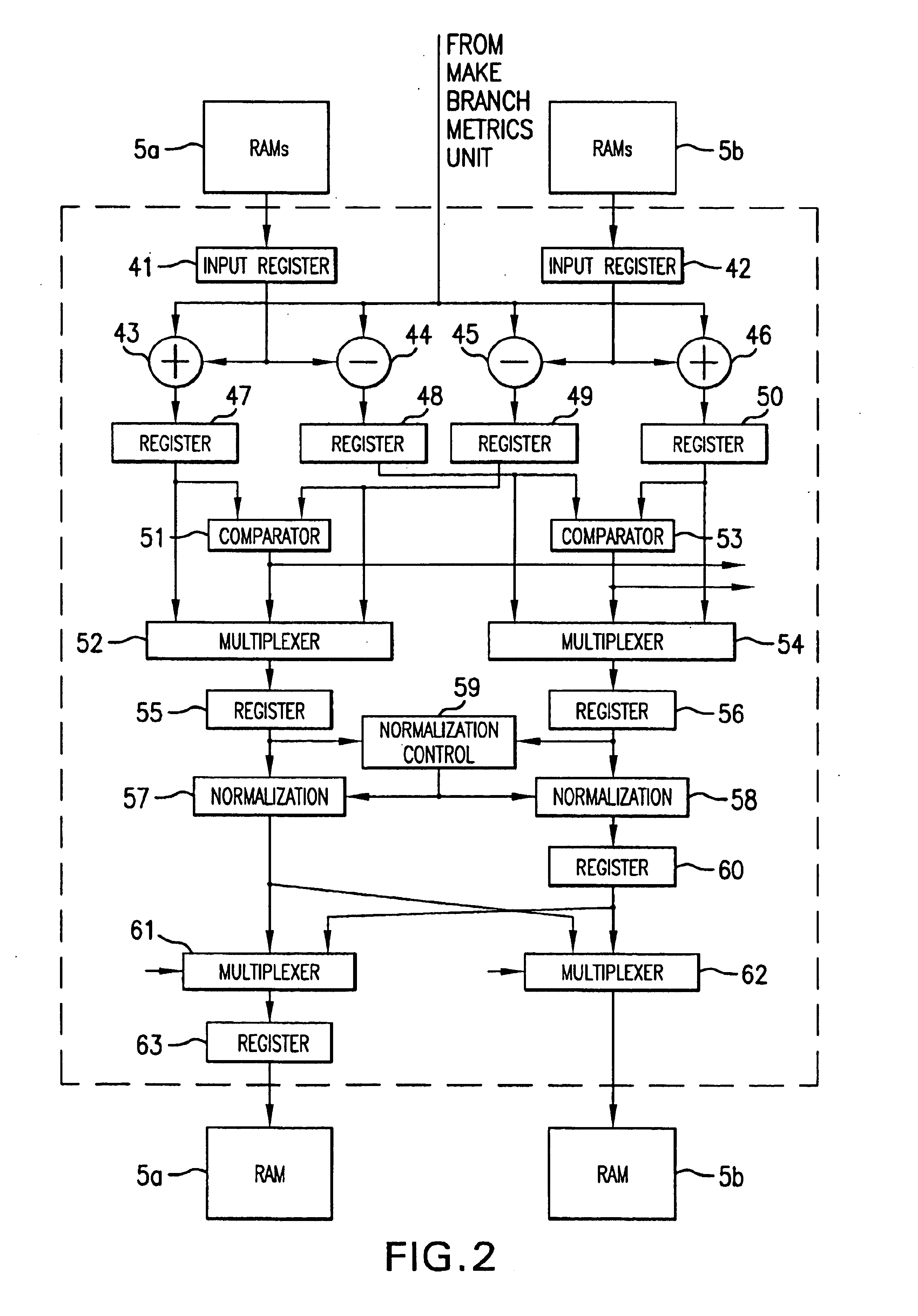
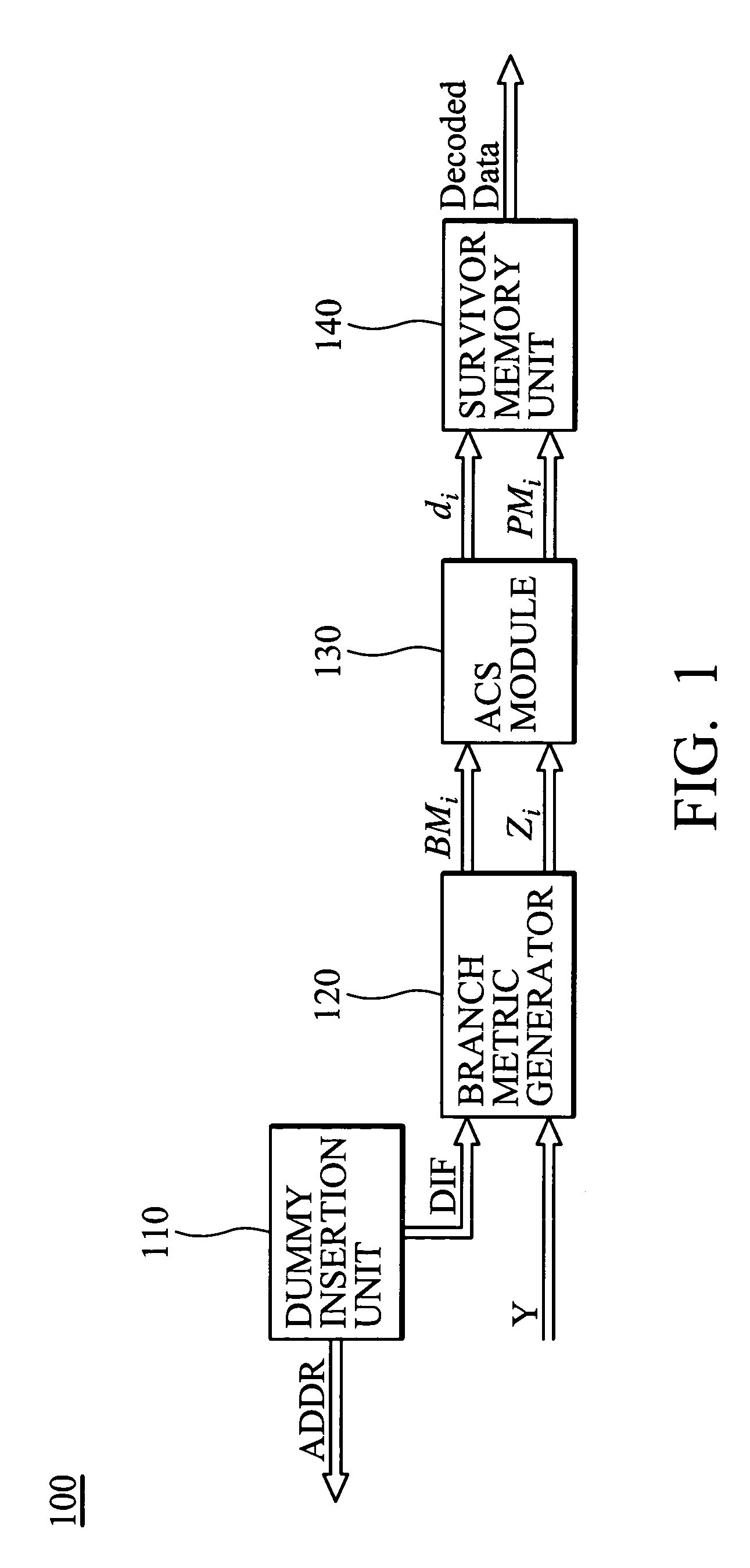
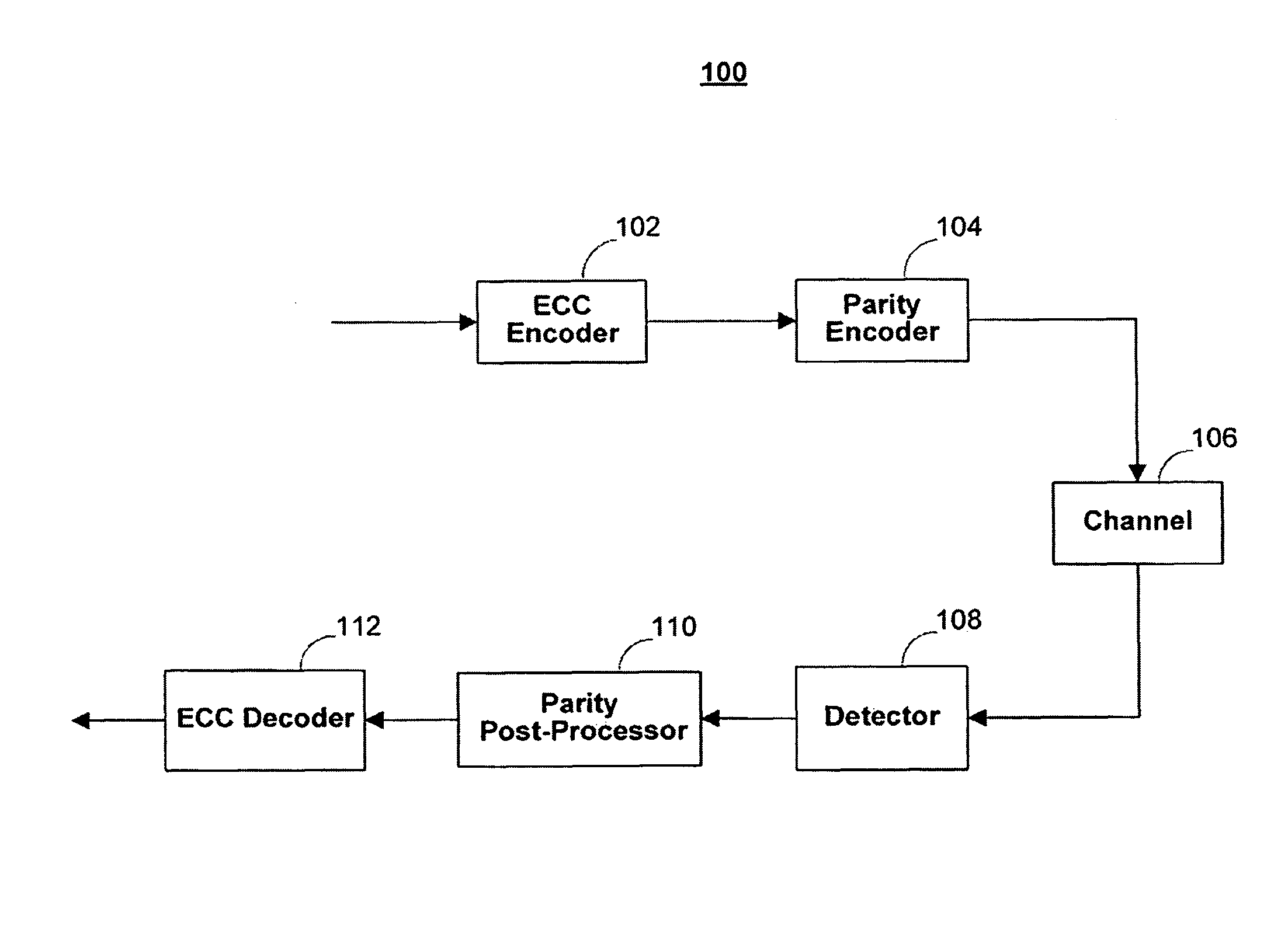
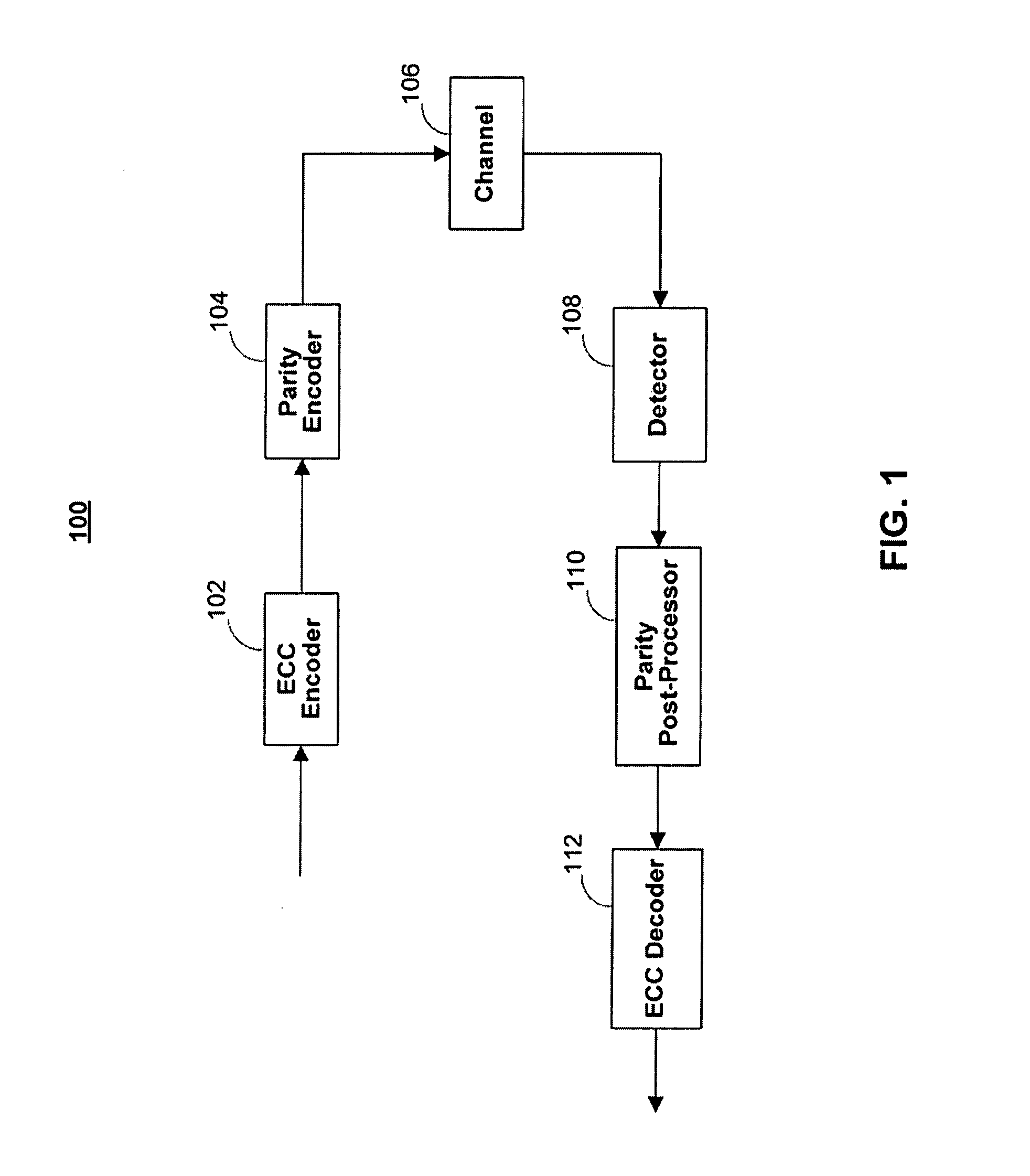
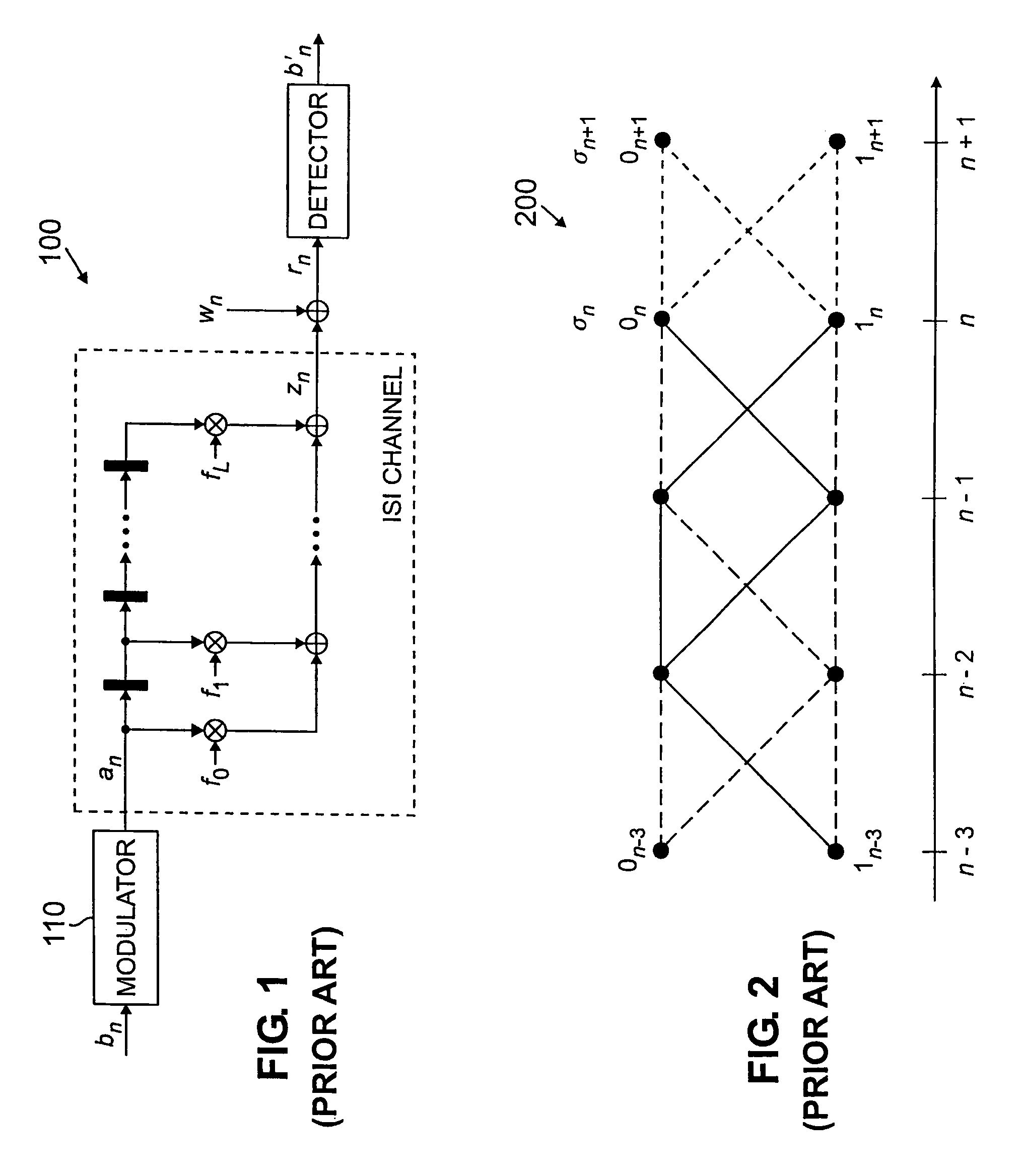
Disk drive comprising a trellis detector having a read signal whitener in the ACS circuit
InactiveUS8201066B1Modification of read/write signalsData representation error detection/correctionComputer scienceData sequences
A disk drive is disclosed comprising a disk, a head actuated over the disk to generate a read signal, and a trellis detector for detecting an estimated data sequence from the read signal. The trellis detector comprises a sampling device operable to sample the read signal to generate a sequence of signal sample values, and a plurality of add / compare / select (ACS) circuits each corresponding to a state in a trellis. Each ACS circuit comprises a first and second branch metric calculators for computing first and second branch metrics in response to first and second errors adjusted in response to first and second deltas that compensate for a distortion in the read signal.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
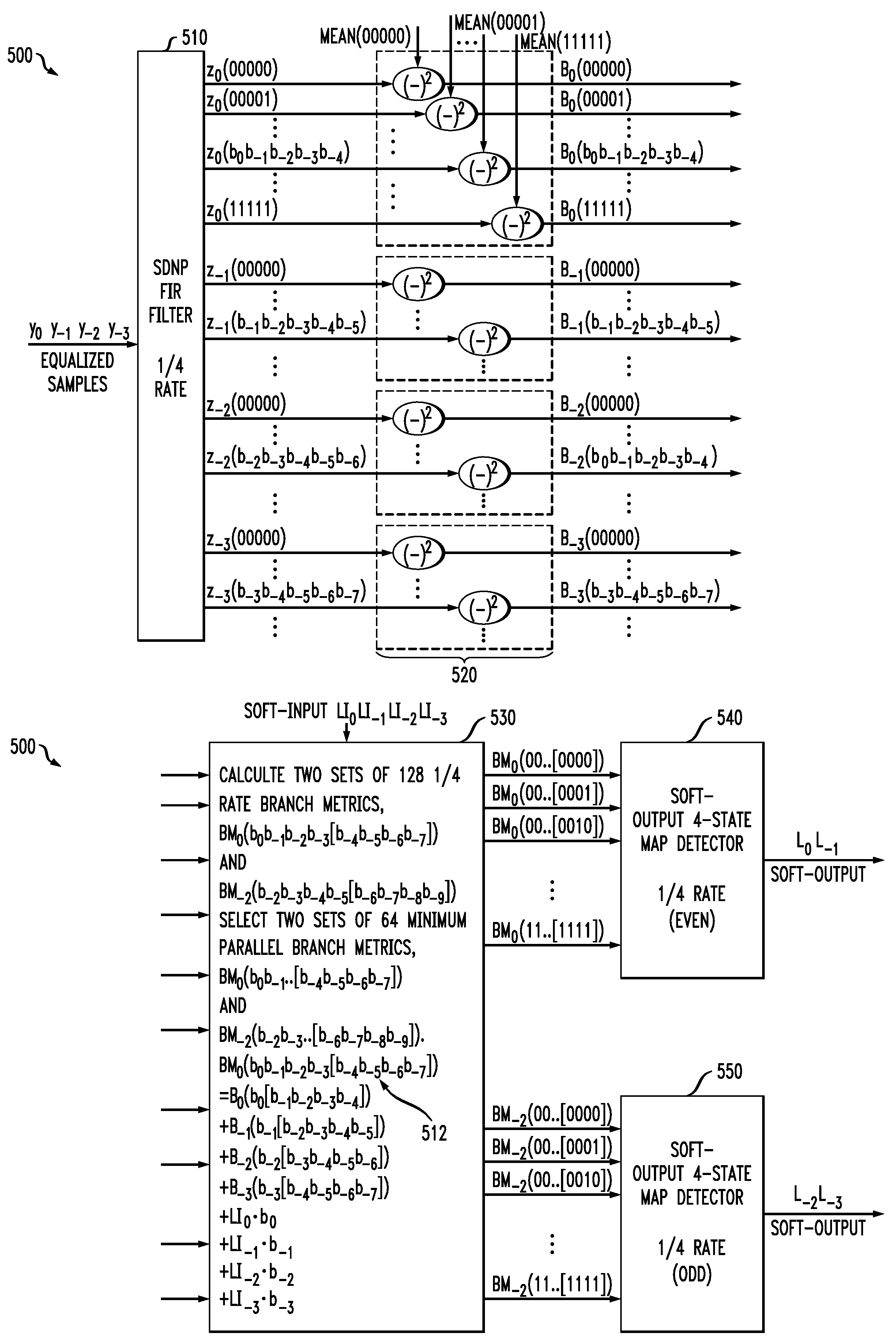
Methods and Apparatus for Map Detection with Reduced Complexity
ActiveUS20090185643A1Reduce complexityDependence moreDriving/moving recording headsError preventionLog likelihoodComputer science
Methods and apparatus are provided for high-speed, low-power, high-performance channel detection. A soft output channel detector is provided that operates at a rate of 1 / N and detects N bits per 1 / N-rate clock cycle. The channel detector comprises a plurality, D, of MAP detectors operating in parallel, wherein each of the MAP detectors generates N / D log-likelihood ratio values per 1 / N-rate clock cycle and wherein at least one of the plurality of MAP detectors constrains each of the bits. The log-likelihood ratio values can be merged to form an output sequence. A single MAP detector is also provided that comprises a forward detector for calculating forward state metrics; a backward detector for calculating backward state metrics; and a current branch detector for calculating a current branch metric, wherein at least two of the forward detector, the backward detector and the current branch detector employ different trellis structures.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Media noise optimized detector for magnetic recording
InactiveUS7173783B1Significant disk drive yield benefitImprove reliabilityTelevision system detailsModification of read/write signalsPattern recognitionViterbi detector
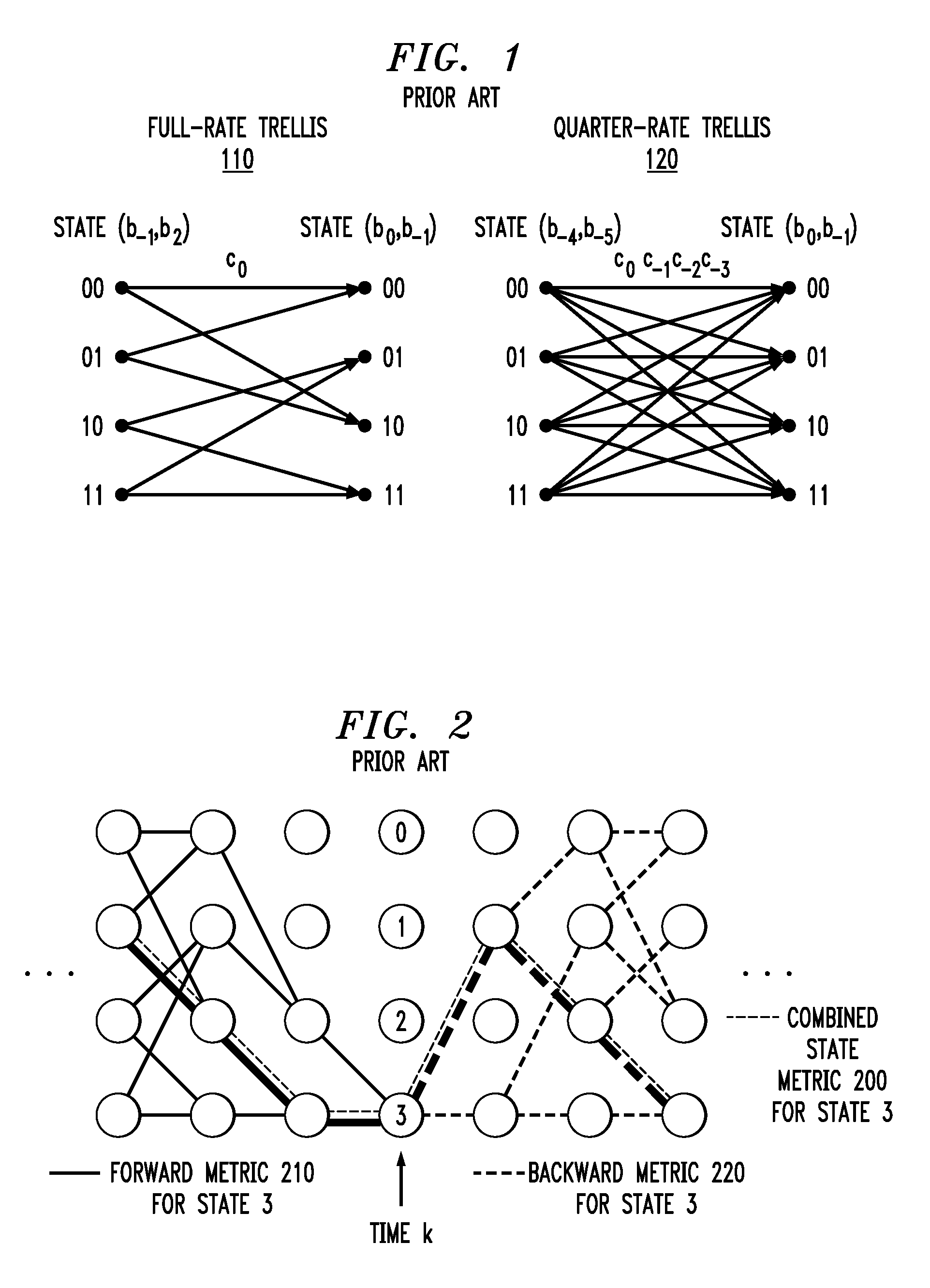
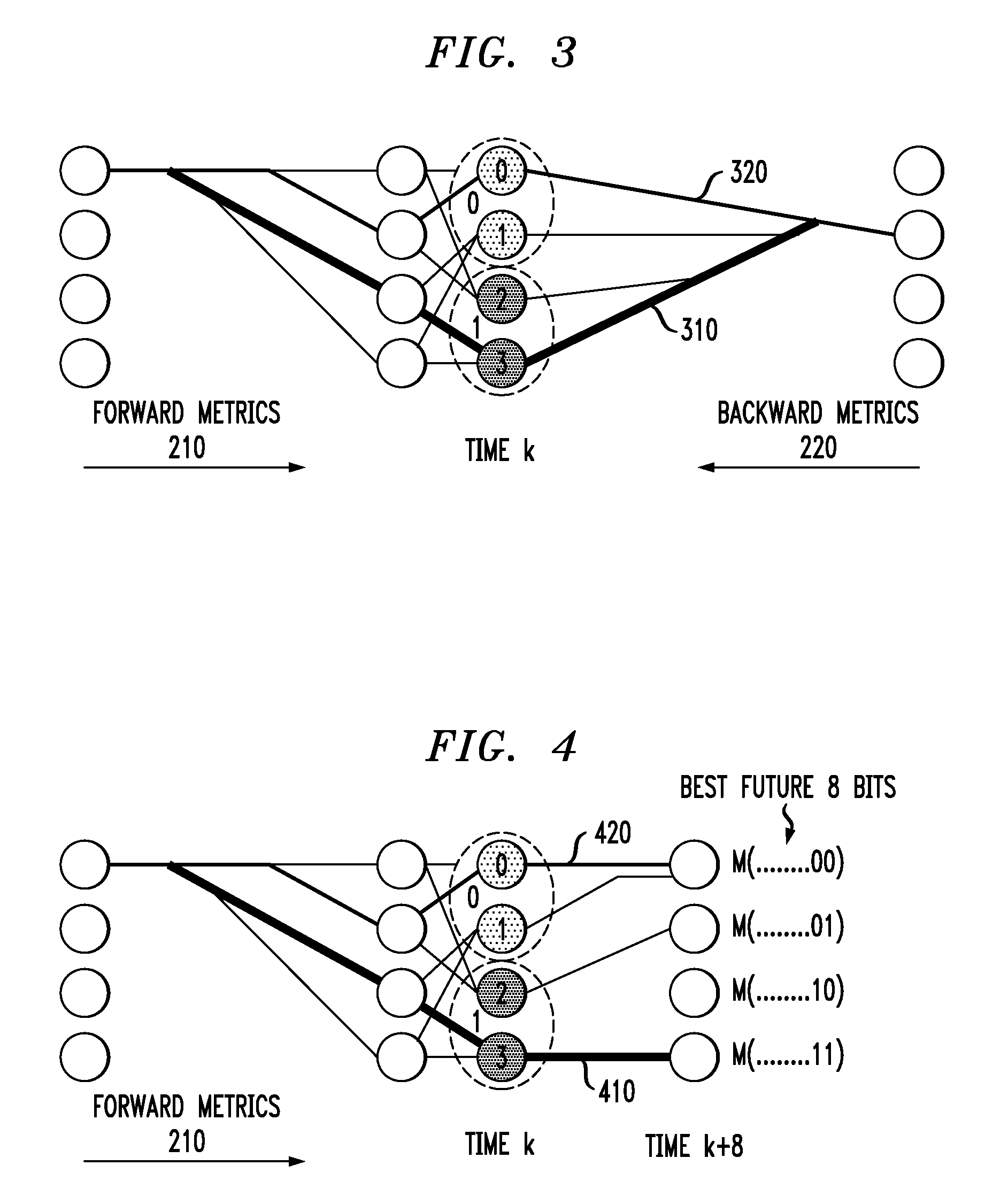
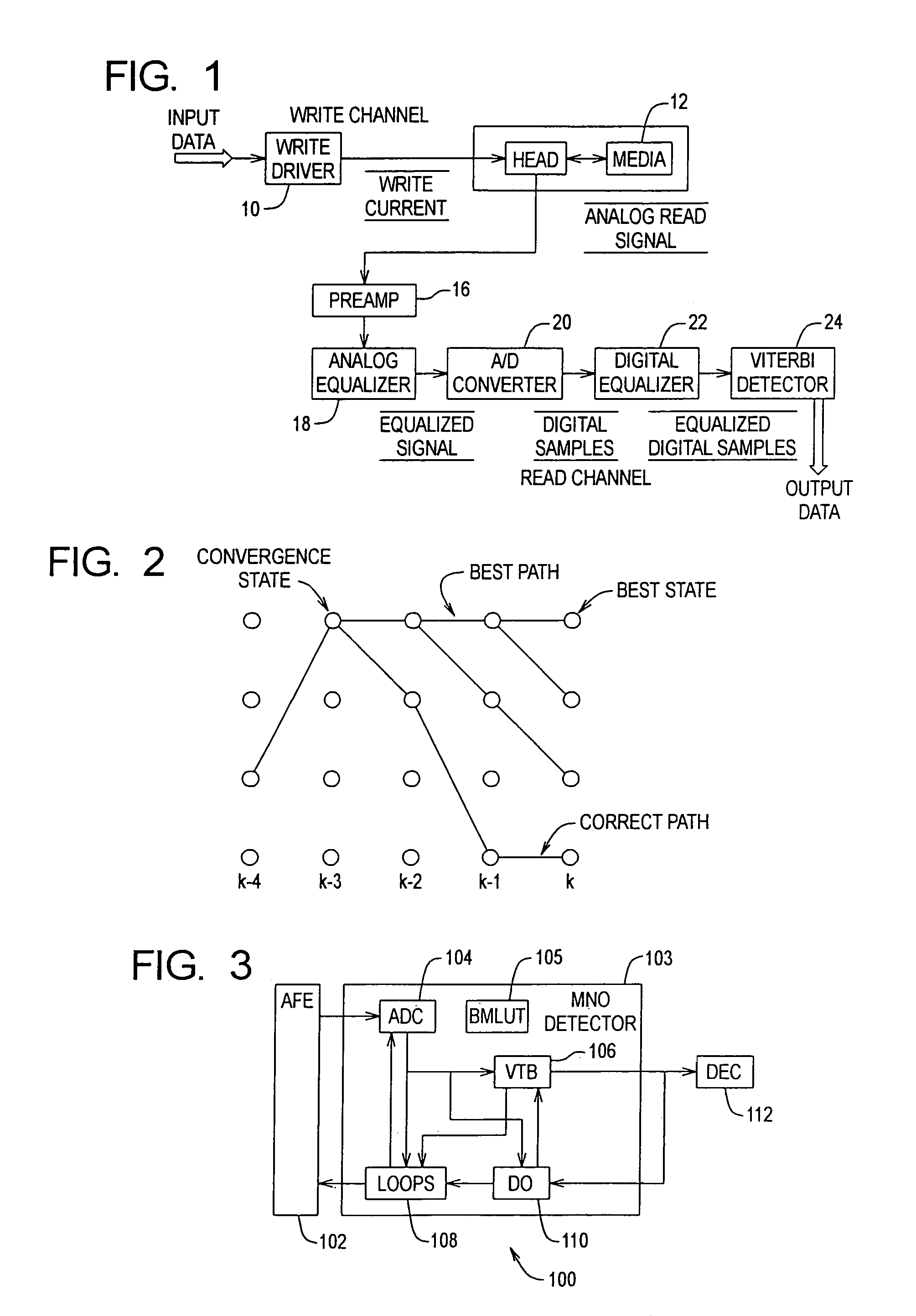
A media noise optimized (MNO) detector for a read channel compensates for pattern dependent media noise, and compensates for nonlinearities from many sources such as residual MR nonlinearity, residual nonlinear transition shift, partial erasure, write-induced nonlinearity, and steady-state mis-equalization. The MNO detector is implemented by adjusting a conventional Viterbi detector branch metric so that the channel output value (ideal value) can be a nonlinear function of the state / branch bits, and the branch metric scaling factor is a function of the state / branch. For a given state / branch, the ideal value is the mean of analog-to-digital converter samples for the pattern corresponding to the state / branch, and the branch metric scaling factor is proportional to the noise variance for the pattern corresponding to that state / branch.
