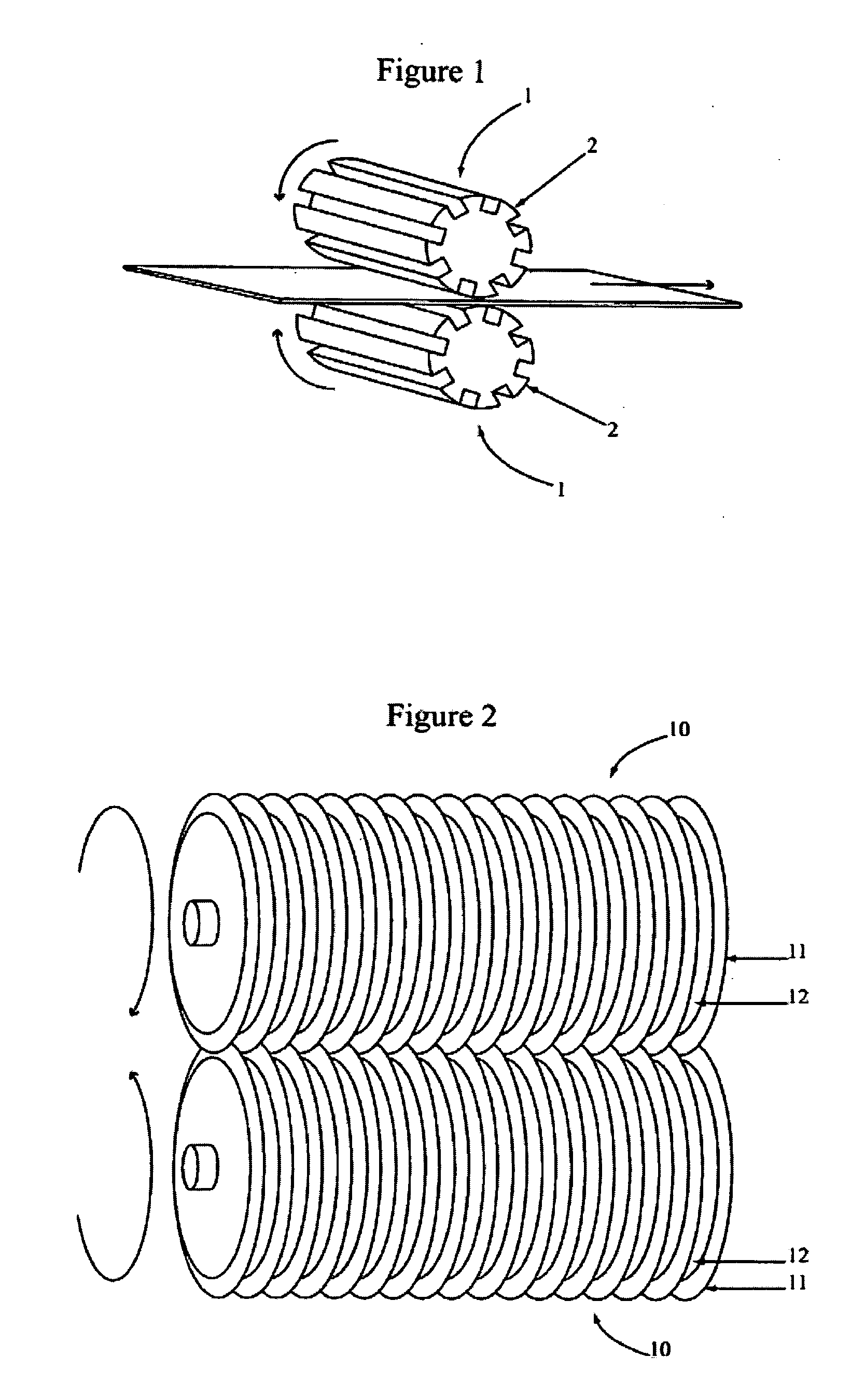
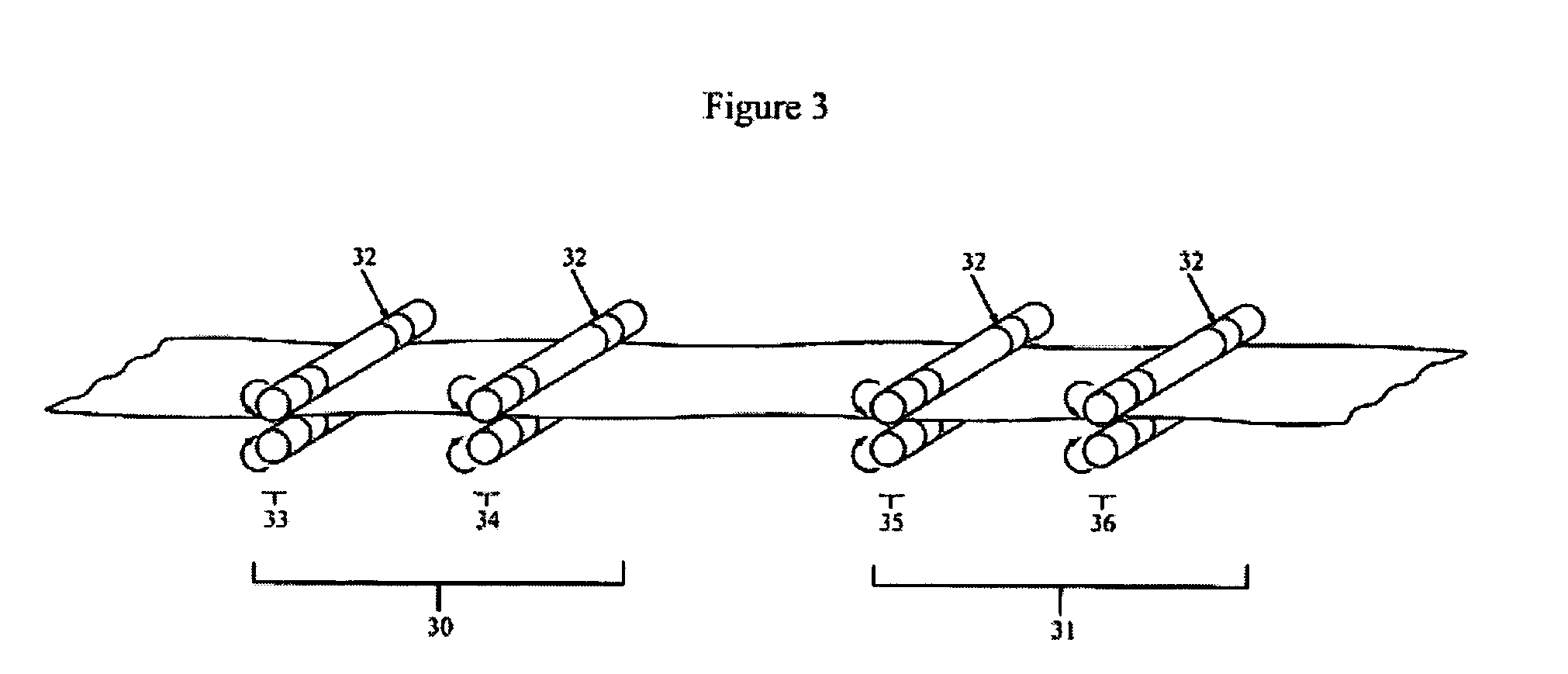
Method of producing low cost elastic web
a nonwoven web and low cost technology, applied in the field of activation of nonwoven webs, laminates, composites, can solve the problems of limited use as textiles, inelastic nature of some nonwoven webs, and use of nonwoven fabrics, and achieve the effect of superior mechanical properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
[0062] Samples of nonwoven (Sofspan® 200 supplied by BBA Nonwovens, One Lakeview Place—Suite 204, Nashville, Tenn. 37124 USA) and elastomeric formed film (Flexaire®, 40 gsm supplied by Tredegar Film Products, 1100 Boulders Parkway, Richmond, Va. 23225 USA) were vacuum bonded and activated between a pair a finned rollers produced by BIAX Fiberfilm (Biax-Fiberfilm Corporation, N992 Quality Drive, Suite B, Greenville, Wis. 54942 USA). The activation pattern as indicated in the tables refers to the depth of engagement of the teeth of the gear rollers. This is the maximum depth at which the ribs, grooves, or teeth of one activation roller penetrate between the ribs, grooves, or teeth of the opposing activation roller. For example, a 200 activation depth refers to a laminate being activated once, and to a depth of 200 mils (thousandths of an inch). A 200 / 200 pattern refers to a laminate being activated twice, to depths of 200 mils each time.
[0063] Samples with a gauge length of 2 inches ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Elongation | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com