Drying apparatus
a drying apparatus and drying technology, applied in the field of drying apparatuses, can solve the problems of miniaturizing such a drying apparatus, shortening the time required to dry clothes, and wasting energy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
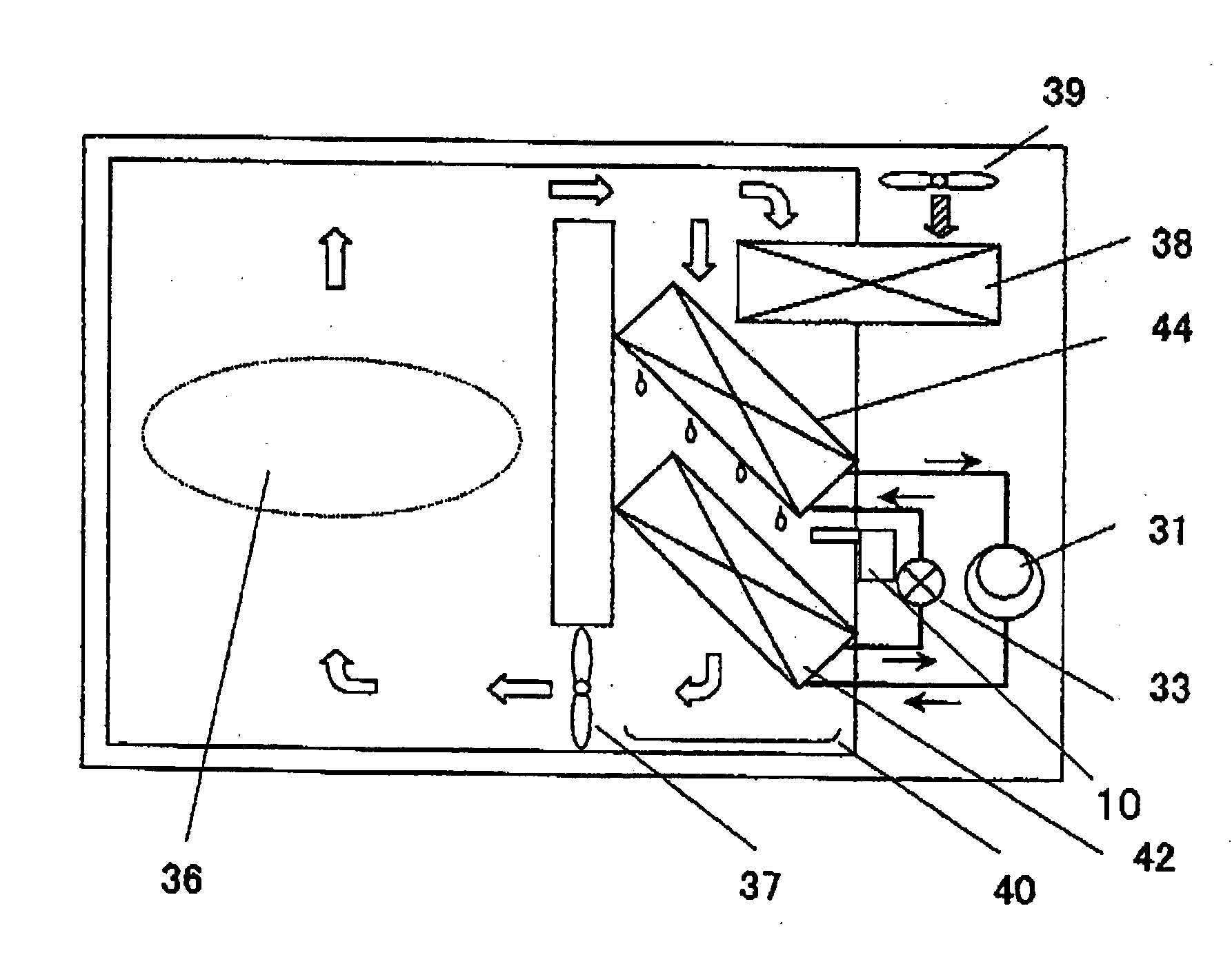
[0045]FIG. 1 is a block diagram of a drying apparatus according to a first embodiment of the present invention. Referring to FIG. 1, a reference number 31 represents a compressor, a reference number 32 represents a radiator, a reference number 33 represents an expansion valve (expansion mechanism), and a reference number 34 represents an evaporator. A heat pump apparatus is constructed by connecting these constituent elements to one another in this order through pipes and charging a refrigerant thereinto. As the refrigerant, a refrigerant which can be brought into the supercritical state on the radiation side (from a discharge section of the compressor 31, to the radiator 32 and to an inset section of the expansion mechanism 33) such as a CO2 refrigerant is charged thereinto. A reference number 36 represents a subject to be dried (for example, clothes, a bathroom space, or the like), a reference number 37 represents a blower fan, a reference number 38 represents a heat exchanger for...
second embodiment
[0055] Hereinafter, a second embodiment of the present invention will now be described with reference to the drawings.