Owner:MAXTOR
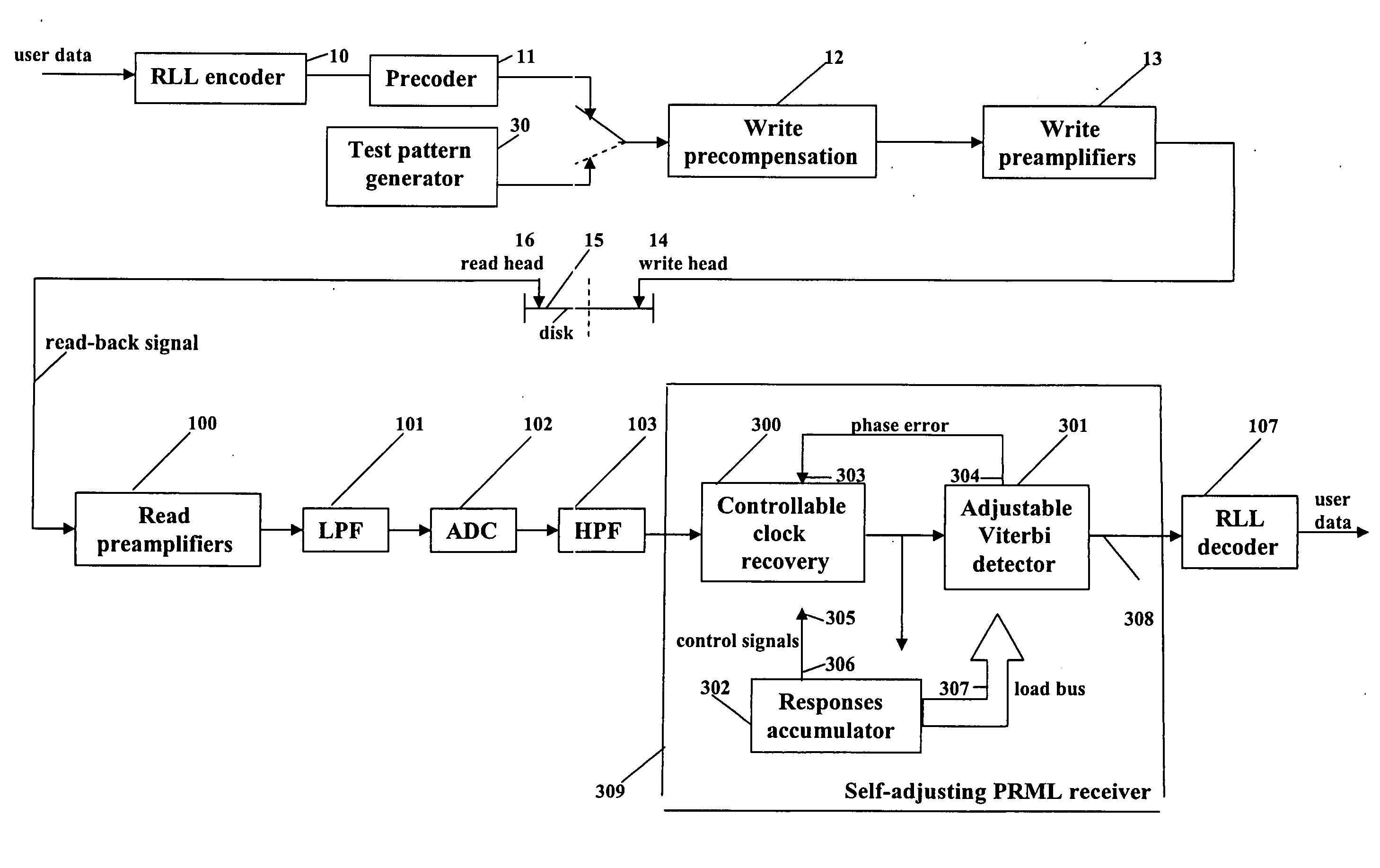
Self-adjusting PRML receiver
Owner:GUZIK TECHN ENTERPRISES
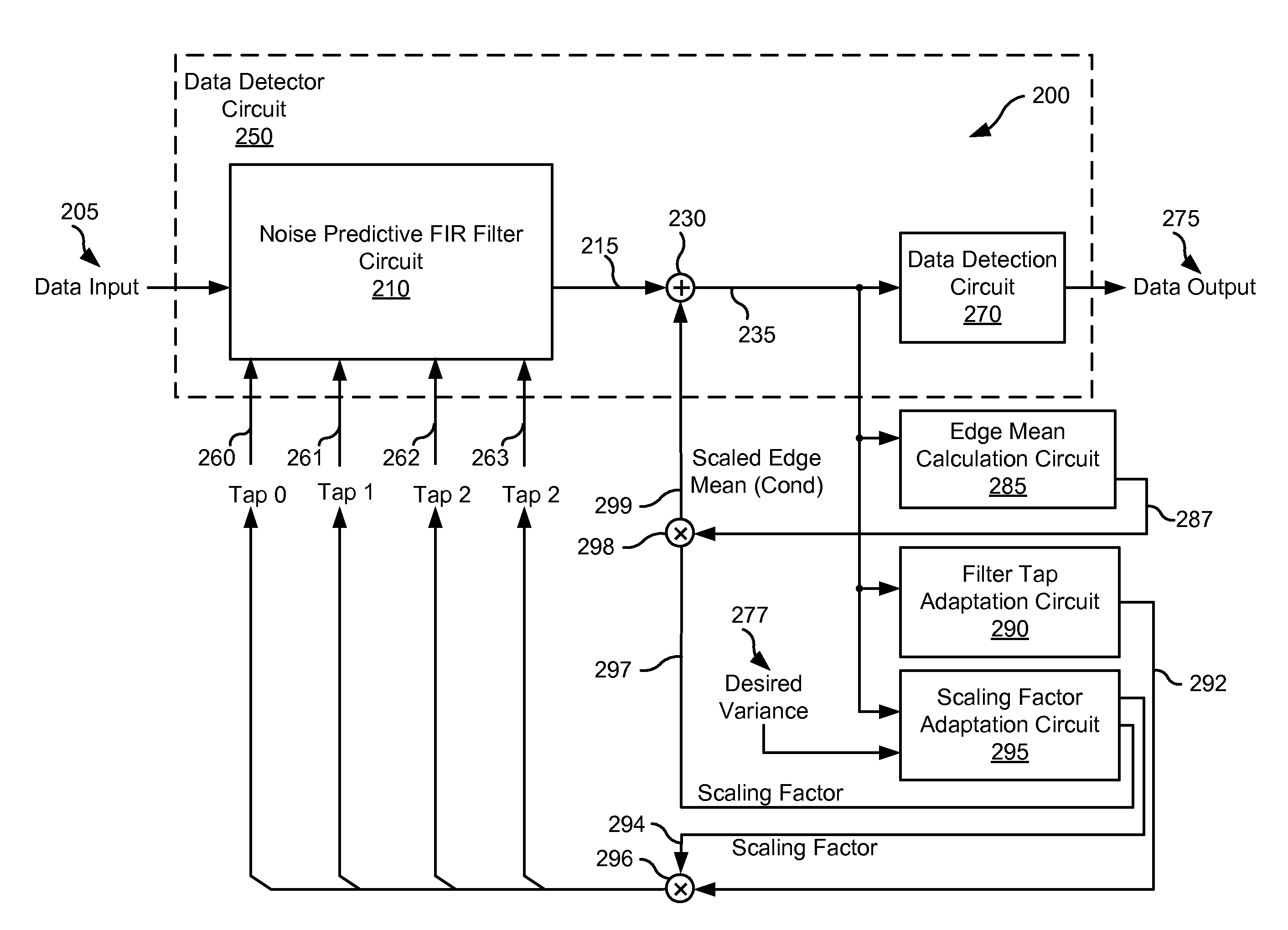
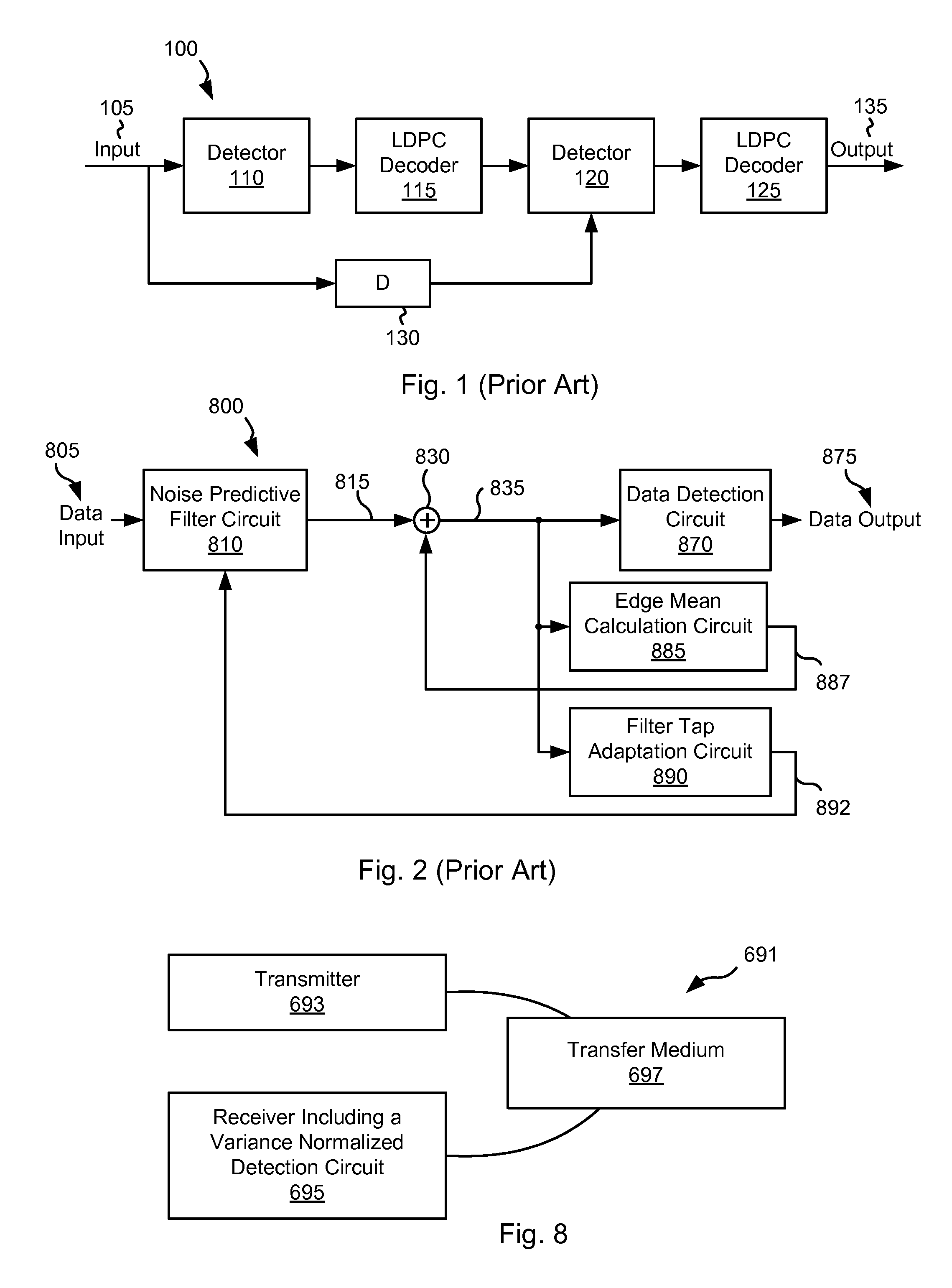
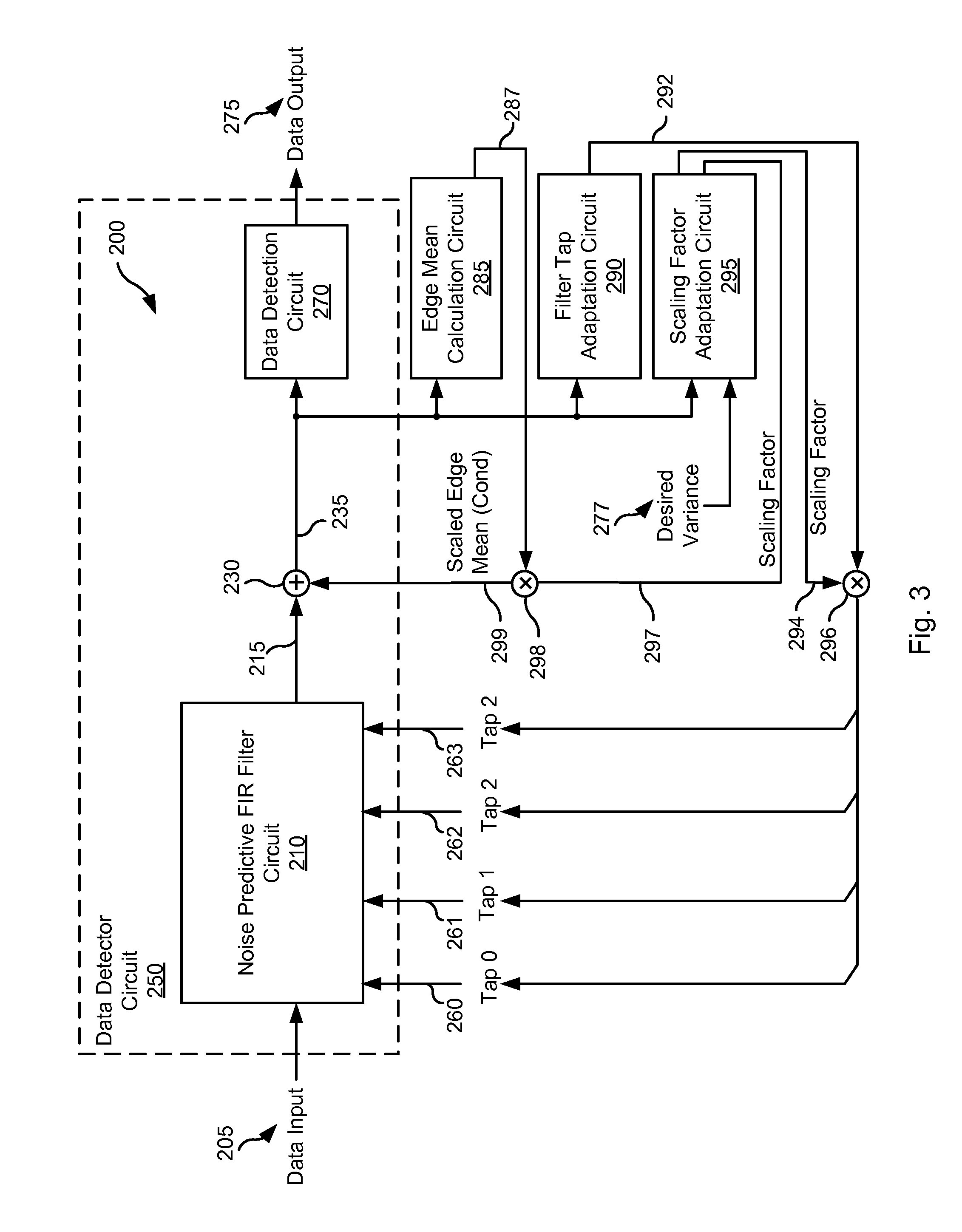
Systems and Methods for Variance Dependent Normalization for Branch Metric Calculation
ActiveUS20120124118A1Baseband systemsComplex mathematical operationsPattern recognitionData treatment
Various embodiments of the present invention provide systems and methods for data processing. As an example, a data processing circuit is disclosed that includes: a noise predictive filter circuit, a scaling factor adaptation circuit, and a scaling factor application circuit. The noise predictive filter circuit is operable to perform a noise predictive filtering process on a data input based on a filter tap to yield a noise filtered output. The scaling factor adaptation circuit is operable to calculate a scaling factor based at least in part on a derivative of the noise filtered output. The scaling factor application circuit is operable to apply the scaling factor to scale the noise filtered output.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
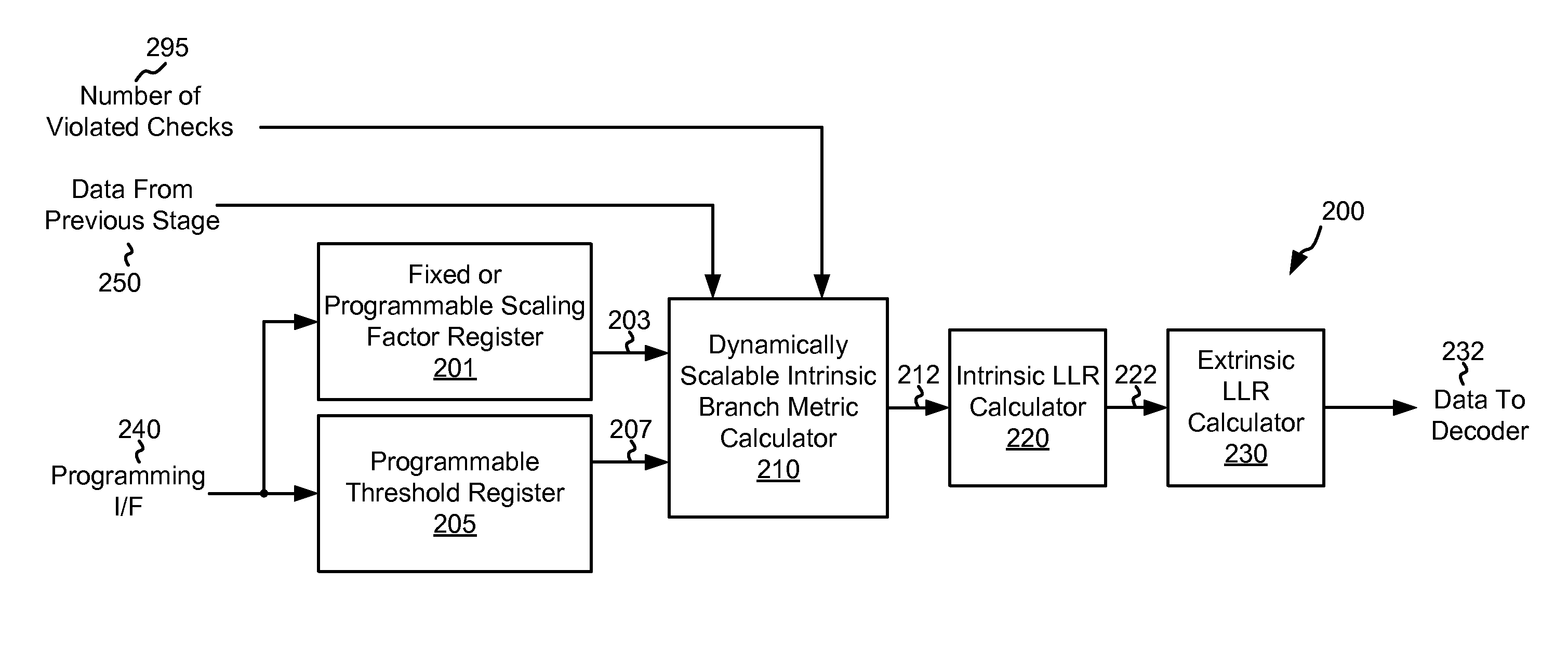
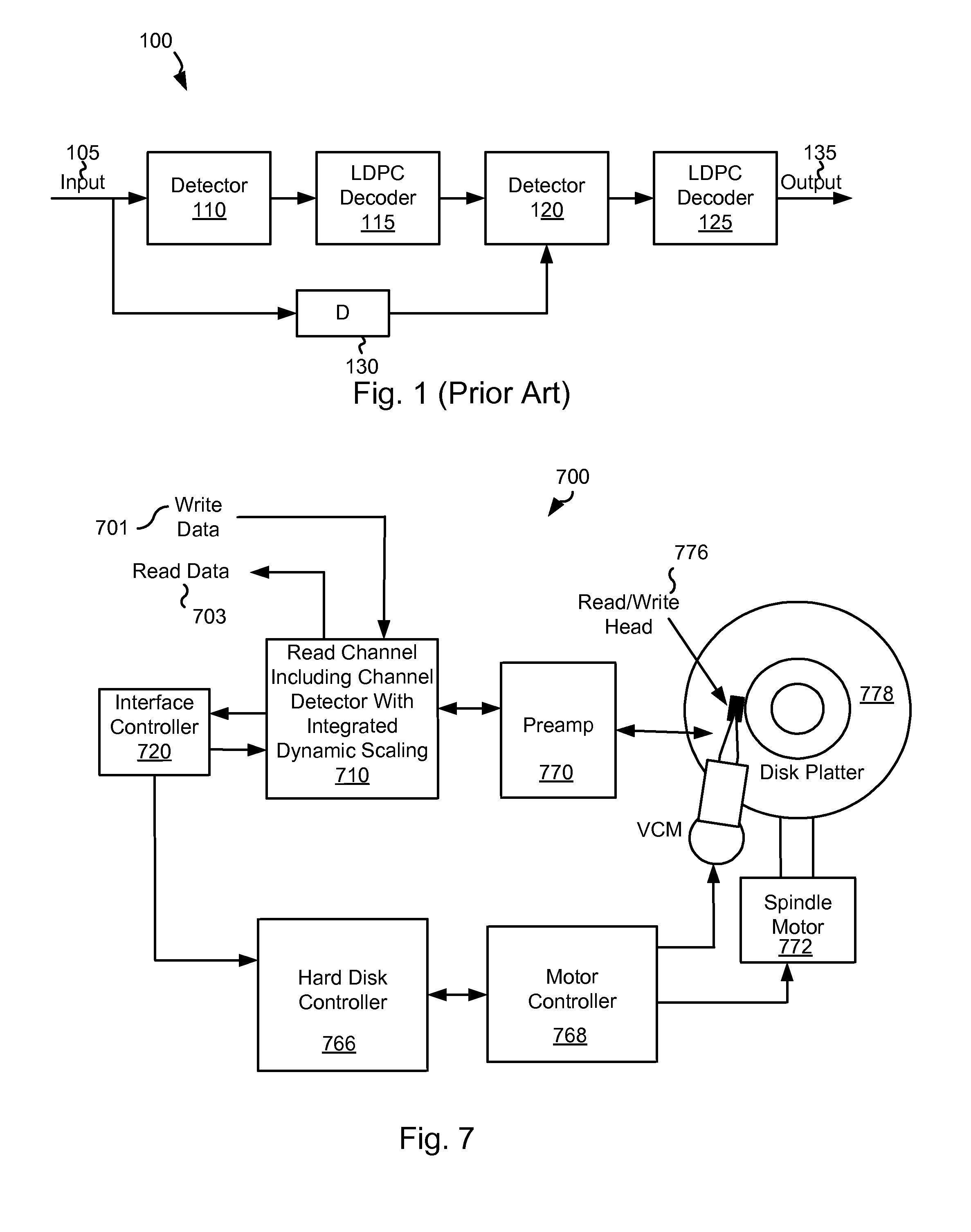
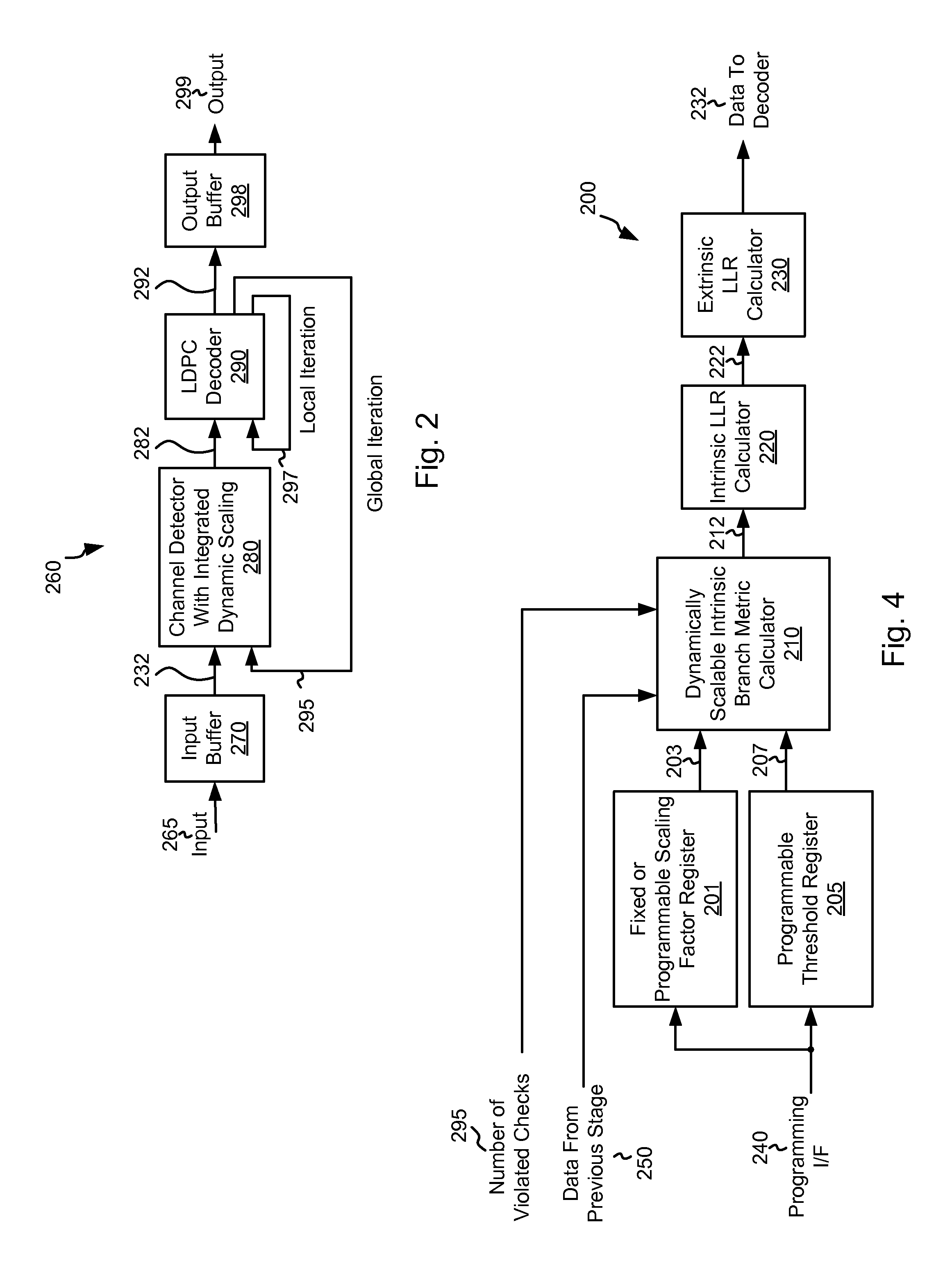
Systems and Methods for Data Detection Including Dynamic Scaling
Various embodiments of the present invention provide systems and methods for data processing. For example, a data processing system is disclosed that includes a channel detector circuit. The channel detector circuit includes a branch metric calculator circuit that is operable to receive a number of violated checks from a preceding stage, and to scale an intrinsic branch metric using a scalar selected based at least in part on the number of violated checks to yield a scaled intrinsic branch metric.