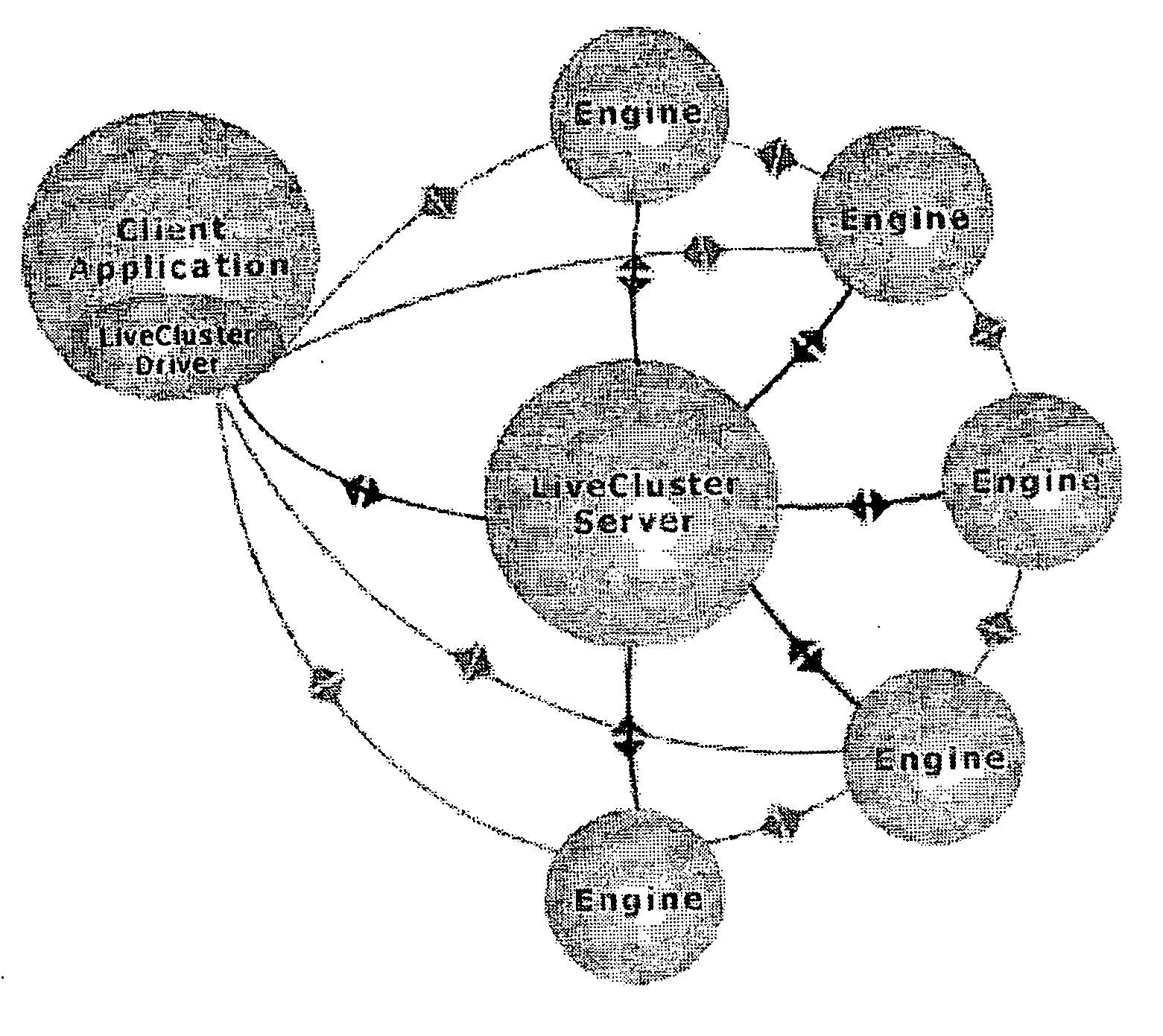
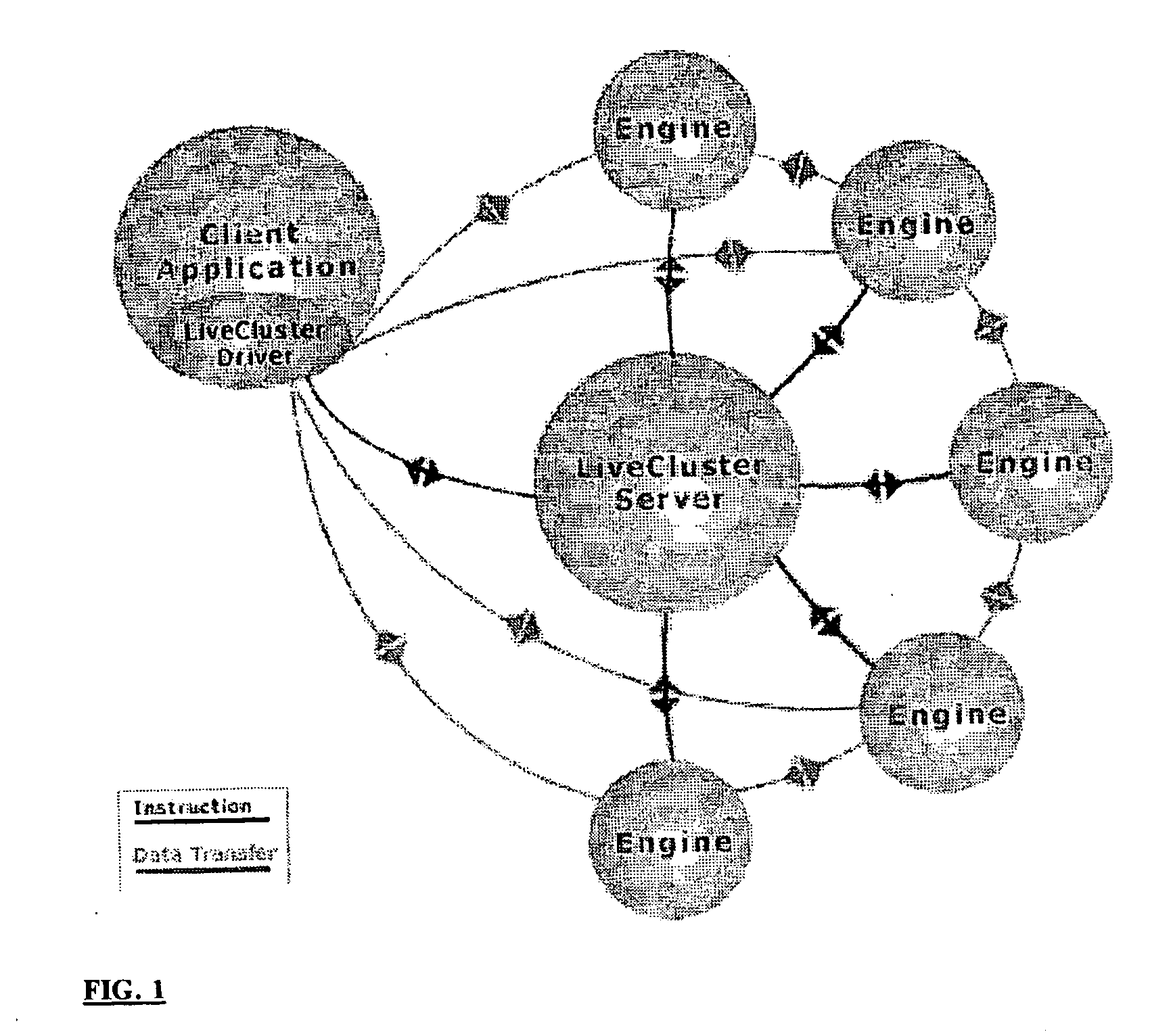
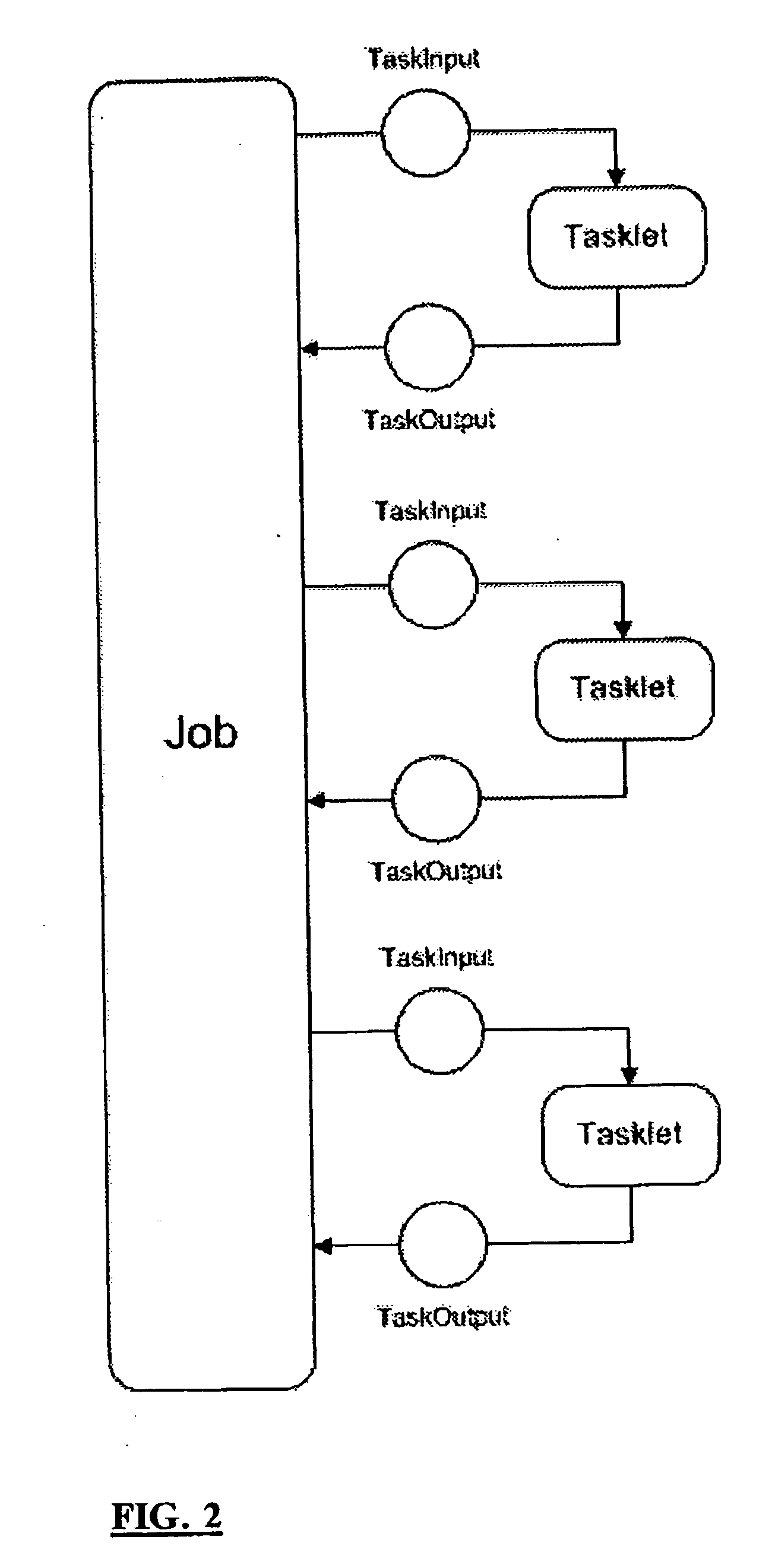
Distributed computing
a distributed computing and computing technology, applied in the field of high-performance computing, can solve the problems of low priority background jobs and restricted utilization to overnight idle periods, and achieve the effects of increasing integration and deployment, on-going savings in maintenance and administrative overhead, and enormous savings
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0263] Discriminators may be attached to Tasks or Jobs to ensure that they are assigned to Engines that are equipped with specific resources. Common examples include: Tasks that must run under a particular operating system or subset of operating systems; Tasks that must have at least a specified minimum of memory or disk space to run; Tasks that must run on