Methods and devices for polarized NMR samples
a polarized nmr and sample technology, applied in the direction of magnetic variable regulation, reradiation, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of loss of polarisation, difficult to get reproducible, lack of sensitivity of mri and nmr spectroscopy,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
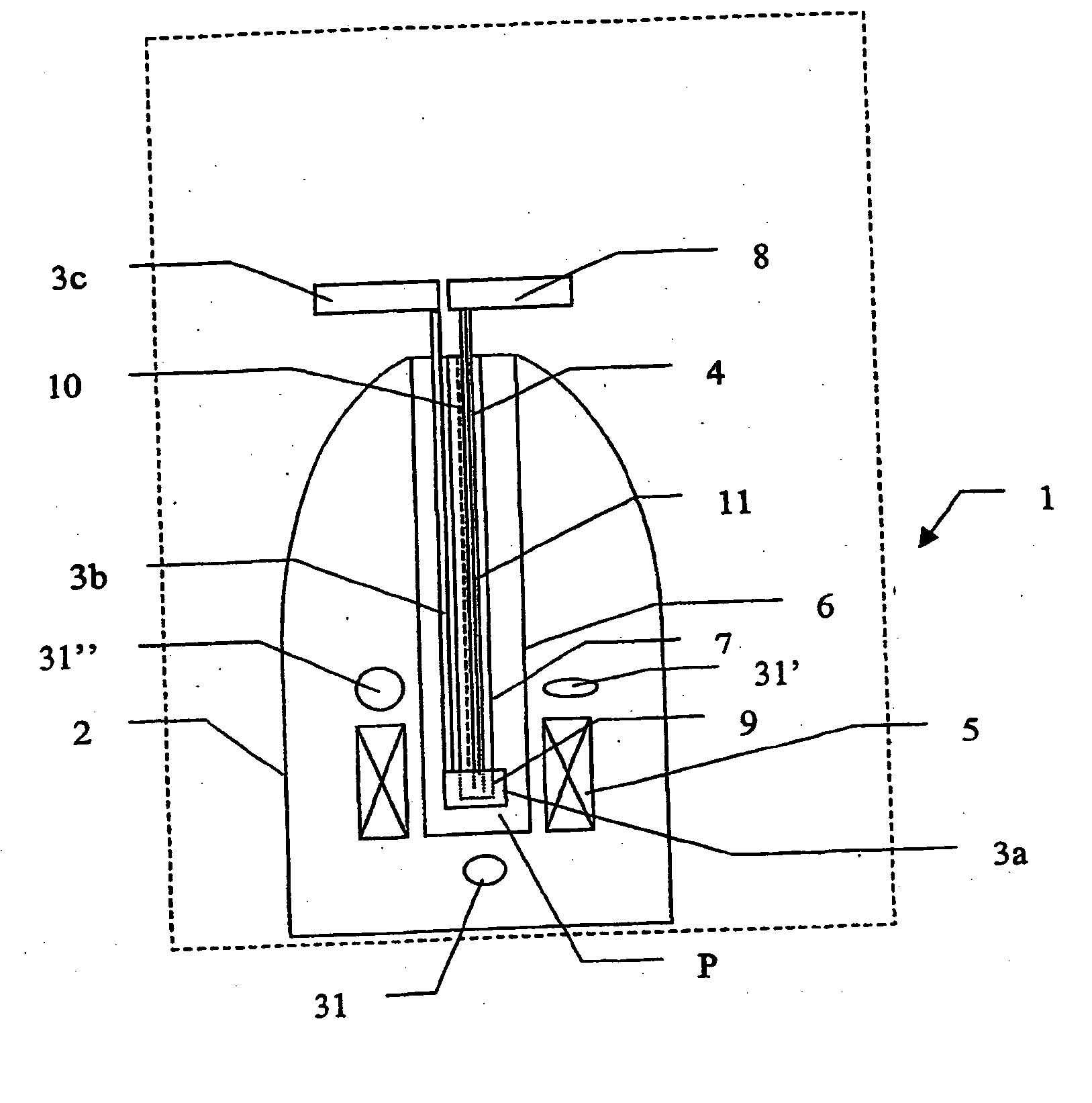
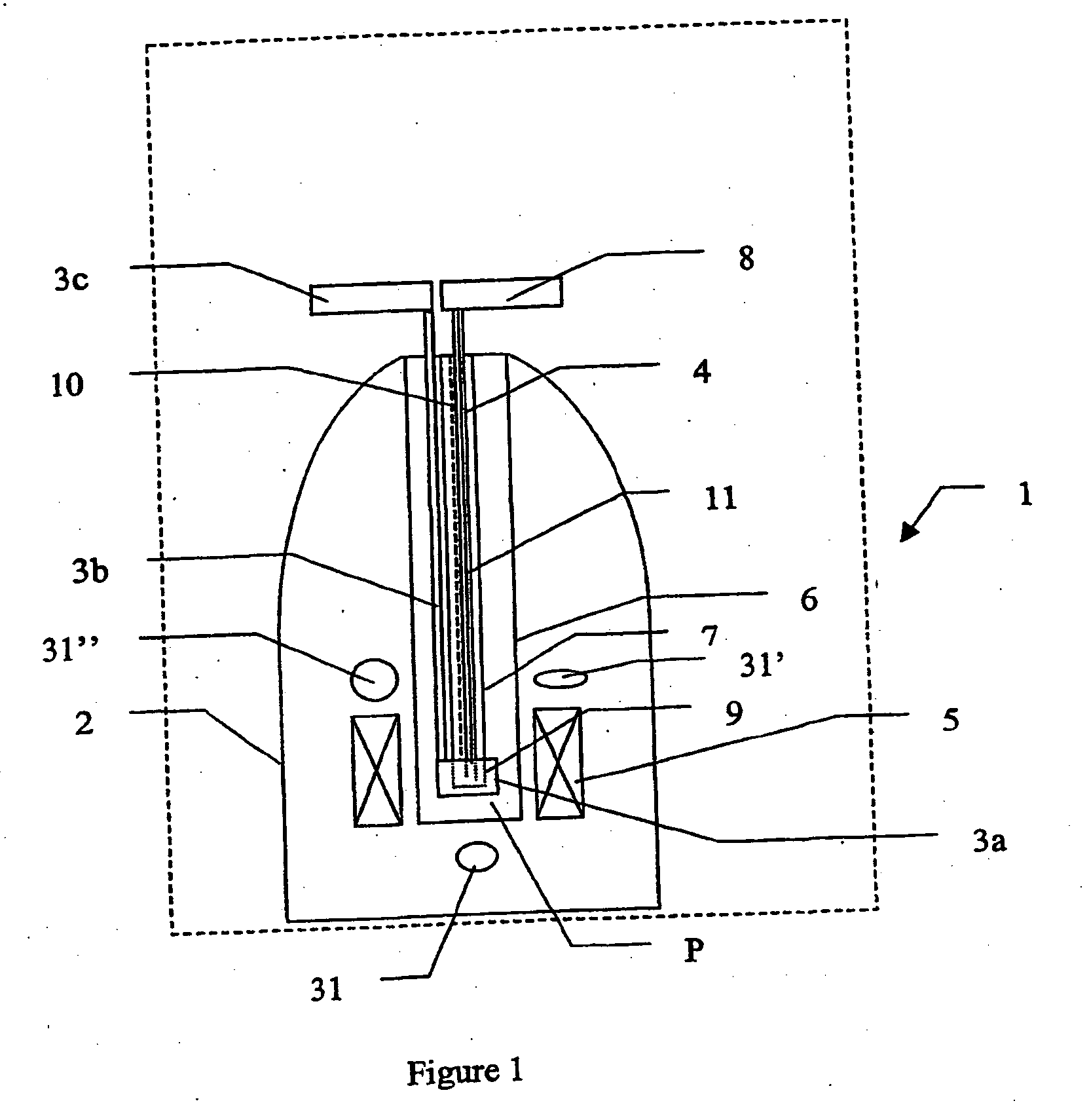
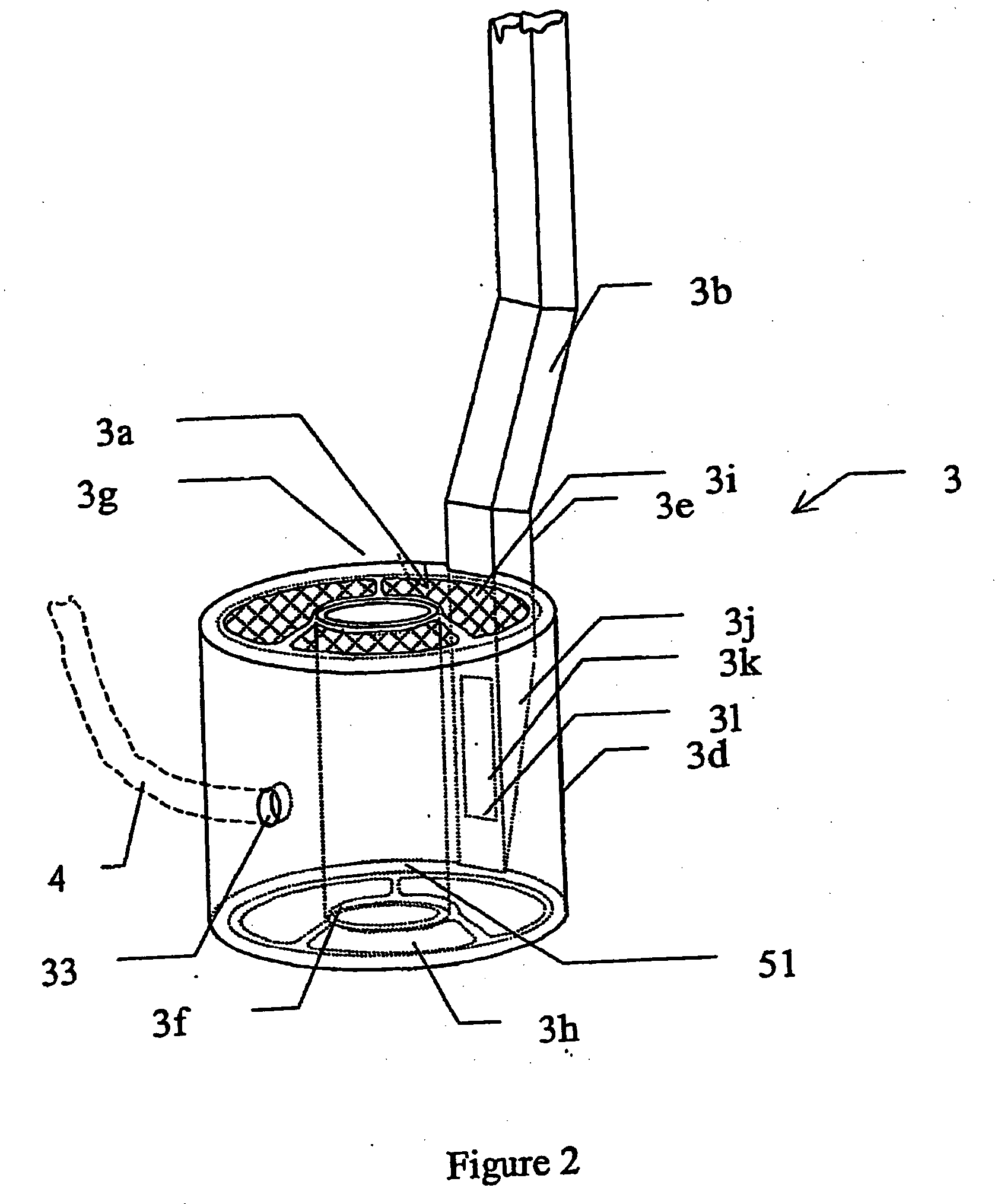
[0013] In methods and devices in accordance with the present invention, a solid sample of the sample to be polarised can be polarised while still in the solid phase by any appropriate known method, e.g. brute force polarisation, dynamic nuclear polarisation or the spin refrigerator method, while being maintained at a low temperature (e.g. under 100 K) in a strong magnetic field (e.g. 1-25 T). After the solid sample has been polarised, it is melted with a minimum loss of polarisation. In the following the expression “melting means” will be considered to mean the following: a device capable of providing sufficient energy to the solid polarised sample to melt it.
[0014] In a embodiment of the present invention the melting takes place in a combined polarisation, melting and NMR analysis device.
[0015] The advantage of the described invention is that it provides means for bringing polarised solid sample into solution with minimal loss of polarisation in a repeatable manner. This is cruci...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| magnetic field | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| magnetic field | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com