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Apparatus and method for detecting a signal in a communication system using multiple antennas
ActiveUS8005170B2Reduce complexityError preventionAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsCommunications systemReal-time computing
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Branch-metric calibration using varying bandwidth values
InactiveUS20110072335A1Data representation error detection/correctionOther decoding techniquesNoise estimationComputer science
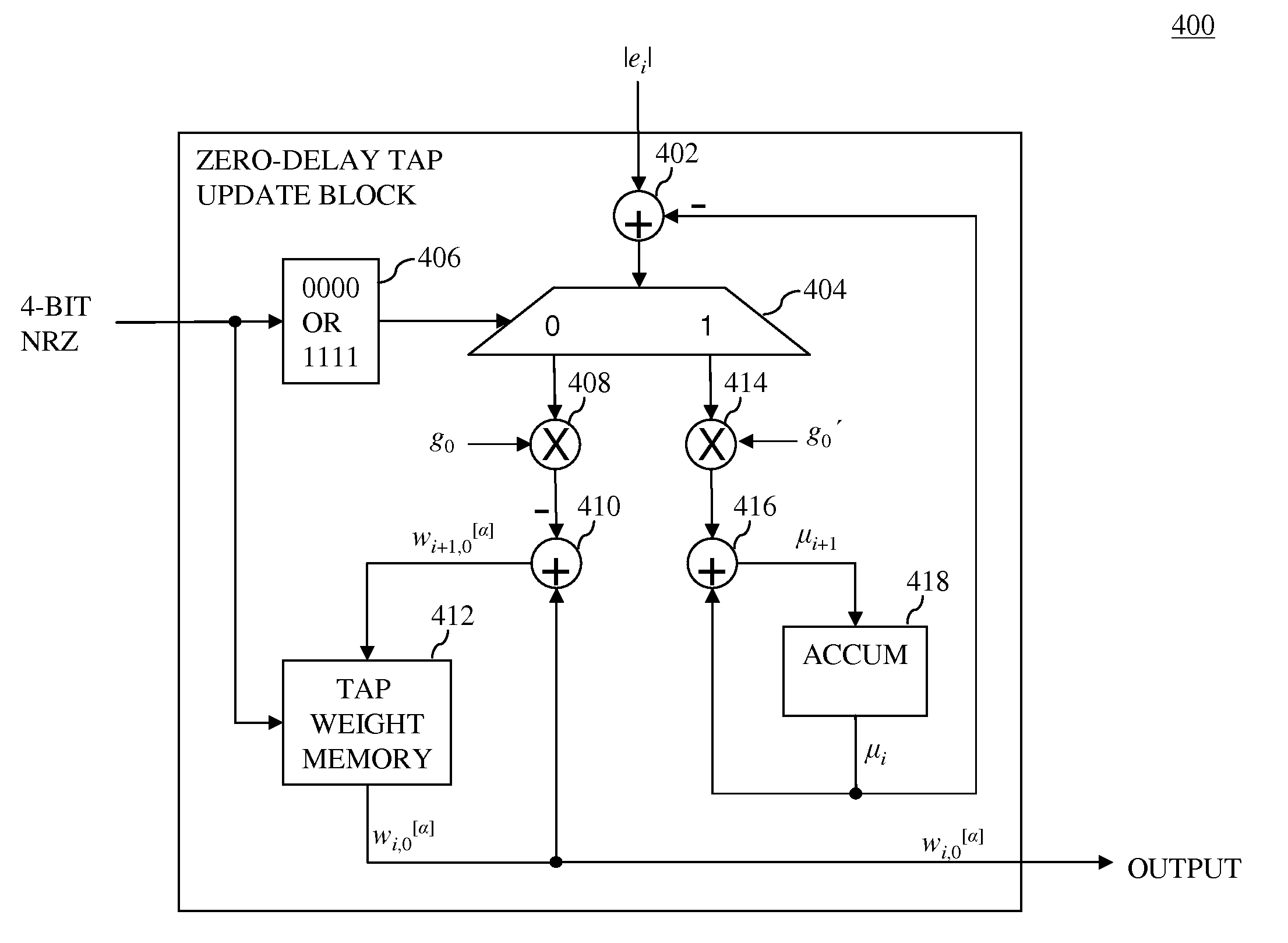
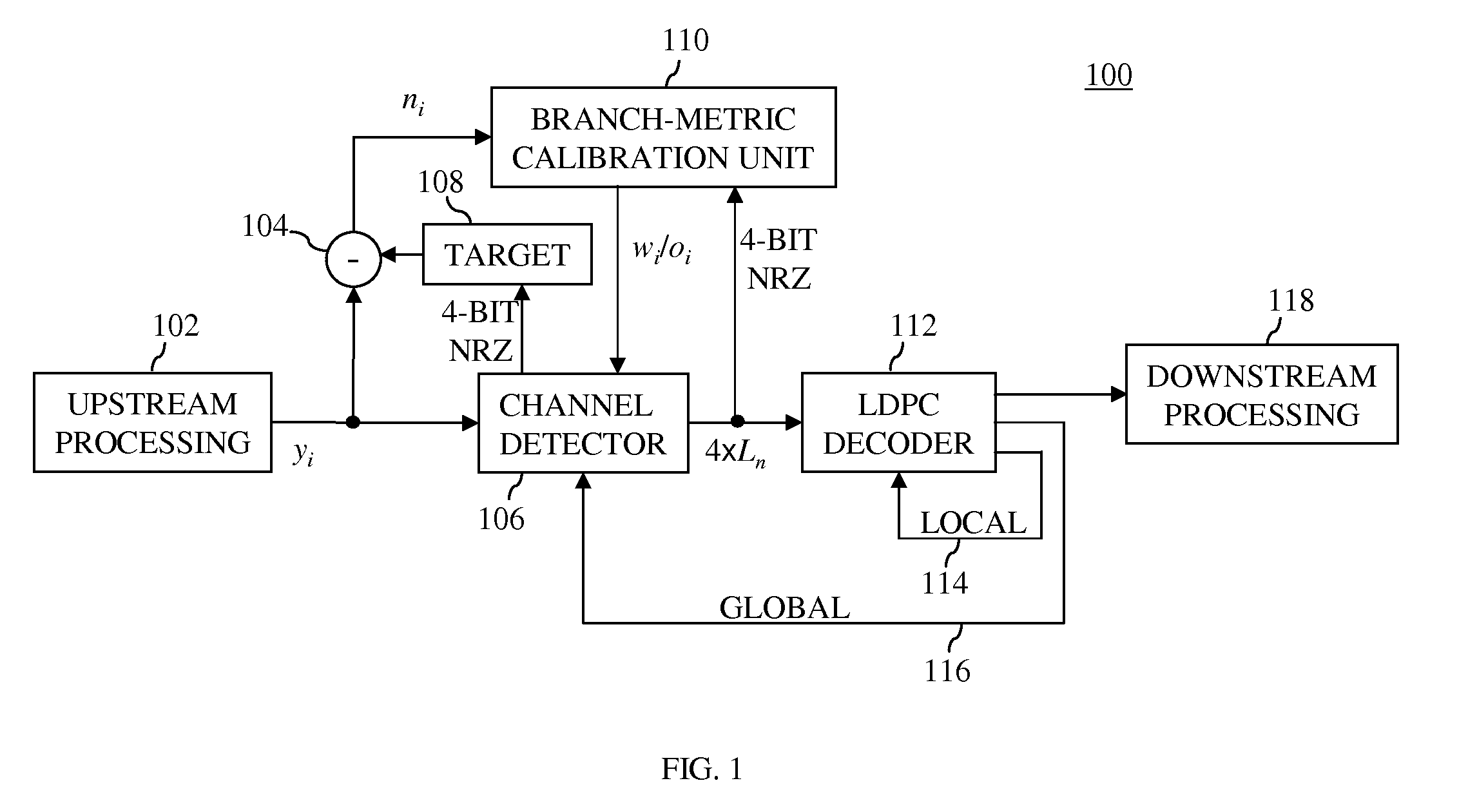
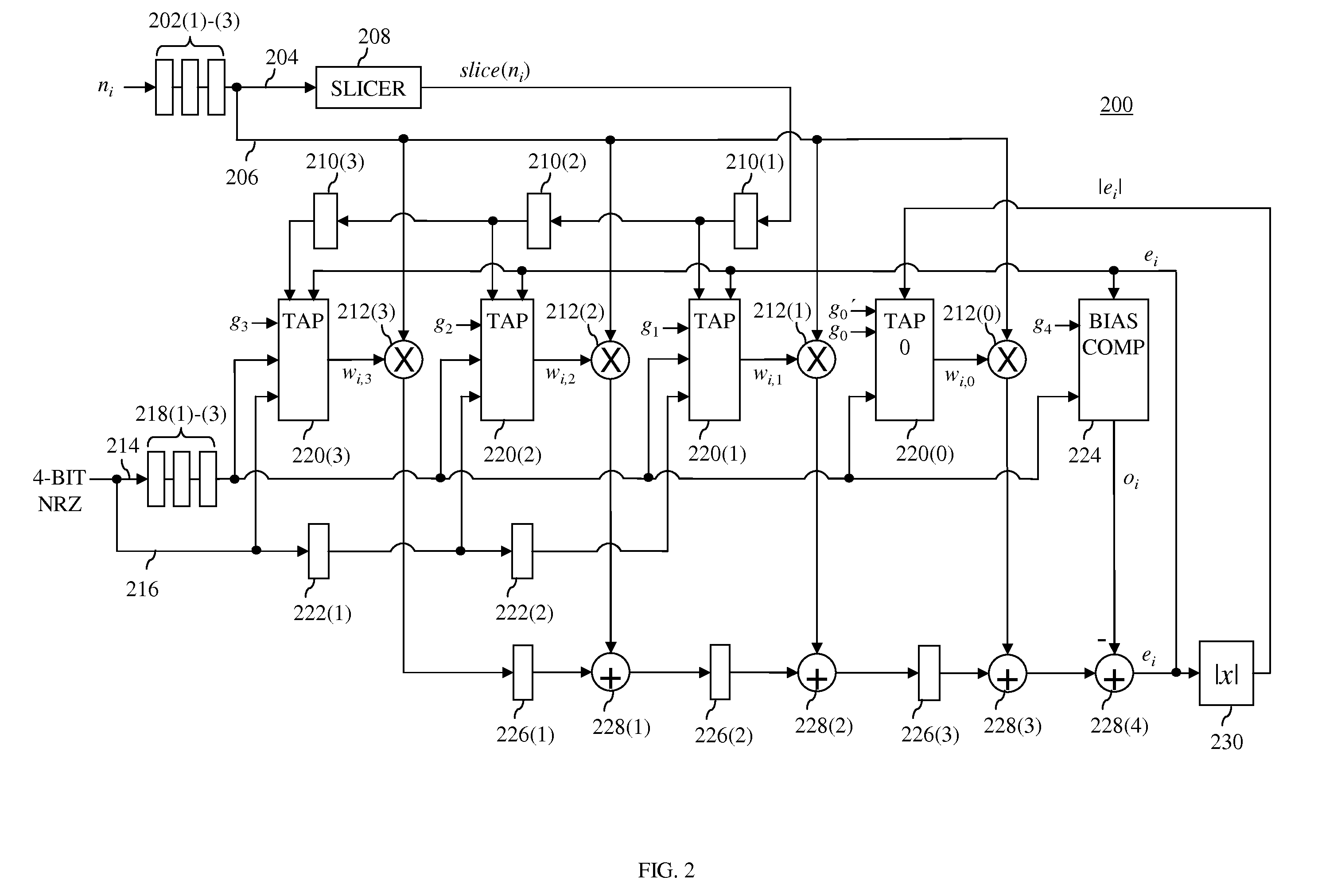
In one embodiment, a signal processing receiver has a branch-metric calibration (BMC) unit that receives (i) sets of four hard-decision bits from a channel detector and (ii) a noise estimate. The BMC unit has two or more update blocks (e.g., tap-weight update and / or bias-compensation blocks) that generate updated parameters used by a branch-metric unit of the channel detector to improve channel detection. The two or more update blocks generate the updated parameters based on (i) the sets of four hard-decision bits, (ii) the noise estimate, and (iii) bandwidth values. The bandwidth values for at least two of the two or more update blocks are selected such that they are different from one another. Selecting different bandwidth values may reduce the bit-error rate for the receiver over the bit-error rate that may be achieved by selecting the bandwidth values to be the same as one another.
