Method for detecting medical polyethylene glycol
A technology of polyethylene glycol and glass rods, which is applied in thermal analysis of materials, instruments, measuring devices, etc., and can solve problems such as description of crystallization morphology
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
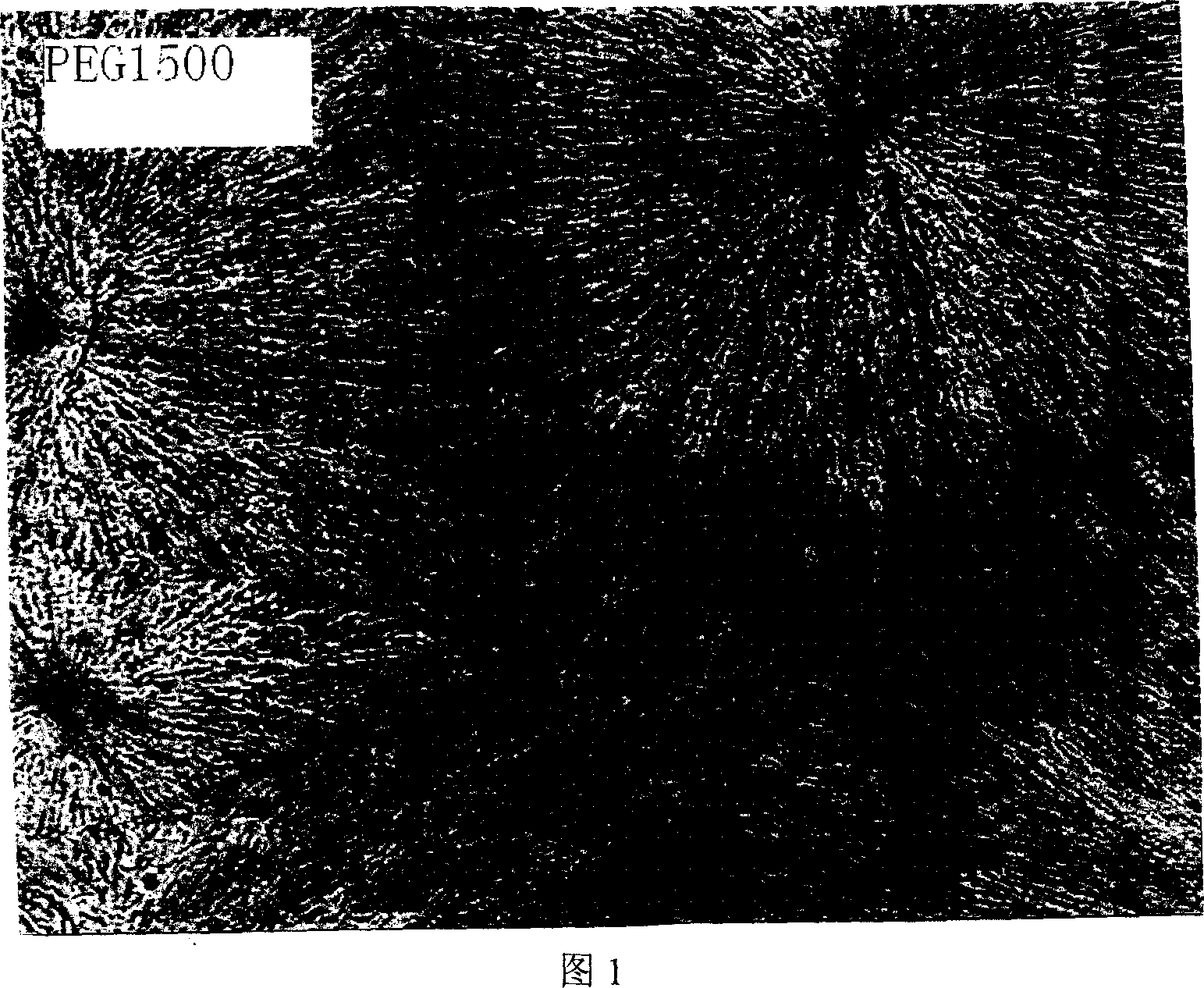
[0018] Heat medicinal polyethylene glycol 1500 to 90°C to melt, dip a small amount of liquid with a glass rod, and spread it thinly on the glass slide heated to the same temperature (the thickness of the liquid applied on the glass slide can be controlled at 0.02 mm-0.5mm), after cooling and solidifying, place it under an optical microscope to observe the crystal form of pharmaceutical polyethylene glycol 1500. (see picture 1)
