Browser for use in navigating a body of information, with particular application to browsing information represented by audiovisual data
a technology of audiovisual data and navigation information, which is applied in the direction of selective content distribution, television systems, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of large body of information that is overwhelming, system not automatically displaying such related segments of information, and not enabling the determination of relatedness between segments of information represented by different types of data, so as to determine the relatedness of the compared segments
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0031] I. Overview
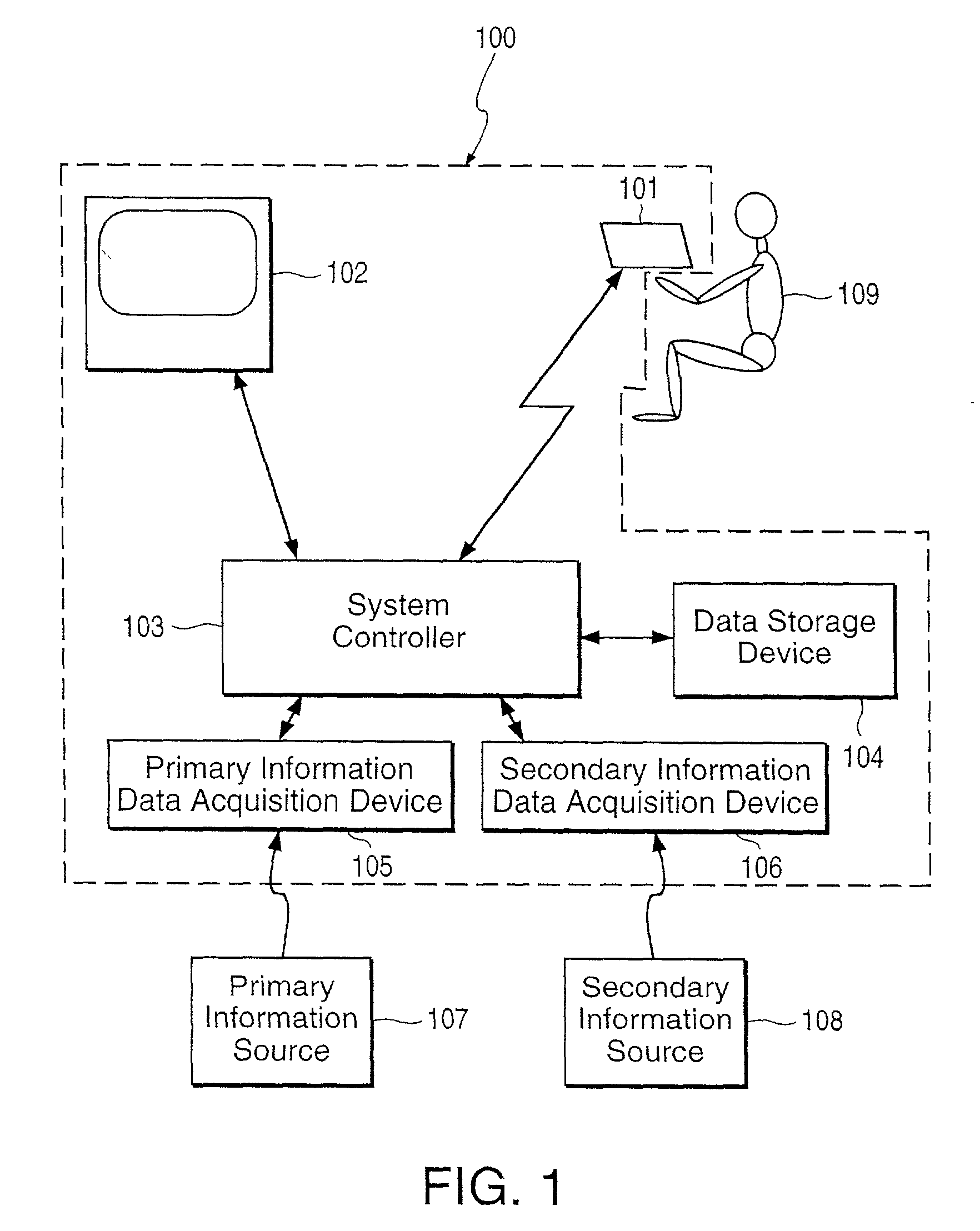
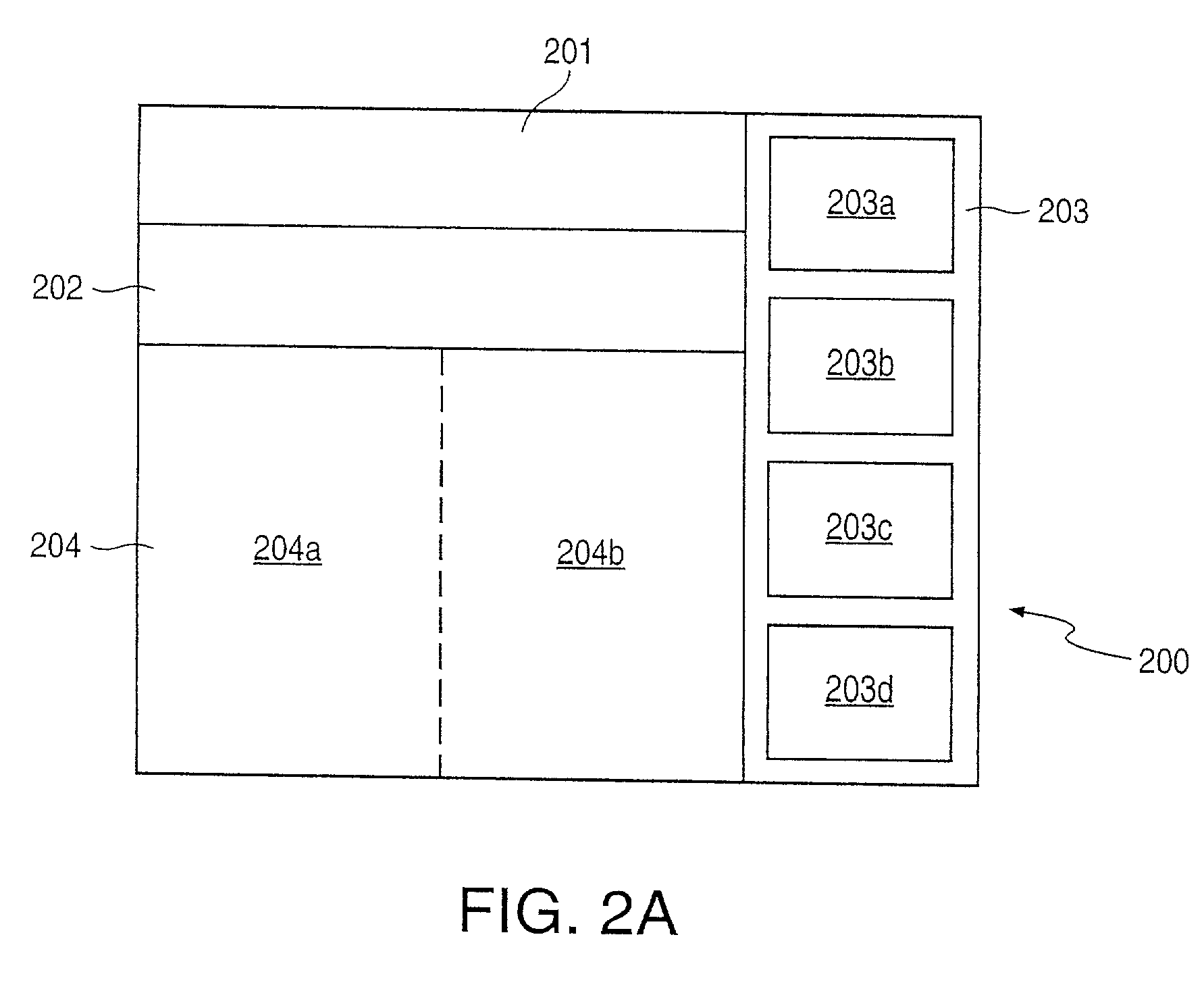
[0032] Generally, the invention enables the acquisition of a body of information and review of the content of the body of information. In particular, the invention includes various features that facilitate and enhance review of the body of information. The invention enables the body of information to be quickly reviewed to obtain an overview of the content of the body of information or some portion of the body information. The invention also allows flexibility in the manner in which the body of information is reviewed. For example, the invention enables a user to move quickly from one segment of a body of information to another, enabling the user to rapidly begin observing particular information of interest. Further, the invention enables a user to quickly locate information within the body of information that pertains to a particular subject in which the user has an interest. The invention also enables a user to, when observing particular information, quickly find...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com