Owner:BROADCOM INT PTE LTD
Soft output decoder for convolutional codes
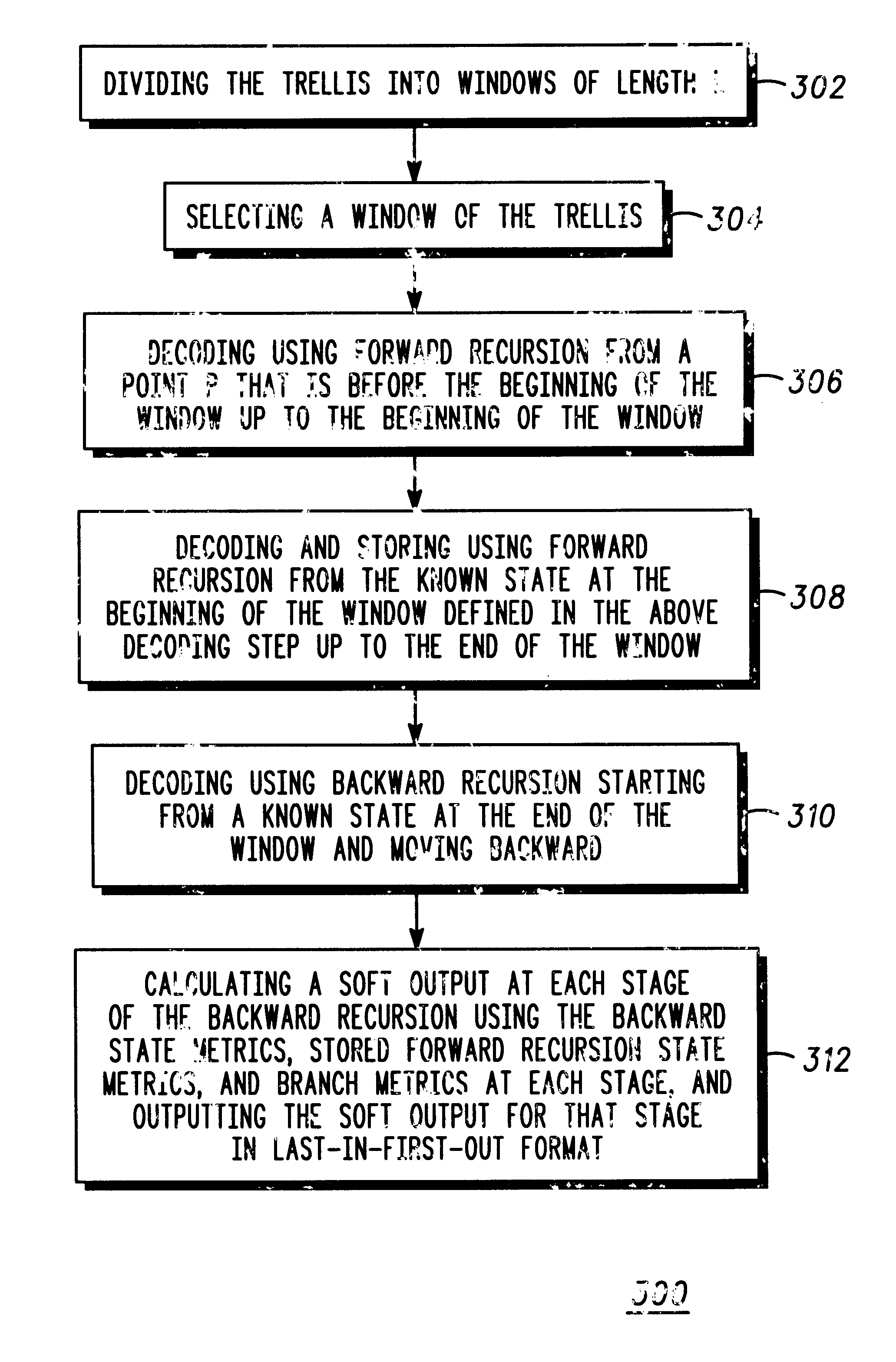
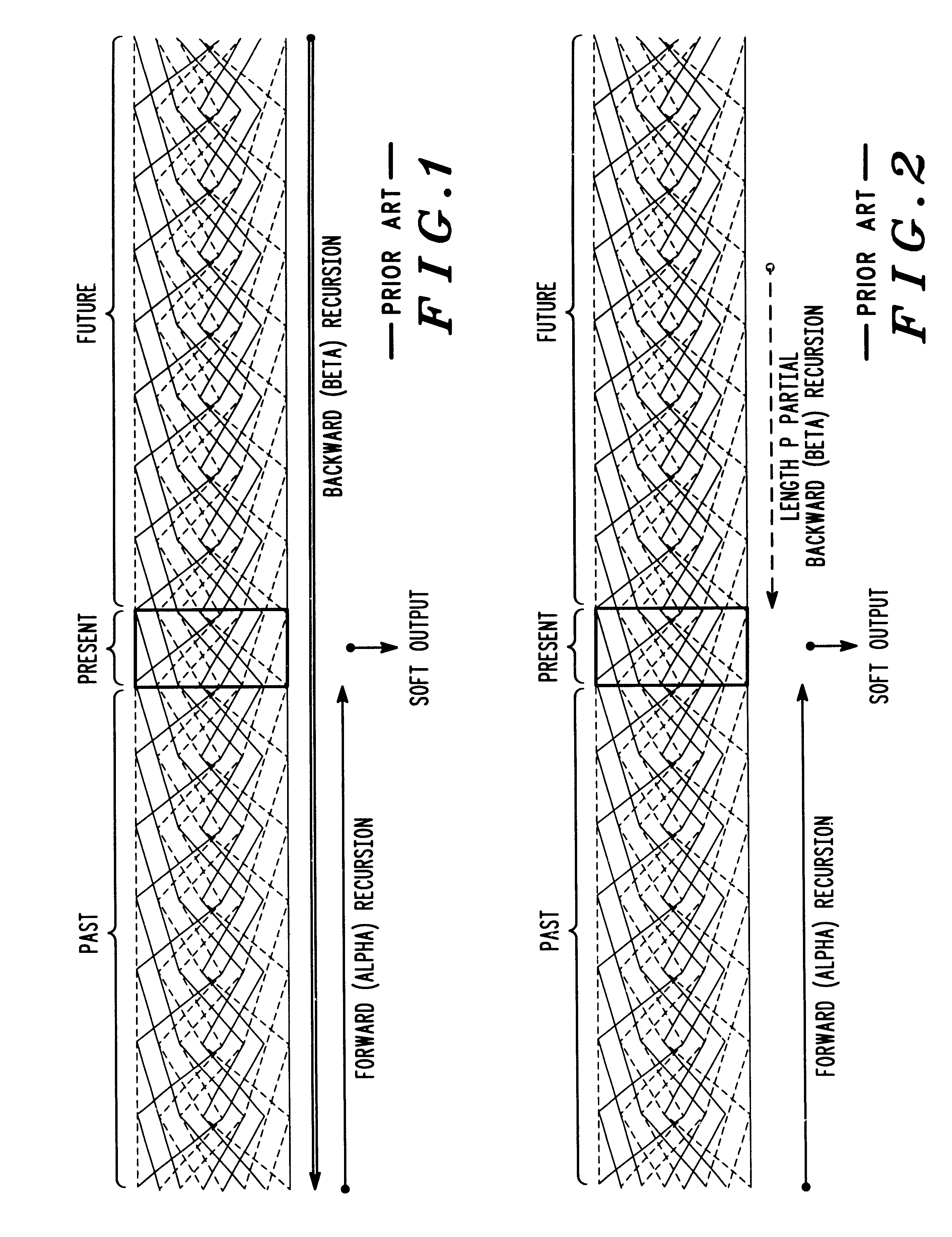
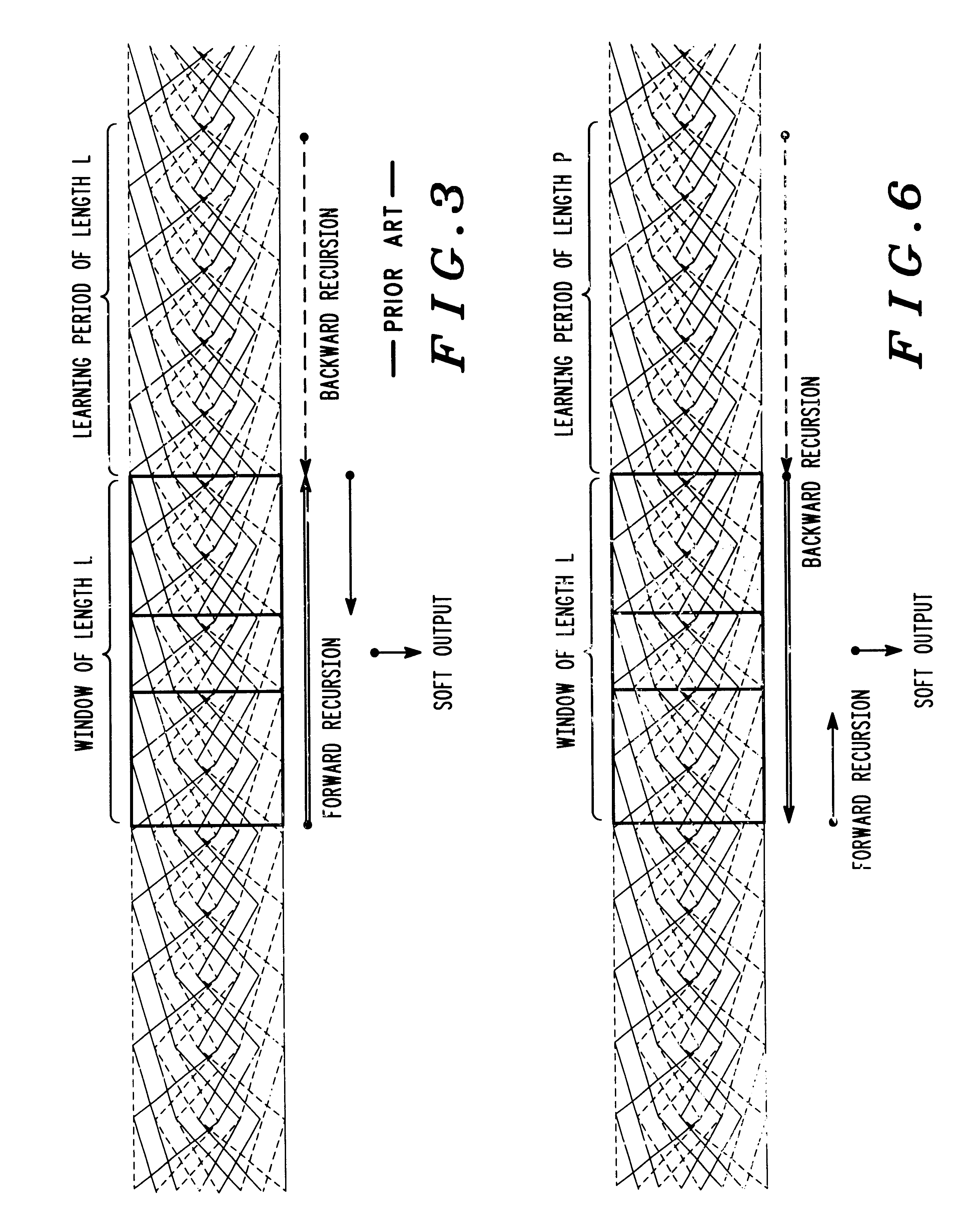
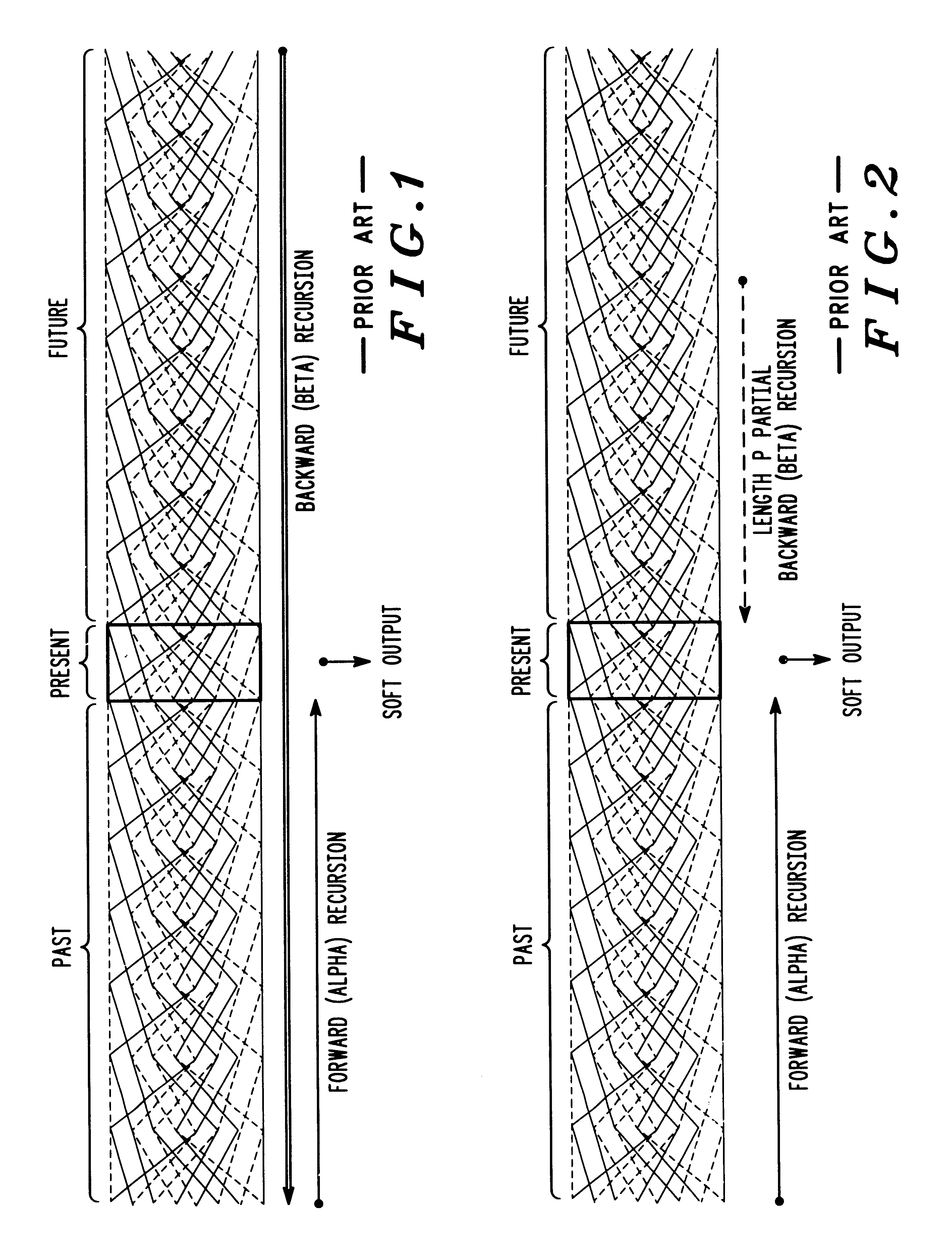
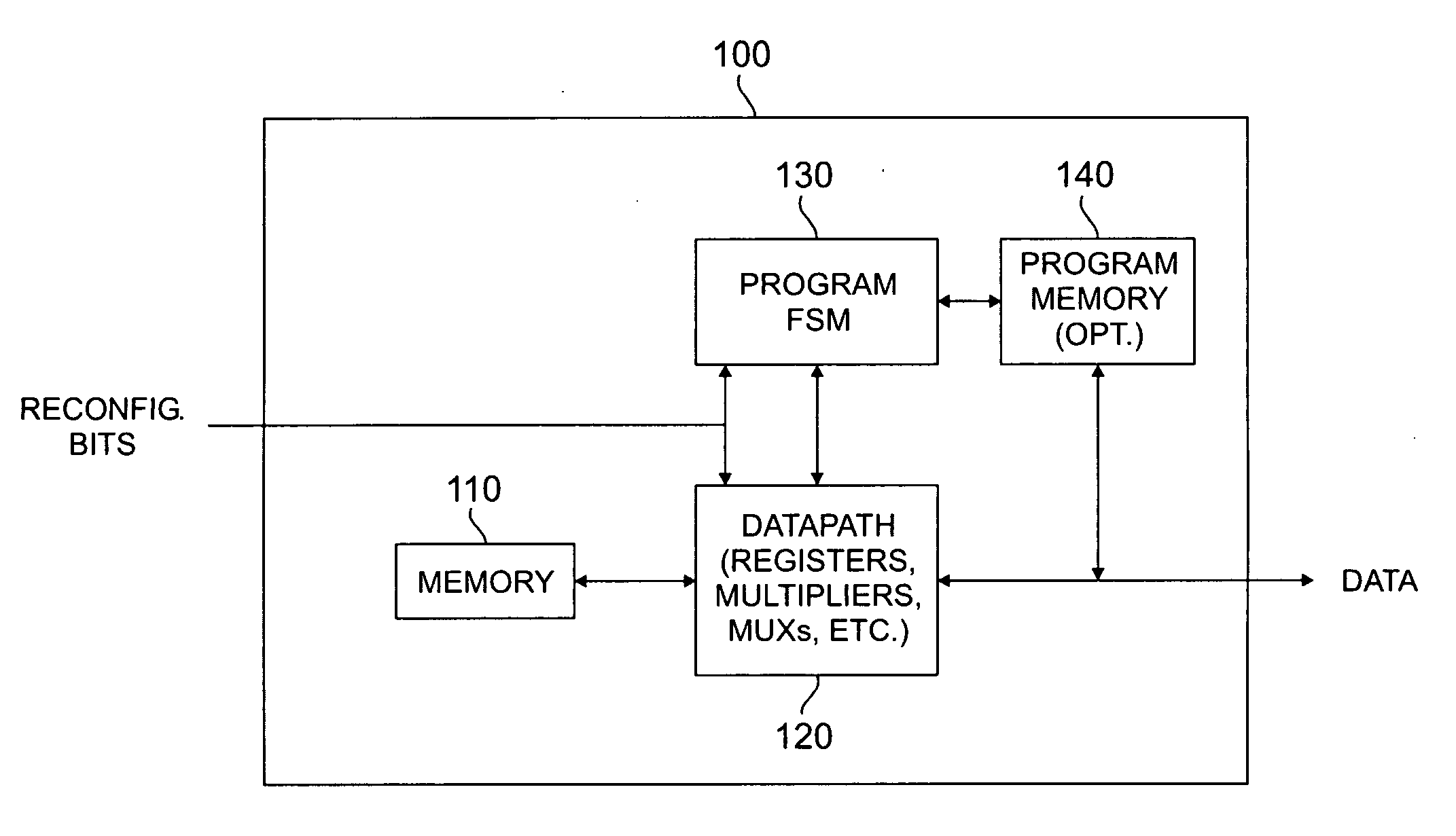
InactiveUS6901117B1Error correction/detection using convolutional codesOther decoding techniquesConvolutional codeForward recursion
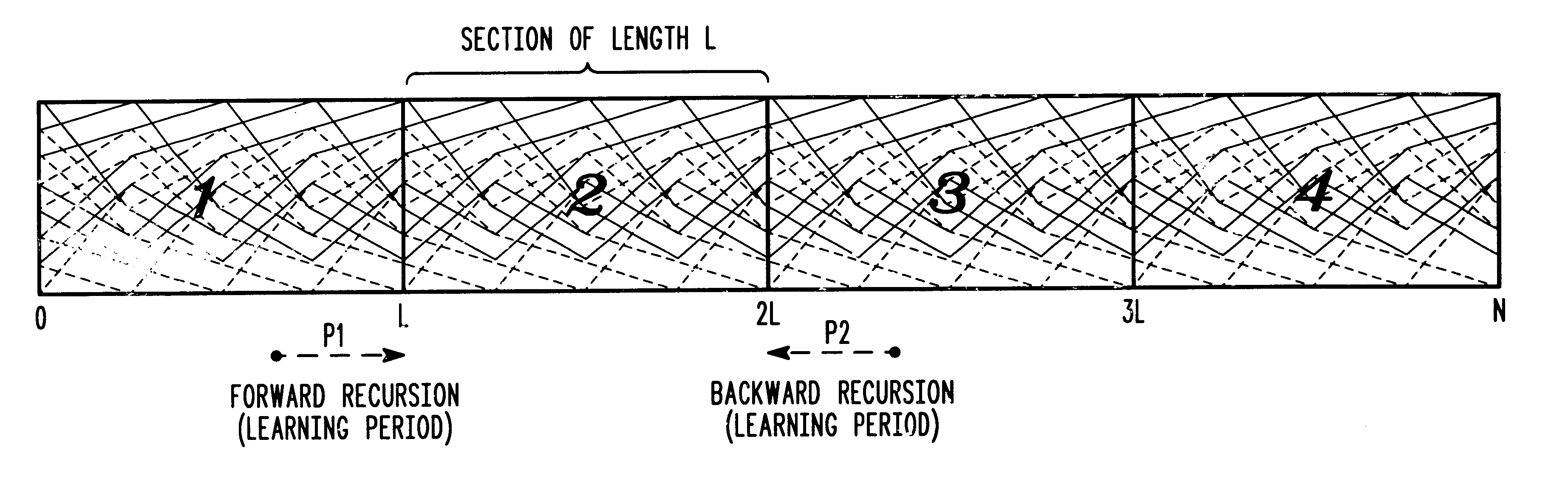
Decoding signals represented by a trellis of block length N divided into windows of length L includes a step of decoding a forward recursion from a point P that is before the beginning of a window up to the beginning of the window. P is chosen at a sufficient distance from the beginning of the window such that forward recursion determines a known state metric at the beginning of the window. A next step includes decoding the window using forward recursion from the known state at the beginning of the window up to the end of the window to define a set of known forward recursion state metrics which are stored. A next step includes decoding using backward recursion starting from a known state at the end of the window and moving backward. A next step includes calculating a soft output at each stage of the backward recursion using the stored forward recursion state metrics, and branch metrics at each stage, and outputting the soft output for that stage in a LIFO format.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
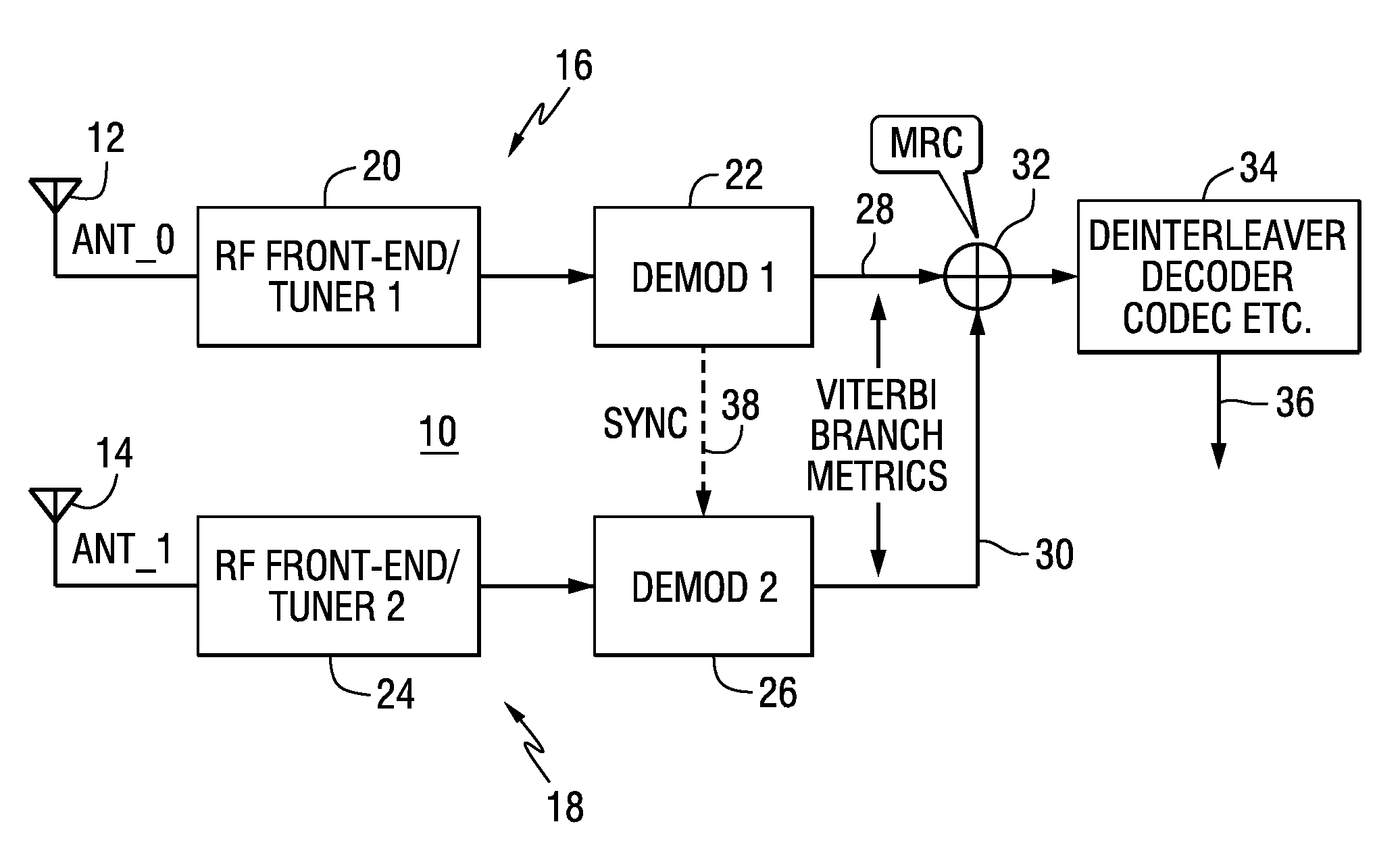
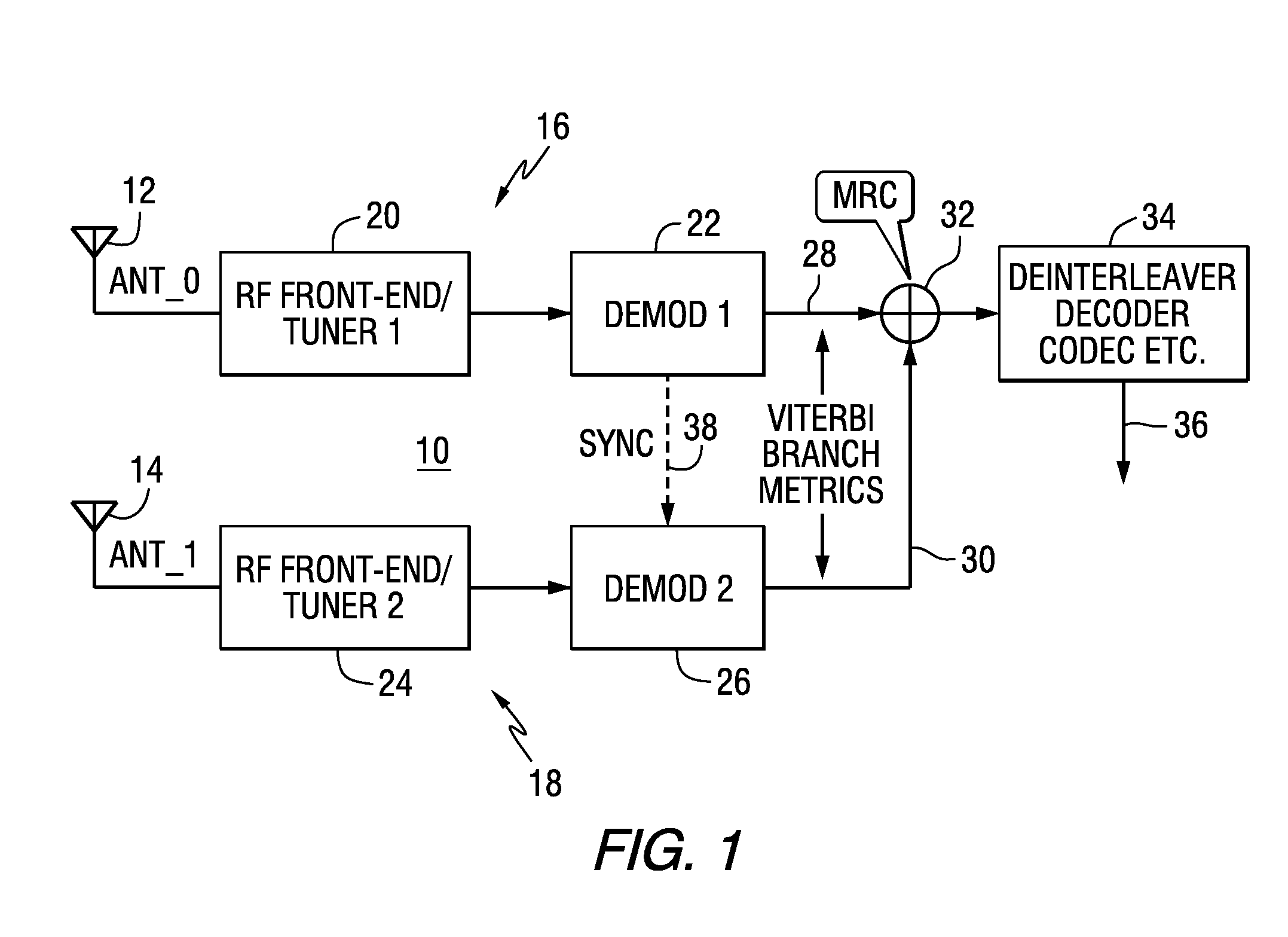
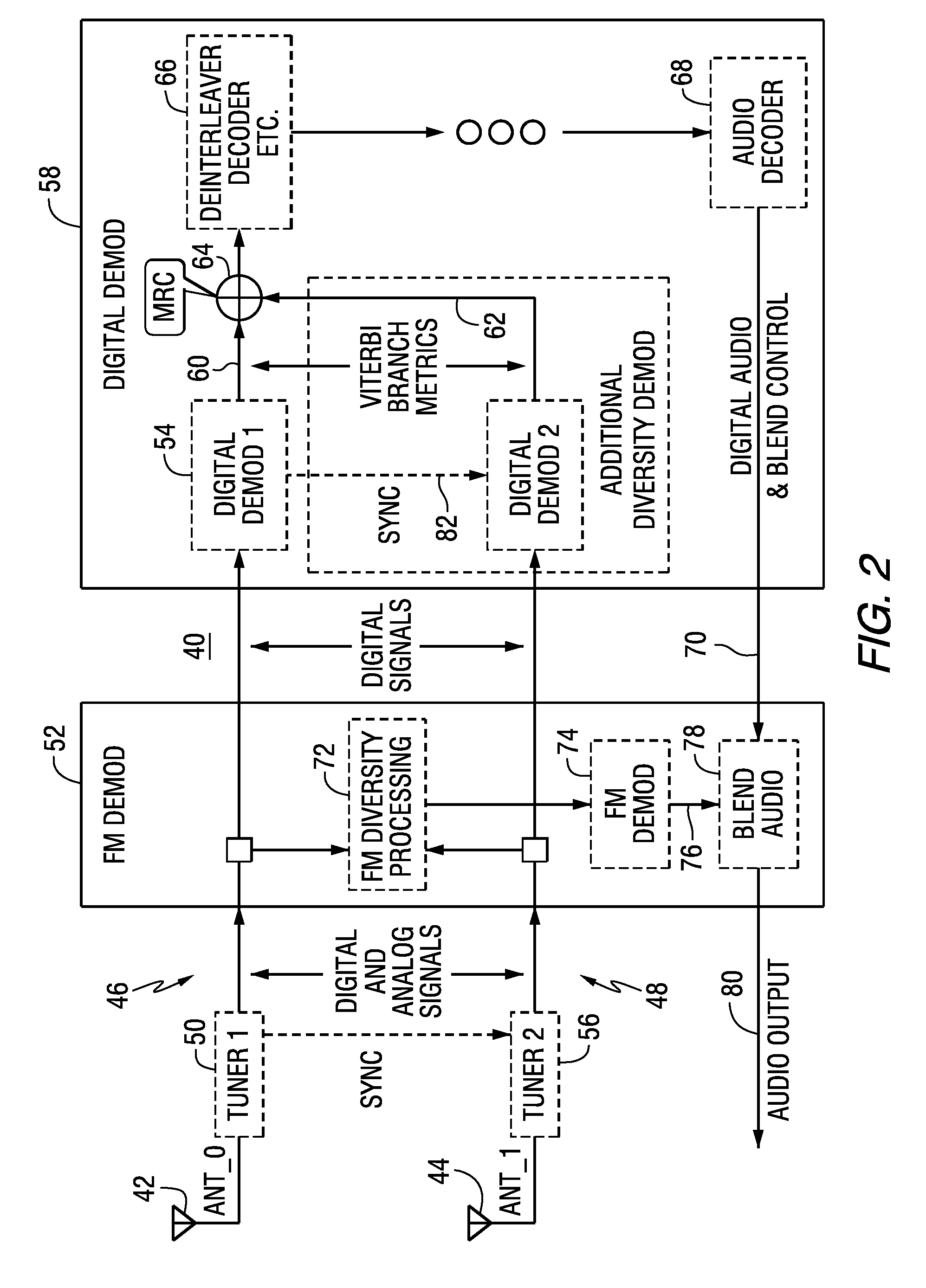
Mrc antenna diversity for FM iboc digital signals
A radio receiver includes a first signal path including a first tuner configured to receive a first signal from a first antenna, and a first demodulator configured to demodulate symbols from an output of the first tuner to produce first branch metrics derived from the demodulated symbols; a second signal path including a second tuner configured to receive a second signal from a second antenna, and a second demodulator configured to demodulate symbols from an output of the second tuner to produce second branch metrics derived from the demodulated symbols; a combiner for maximum ratio combining the first branch metrics and the second branch metrics; and processing circuitry to process the combined first and second branch metrics to produce an output signal.
