Method and apparatus for detecting guideway breaks and occupation
a guideway and break technology, applied in the field of track detection systems, can solve the problems of burdening the cost per mile of new track installation, small separation gap at the break, and existing external detection system requires significant wayside infrastructur
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
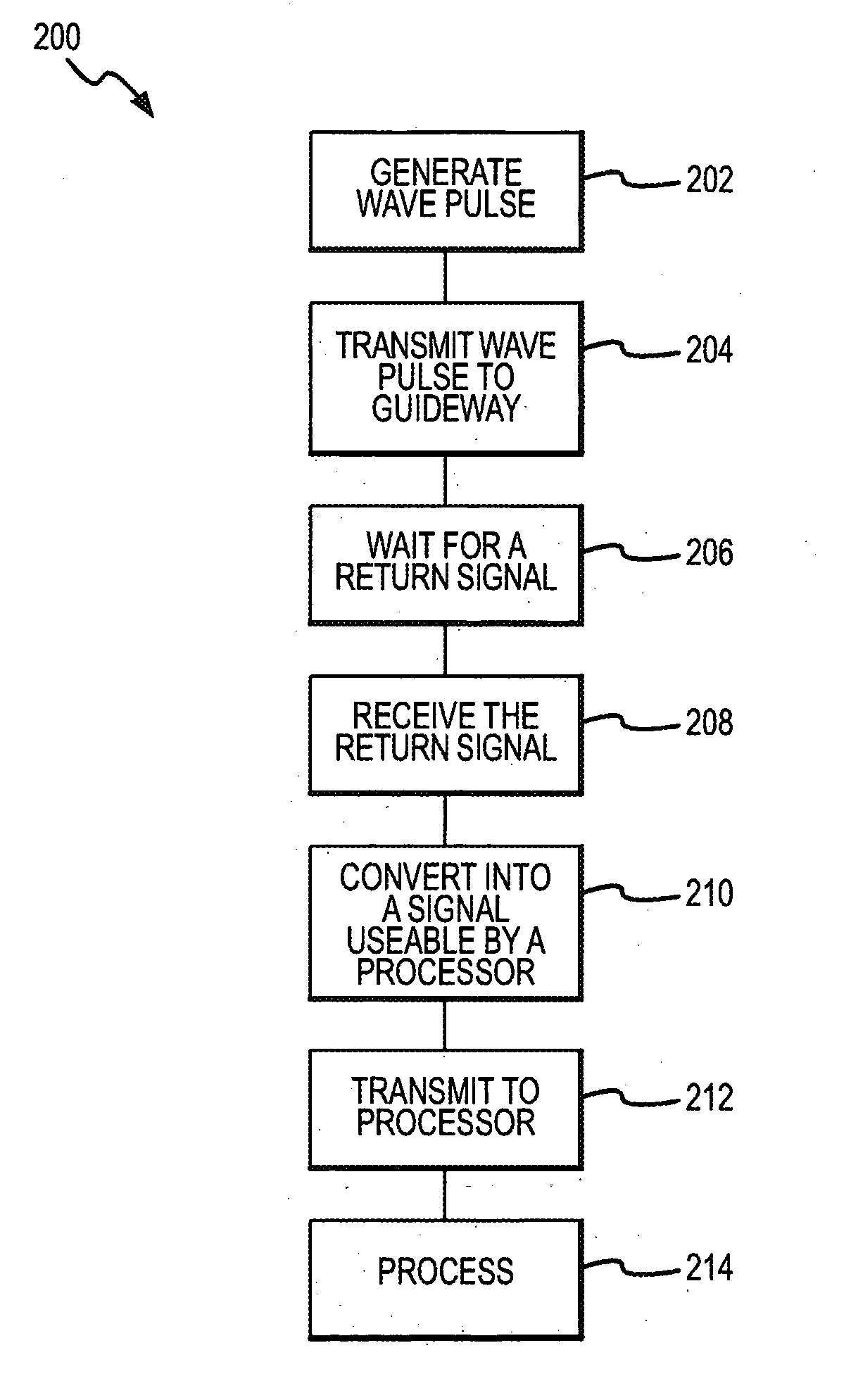
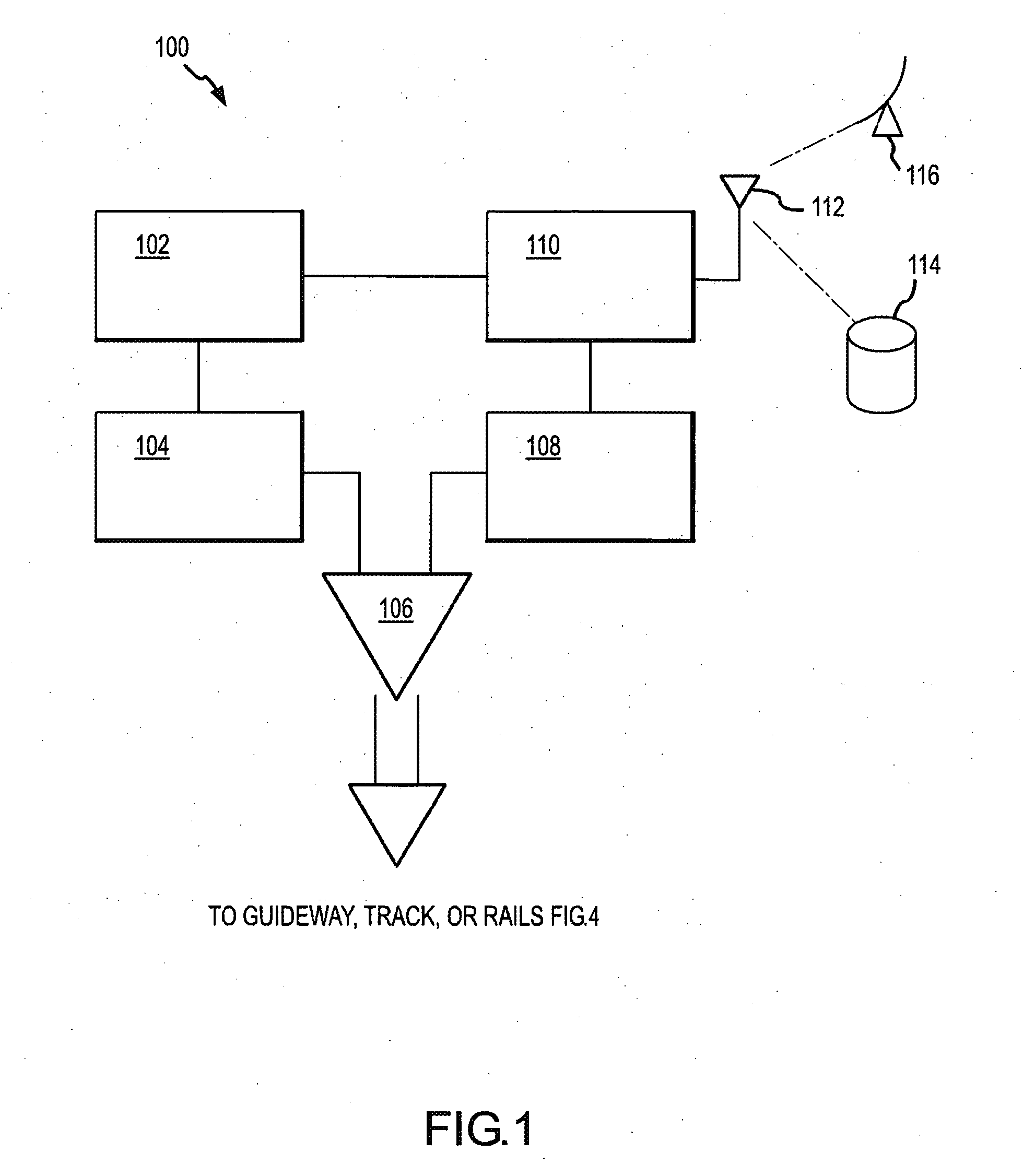
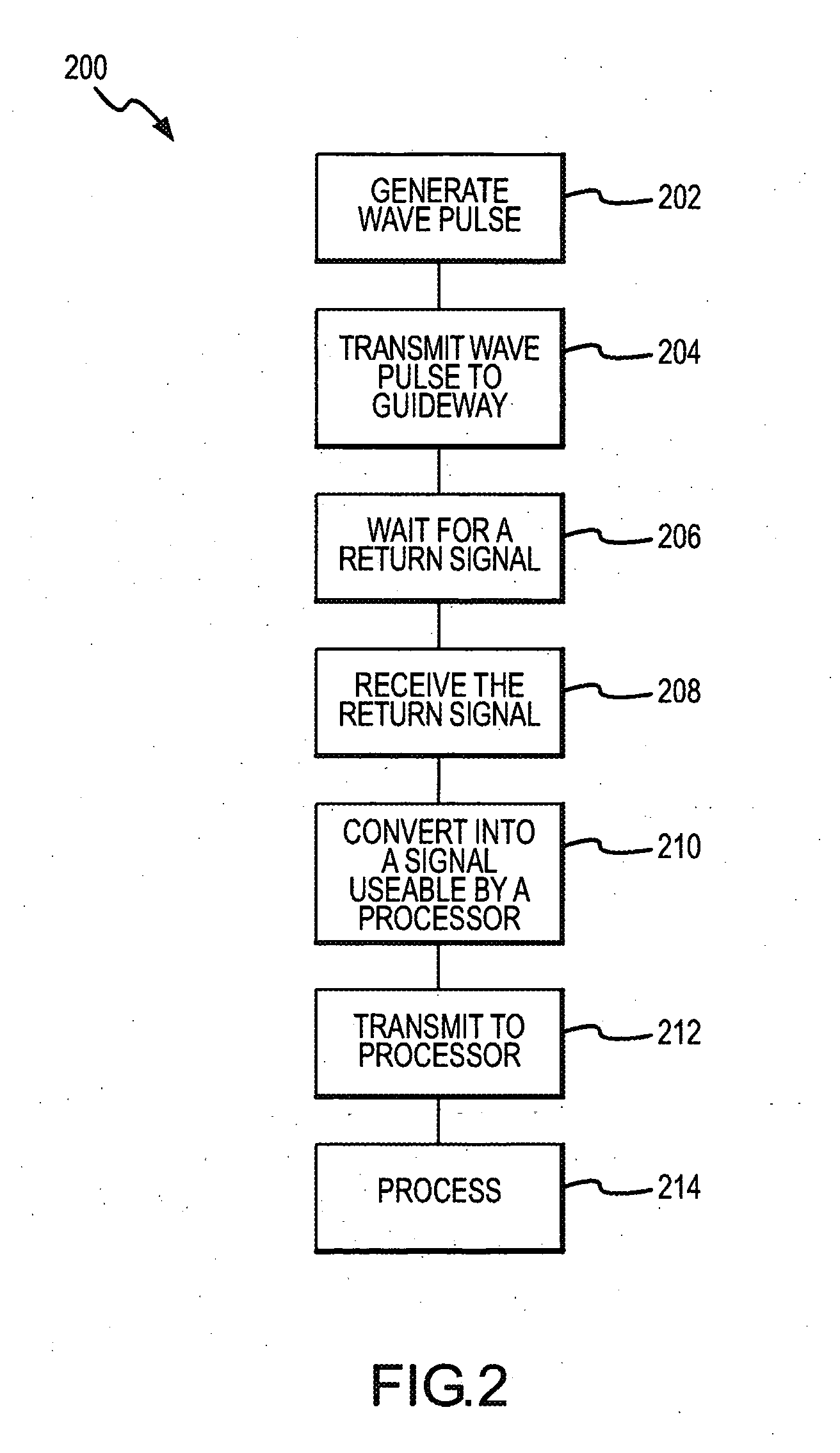
[0019] The present invention will now be described with particular reference to the figure(s). While the present invention is described with particular reference to railroads, locomotives, and the associated tracks, one of ordinary skill in the art will now recognize that the present invention could be used with any system that has a “guideway” where a signal can be transmitted along the guideway. Such guideways include, for example, rail tracks, conveyer belt systems, assembly lines, and other systems where the longitudinal members of the guideways are conductive and at least partially isolated from each other. Alternatively, non-conductive guideways can be made conductive by adding conductors, such as wires or conductive rods.
[0020] The present invention describes an improved rail break detection system operating independently from the existing wayside signaling system. The invention may be used in conjunction with present signaling systems to provide specific advantages such as ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com