Variable speed drive for oblique feeding drums
a variable speed drive and feeding drum technology, applied in the field of variable speed drive for oblique feeding drums, can solve the problems of increasing the increasing the power requirement of the drive, and increasing the wear of the cutting knife and the braking arrangement of the header, so as to achieve the effect of constant rotational speed of the mower and the intake drive assembly
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
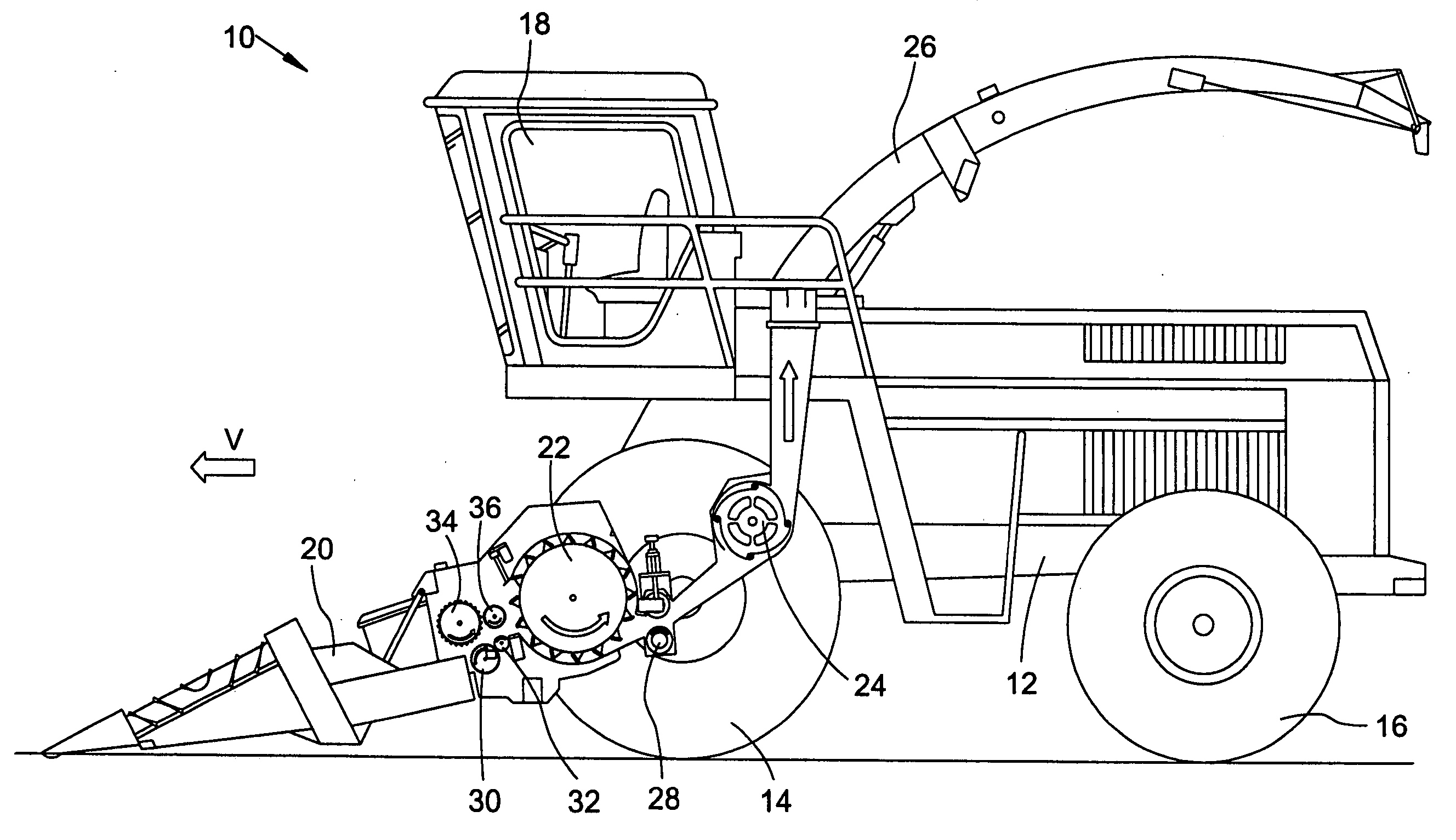