Owner:IBIQUITY DIGITAL CORP
Pattern-dependent equalization and detection
InactiveUS20050169412A1Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsAmplitude demodulationViterbi detectorEngineering
A system for pattern dependent equalization has an equalizer bank and a detector. The equalizer bank has a plurality of equalizers, which are each tuned to a selected data pattern. The detector may be a standard sequence detector or a modified Viterbi detector, which calculates the branch metric using a pattern dependent equalized output and a pattern-dependent target. A method of decoding data uses a pattern dependent equalizer bank. The pattern dependent equalizer bank processes a segment of a bit sequence to produce an equalized pattern-dependent output for each equalizer in parallel. The detector then detects the bit sequence using the branch metric calculation to select the smallest accumulated path metric.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
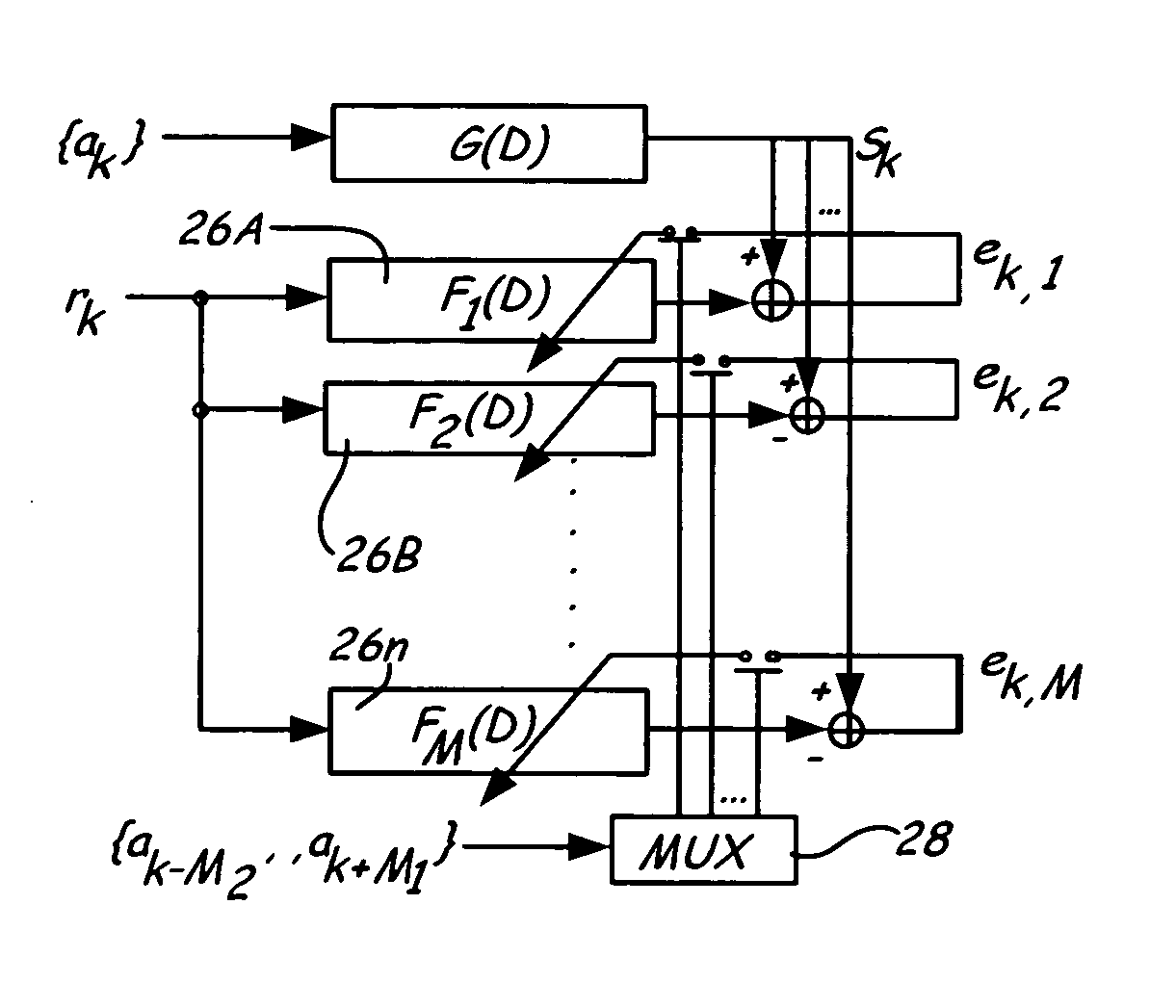
Method and apparatus for shortening the critical path of reduced complexity sequence estimation techniques
InactiveUS6999521B1Reduce computing loadReduce complexityData representation error detection/correctionOther decoding techniquesMultiplexerPrecomputation
A method and apparatus are disclosed for improving the processing time of reduced complexity sequence estimation techniques, such as reduced state sequence estimation. Precomputing the branch metrics for all possible symbol combinations in the channel memory makes it possible to remove the branch metrics unit and decision-feedback unit from the feedback loop, thereby reducing the critical path. A set of multiplexers select the appropriate branch metrics based on the survivor symbols in the corresponding survivor path cells. The computational load of the precomputations is reduced for multi-dimensional trellis codes by precomputing each dimension of the multi-dimensional trellis code separately. A hybrid survivor memory architecture is also disclosed for a RSSE for a channel having a channel memory of length L, where the survivors corresponding to the L past decoding cycles are stored in a register exchange architecture (REA), and survivors corresponding to later decoding cycles are stored in a trace-back architecture (TBA) or REA.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC +1
Maximum likelihood sequence estimator which computes branch metrics in real time
InactiveUS7277506B1Lower requirementImprove MLSE accuracyAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsAmplitude demodulationParallel computingMaximum likelihood sequence estimator
An improved method and apparatus for Viterbi Algorithm calculations for maximum likelihood sequence estimators in communication receivers is disclosed. The calculations for the maximum likelihood sequence estimator, in accordance with the invention, utilizes a variant of the Viterbi algorithm developed by Ungerboeck in which the associated branch metric calculations for the trellis require the computation of a set of branch metric parameters. An embodiment of the present invention provides for an improved recursive method and apparatus for calculation of the branch metric parameters that reduces the number of processor clock cycles required per state metric calculation. This enables real time computation of the branch metric parameters during execution of the Viterbi Algorithm.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Butterfly processor for telecommunications
InactiveUS6865710B2Reduction in hardwareError correction/detection using convolutional codesError preventionExternal dataComputer module
The present invention discloses a butterfly processor capable of performing convolutional decoding and LogMAP decoding in telecommunications systems. First and second add-compare-select modules are provided for receiving input path metrics. A branch metric calculator is also provided for receiving input data and extrinsic data. The branch metric calculator generates output branch metrics to each of the first and second add-compare-select modules. Each of the add-compare-select modules includes a log-sum correction means coupled to compare and select components. A controllable switch selectively couples outputs of the select components and the log-sum corrections means to enable either one of convolutional or LogMAP decoding.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Method and apparatus for parallel turbo decoding in long term evolution system (LTE)
InactiveUS20120106683A1Reduce consumptionReduce processing latencyOther decoding techniquesCode conversionSlide windowComputer science
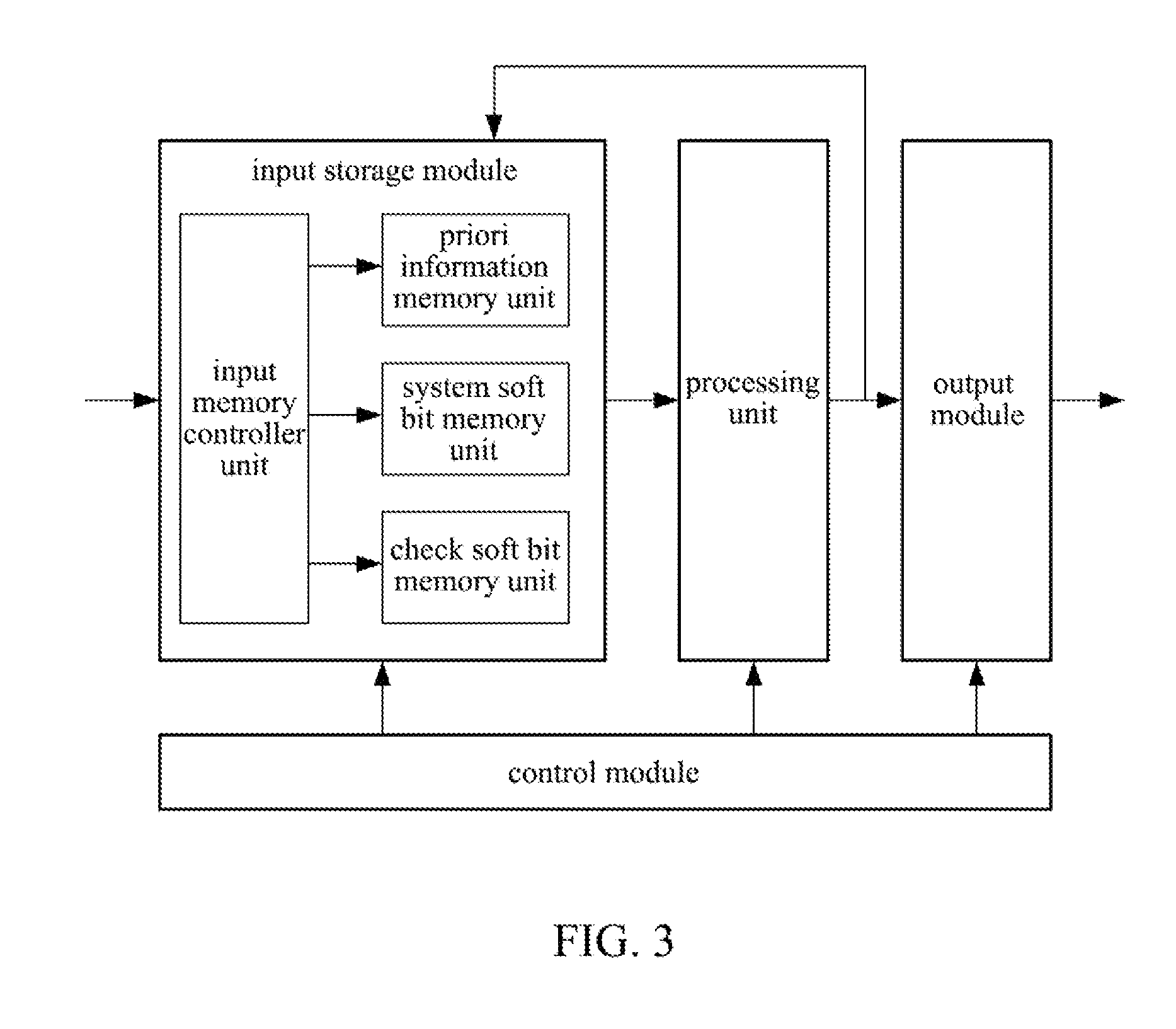
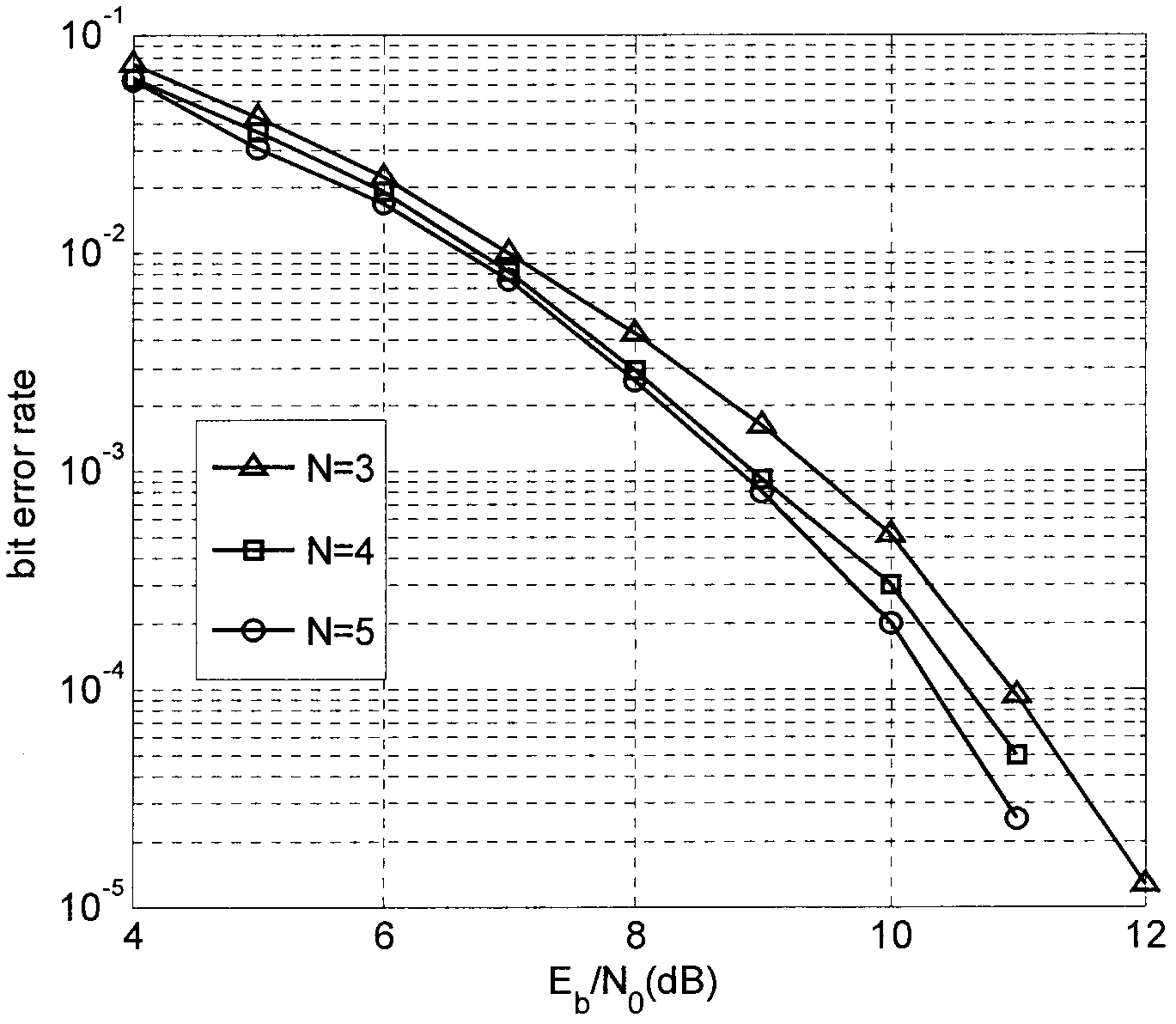
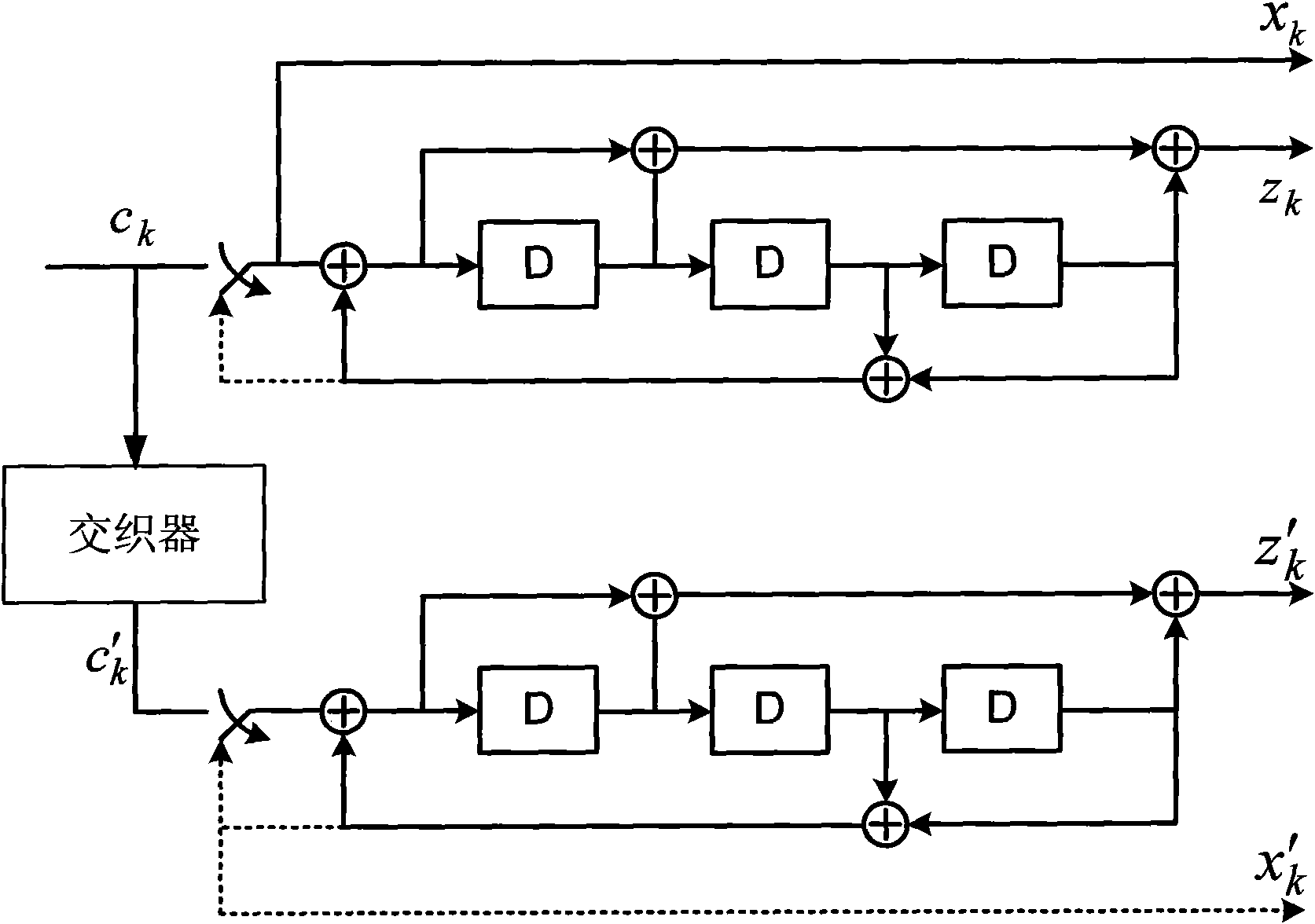
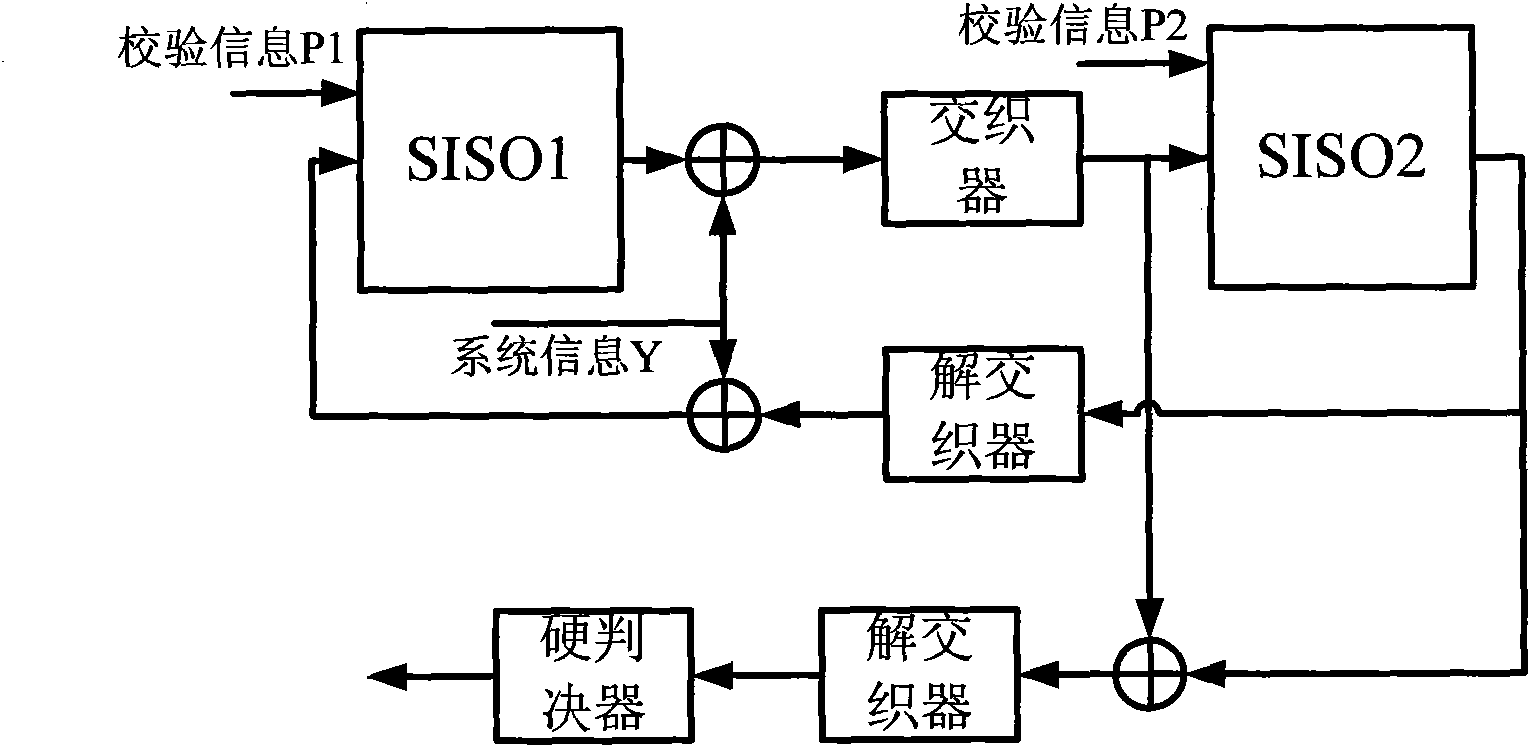
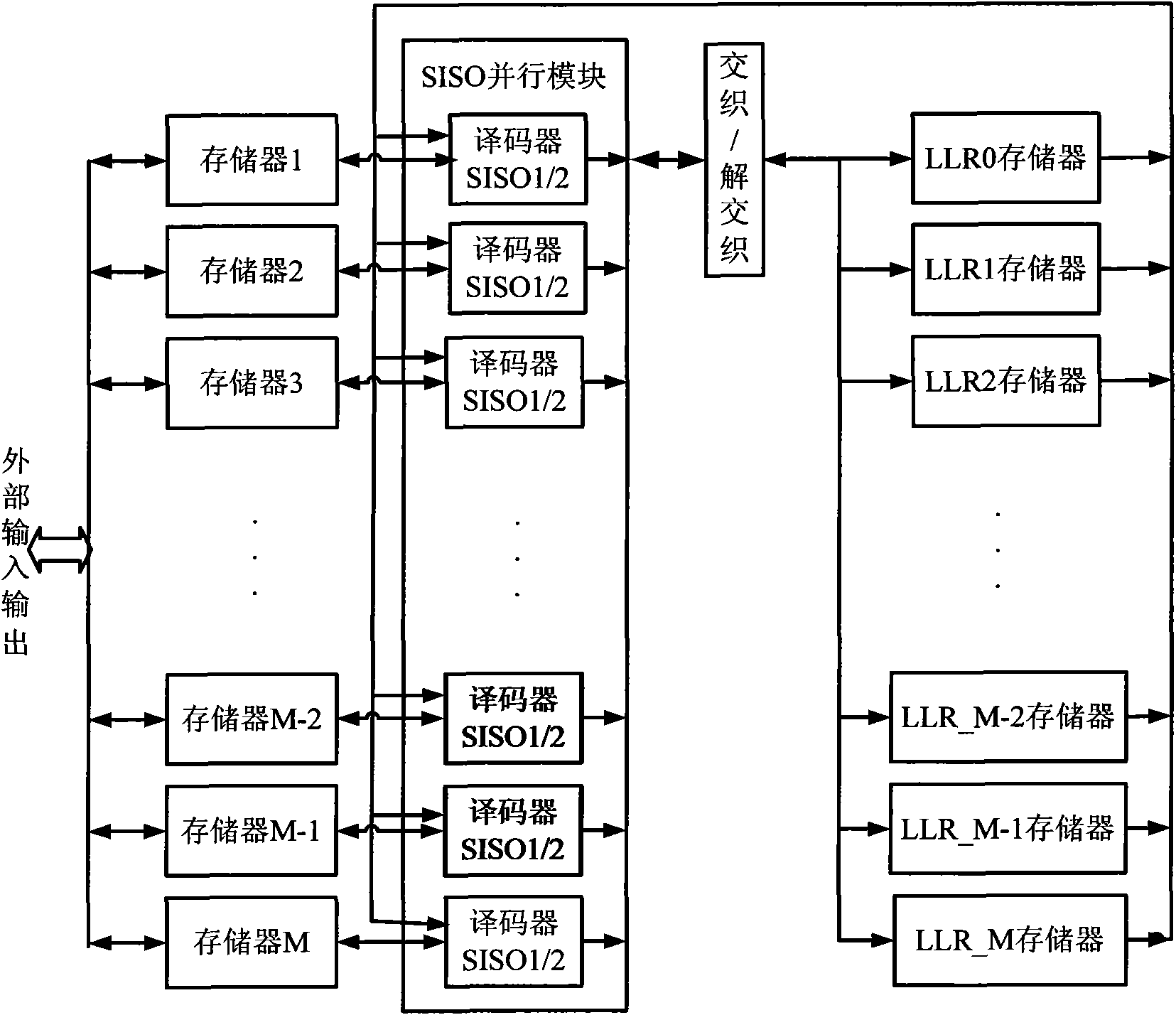
Provided are a method and an apparatus for parallel Turbo decoding in LTE, comprising: storing input check soft bits and a frame to be decoded, when storing said frame, dividing the frame into blocks, storing each block respectively as system soft bits; simultaneously performing component decoding once for several blocks of one said frame, and in the process of component decoding, dividing each block into several sliding windows according to a sliding window algorithm, calculating the following parameters according to system soft bits, check soft bits and priori information: branch metric value γ, forward state vector α, backward state vector β, LLR, and priori information, storing the priori information for use in a next component decoding; completing a decoding process after several component decoding; performing a hard decision on LLR, and if judged that a result of the hard decision meets an iteration ending condition, outputting a decoding result, otherwise, performing next iteration decoding.
