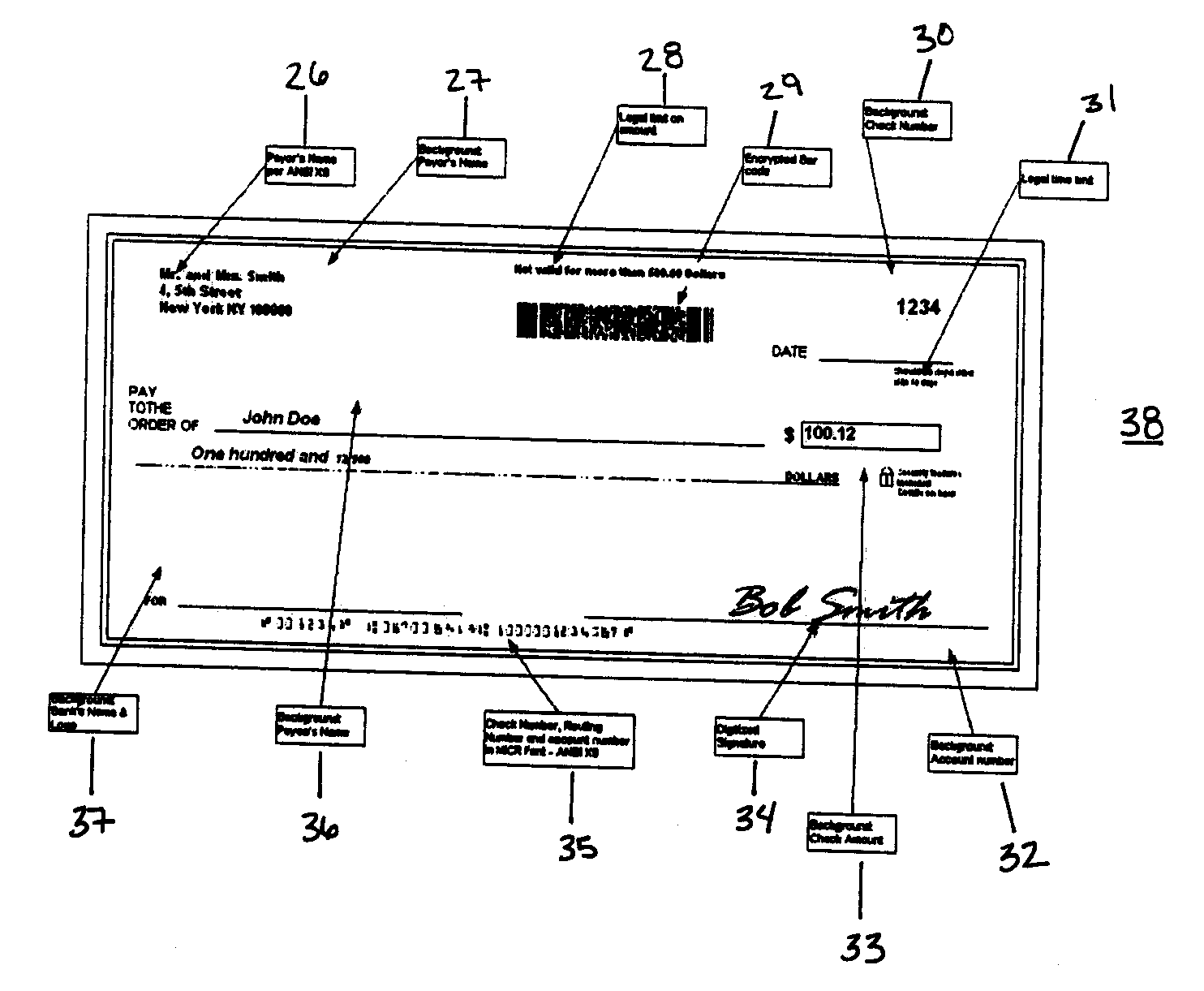
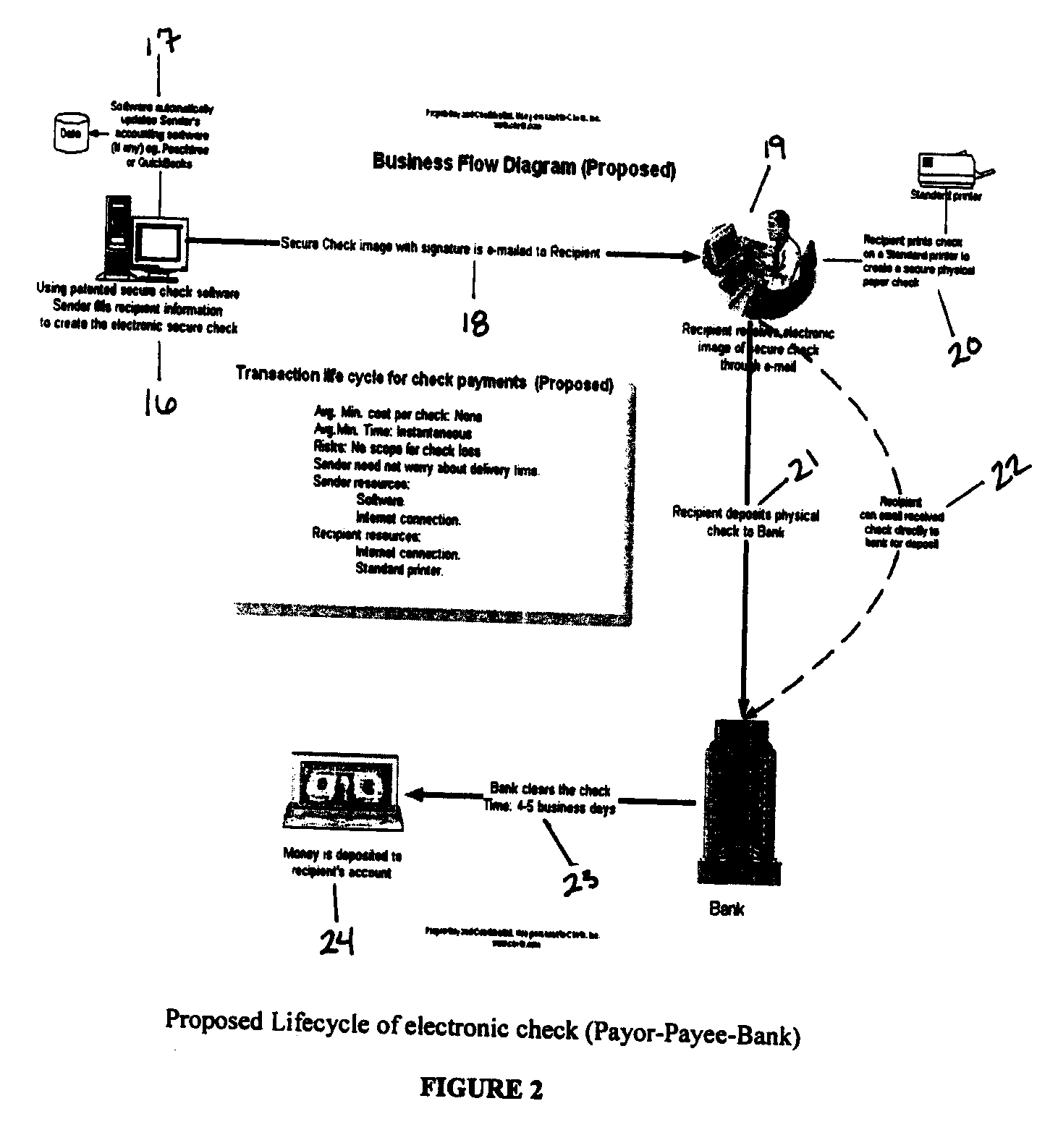
Electronic Check
a technology of electronic check and electronic signature, applied in the field of electronic signature, can solve the problems of third-party entities that not only route electronic transaction data, gateways, and charge additional fees for their involvement, and the sensitive information disclosed by the payee could be used fraudulently by an unauthorized party
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
