End winding restraint in an electrical machine
a technology of end windings and electrical machines, applied in the field of electrical machines, can solve the problems of axial displacement, elliptical deformation, loss of concentricity, etc., and achieve the effect of preventing rotor imbalan
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
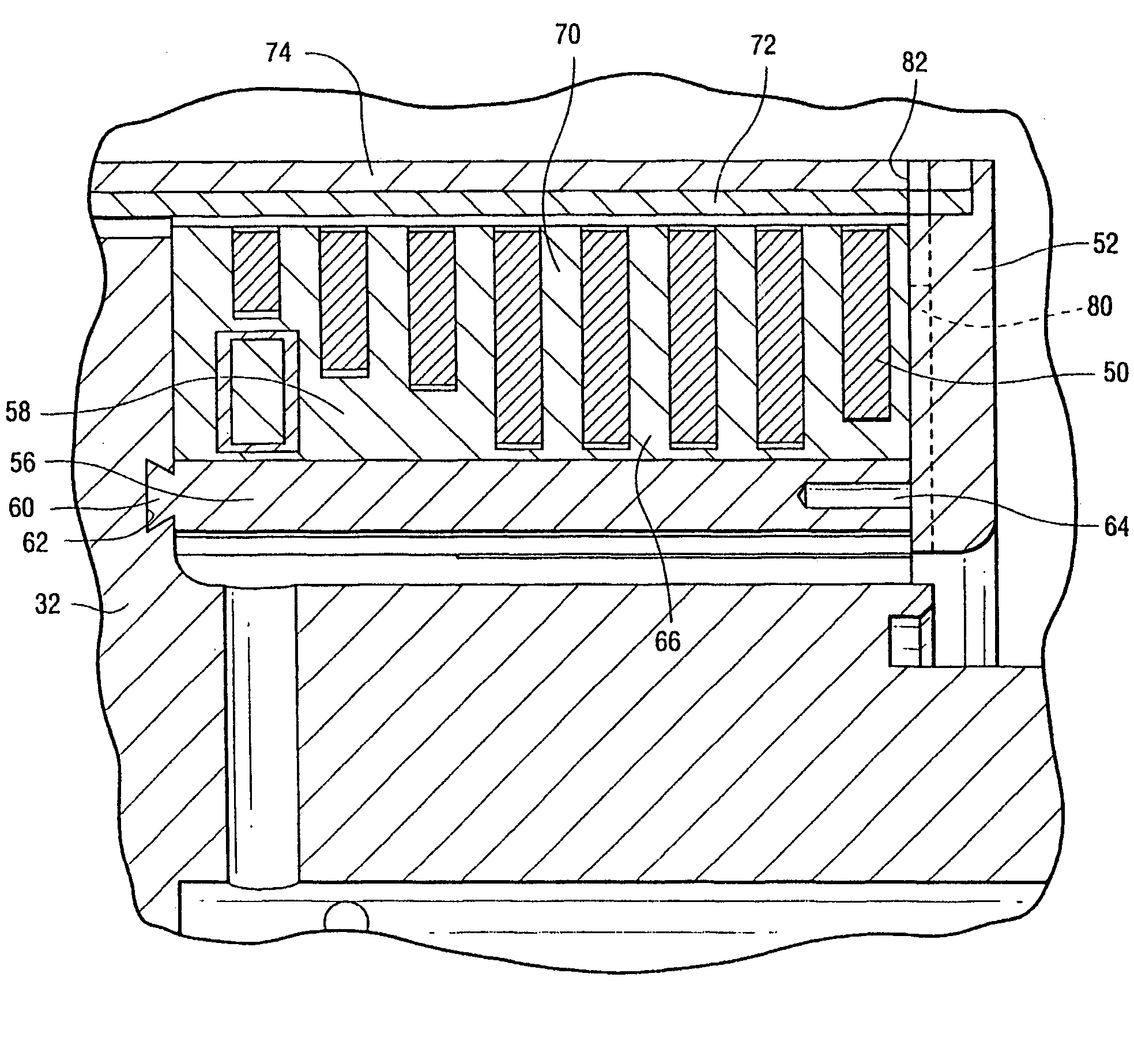
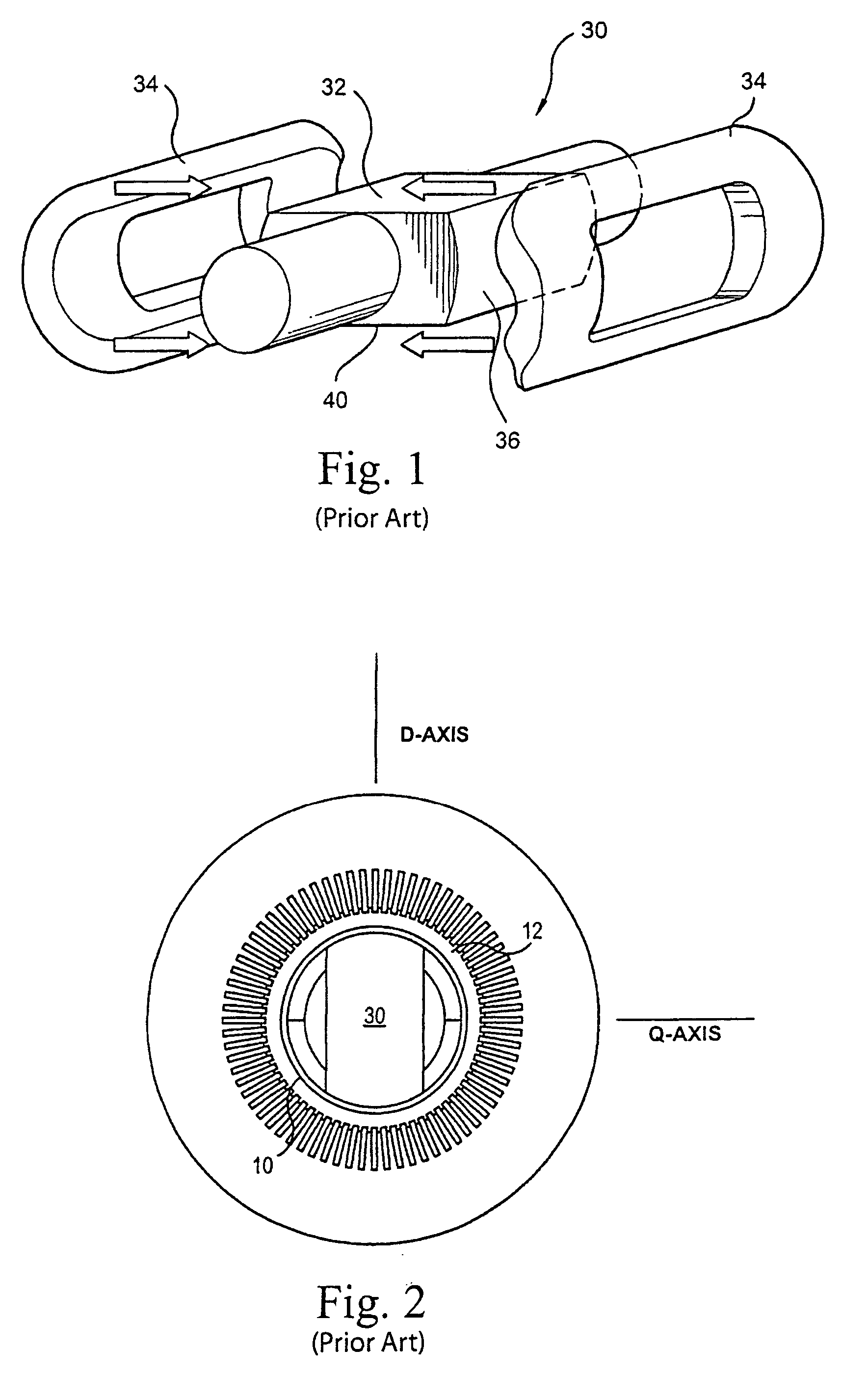
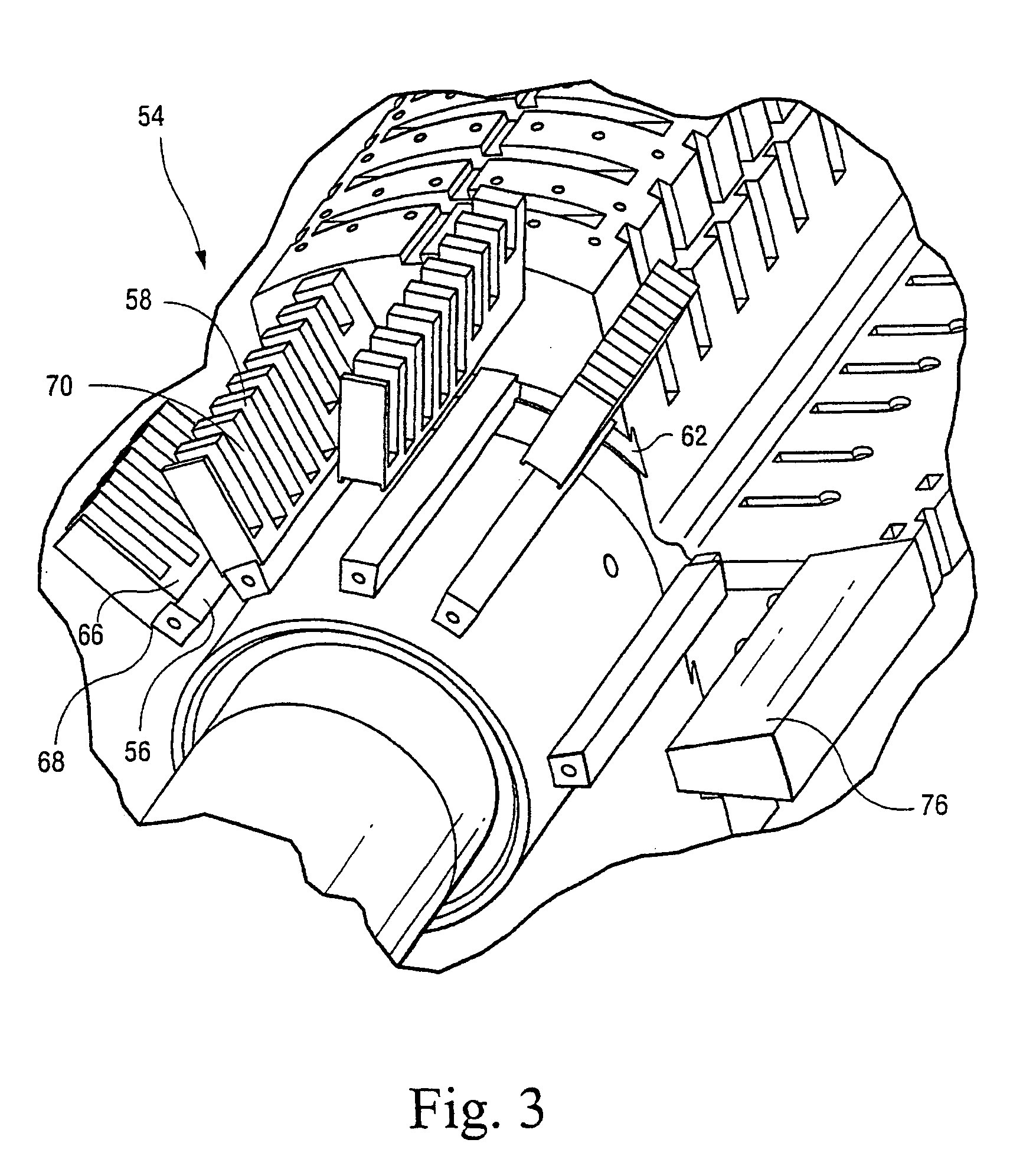
[0013] As illustrated in drawing FIGS. 1 and 2, a generator rotor 30 includes a multi-pole magnetic core 32 (a two-pole core being shown) and a plurality of prefabricated winding assemblies 34, one for each pole, and corresponding pole faces 36. The construction and materials of the magnetic core 32 and winding assemblies 34 are known. The prefabricated winding assemblies are disposed over the parallel side forging forming the rotor body 40, and are curved in an arc generally concentric with the rotor body. As illustrated in FIG. 2, the rotor is disposed within a stator and an air gap 12 exists between an enclosure 10 about the rotor and the inner surface of the stator. For orientation purposes, there is illustrated in FIG. 2 a quadrature axis Q extending normal to both the axis of rotation of the rotor and the flat side surfaces. The direct axis D extends normal to the Q axis and the axis of rotation. While the present specification discloses an advanced carbon fiber rotor enclosur...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com