Owner:ZTE CORP
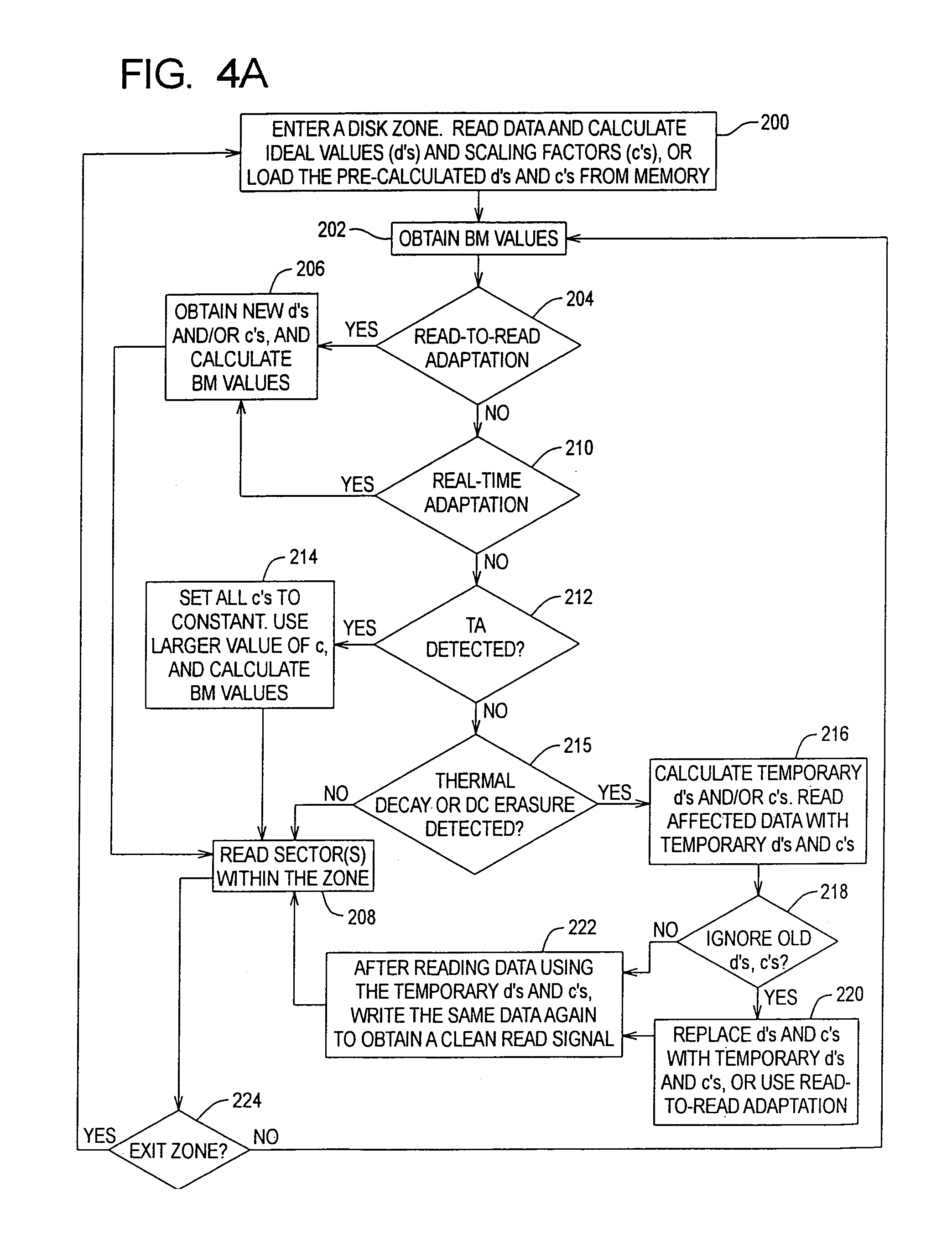
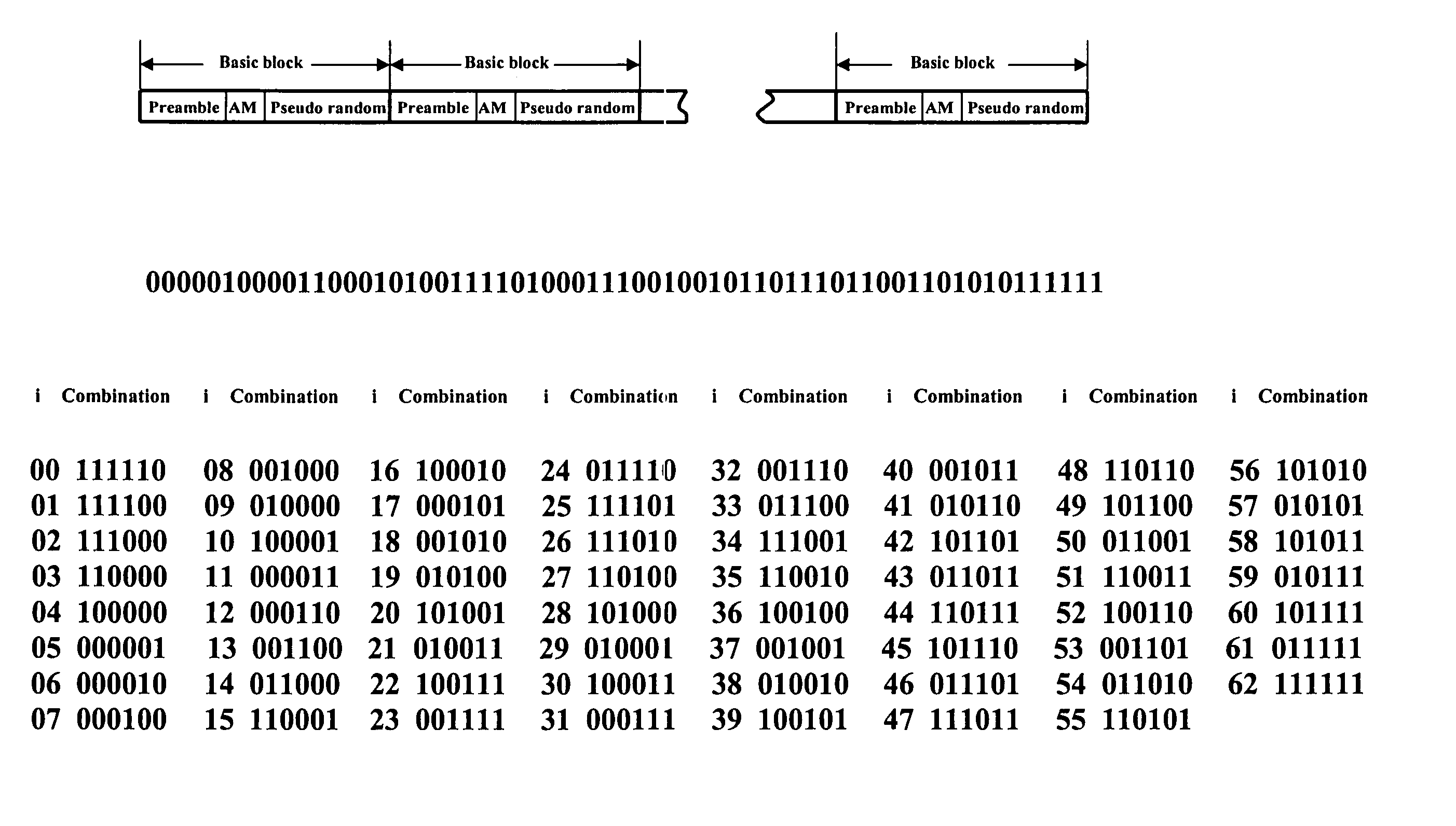
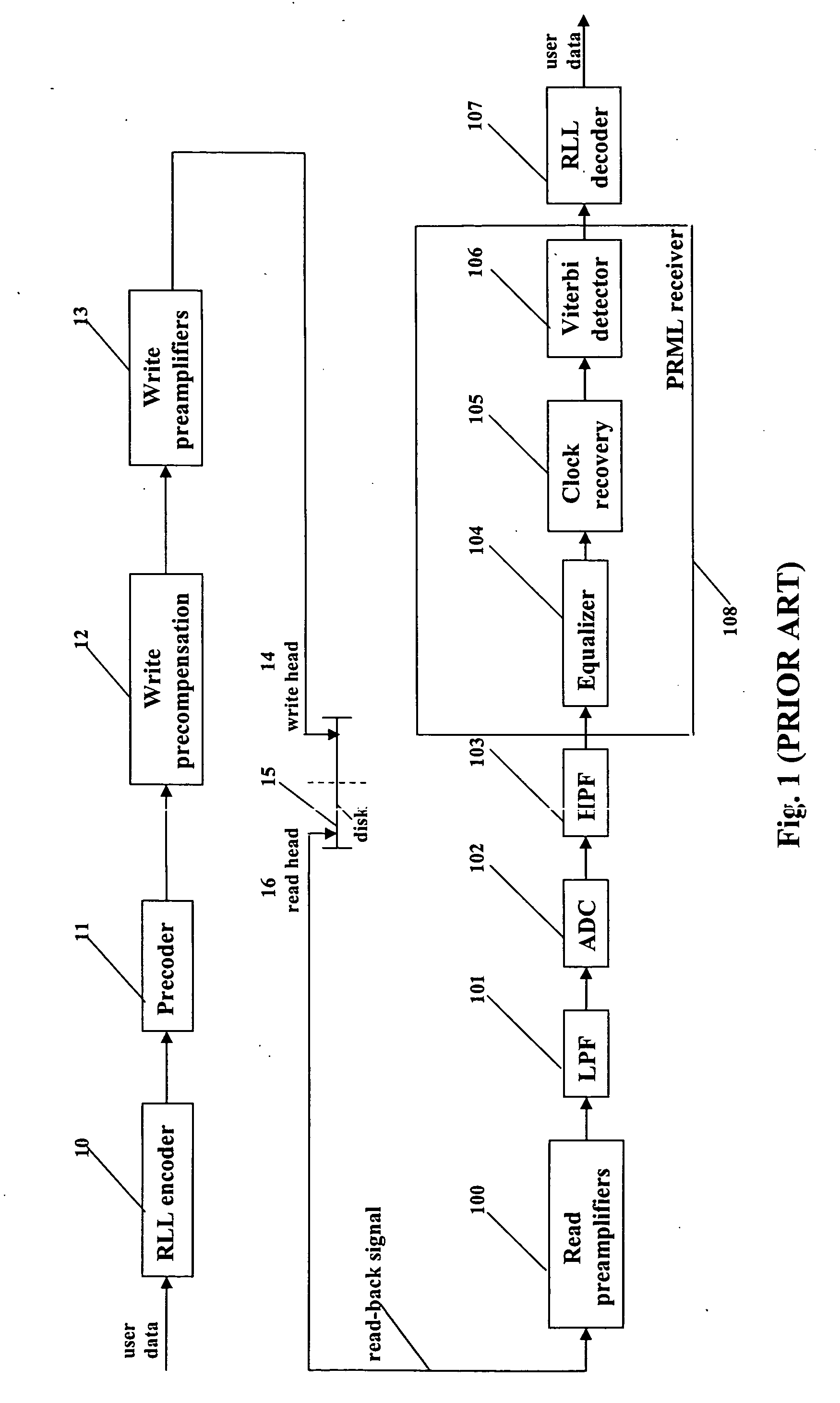
Self-adjusting PRML receiver
InactiveUS20060061496A1Modification of read/write signalsCode conversionViterbi detectorClock recovery
A partial response maximum likelihood (PRML) data detecting in a magnetic recording storage device is carried out with a preliminary measuring of write-read channel responses to all nonzero binary combinations of a given length. Decoding of the user data is performed according to a Viterbi algorithm, where the previously measured responses are used as expected samples for branch metric calculations. The measurement of the write-read channel responses and the decoding of the user data are fulfilled by a self-adjusting PRML receiver that contains a controllable clock recovery, a responses accumulator and an adjustable Viterbi detector. The controllable clock recovery produces a set of read-back signal samples containing exactly one sample per bit with or without phase error correction. The responses accumulator calculates averaged responses of the write-read channel. The adjustable Viterbi detector reconstructs the user data that were written to the disk.
Owner:GUZIK TECHN ENTERPRISES
Hybrid memory architecture for reduced state sequence estimation (RSSE) techniques
InactiveUS20060039492A1Extended processing timeShortening of the critical pathData representation error detection/correctionOther decoding techniquesComputation complexityPrecomputation
A method and apparatus are disclosed for improving the processing time of reduced complexity sequence estimation techniques, such as reduced state sequence estimation (RSSE). The possible values for the branch metrics in the RSSE are precomputed to permit pipelining and the shortening of the critical path. The computational load of the precomputations is reduced for multi-dimensional trellis codes by precomputing each dimension of the multi-dimensional trellis code separately. Prefiltering techniques are used to reduce the computational complexity by shortening the channel memory. A hybrid survivor memory architecture is disclosed for RSSE for a channel having a channel memory of length L, where the survivors corresponding to the L past decoding cycles are stored in a register exchange architecture, and survivors corresponding to later decoding cycles are stored in a trace-back architecture (TBA) or register exchange architecture (REA). Symbols are mapped to information bits to reduce the word size before being moved from the first register exchange architecture to the trace-back architecture (TBA) or the second register exchange architecture.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
Soft output decoder for convolutional codes
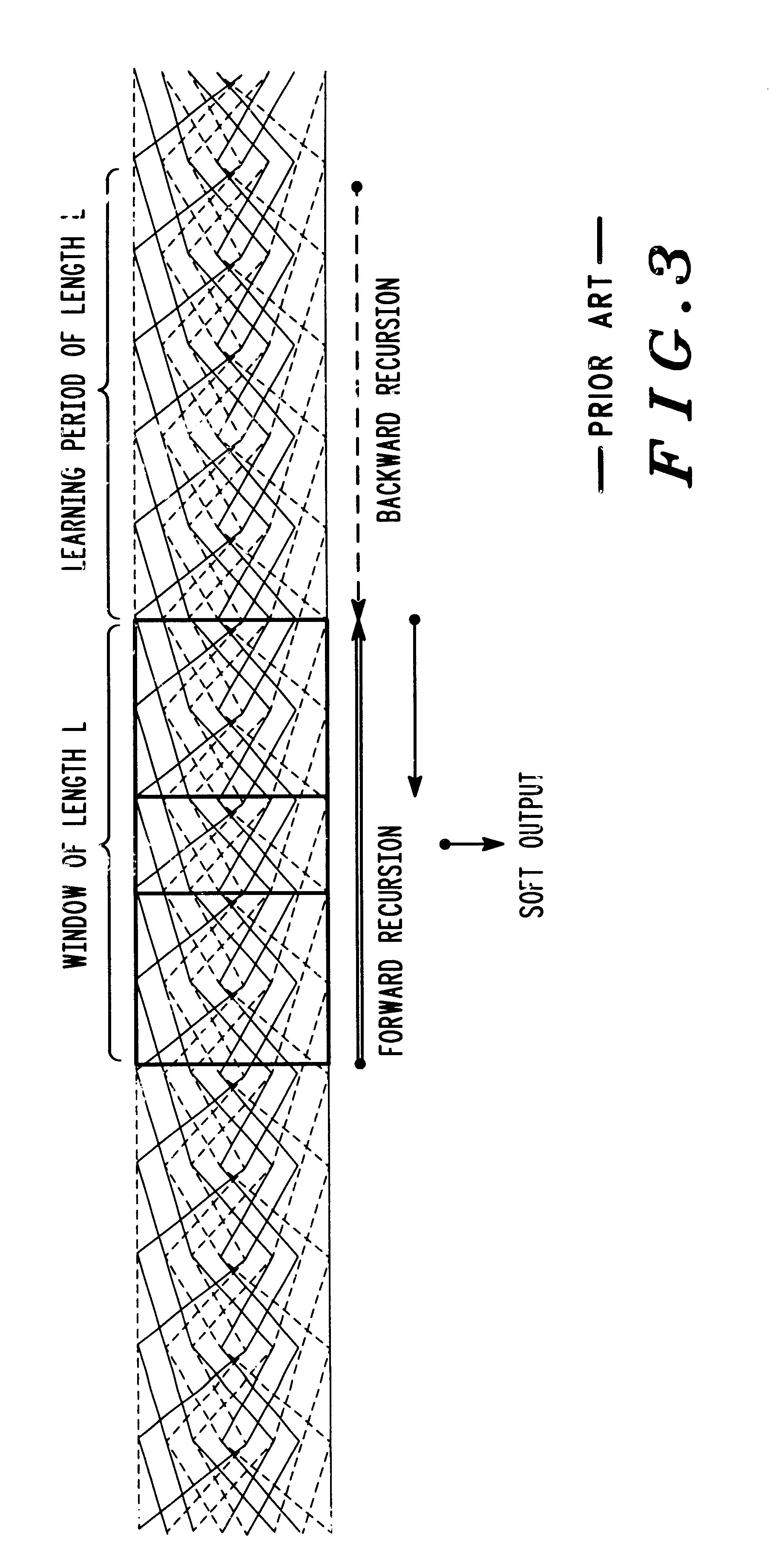
InactiveUS6856657B1Reduce memory requirementsMinimize limitationError correction/detection using convolutional codesOther decoding techniquesConvolutional codeForward recursion
Decoding signals represented by a trellis of block length N divided into windows of length L includes a step of decoding a forward recursion from a point P1 that is before the beginning of a window up to the beginning of the window and decoding a backward recursion from a point P2 that is after the end of a window back to the end of the window to define known states at the beginning and end of the window. A next step includes decoding the window using backward recursion from the known state at the end of the window back to the beginning of the window to define a set of backward recursion state metrics. A next step includes decoding using forward recursion starting from a known state at the beginning of the window and moving forward to the end of the window to define a set of forward recursion state metrics. A next step includes calculating a soft output at each stage of the window using the forward and backward recursion state metrics, and branch metrics at each stage, and outputting the soft output for that stage.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
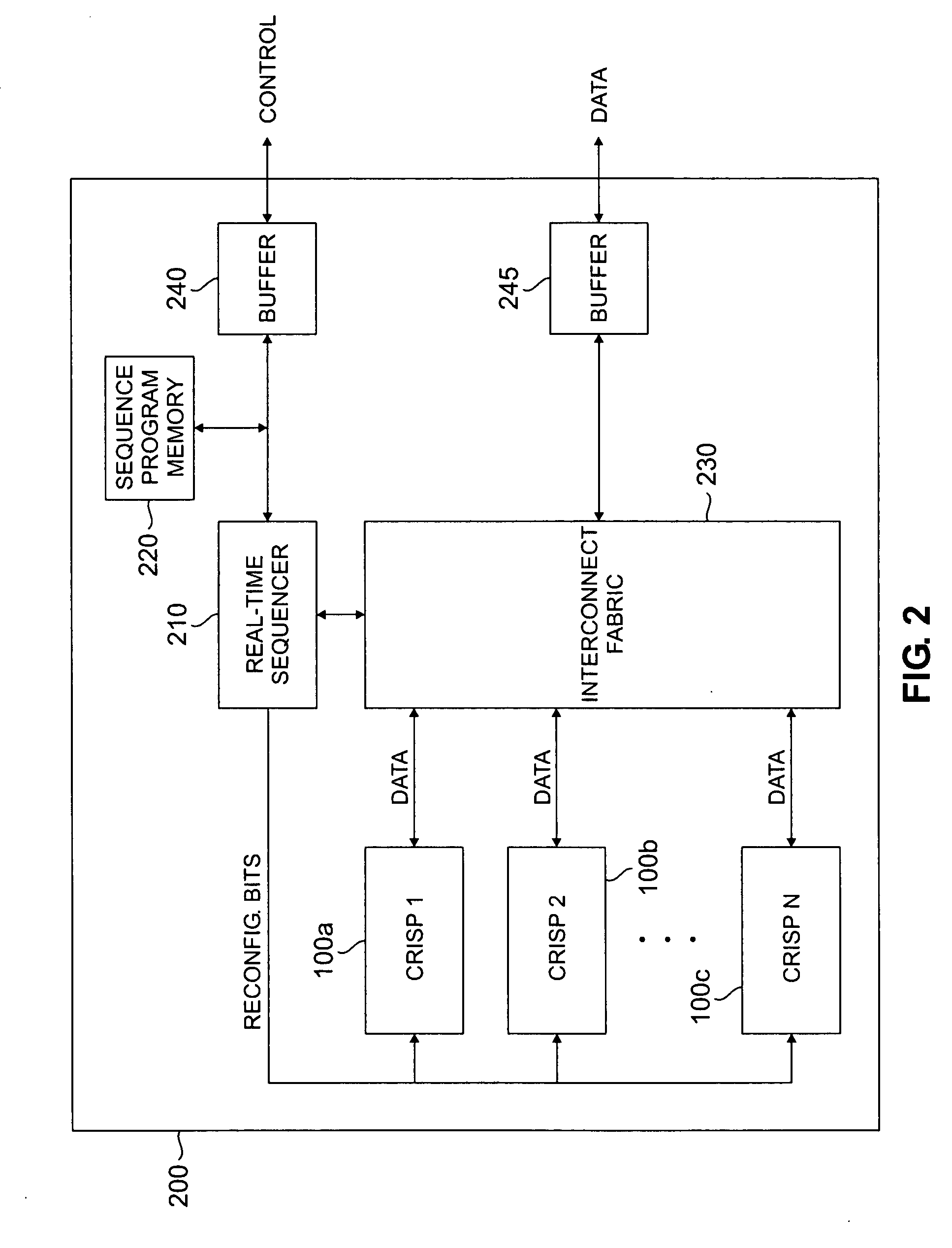
Viterbi decoder architecture for use in software-defined radio systems
InactiveUS20060195773A1Data representation error detection/correctionError preventionMultiple contextComputer architecture
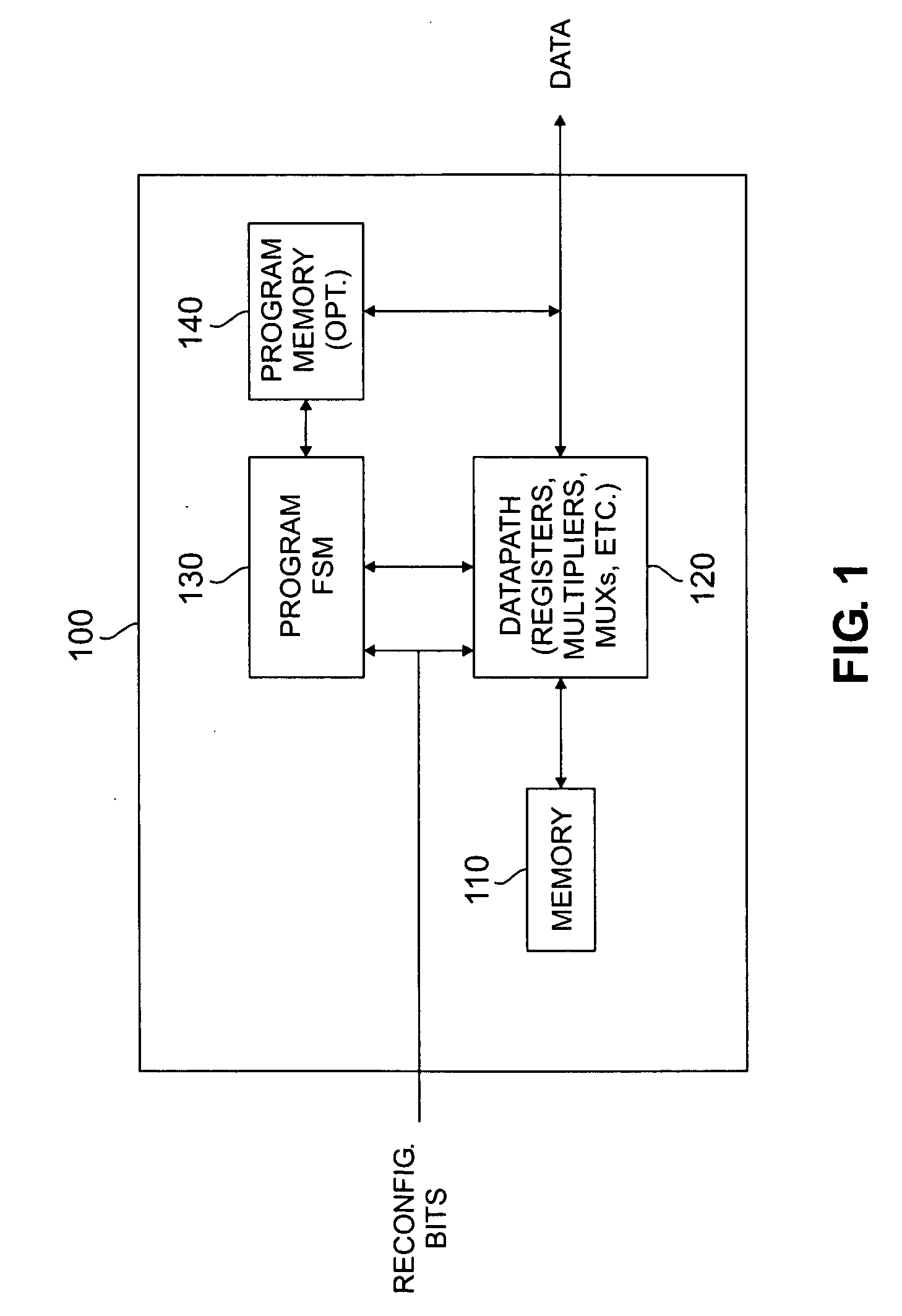
A reconfigurable Viterbi decoder comprising a reconfigurable data path and a programmable finite state machine that controls the reconfigurable data path. The reconfigurable data path comprises a plurality of reconfigurable functional blocks including: i) a reconfigurable branch metric calculation block; and ii) a reconfigurable add-compare-select and path metric calculation block. The programmable finite state machine executes a plurality of context-related instructions associated with the reconfigurable Viterbi decoder.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
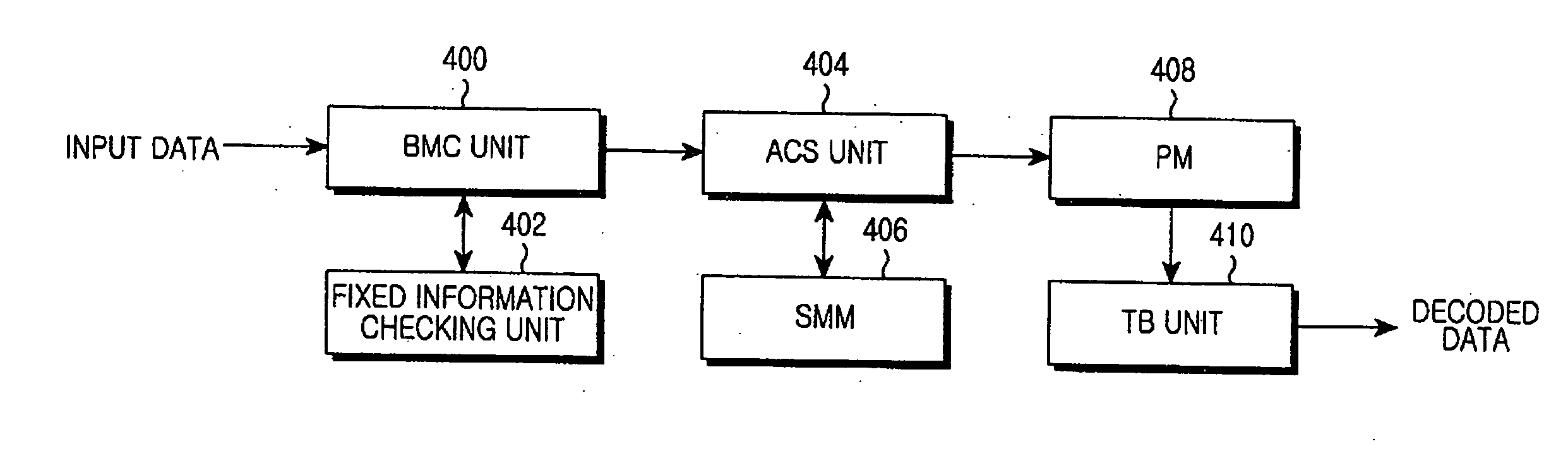
Decoder and decoding method in consideration of input message characteristics
InactiveUS20080034274A1Avoid excessive errorLess errorData representation error detection/correctionOther decoding techniquesComputer engineeringBranch Metrics