a specific subset of Engines because of administrative or security restrictions, possibly including database or file system access restrictions; etc. Discriminators may also be used to impose analogous restrictions in order to optimize performance. For example, they may restrict very long-running Tasks to run only on processors meeting minimum performance requirements or on dedicated (as opposed to interruptible) Engines.
example 2
[0264] Scoring Discriminators may be used in connection with distributed caching to maximize reuse of distributed resources, such as objects or data. In this case, the Engines maintain a local cache, and update their associated property list whenever entries are added or removed from the cache. The Scoring Discriminator associated with each Task returns a score for each Engine based on the overlap between the resources that are available in the Engine's local cache and the resources specifically required by the Task.
[0265] The simplest examples of this kind are those in which each Task requires a single object, for example, each Task within a portfolio pricing application might look for a single deal or subportfolio. In this case, the Scoring Discriminator might return 1 in case the relevant deal or subportfolio is present in the cache, and 0 otherwise. A slightly more complex example would be one in which the Scoring Discriminator examines the Engine property list for multiple key...
example 3
[0266] Engine Discriminators may be used to dedicate some number, N, of Engines to a specific Job. This is accomplished by having the first N Tasks within the Job install an Engine Discriminator that imposes two requirements: (1) The Job Id must match the Job Id for the given Task, and (2) the Task Id must be greater than N.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com