Stand, in particular for surgical microscopes, having an energy storage element
a technology of energy storage element and stand, which is applied in the field of stand, can solve the problems of insufficient working range of conventional gas springs and present bracing effect, and achieve the effect of reducing the disadvantageous cosine effect of horizontal support and removing the disadvantageous effect of horizontal suppor
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
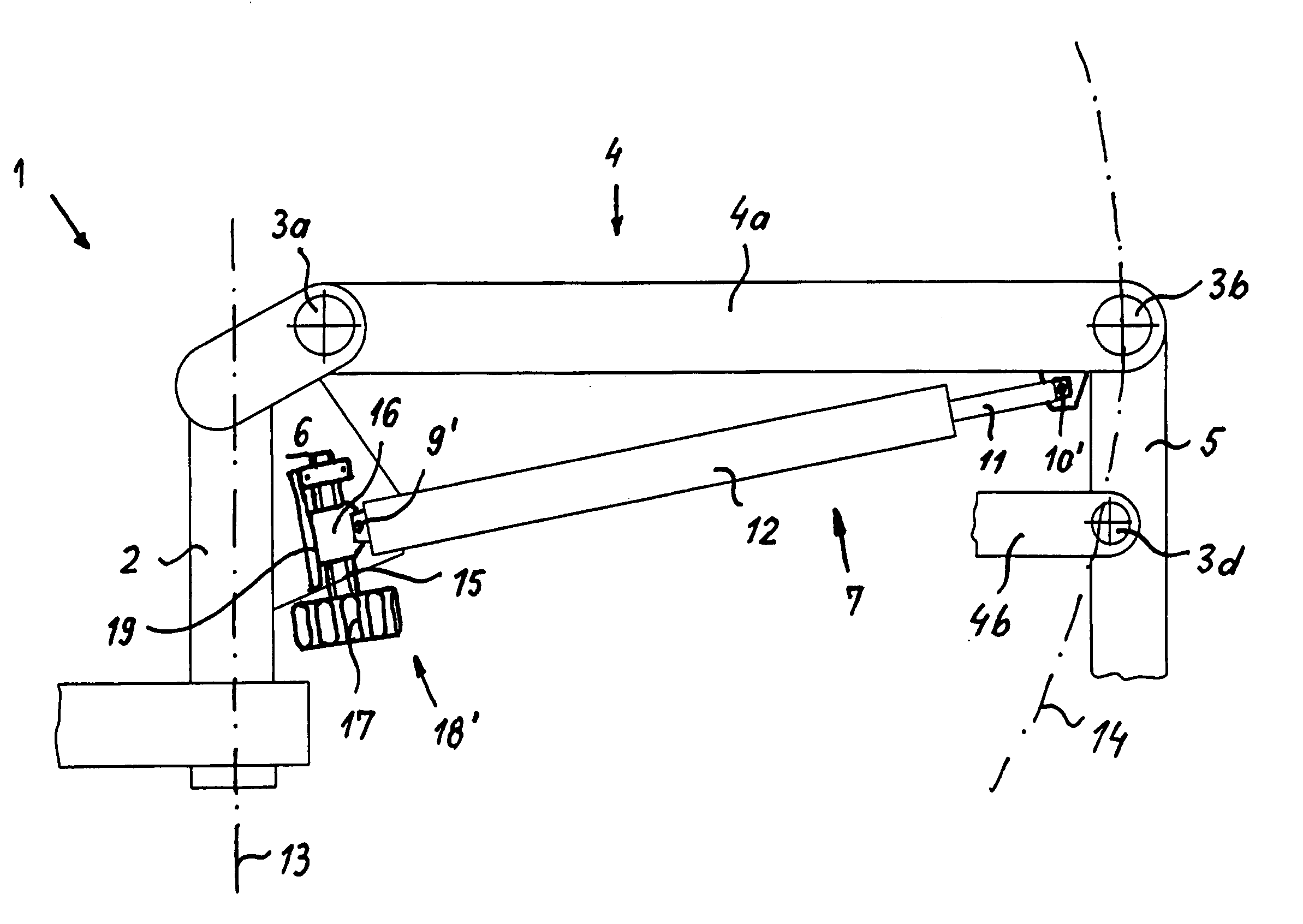
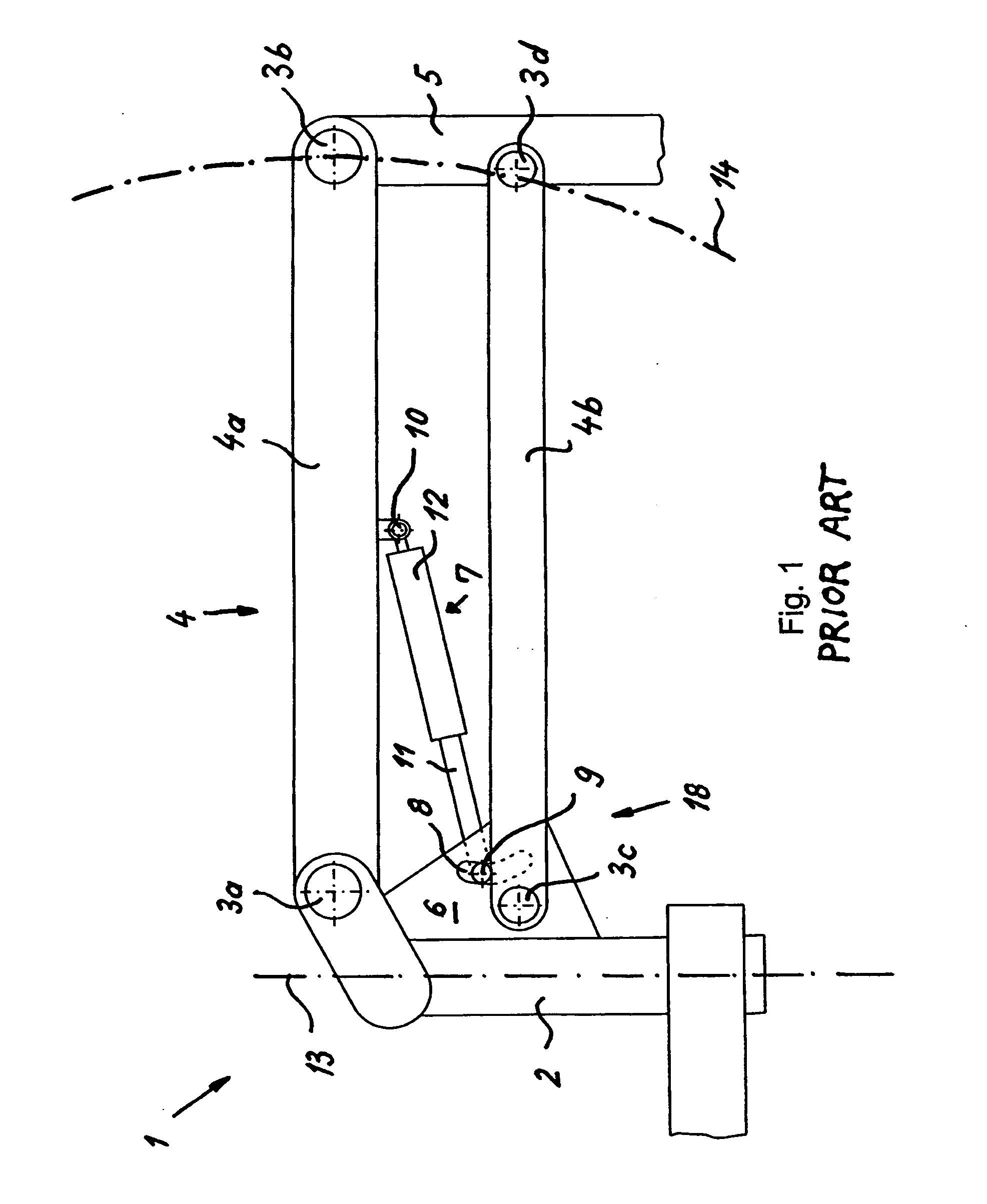
