Cardiac mapping instrument with shapeable electrode
a technology of shapeable electrodes and mapping instruments, which is applied in the field of epicardial pacing and mapping of the heart, can solve the problems of affecting the treatment effect, and affecting the treatment effect, and avoiding the use of drugs. , the effect of reducing the risk of strok
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
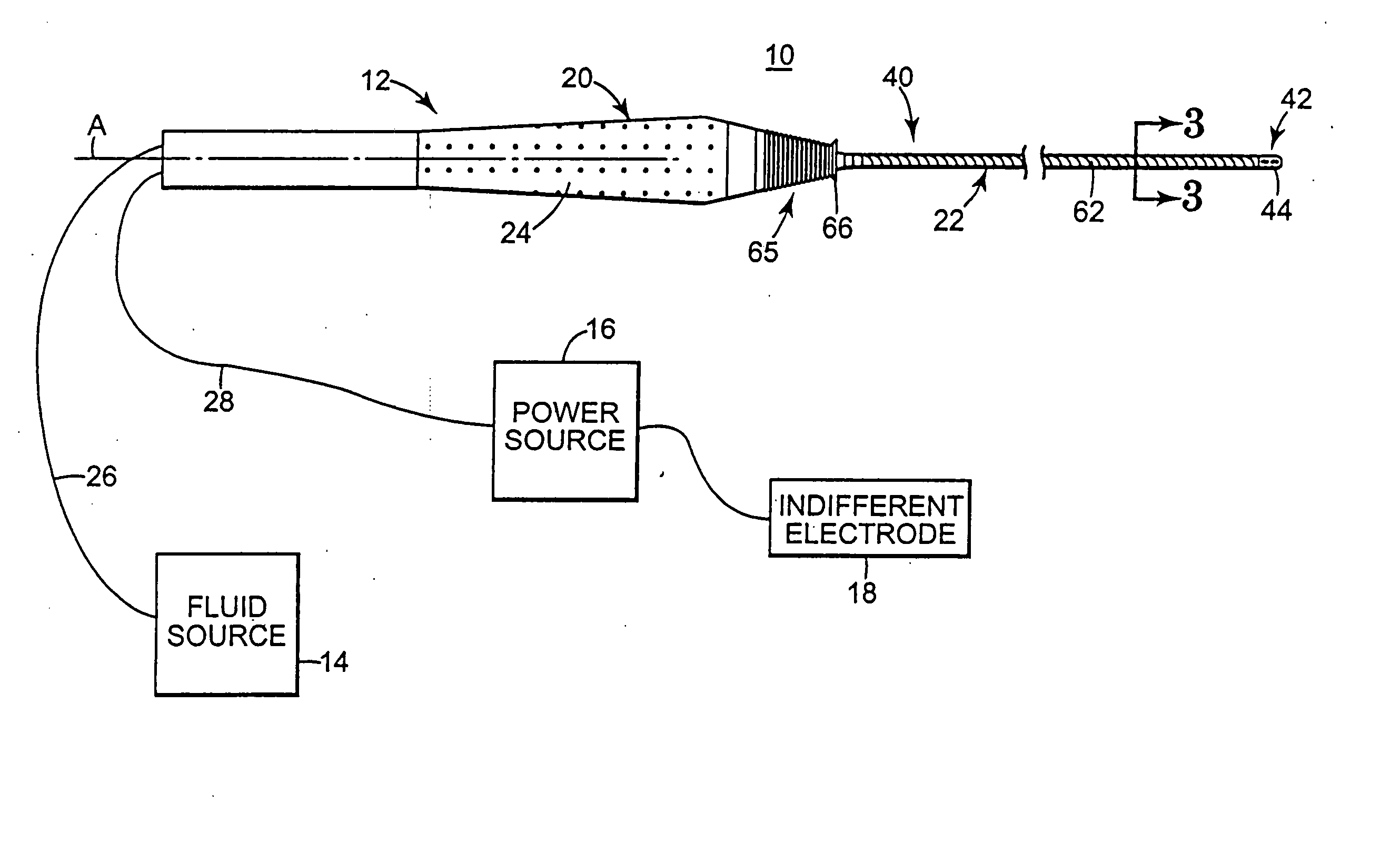
[0062] One preferred embodiment of an electrosurgical system 10 in accordance with the present invention is shown in FIG. 1. The system 10 is comprised of an electrosurgical instrument 12, a fluid source 14, a power source 16, and an indifferent electrode 18. The various components are described in greater detail below. In general terms, however, the fluid source 14 is fluidly connected to the electrosurgical instrument 12. Similarly, the power source 16 is electrically connected to the electrosurgical instrument 12 and to the indifferent electrode 18. During use, conductive fluid is delivered from the fluid source 14 to a distal portion of the electrosurgical instrument 12. The distributed fluid is energized by the electrosurgical instrument 12 via the power source 16. The so-energized conductive fluid is capable of forming a virtual electrode, which is capable of ablating or cauterizing contacted tissue.