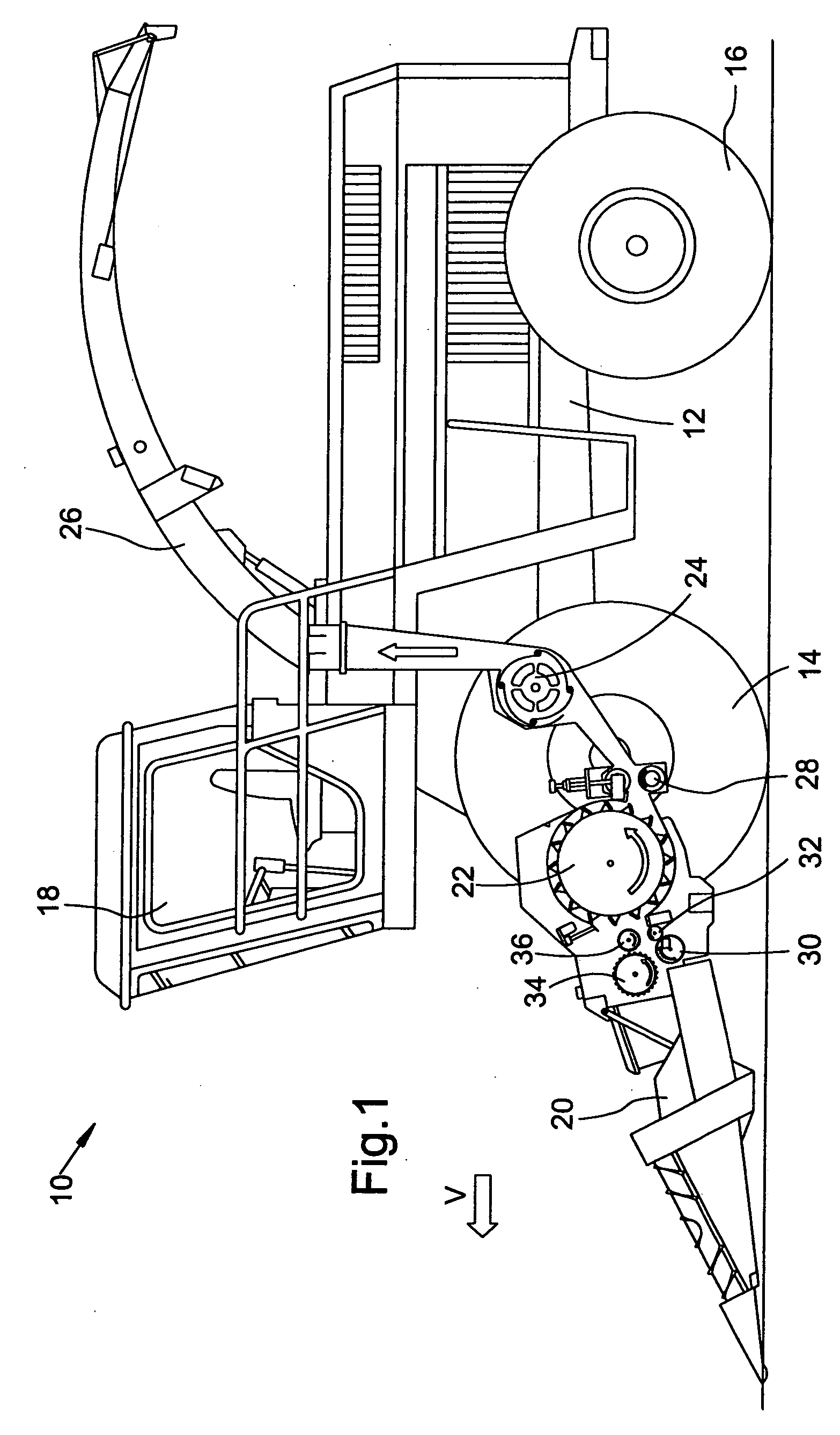
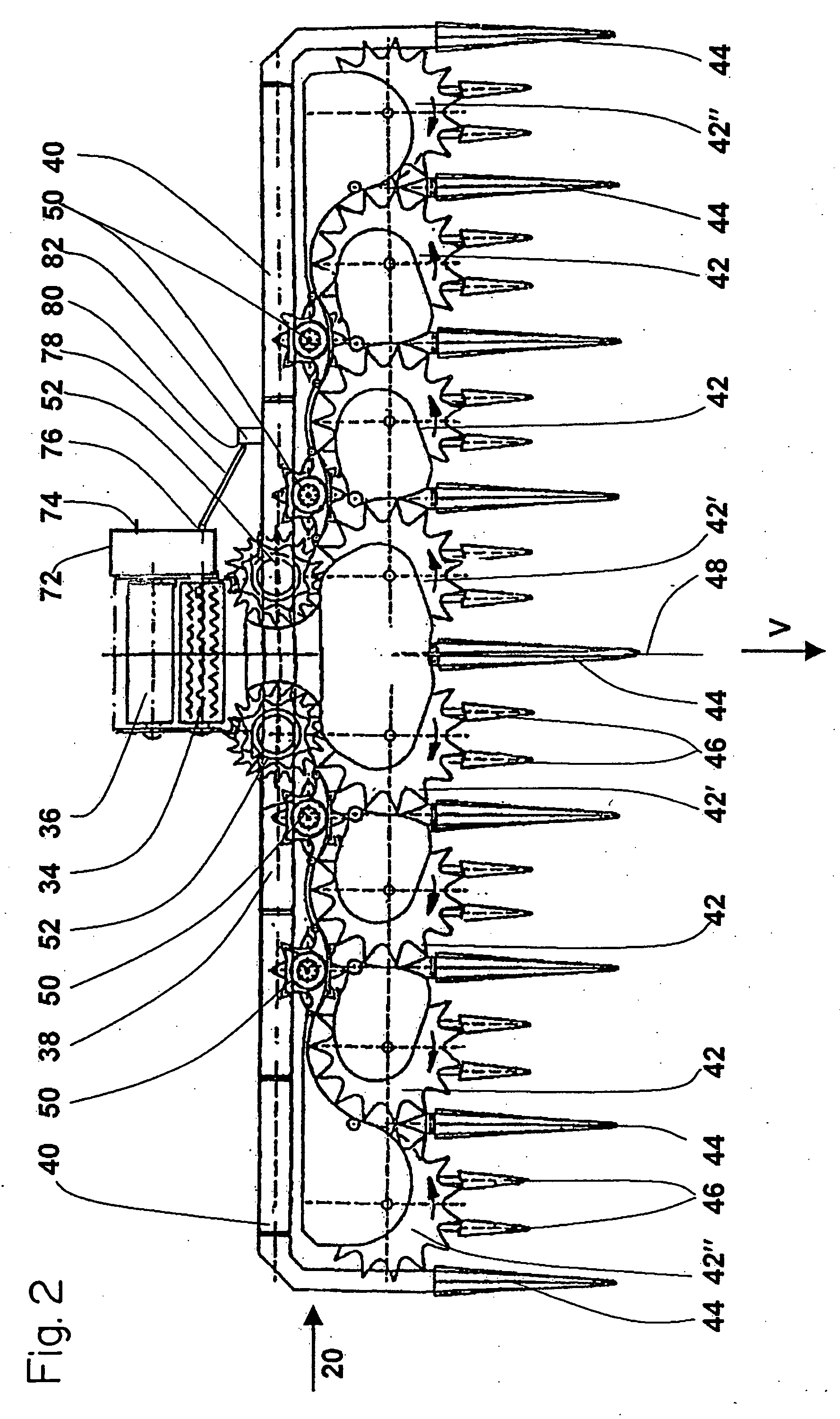
[0018] A self-propelled forage harvester 10, as shown in FIG. 1, is supported on a frame 12 that is carried by driven front wheels and steerable rear wheels 14 and 16. The forage harvester 10 is controlled from an operator's cab 18 from which a header 20 for mowing crops to be harvested can be viewed. Crop taken up from the ground by means of the header 20, for example, corn, grass or the like is conducted to a chopper drum 22 by lower rough pressing rolls 30, 32 and upper rough pressing rolls 34, 36 arranged in an intake channel of the harvesting machine 10. The chopper drum 22 chops the crop into small pieces and delivers it to a conveyor arrangement 24. As a rule, the upper rough pressing rolls 34, 36 are arranged so that they can move relative to the lower intake rolls 30,32 and are forced against the latter by spring force. The crop leaves the harvesting machine 10 to an accompanying trailer over a duct 26 mounted for being selectively rotated about an upright axis. A post chop...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com