Embodiment 2
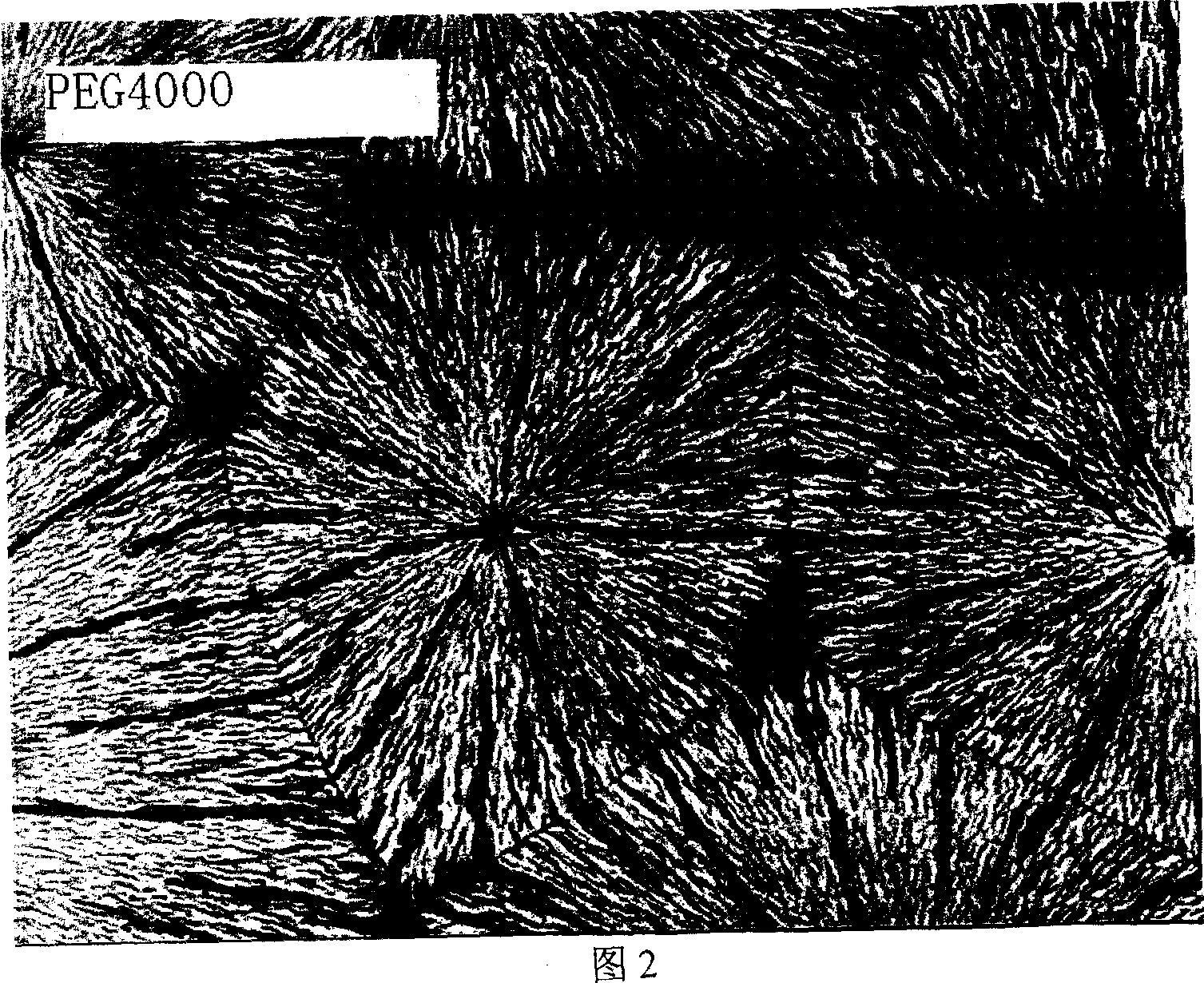
[0020] Heat medicinal polyethylene glycol 4000 to 110°C to melt, dip a small amount of liquid with a glass rod, and spread it thinly on the glass slide heated to the same temperature (the thickness of the liquid applied on the glass slide can be controlled at 0.02 mm-0.5mm), after cooling and solidifying, place it under an optical microscope to observe the crystal form of pharmaceutical polyethylene glycol 4000. (See Figure 2)
Embodiment 3
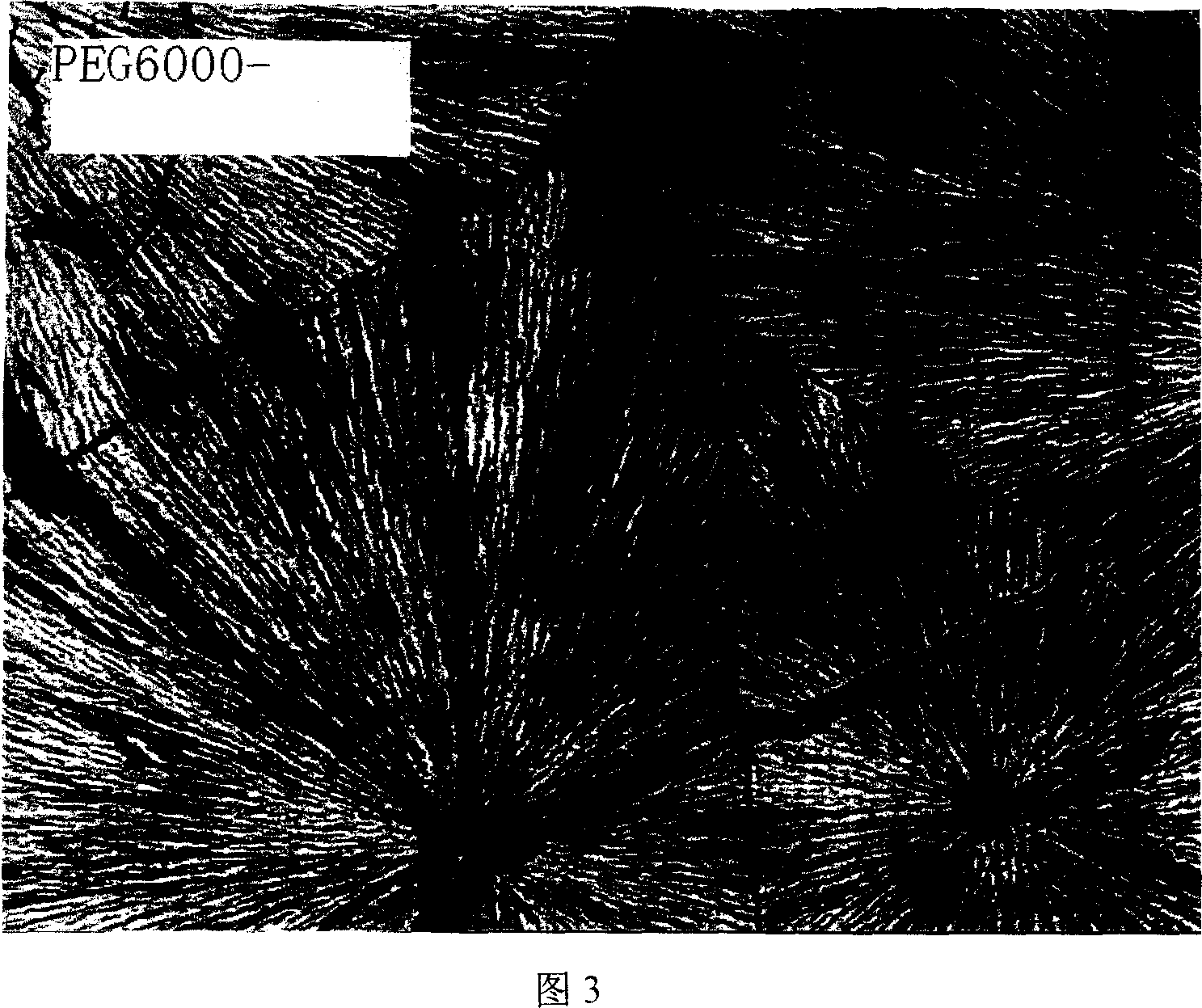
[0022] Heat medicinal polyethylene glycol 6000 to 110°C to melt, dip a small amount of liquid with a glass rod, and spread it thinly on the glass slide heated to the same temperature (the thickness of the liquid applied on the glass slide can be controlled at 0.02 mm-0.5mm), after cooling and solidifying, place it under an optical microscope to observe the crystal form of pharmaceutical polyethylene glycol 6000. (See Figure 3)
[0023] Fig. 4, Fig. 5 and Fig. 6 show respectively the photo of S-40, poloxamer and stearyl alcohol under the microscope (40 times of magnification); the difference.
[0024] Figure 7 shows that the Qingyan dripping pill with polyethylene glycol as the auxiliary material is heated to 110 ° C to melt, dipped in a small amount of liquid with a glass rod, and spread it thinly on the glass slide heated to the same temperature (the amount of liquid applied on the glass slide The thickness can be controlled at 0.02mm-0.5mm), after cooling and solidificatio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com