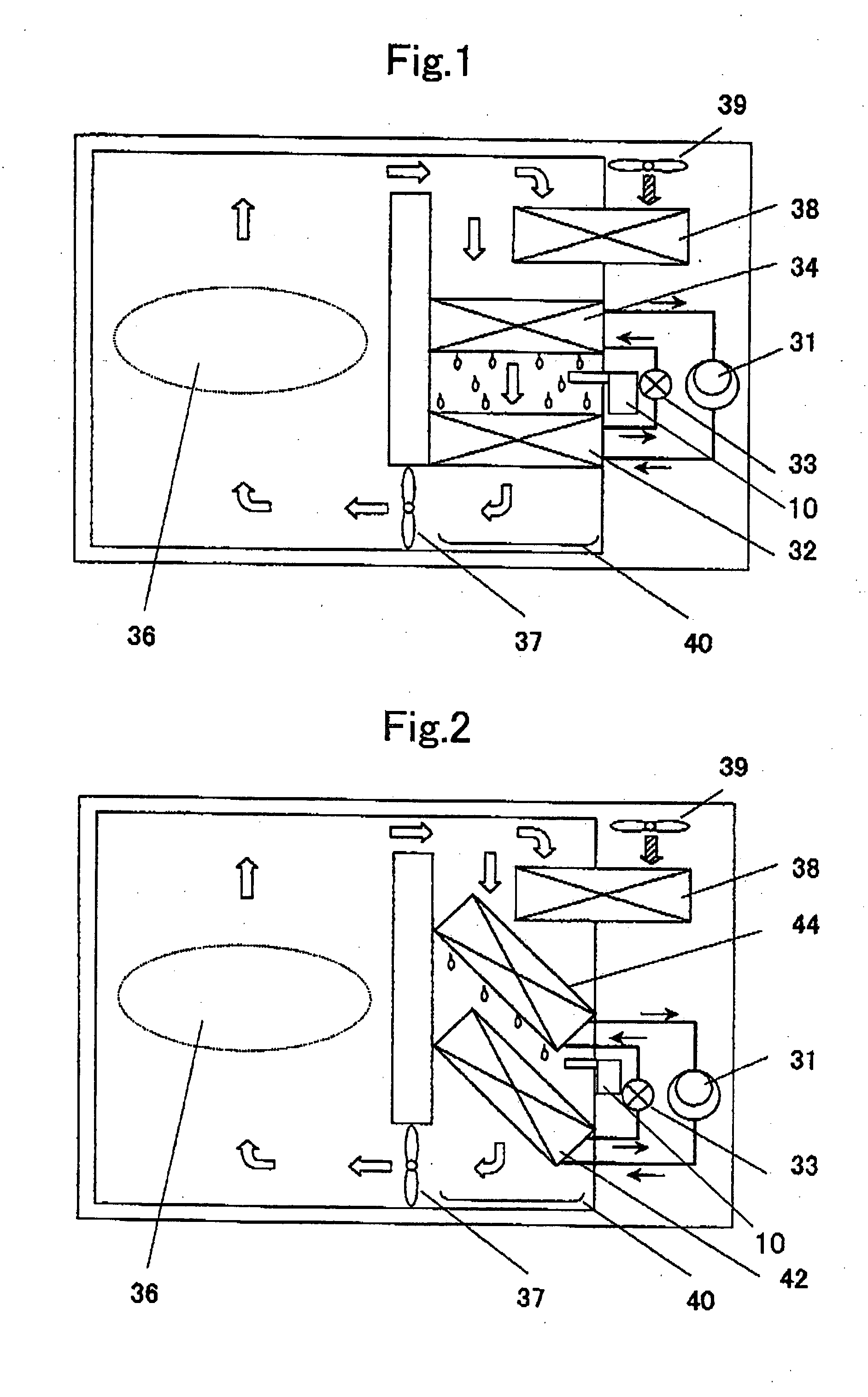
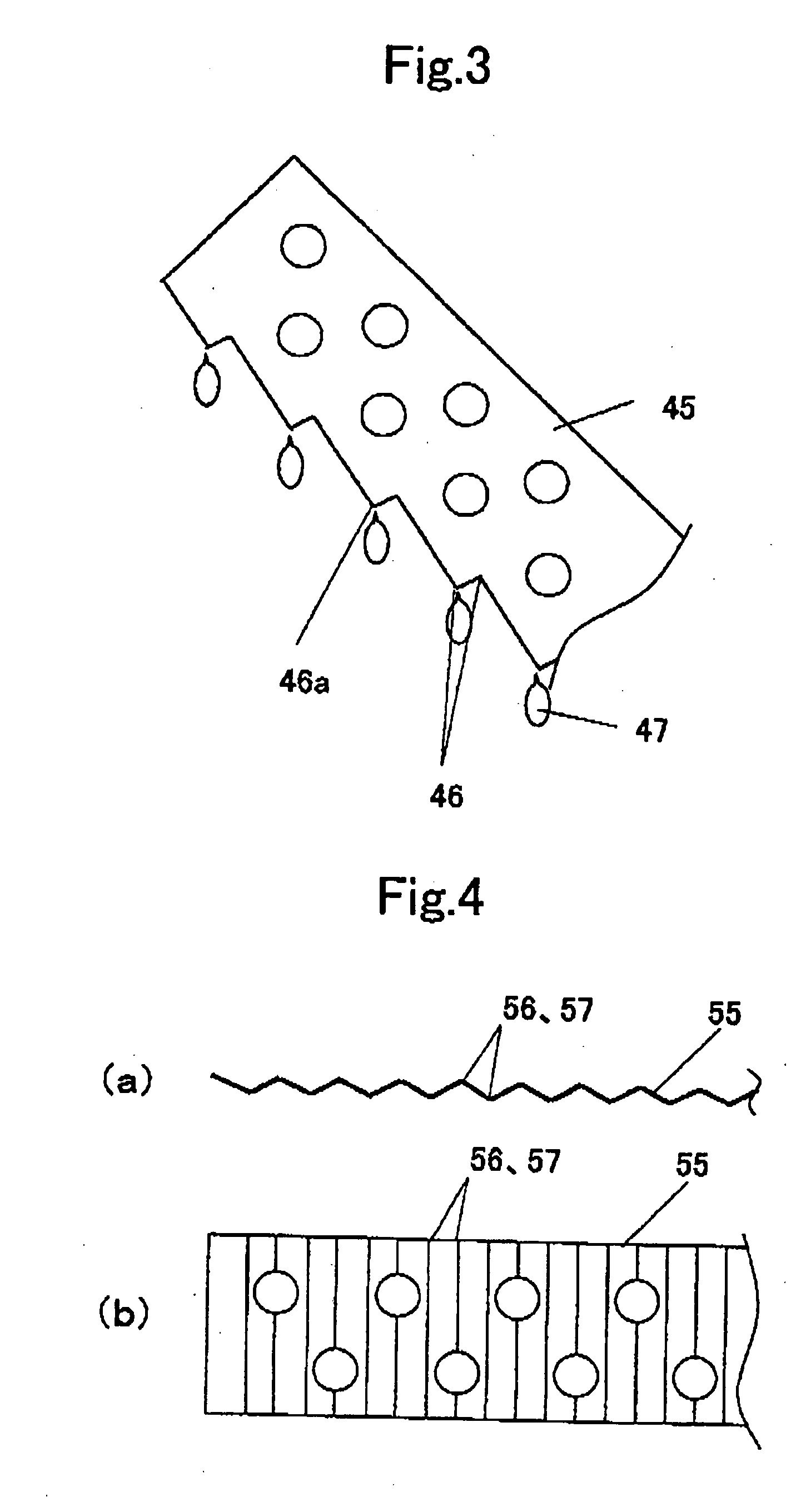
[0056]FIG. 2 is a block diagram of a drying apparatus according to a second embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 3 is an enlarged view of a main portion of a fin constituting an evaporator according to the second embodiment of the present invention. In FIG. 2, common constituent elements shown in FIG. 1 are designated with the same reference numbers, and explanation thereof will be omitted. A reference number 31 represents a compressor, a reference number 42 represents a radiator, a reference number 33 represents an expansion valve (expansion mechanism), and a reference number 44 represents an evaporator. A heat pump apparatus is constructed by connecting these constituent elements to one another in this order through pipes and charging a refrigerant thereinto. As the refrigerant, a CO2 refrigerant which can be brought into the supercritical state on the radiat...
third embodiment
[0063] Hereinafter, a third embodiment of the present invention will now be described with reference to the drawing.
[0064]FIG. 5 is a block diagram of a drying apparatus according to a third embodiment of the present invention. In FIG. 5, common constituent elements shown in FIG. 1 are designated with the same reference numbers, and explanation thereof will be omitted. A reference number 31 represents a compressor, a reference number 62 represents a radiator, a reference number 33 represents an expansion valve (expansion mechanism), and a reference number 64 represents an evaporator. A heat pump apparatus is constructed by connecting these constituent elements to one another in this order through pipes and charging a refrigerant thereinto. As the refrigerant, a CO2 refrigerant which can be brought into the supercritical state on the radiation side is charged thereinto. Difference between the first and third embodiments is a point that drain water condensed and generated by dehumidi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com