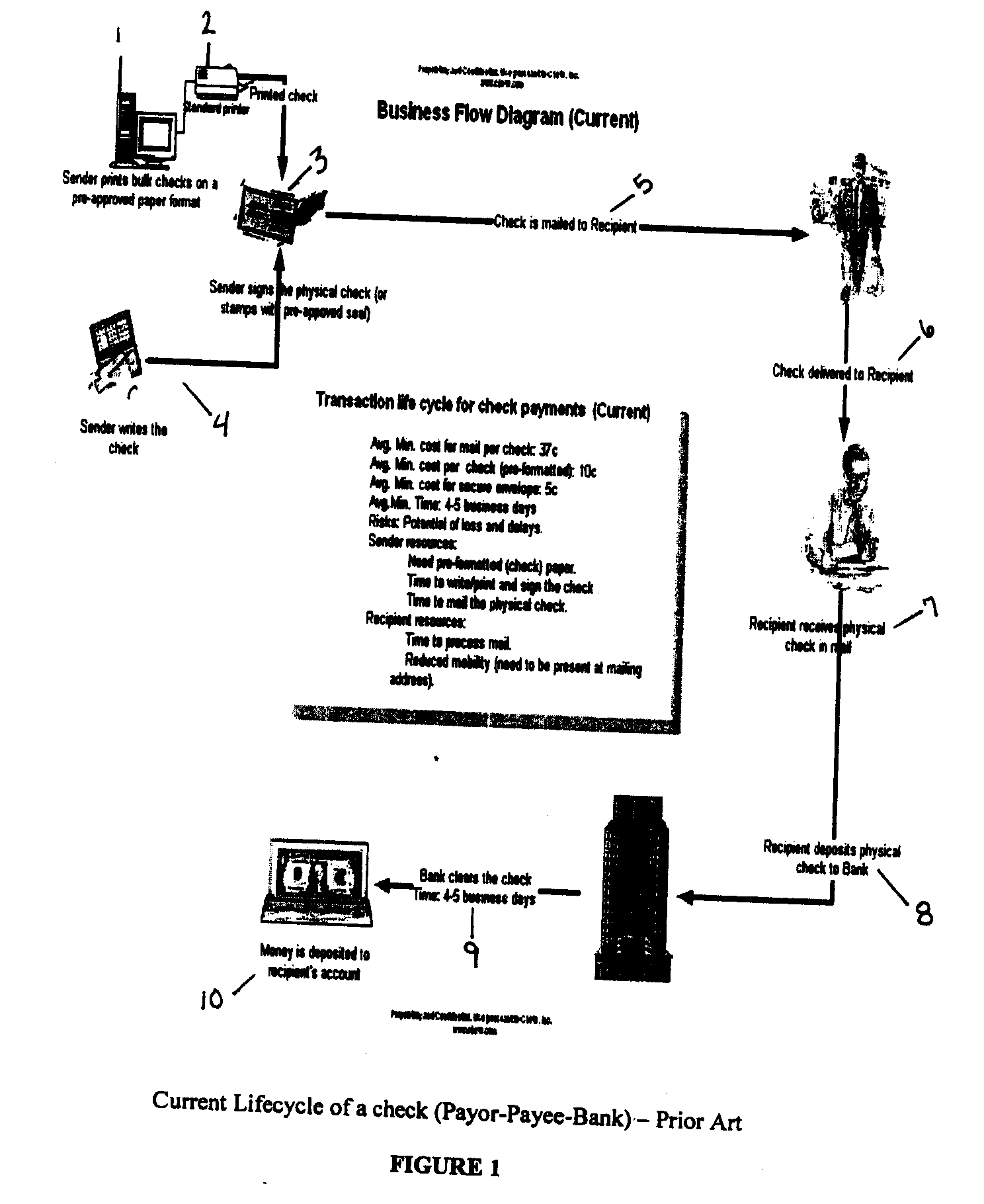
[0043]FIG. 1 is a flow diagram of the current lifecycle of a paper check as known in the prior art. If the checks are being generated in bulk quantities, such as for a company, the sender prints the bulk checks on a pre-approved paper format from a computer in step 1. The printer 2 can be a standard printer. If the checks are being written by an individual, the sender writes the check with a pen on a pre-approved check 4. The check is then mailed to the recipient in step 5. The check is delivered to the recipient 6. In step 7, the recipient receives the physical check in the mail. Step 8 involves the recipient depositing the physical check in the bank. In step 9, the bank processes and clears the check, which can take an average of four to five business days. The money is then deposited into the recipient's bank account in step 10.
[0044] There are many disadvantages to this system. First, there is a cost related to sending checks by mail, which include the cost of stamps and the co...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com