Method and apparatus for utility-based dynamic resource allocation in a distributed computing system
a distributed computing system and resource allocation technology, applied in the field of data processing systems, can solve the problems of dynamic and rapid variation of demand rate, fast idleness of nearly all its time, etc., and achieve the effect of optimizing the business value of the enterpris
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
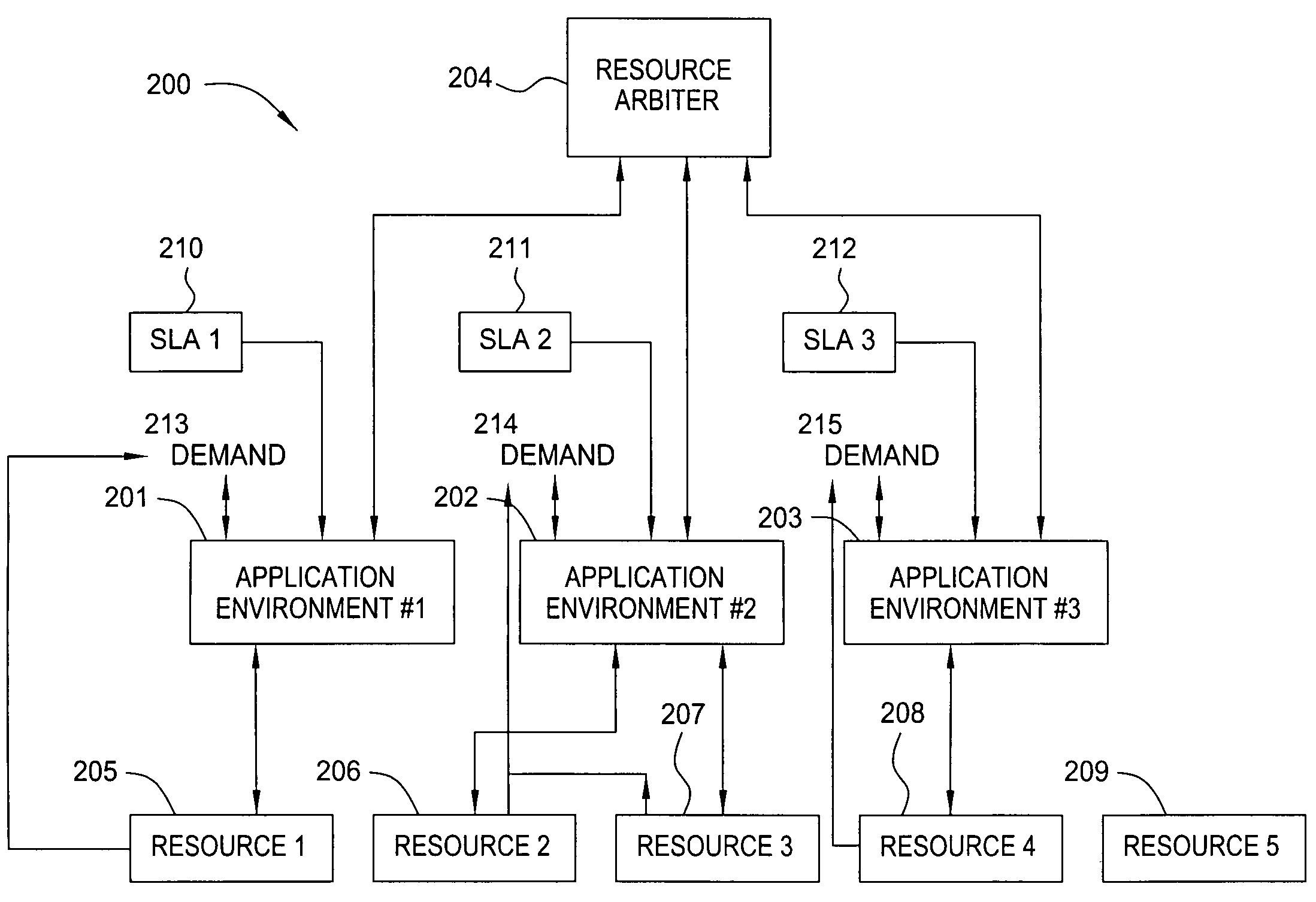
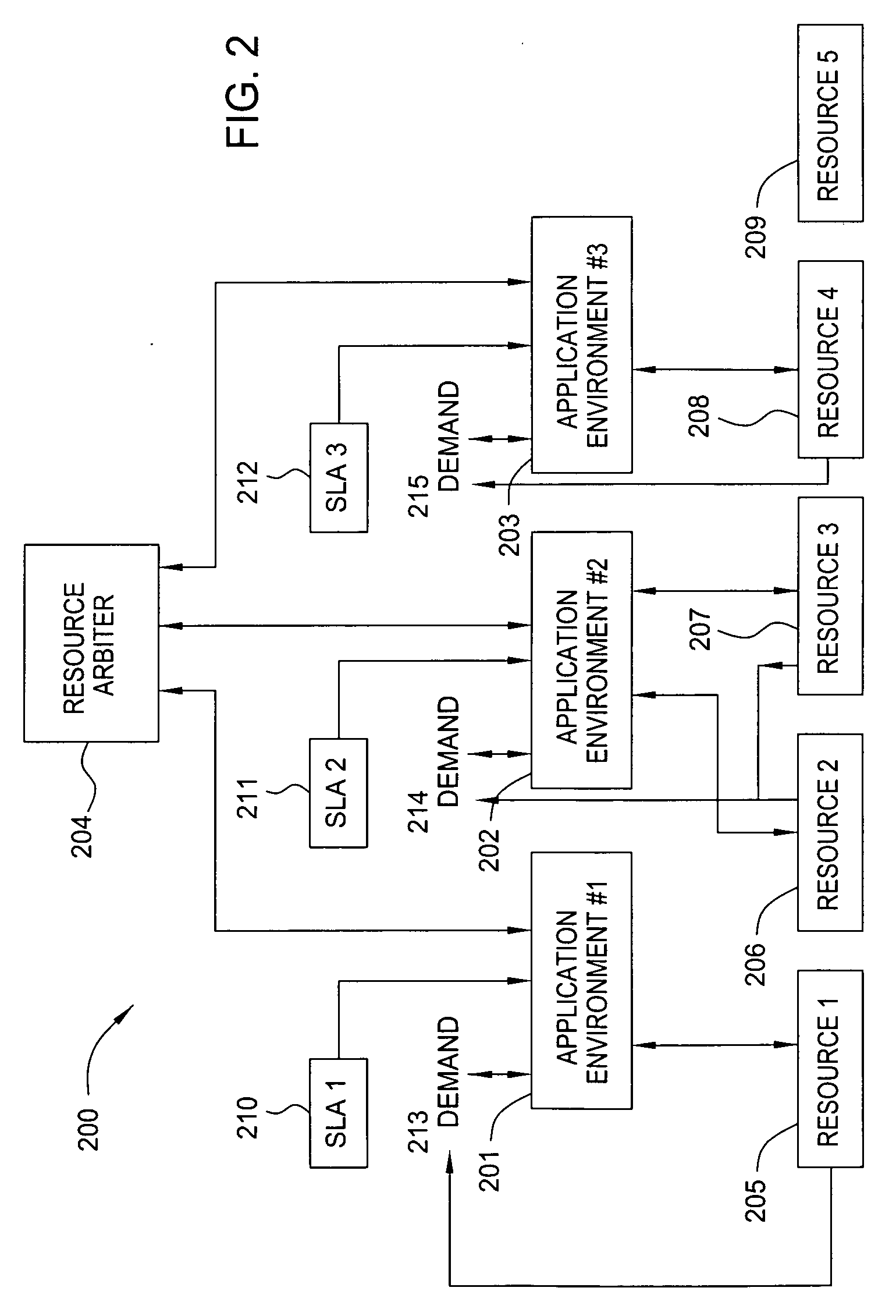
[0013] In one embodiment, the present invention is a method for optimal and automatic allocation of finite resources amongst multiple entities that can perform computational work given the resource(s). For the purposes of the present invention, the term “resource” may indicate an entire hardware or software component (e.g., a compute server, a storage device, a RAM circuit or a database server), or a portion of a component (e.g., bandwidth access or a fraction of a server). The method may be implemented, for example, within a data processing system such as a network, a server, or a client computer. The invention is capable of making allocation decisions in real time, according to time-varying need or value of the resources by each of the entities, thereby resolving the shortcomings associated with typical static resource allocation techniques. In addition, the method is structured to optimize the business value of an enterprise that provides computing services to multiple entities u...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com