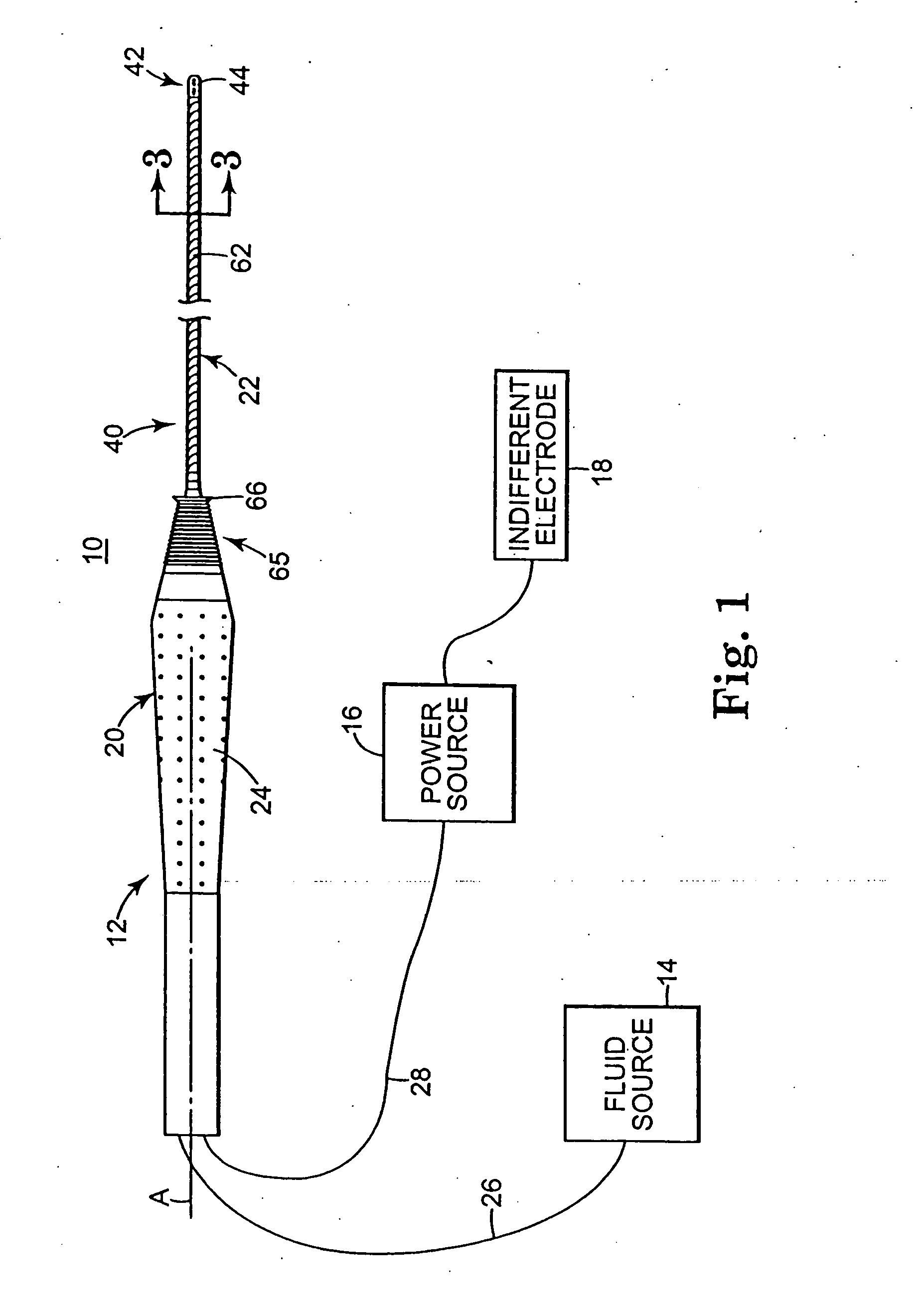
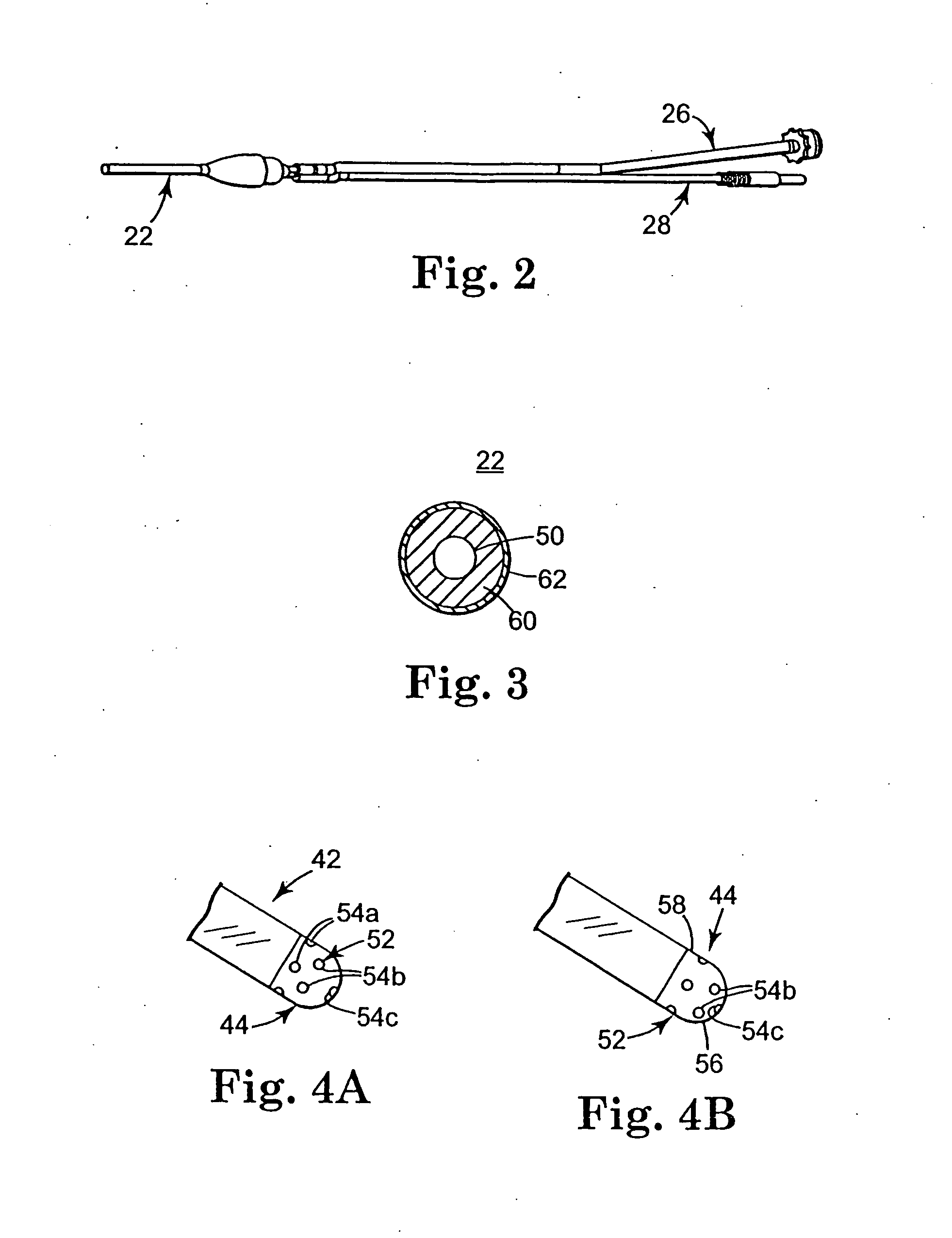
[0063] The electrosurgical instrument 12 includes a handle 20 and a shaft 22....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com