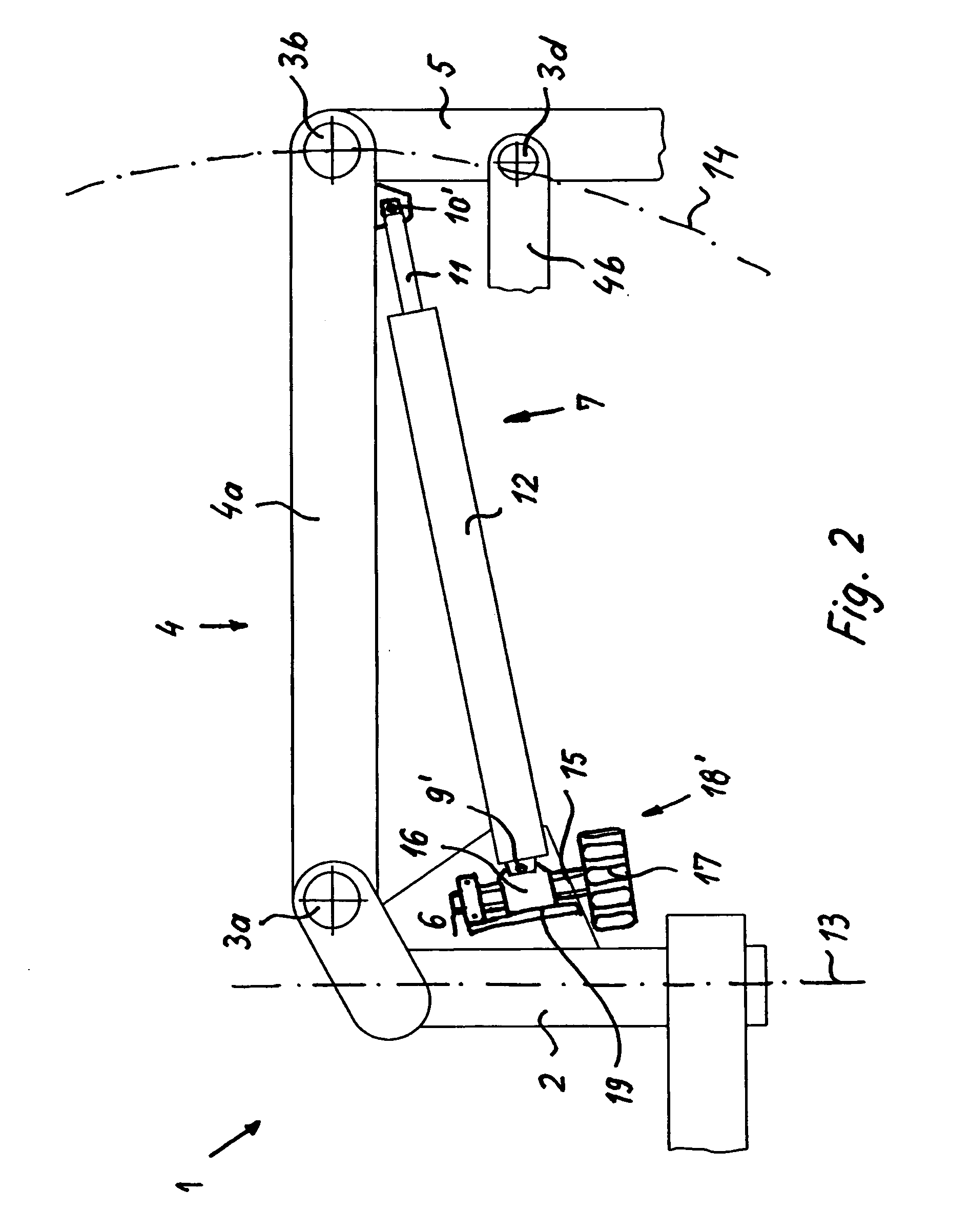
[0025]FIG. 1 schematically depicts a stand arrangement 1 according to the existing art. Stand 1 comprises a vertical support 2 and a horizontal support 4 that is implemented as a parallelogram support having an upper horizontal support arm 4a and a lower horizontal support arm 4b. A gas spring is arranged, as a supporting energy storage element 7, at an articulation point 10 on upper horizontal support arm 4a of horizontal support 4 and at an articulation point 9 in a plate 6. Stand 1 has, as a means for positively influencing hysteresis properties, a displacement apparatus 18 that does not act linearly but instead permits, by way of an arc-shaped elongated guide hole 8, a radial displacement of articulation point 9.
[0026] Gas spring 7 is arranged with a cylinder 12 at distal articulation point 10 and with a piston rod 11 at articulation point 9.
[0027] This stand arrangement furthermore comprises joints 3a-d and a microscope carrier 5. Horizontal support 4 pivots about pivot axis ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com