Treatment of wood chips using enzymes
a technology of enzymes and wood chips, applied in the field of managing wood pitch, can solve the problems of overall decrease in the pitch content of stored wood, decrease in wood extractives, so as to reduce the content of total extractives, short treatment times, and the effect of reducing brightness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Measurement of the Apparent Pitch Content (“APC”) in a Wood Chip Sample Using Different Enzyme Formulations
[0050] Materials and Methods
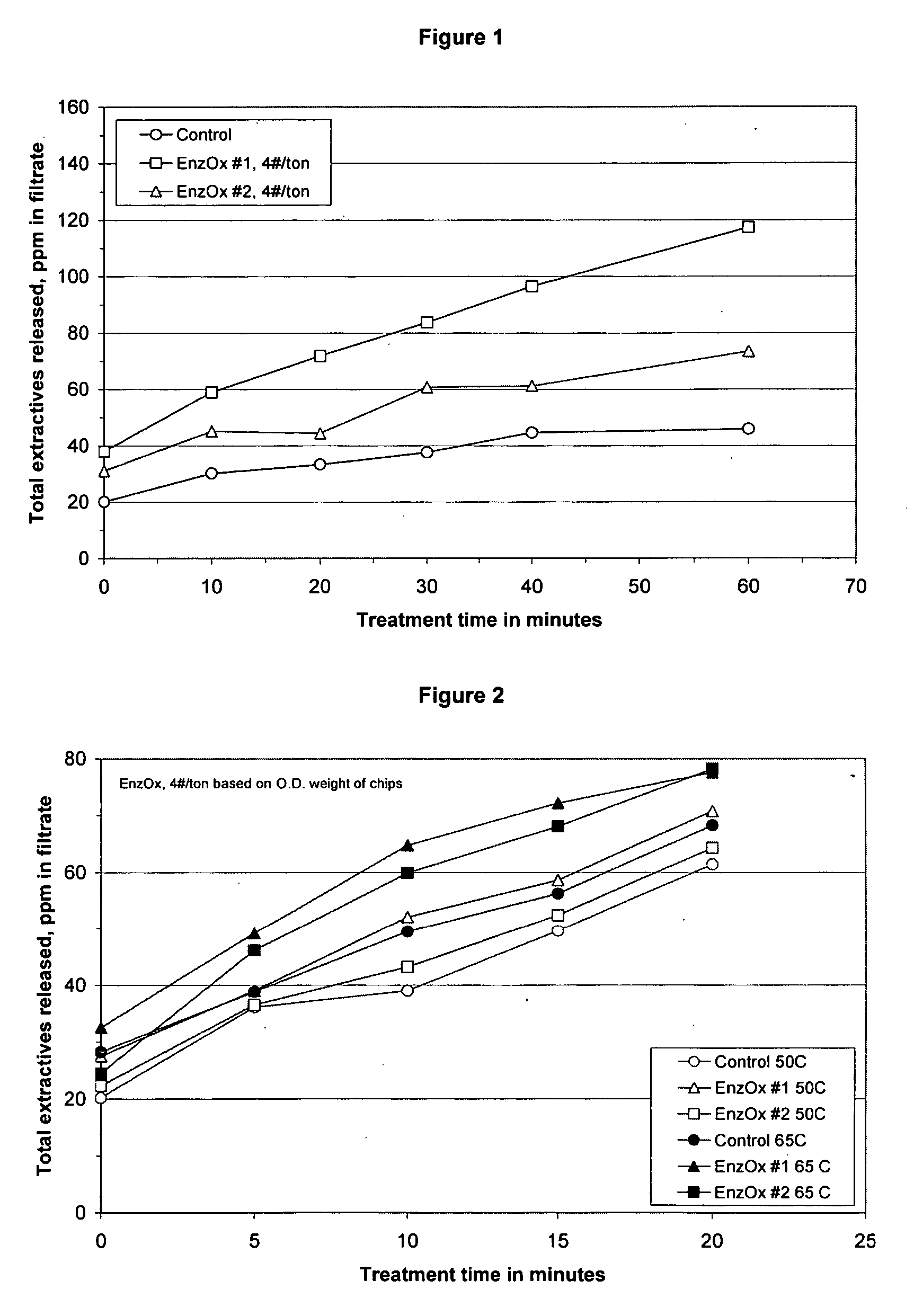
[0051] Wood chip samples were treated with two different formulations, EnzOx® #1 and EnzOx®#2 and the apparent pitch content (“APC”) was measured. 800 grams of water was heated to 50° C. 200 grams of freshly cut wood chips were added to the water and mixed at 200 rpm using a standard mixer while maintaining the temperature of the water bath at 50° C. EnzOx® #1 or #2 was added in the desired amount of 0.20 grams, and the mixing was continued for 100 minutes at 50° C. The pH was 5.2 due to the natural pH of the wood chips.
