Channel estimation by adaptive interpolation
An adaptive, channel technology, applied in channel estimation, transmission path sub-channel allocation, pilot signal allocation and other directions, which can solve problems such as large number of subcarriers, difficult interpolation, and complex filters.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
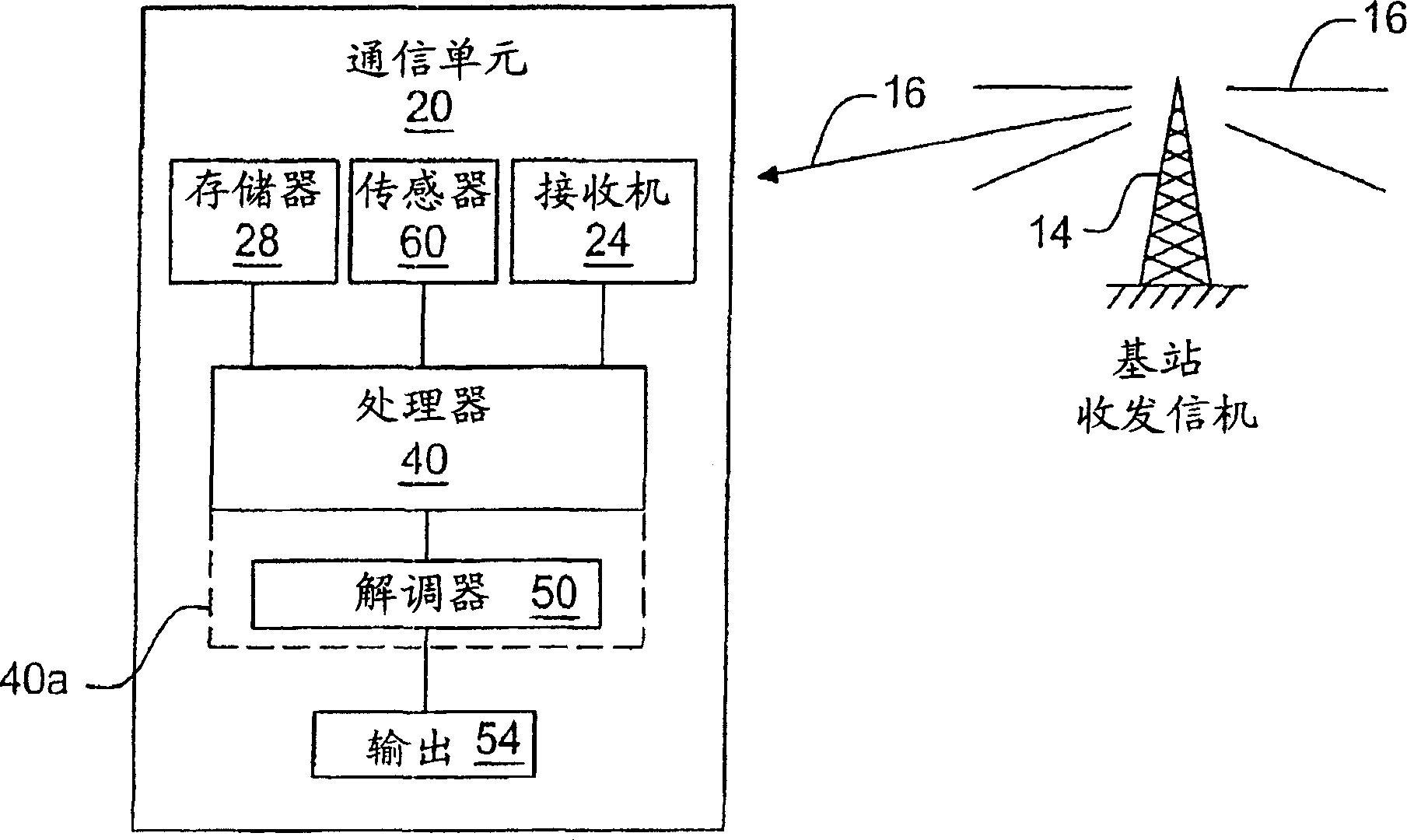
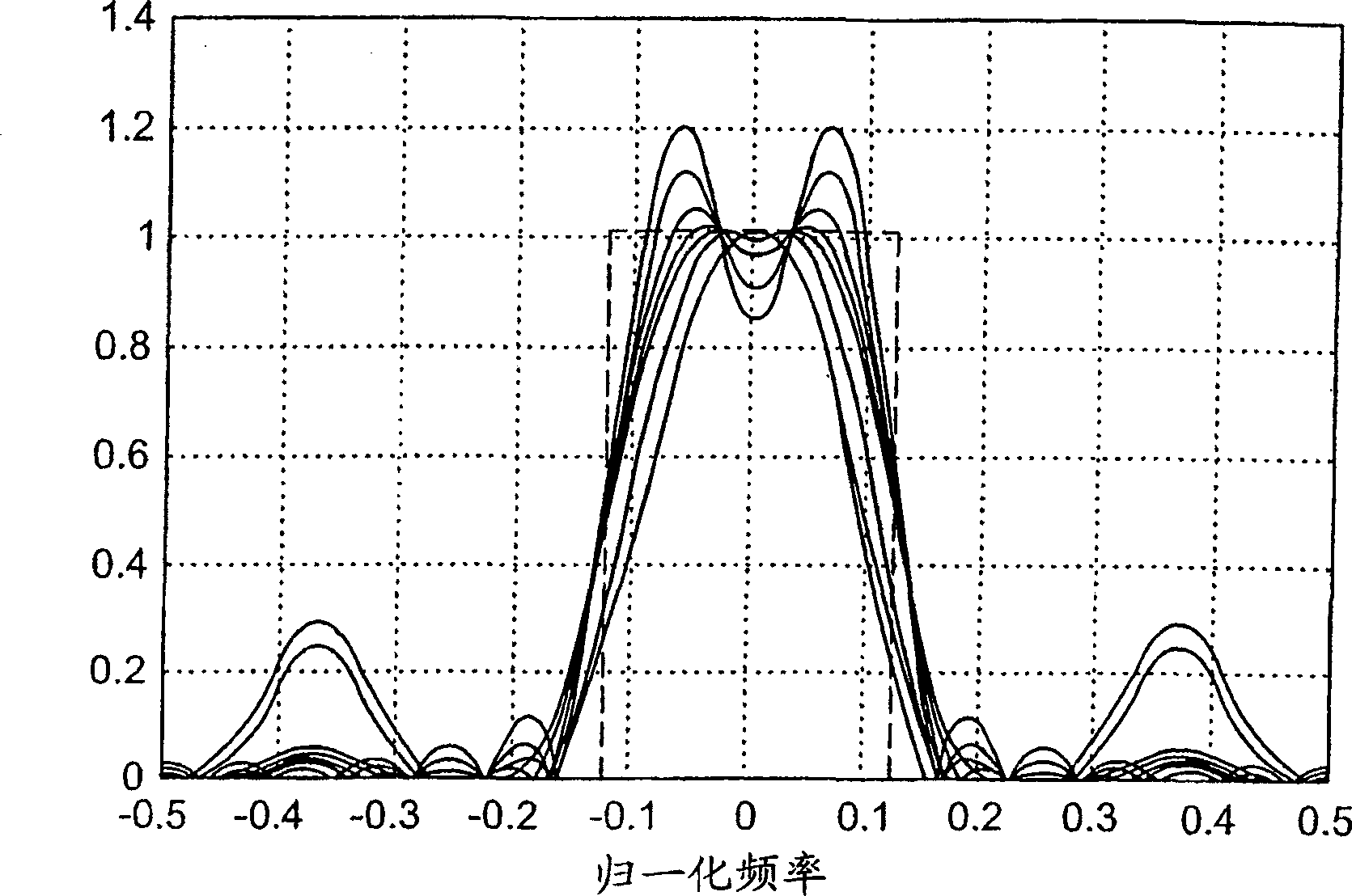
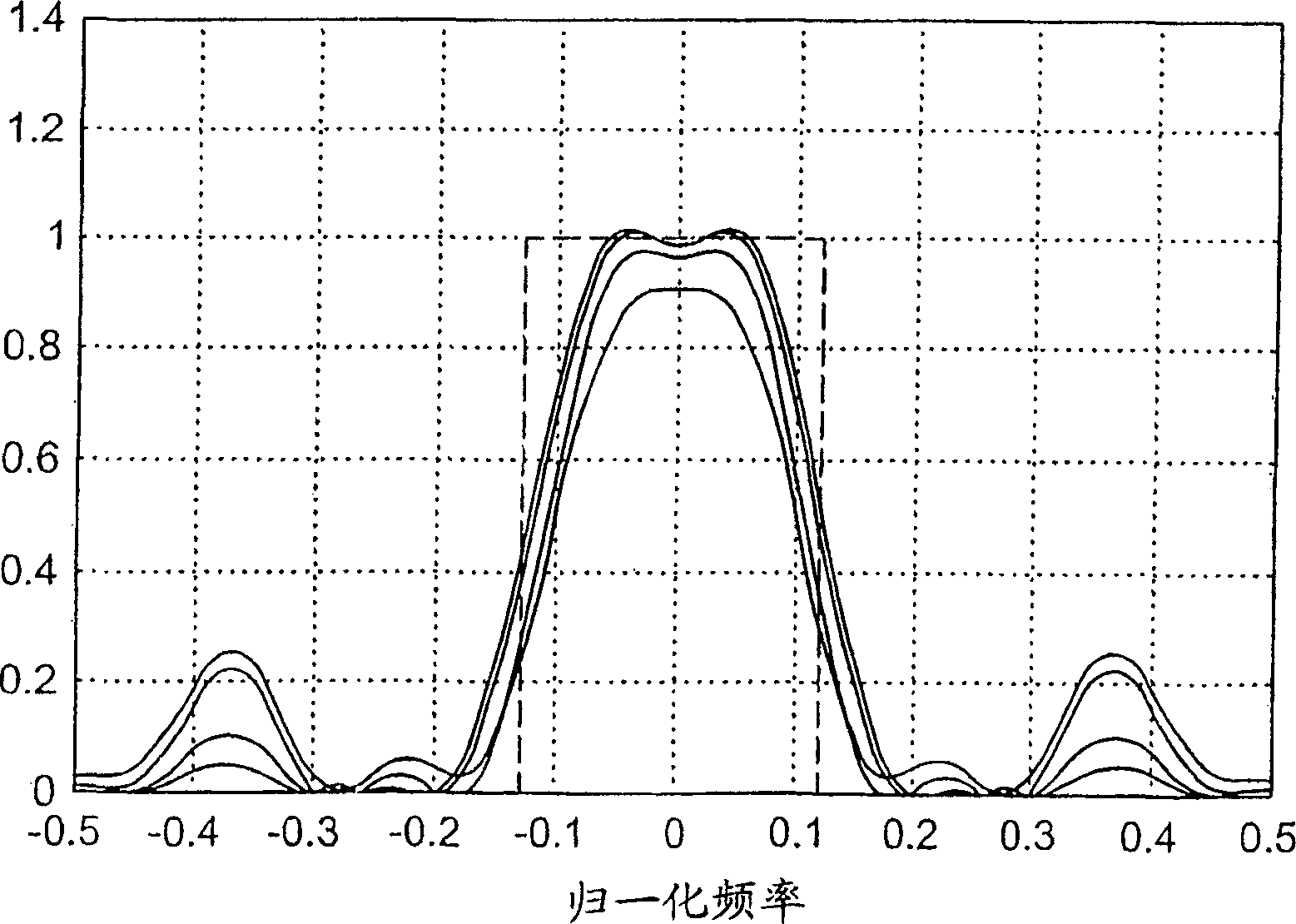
[0045] In order to facilitate the understanding of the disclosed method and equipment, this specification is based on an example whose data is very similar to the parameters in DVB-T, the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) EN 300 744V.1.4.1 (Jan.2001) Digital TV Broadcasting (DVB) The standard of terrestrial digital television broadcasting announced; the framing structure, channel coding and modulation of digital terrestrial television. Specifically, assume that the symbol rate R s It is 1K symbols / second, and the distance between different carriers is 1 kHz. For time interpolation, every fourth symbol is a pilot, and after interpolation is performed in the time direction, every third carrier is a pilot. In addition, let C / N represent the carrier-to-noise ratio or carrier-to-interference ratio, and let f D Represents the (maximum) Doppler frequency shift, and let T m Represents the (maximum) delay spread. Obviously, the present invention is not limited to DVB o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com