Provided are a decoder and decoding method wherein decoding is performed in consideration of input message characteristics. The decoder includes a fixed information checking unit for checking whether input data corresponds to fixed information; and a Branch Metric Calculation (BMC) unit for allowing the fixed information checking unit to check whether the input data corresponds to the fixed information upon receiving the input data, and if the input data corresponds to the fixed information, for computing branch metrics for a path by the use of the fixed information. Accordingly, error correction is improved.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
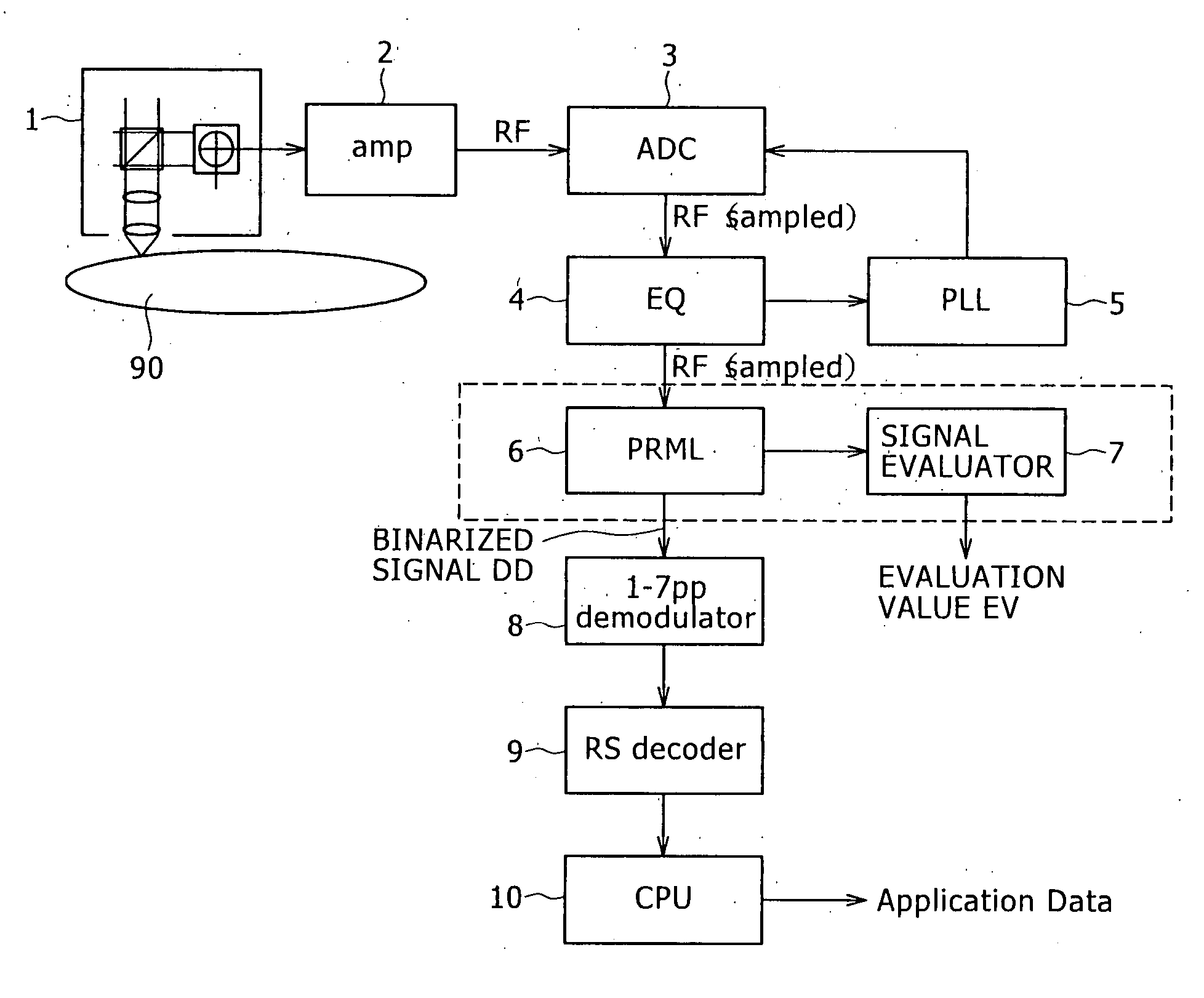
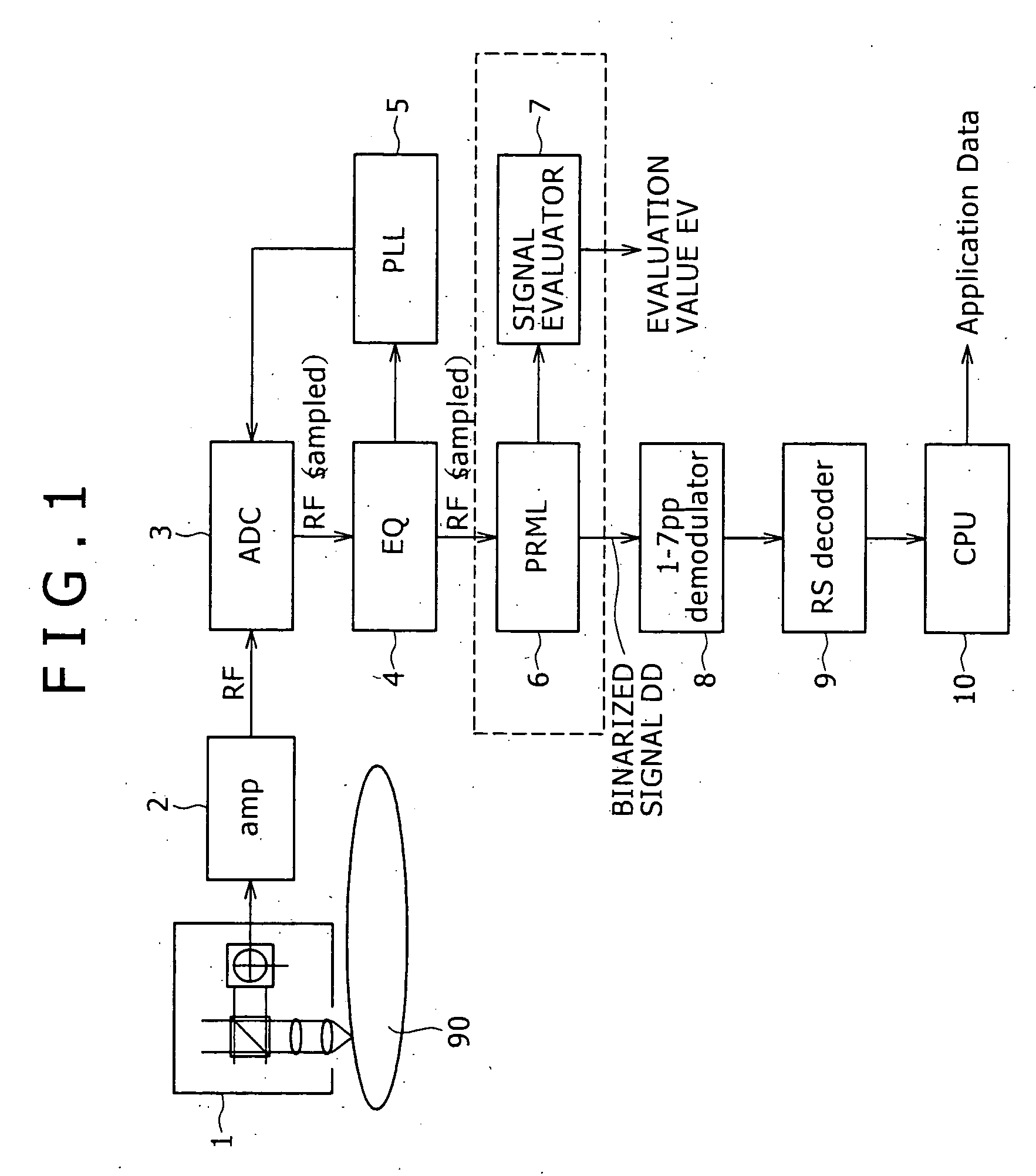
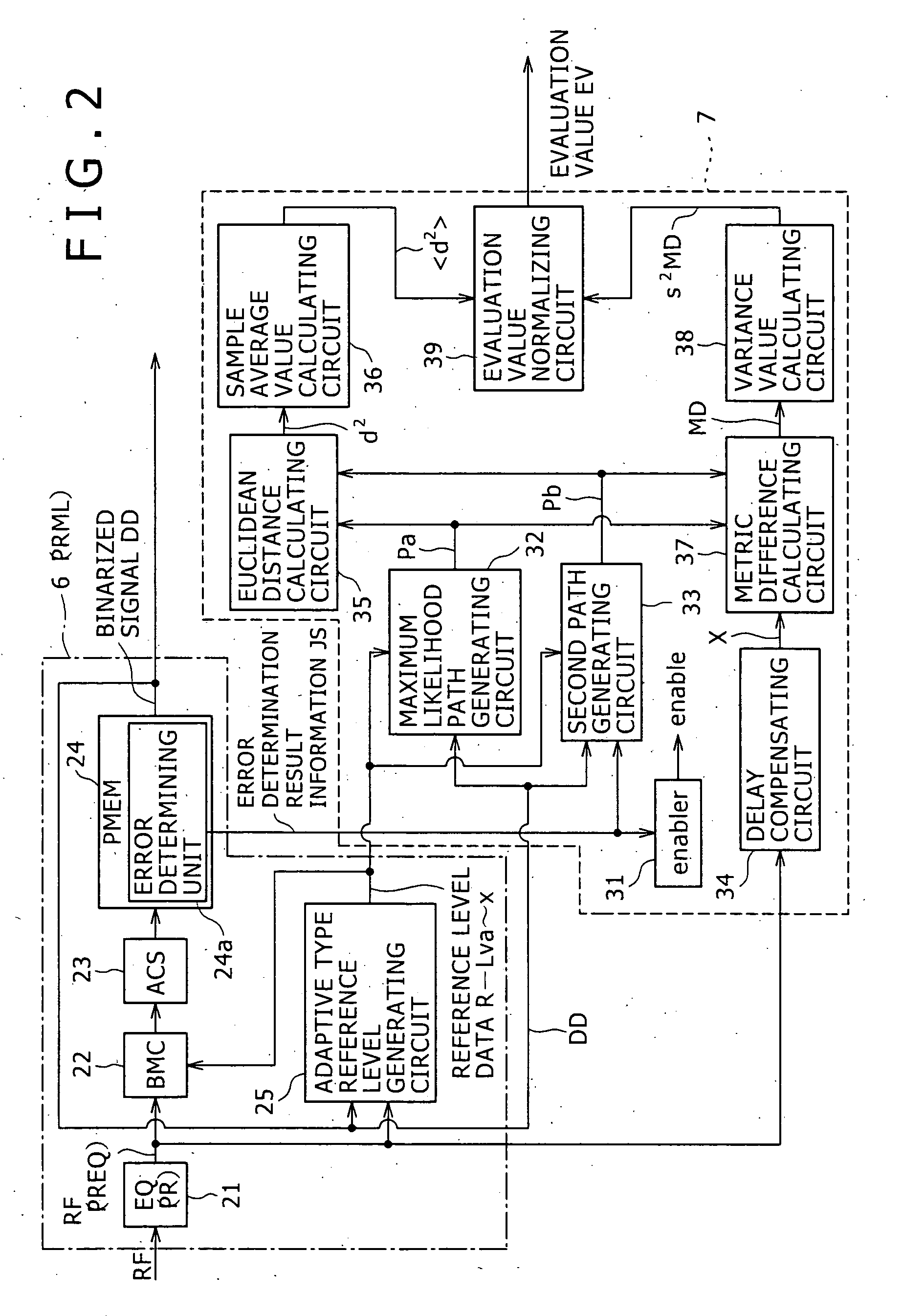
Maximum likelihood decoding device, signal evaluating method, and reproducing apparatus
InactiveUS20070234188A1Accurate calculationModification of read/write signalsData representation error detection/correctionAlgorithmEuclidean distance
Owner:SONY CORP
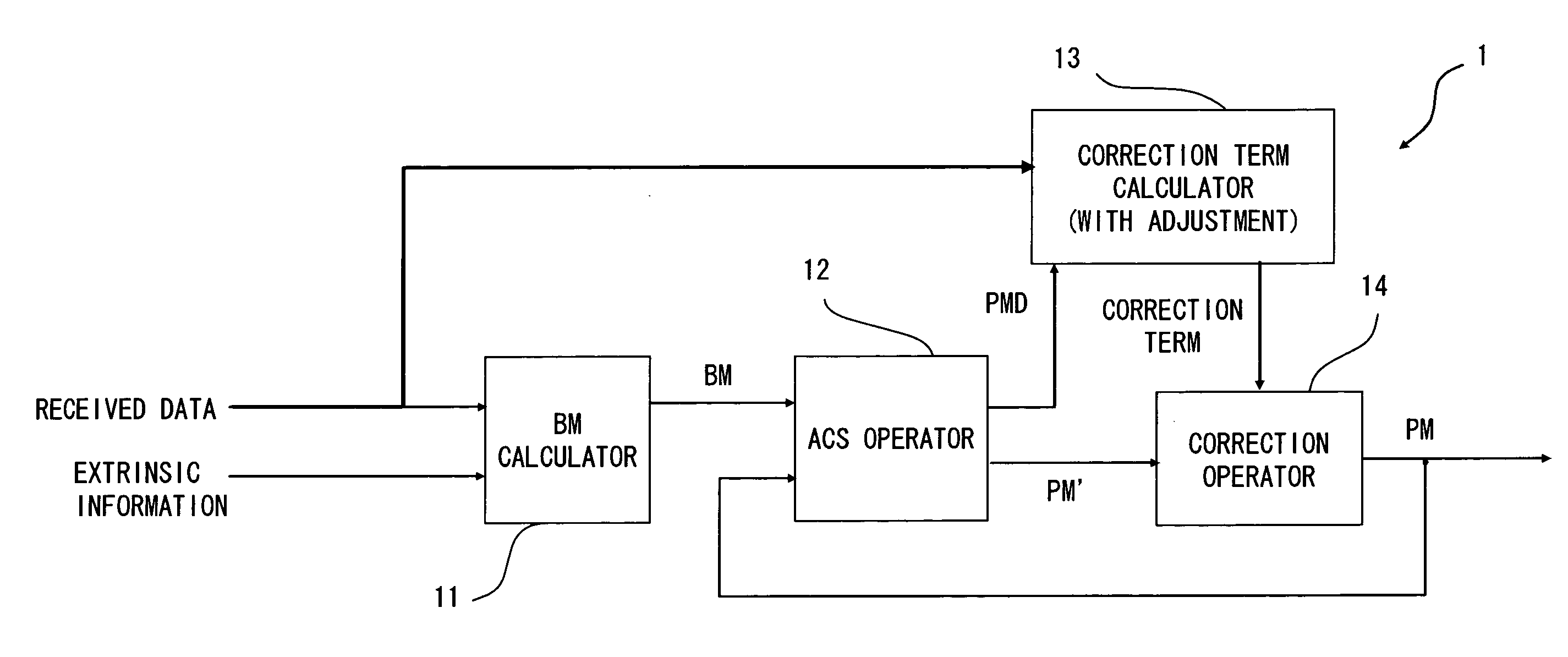
Deconding device and decoding method
InactiveUS20080092028A1Reduce degradationData representation error detection/correctionFault responseDecoding methodsLog map algorithm
A decoding device includes a BM calculator calculating a branch metric in a Log-MAP algorithm from received data and extrinsic information, an ACS operator calculating a maximum value of a path metric based on the branch metric, a correction term calculator calculating a Jacobian correction value of the path metric, and a correction operator correcting the path metric by adjusting a value of the Jacobian correction value based on a size of the received data and adding the adjusted correction value to the maximum value.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
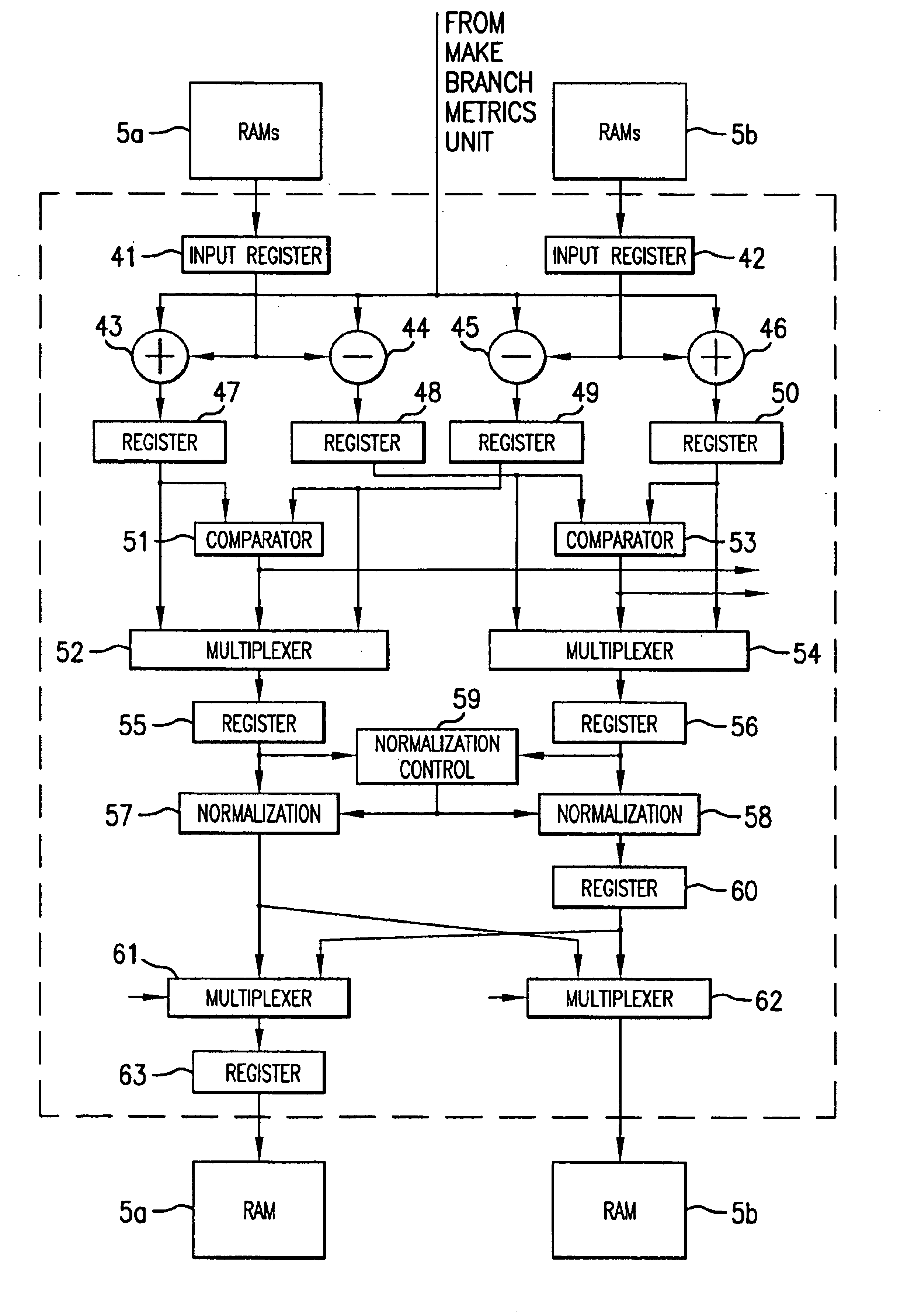
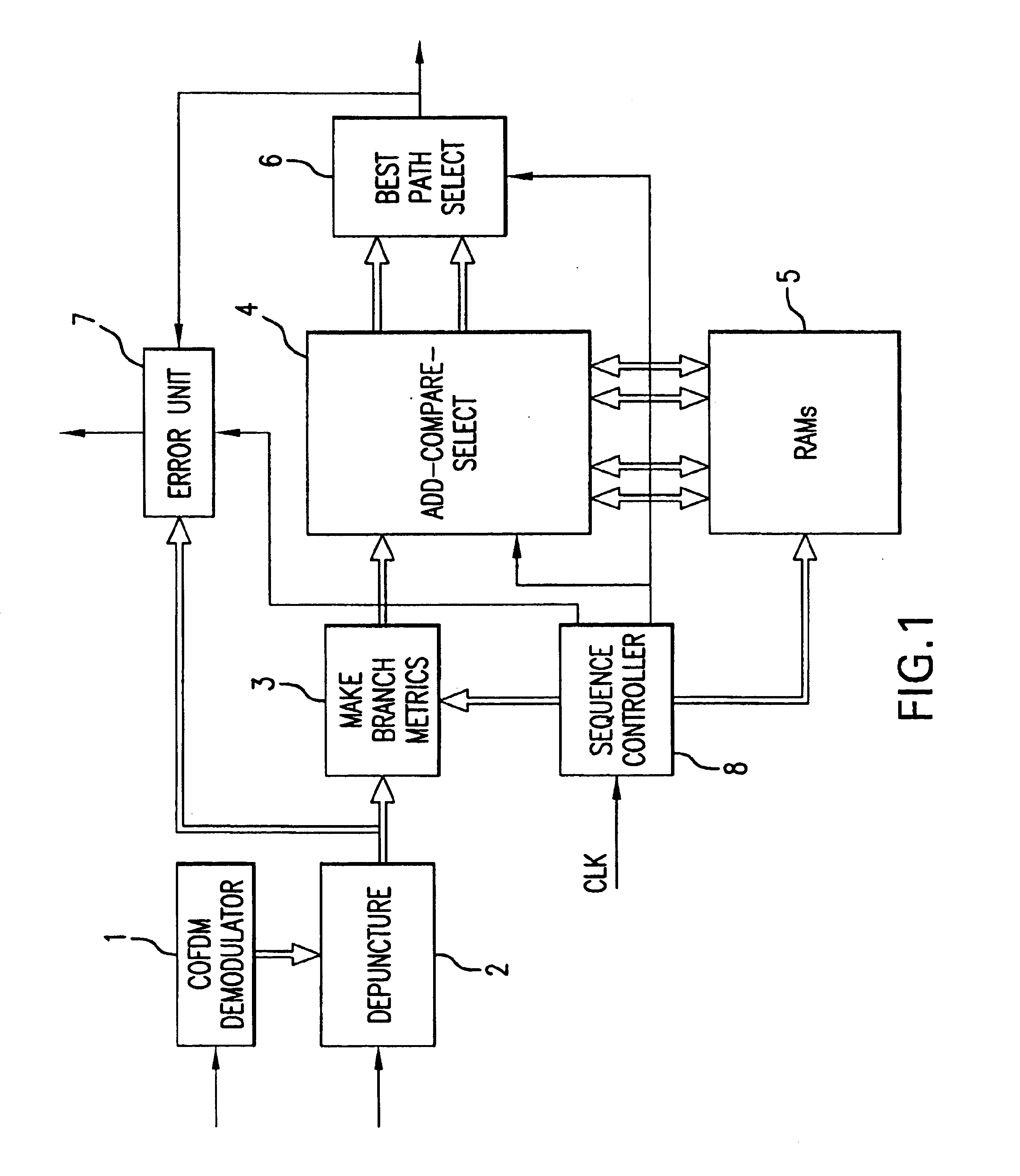
Viterbi decoder with pipelined parallel architecture
InactiveUS6810094B1Improve data throughputEasy to useError correction/detection using convolutional codesOther decoding techniquesParallel processingUnit process
A Viterbi decoder comprises a COFDM modulator, depuncture unit, a branch metrics unit an add-compare-select unit, memory, a best path unit, an error unit and a sequential controller for controlling the operation of the other units. The add-compare-select unit processes path metrics for pairs of states in parallel using a pipeline architecture. The add-compare-select unit also processes path data for pairs of states in parallel using a pipeline architecture. The best path select unit identifies the lowest cost surviving path which is in one frame and outputs a path data bit, produced a predetermined number of frames earlier, as decoded data.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
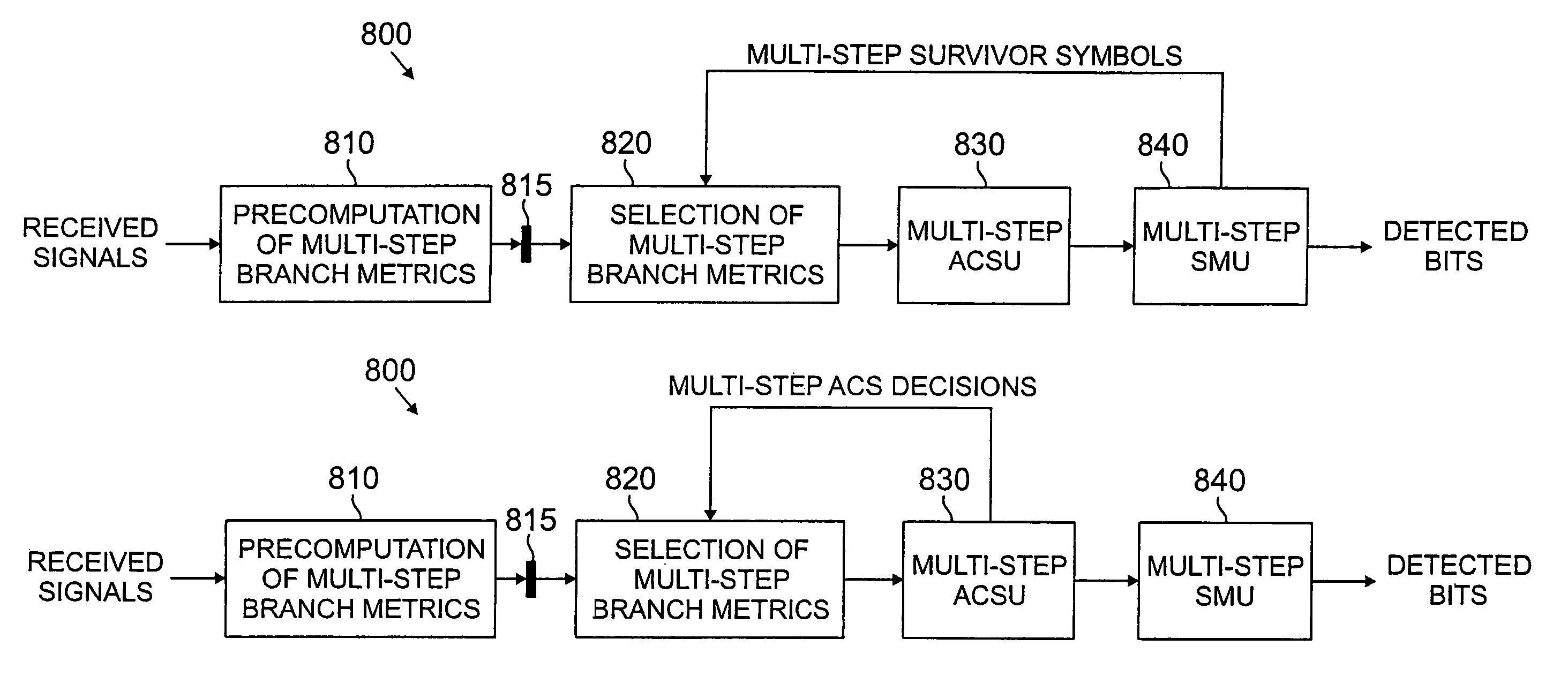
Method and apparatus for multiple step viterbi detection with local feedback
ActiveUS20050268210A1Large data-rateReduced-state Viterbi detectors is improvedData representation error detection/correctionOther decoding techniquesViterbi detectorDecision taking
A reduced-state Viterbi detector is disclosed that precomputes branch metrics for a multiple-step trellis for speculative sequences of one or more channel symbols; selects one of said precomputed branch metrics for multi-step state transitions based on at least one multi-step decision from at least one corresponding state; and selects a path having a best path metric for a given state.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
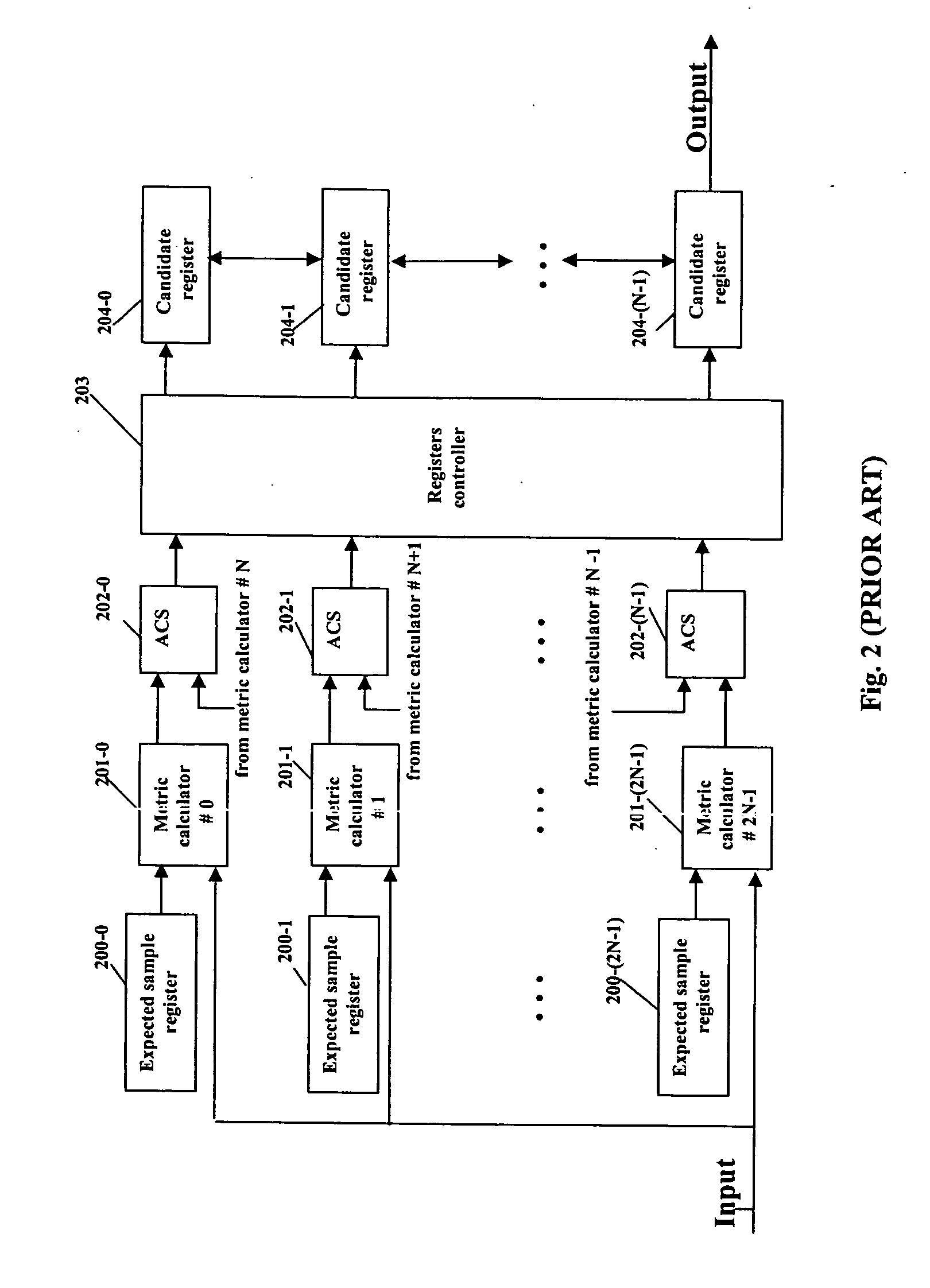
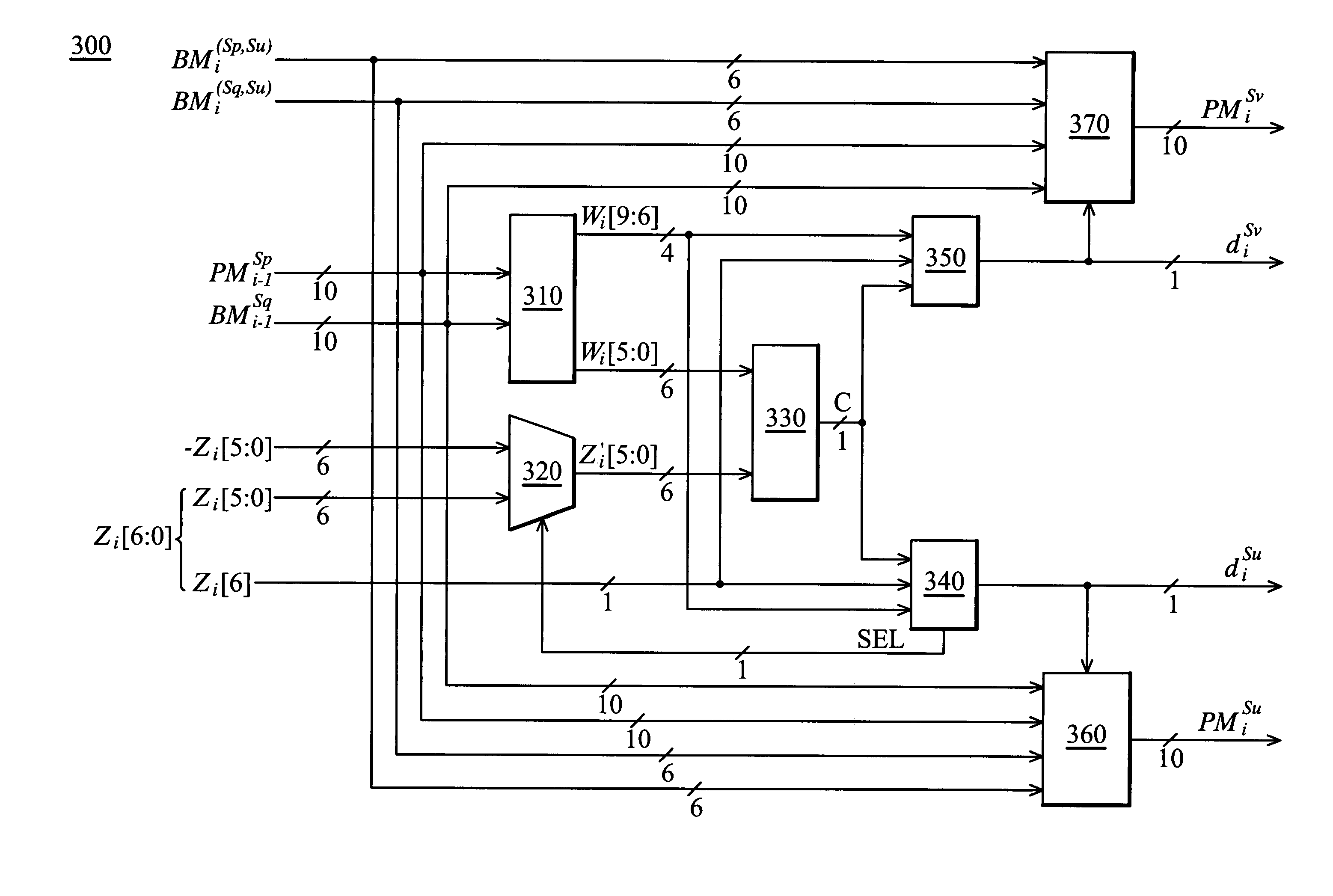
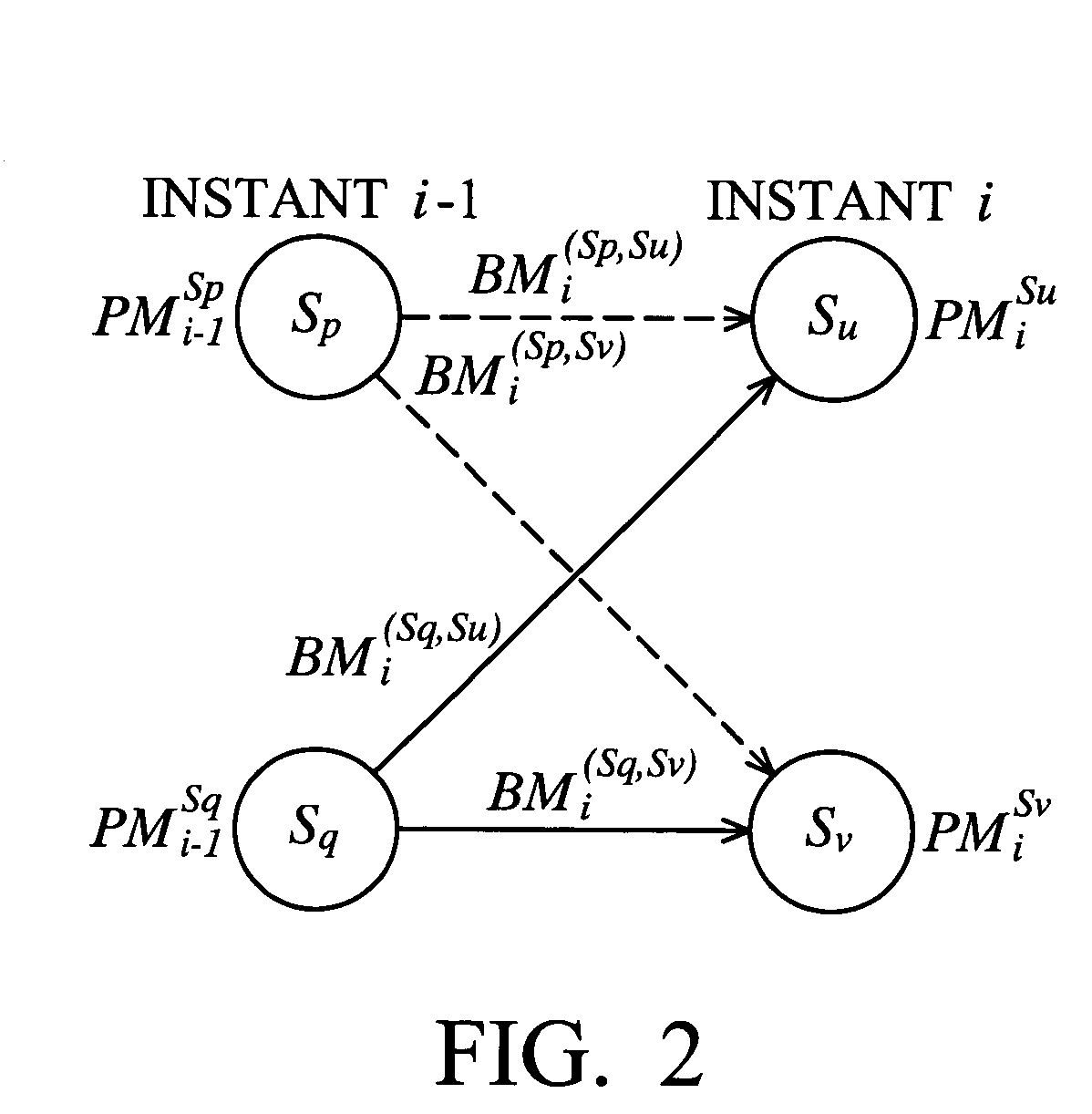
Branch metric computation and add-compare-select operation in viterbi decoders
ActiveUS7117426B2Data representation error detection/correctionOther decoding techniquesParallel computingSymbol of a differential operator
An apparatus for branch metric computation and add-compare-select operation in a rate 1 / n Viterbi decoder with a constraint length of K. The apparatus of the invention includes a branch metric generator and an add-compare-select unit. The branch metric generator calculates a plurality of branch metrics each of which is a measure between a currently received data symbol and a corresponding branch label. The add-compare-select unit can generate respective decision bits for a pair of odd and even states at next instant with a novel pre-computational architecture. Further, a local winner between the odd and even states is predetermined in a manner providing reduction of the activity required by the computation. Thus the add-compare-select unit outputs a path metric of the local winner, whereby a saving of half the output number of path metrics is achieved.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
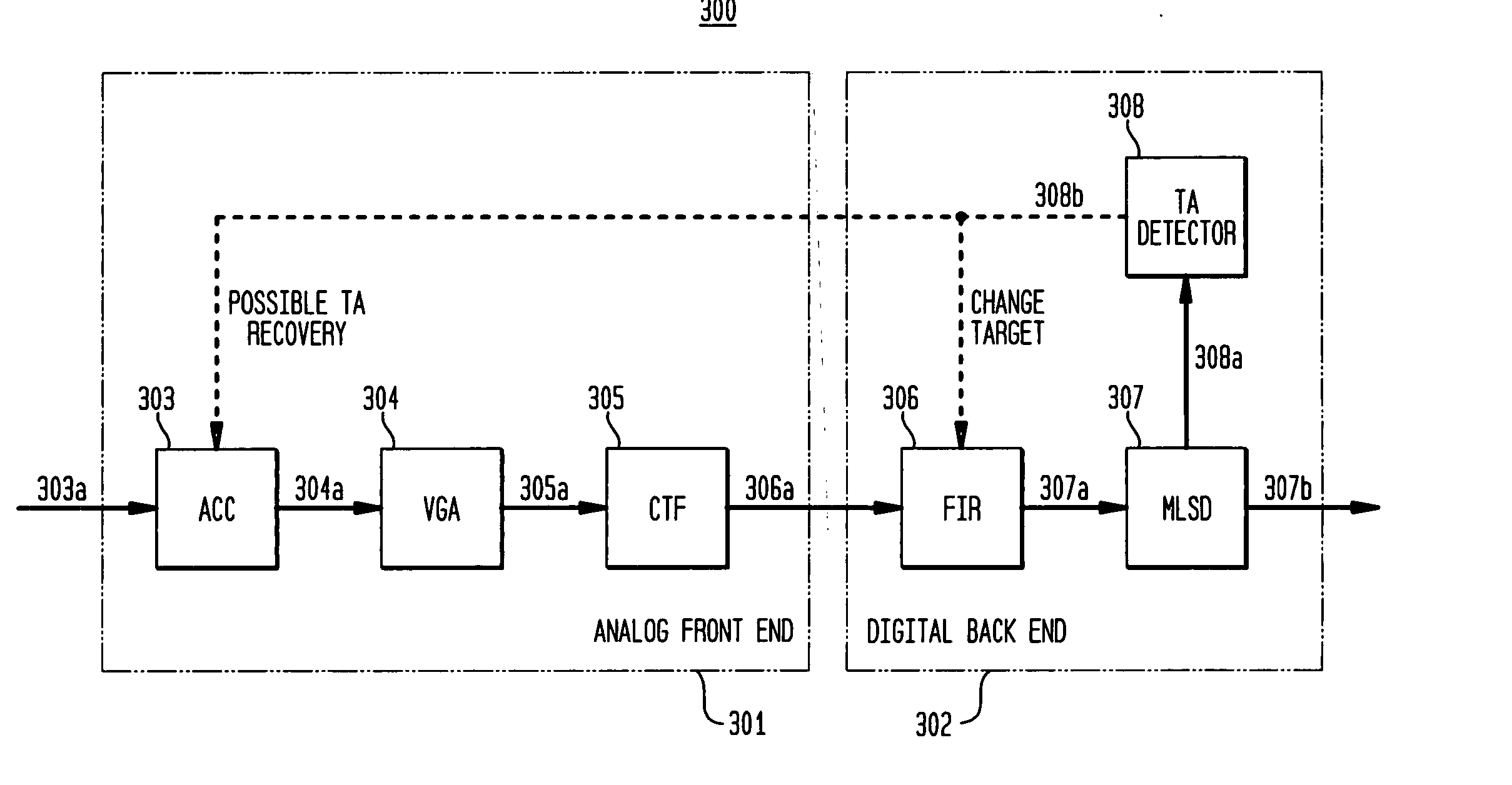
Detection of signal disturbance in a partial response channel
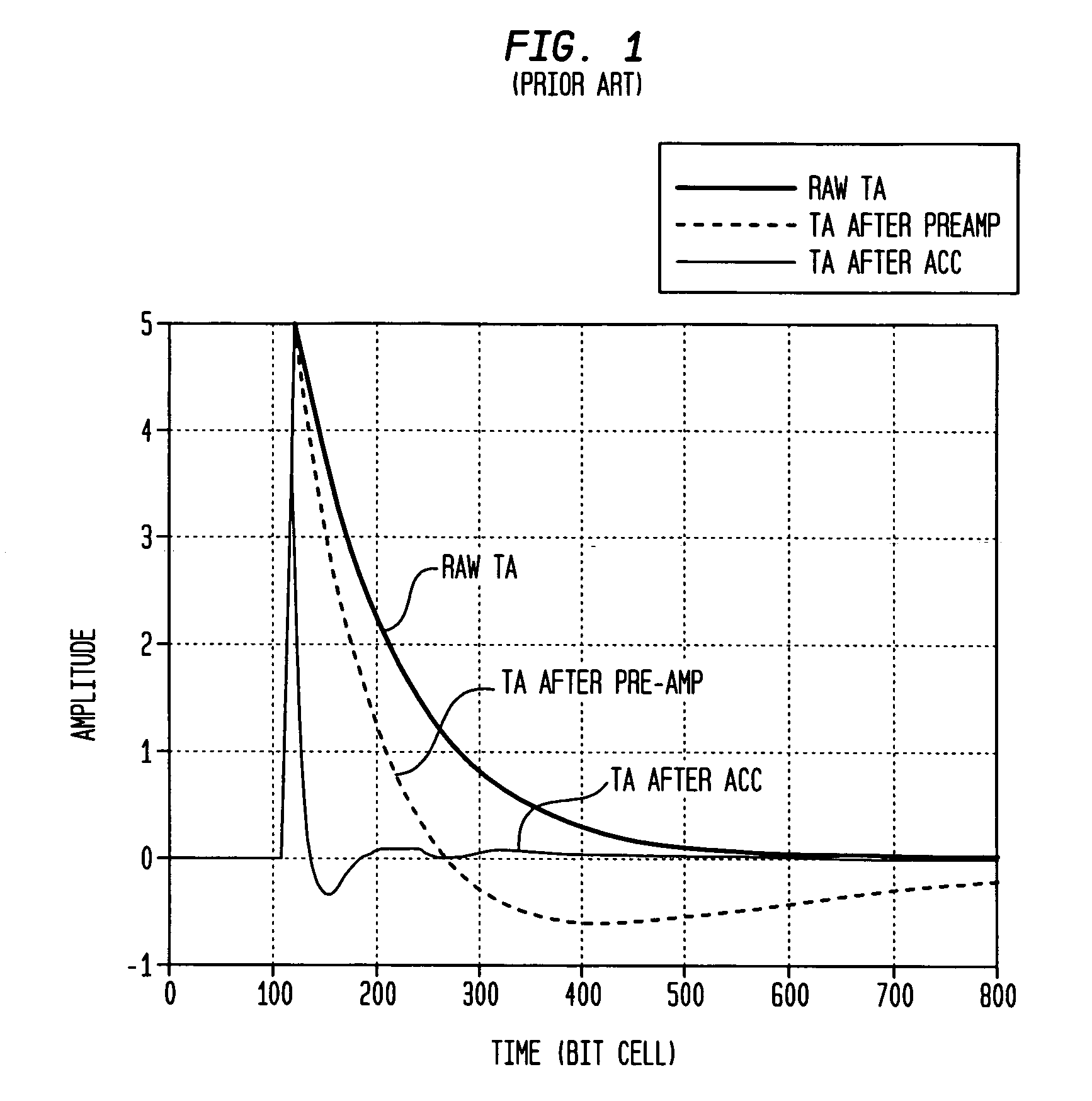
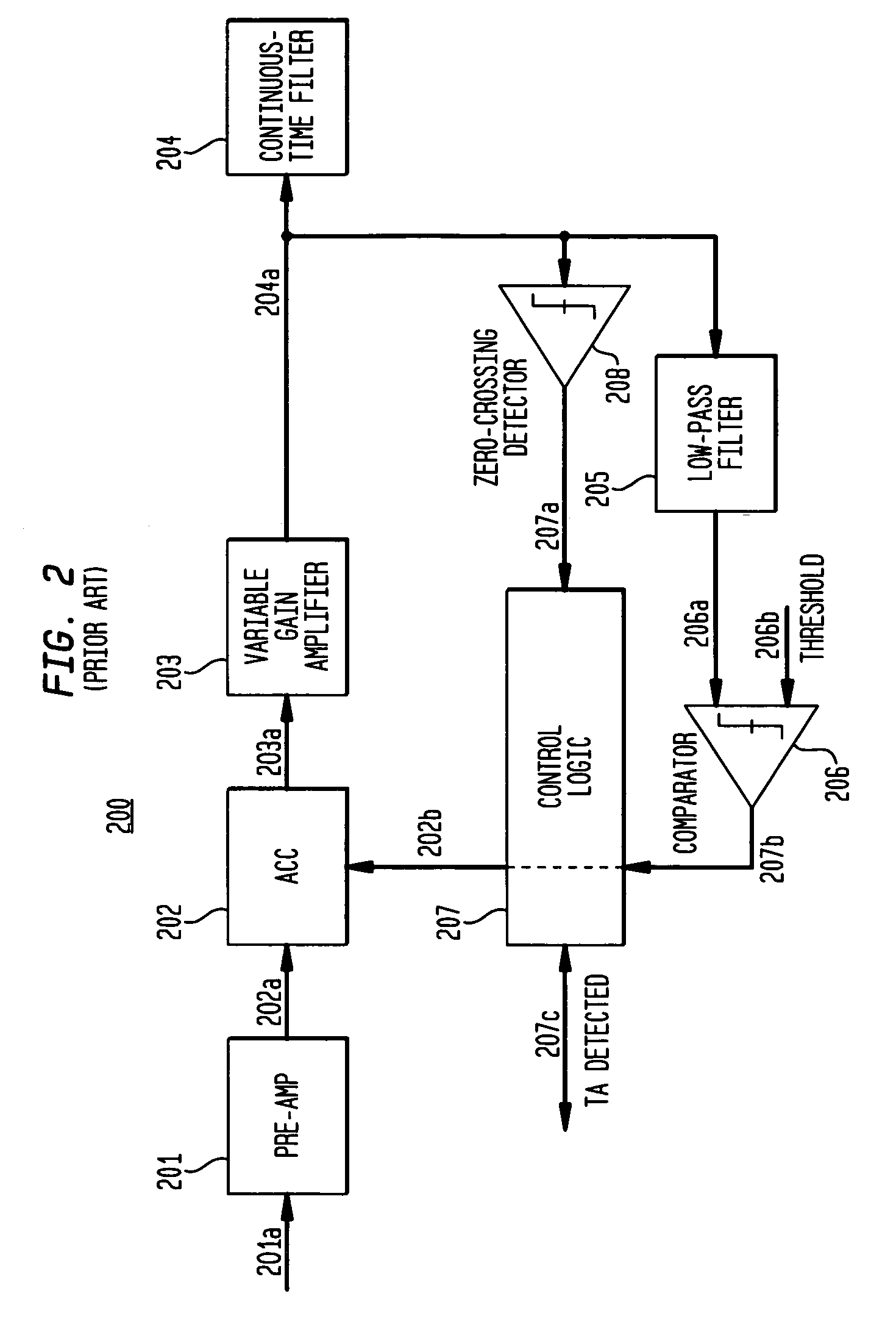
In one embodiment, irregular electronic disturbance signals in a partial-response read channel are detected by a disturbance detector using state metrics generated by maximum-likelihood sequence detector. For example, a thermal asperity (TA) detector detects the occurrence of TAs in the read channel of perpendicularly recorded magnetic media by using the state metrics generated by a Viterbi detector. Changes in state metrics (e.g., magnitudes of the branch metrics of the trellis diagram) used by the Viterbi detector are tracked. If the magnitude of the rise of the path metric increases above a set threshold, then a TA is detected. Alternatively, or additionally, the rate of change of the magnitude of the path metrics is tracked. If the rate of change within a set time window is above a specified threshold, then a TA is detected.
Owner:BROADCOM INT PTE LTD
Incoherent detection technology suitable for DMR digital trunking communication system
InactiveCN102624662AReduce complexityOvercoming the problem of poor non-coherent detection performanceModulated-carrier systemsCommunications systemDigital mobile radio
The invention belongs to the field of wireless communication and relates to an incoherent detection technology suitable for a DMR (Digital Mobile Radio) digital trunking communication system. Firstly, defects of both a conventional incoherent detection technology and an existing multiple symbol detection algorithm are analyzed in detail; then according to the maximum likelihood ratio criterion, an incoherent multiple symbol detection algorithm suitable for a 4-CPFSK (Continuous Phase Frequency Shift Keying) signal in a DMR standard frame is disclosed; and simultaneously, a decomposed linear signal replaces an original reference signal to simplify the structure of a receiver. The receiver corresponding to the algorithm disclosed by the invention is formed by three front-end matched filters and a following viterbi operational part and the complexity of the receiver is effectively reduced. When the calculation of the branch metric is carried out, the judgment accuracy is improved by utilizing information of a plurality of pieces of code element time. A computer simulation result in the Matlab environment proves that with the increase of observing windows, the performance of detecting the 4-CPFSK signal of the algorithm disclosed by the invention gradually becomes better.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Turbo component decoding method, component decoder, branch calculator and Turbo decoder
ActiveCN102111162AReduce overheadError preventionError correction/detection by combining multiple code structuresDecoding methodsParallel computing
The invention provides a Turbo component decoding method, a component decoder, a branch calculator and a Turbo decoder. The method comprises the following steps of: calculating a forward branch metric Alpha, and interlacing and caching in an Alpha cache; and calculating a backward branch metric Beta, deinterlacing and reading the Alpha, calculating a logarithm likelihood ratio (LLR), storing the calculated LLR into the Alpha cache in situ, and outputting sequentially during outputting. By the method, the calculated LLR is stored in the Alpha cache in situ so as to save an LLR cache during the conventional technical component decoding, further save the LLR cache for each circuit branch of the Turbo decoder with a plurality of parallel circuit branches, and greatly save the hardware cost of the whole Turbo decoder. The invention further provides a Turbo decoding component decoder, a branch calculator and the Turbo decoder.
Owner:RDA CHONGQING MICROELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
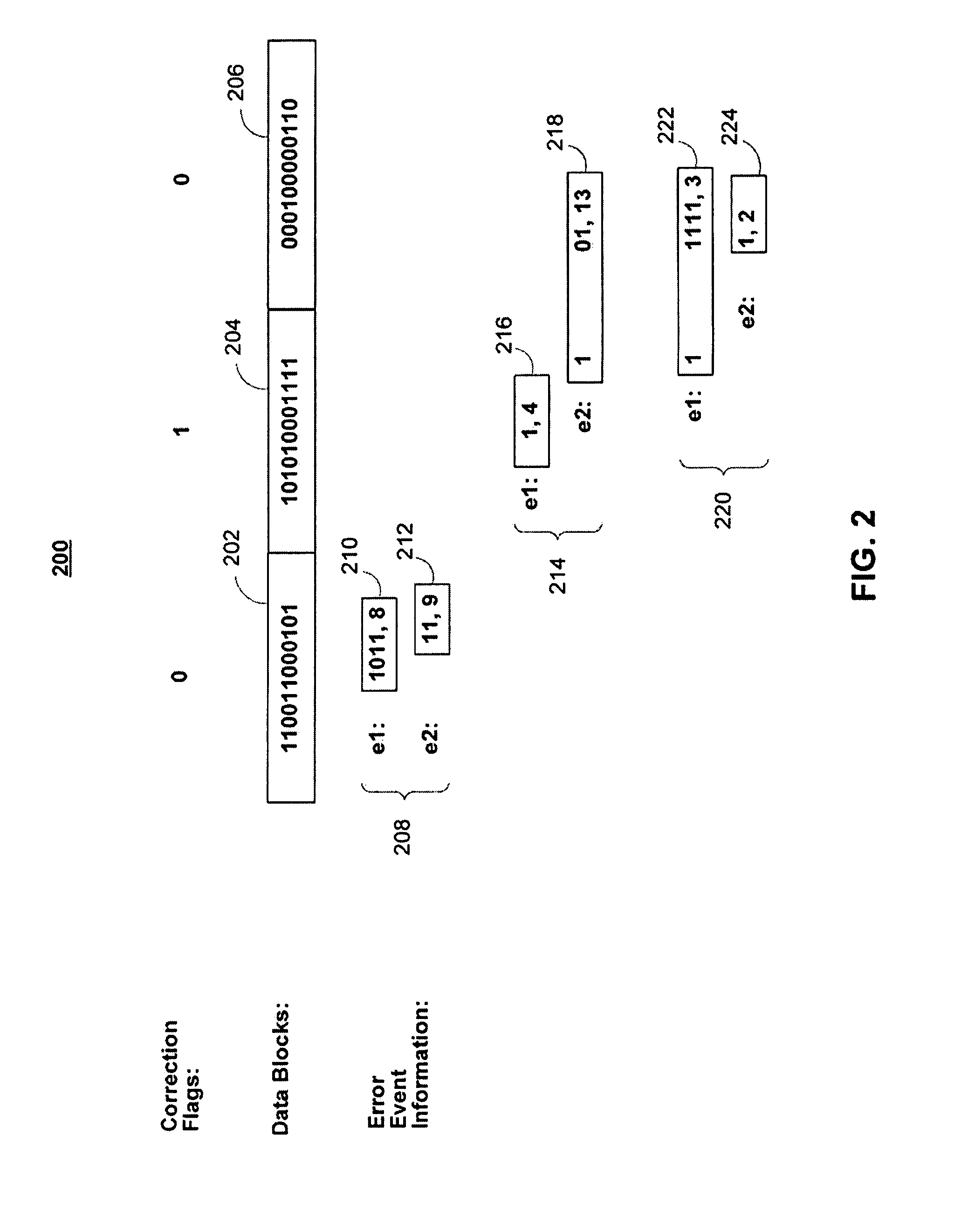
Methods and apparatus for identification of likely errors in data blocks
ActiveUS8145983B1Minimize total branch metricEfficient identificationData representation error detection/correctionCode conversionTheoretical computer scienceEngineering
Methods and apparatus are provided for processing a plurality of data blocks. In accordance with embodiments of the invention, a correction flag for each of the data blocks can be received, along with information on at least one error event for each of the data blocks. Using this received information, a search trellis corresponding to the data blocks can be determined. Determining the search trellis can include determining a plurality of branches and computing a branch metric for each of the branches. A search on the search trellis can be performed to identify at most one error event for each data block, where the search is based on the branch metrics.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Method and apparatus for multiple step Viterbi detection with local feedback
ActiveUS7487432B2Large data-rateReduced-state Viterbi detectors is improvedData representation error detection/correctionOther decoding techniquesViterbi detectorReal-time computing
A reduced-state Viterbi detector is disclosed that precomputes branch metrics for a multiple-step trellis for speculative sequences of one or more channel symbols; selects one of said precomputed branch metrics for multi-step state transitions based on at least one multi-step decision from at least one corresponding state; and selects a path having a best path metric for a given state.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com