[0052] Samples were taken at several different reaction times. The APCs in the filtrate and the organic acid content released from the wood chips were measured. The APC was measured using the same procedure described in U.S. Patent Application Publication No. 2003 / 0046984. The organic acid content was measured by extracting the fil...
example 2
Measurement of the Apparent Pitch Content (“APC”) in a Wood Chip Sample Using Different Enzyme Formulations at Different Temperatures
[0055] Materials and Methods
[0056] Wood chip samples were treated with two different EnzOx® formulations at 50° C. and 65° C. and the apparent pitch content (“APC”) was measured as described in Example 1.
[0057] Results
[0058] The results are shown in FIG. 2. Treatment of the wood chips with the enzyme formulation resulted in an increase in the APC of the filtrate. The increase was greater at 65° C. than at 50° C.
example 3
Measurement of the Apparent Pitch Content (“APC”) at the Decker Accept Before, During and After Enzyme Treatment
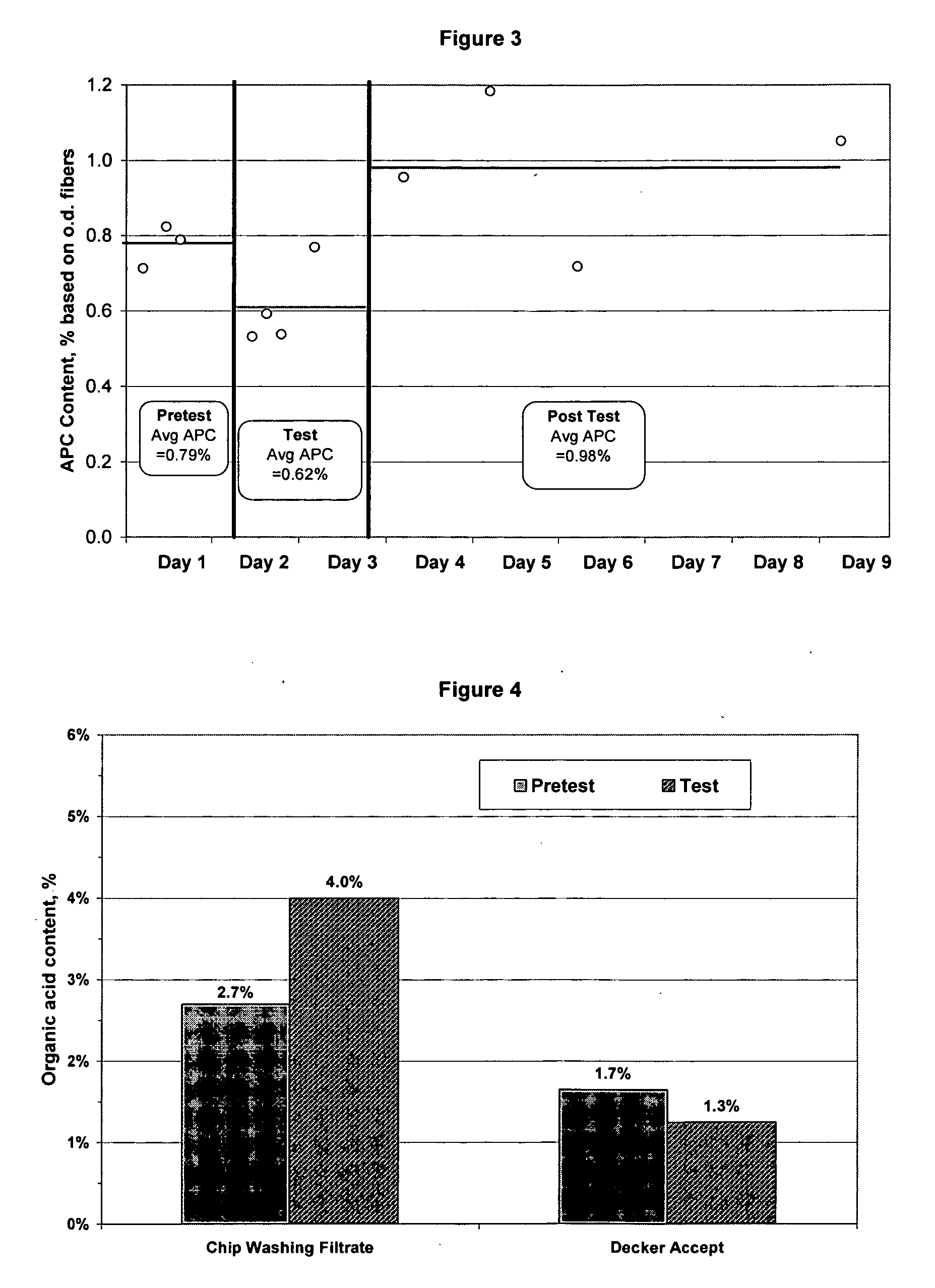
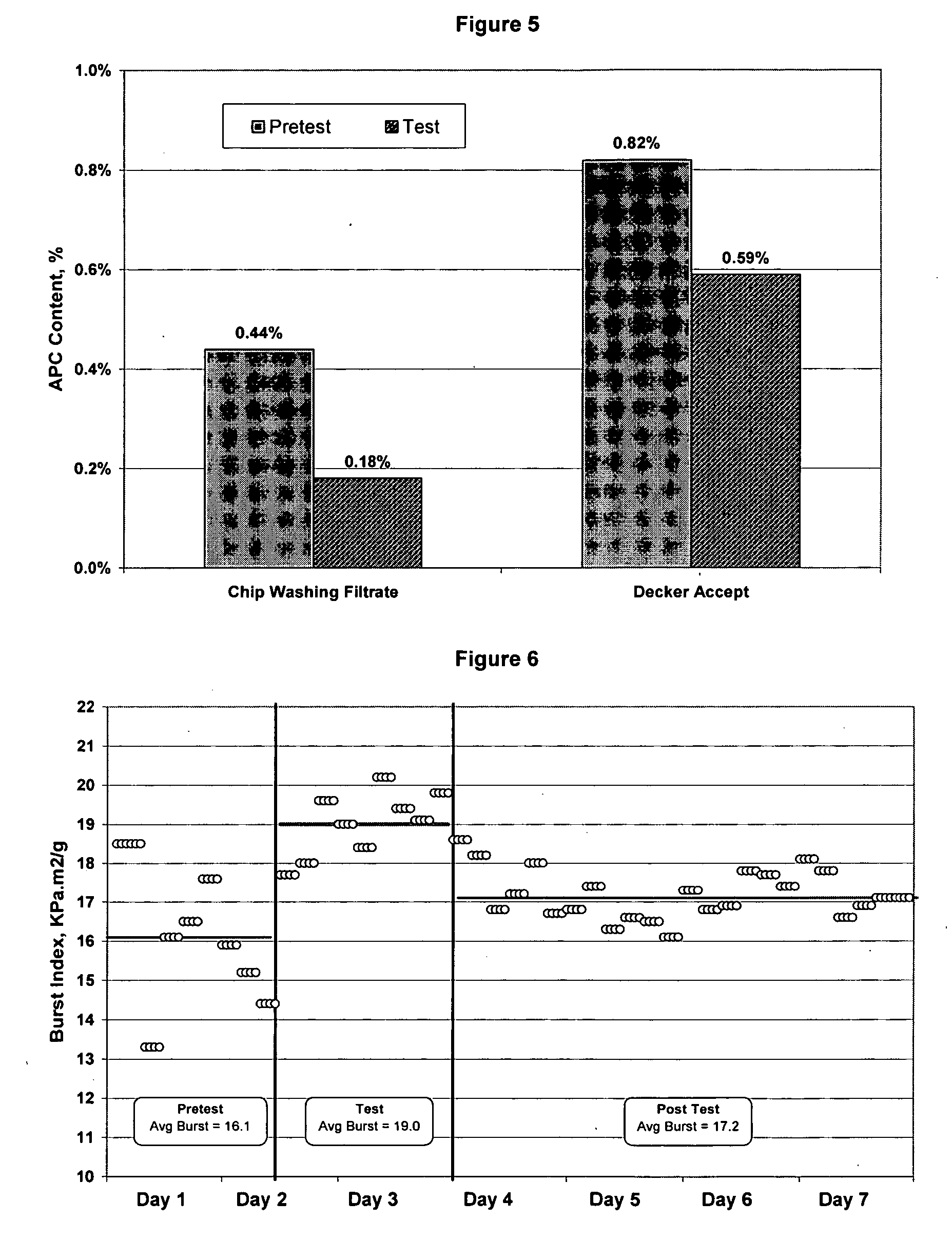
[0059] Wood chips were treated with EnzOx® and the APC of the resulting pulp was measured at the decker accept sample point in the pulping process.
[0060] The results are shown in FIG. 3. The APC levels measured at the decker accept sample point were lower due to the fact that a greater amount of wood extractives were released from the wood chips upon treatment with the enzyme formulation. The wood extractives were removed in the chip washing filtrate prior to the pulp reaching the decker accept sample point.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap