Stairway construction
a technology for stairs and stairs, applied in the field of stairs, can solve the problems of using lower-cost materials and methods, and achieve the effect of reducing costs and cos
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
Introduction
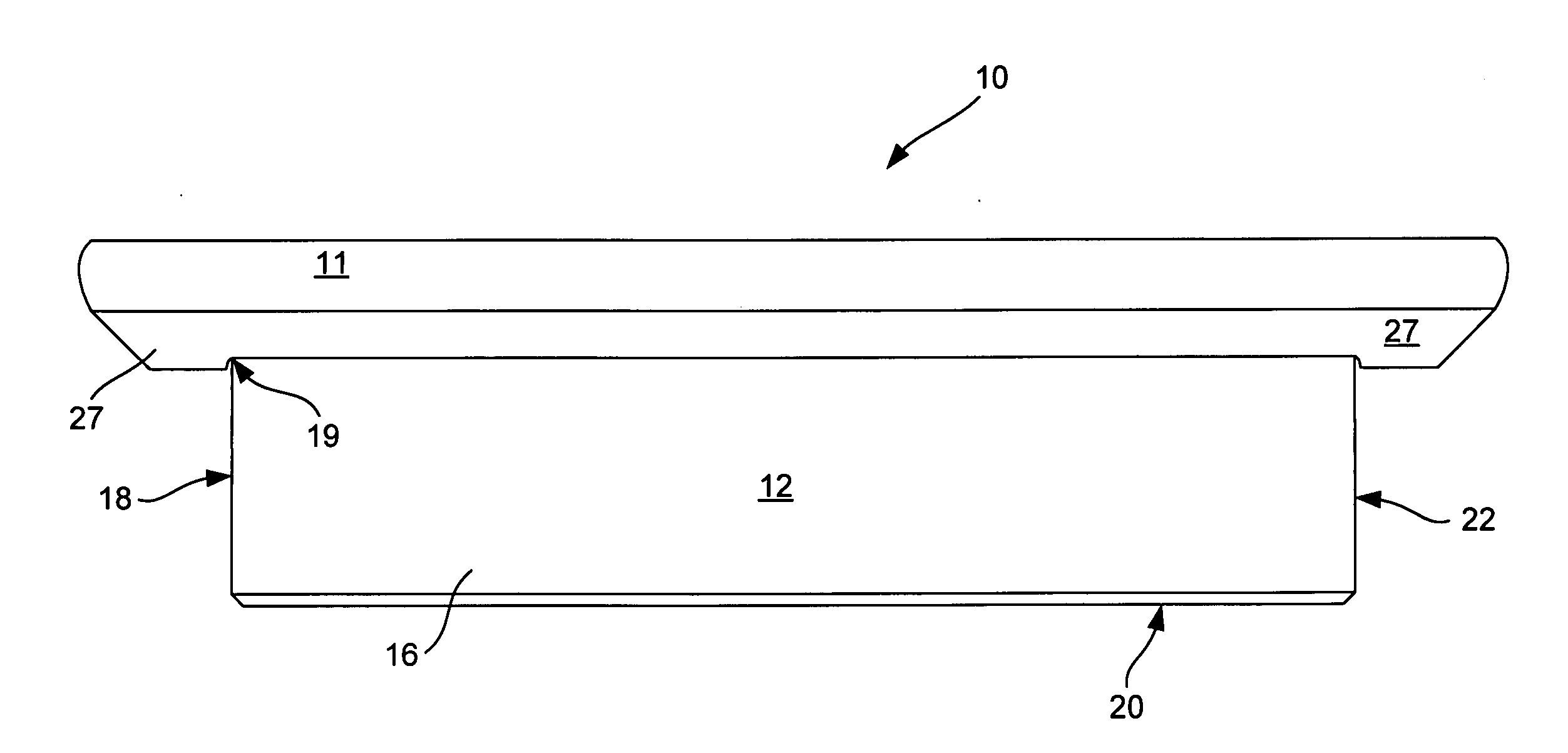
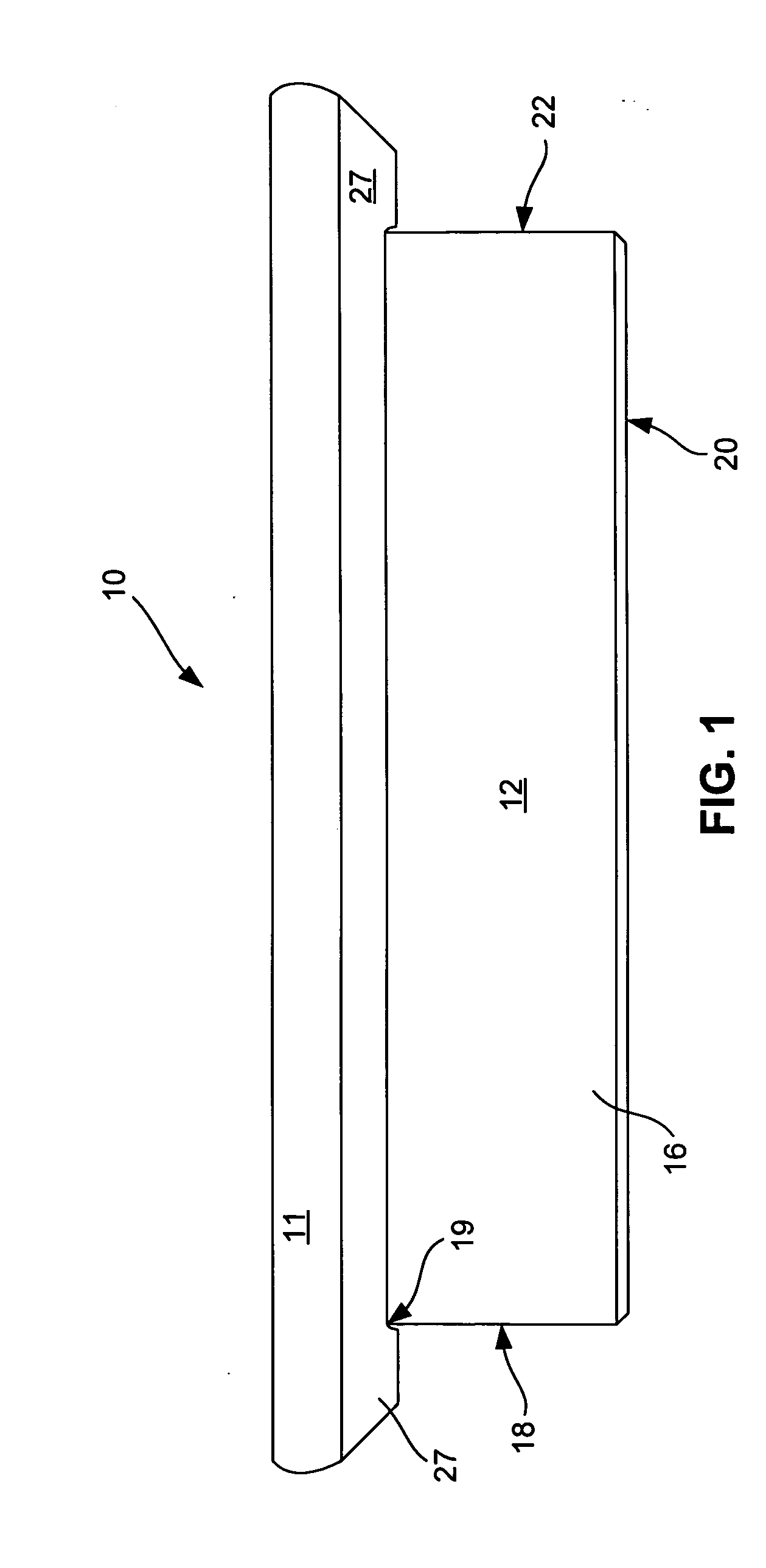
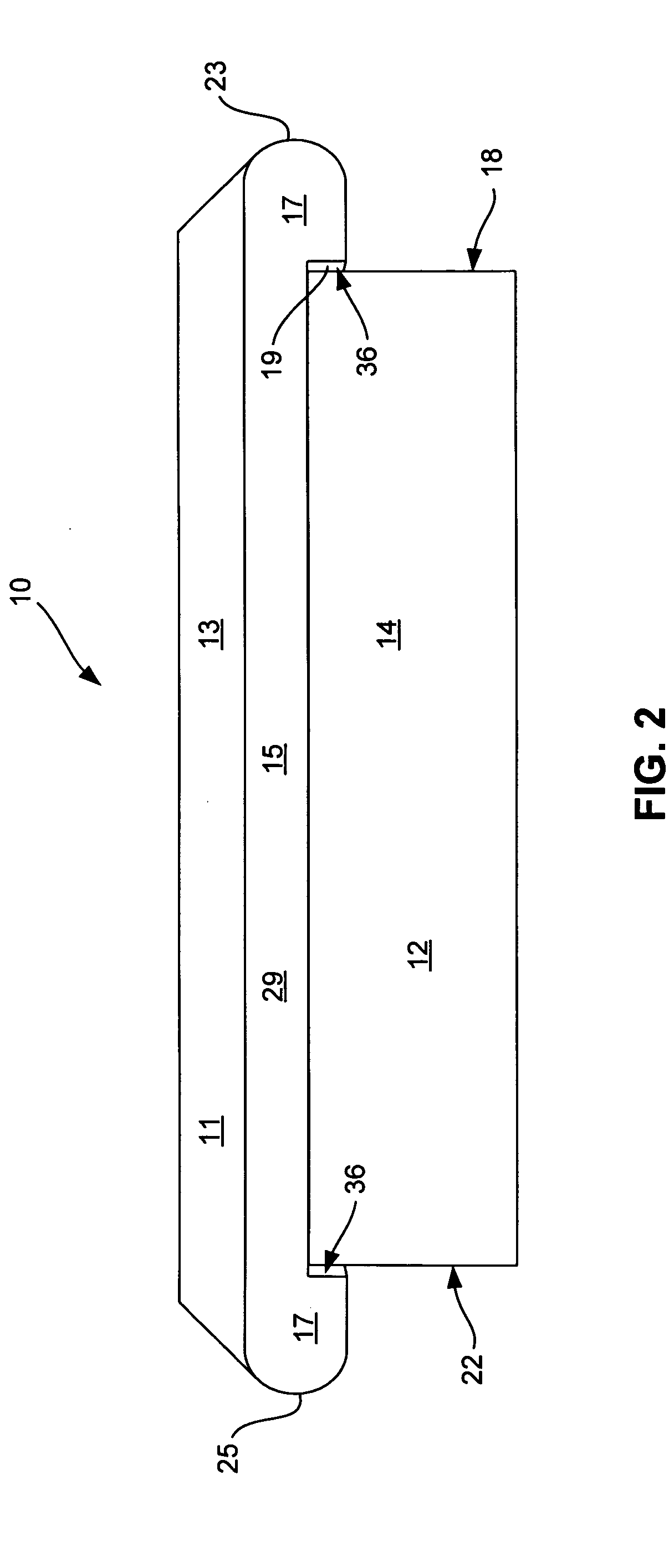
[0022] In the conventional approach to building a stairway, the layout shown in the prior art view of FIG. 7 is utilized. Each of the parts of the conventional stairway is called out by name. This conventional mode of construction utilizes a pair of stringers, each of which is an elongated plank of wood with a series of offset Z-shaped surfaces, each Z-shape is one horizontal surface and one vertical surface. These stringers are generally each attached to a respective rectangular piece of 1×12 inch wood designated “plate”, the pair of plates being spaced apart a finite distance approximately equal to the width of the stairway to be constructed. This is the framework for the stairway. In a high-end installation, individual treads used horizontally and individual risers used vertically are then installed in a conventional manner as by nailing or high-speed stapling.
[0023] As is known in the art, treads have milled forward edges and milled outer edges. Much of this millin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com