Micro-fabricated device with thermoelectric device and method of making
a thermoelectric device and micro-fabricated technology, applied in semiconductor devices, semiconductor/solid-state device details, electronic beam carrier recording, etc., can solve the problems of significant increase in chip heat flux, significant rise in power dissipation, and destruction or damage of silicon-based devices on which microprocessors are based
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
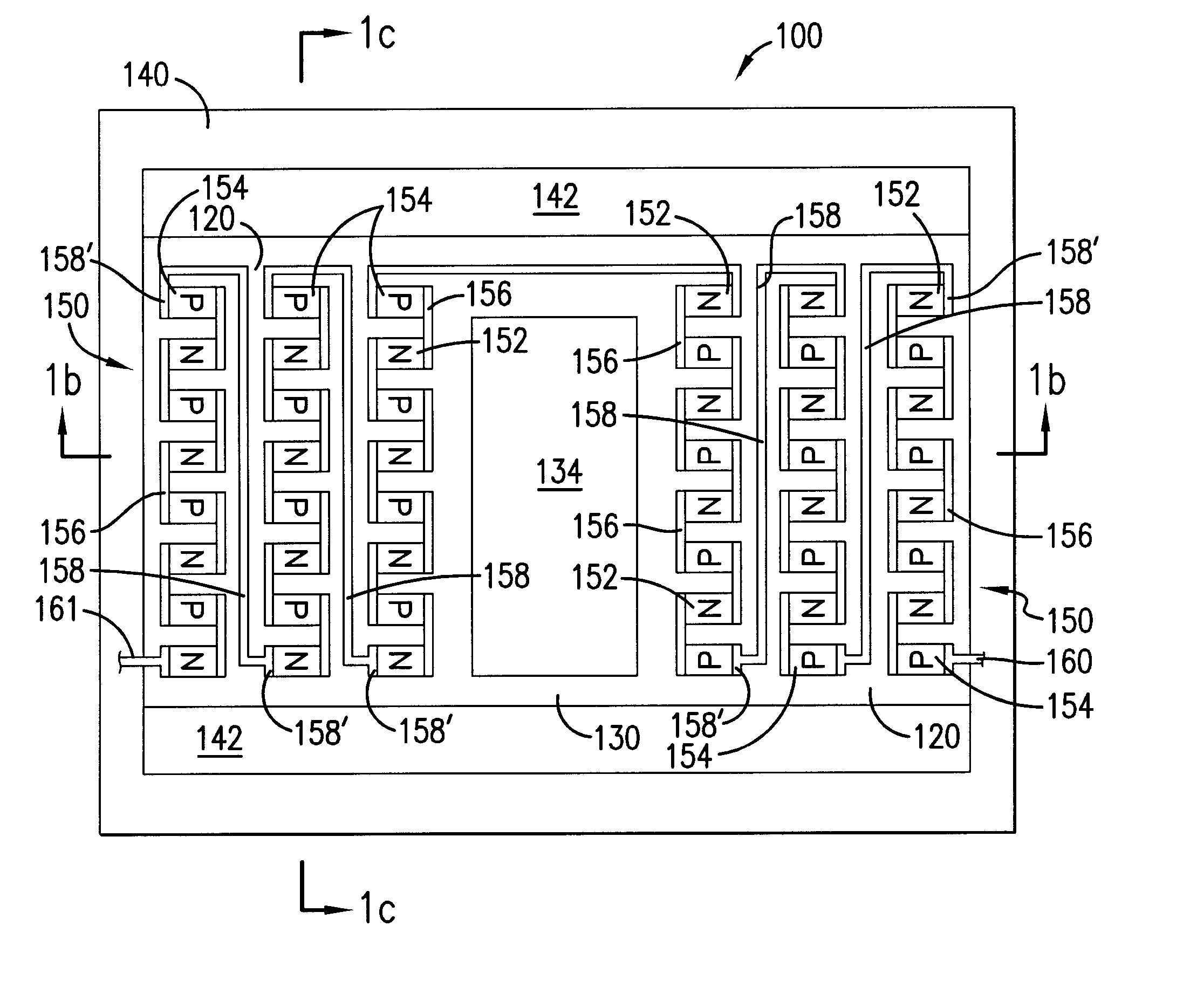
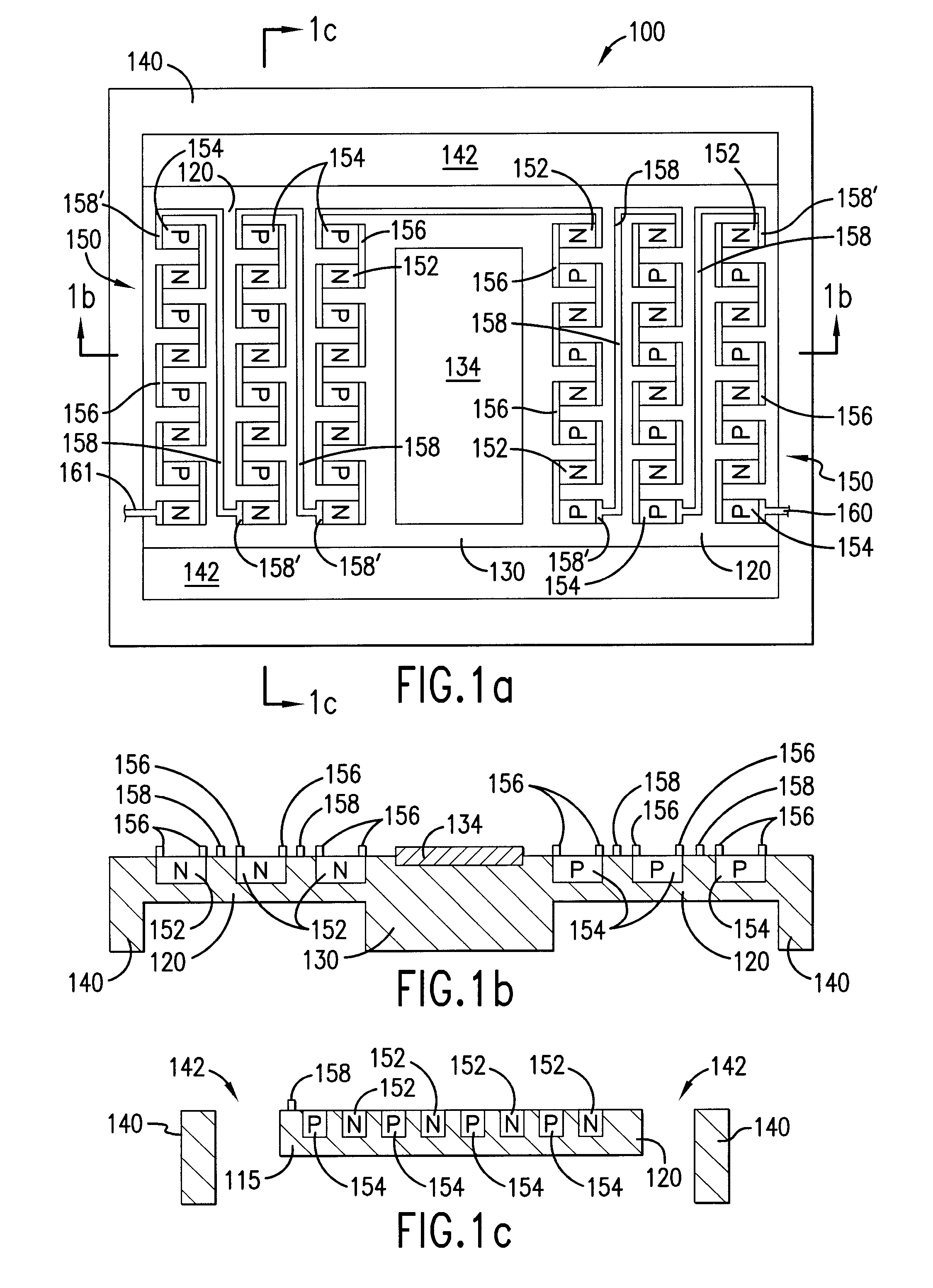
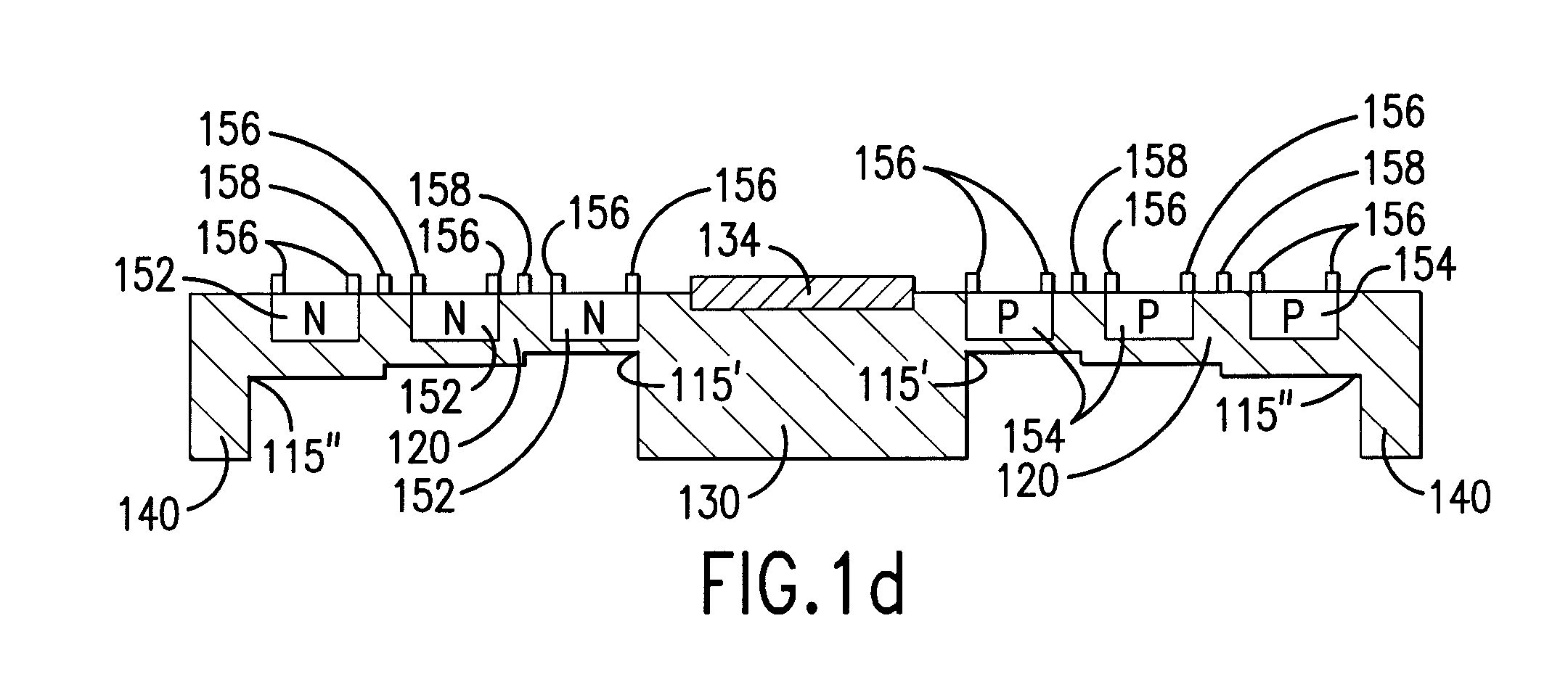
[0021] Referring to FIG. 1a, a top view is shown of an embodiment of micro-fabricated device 100 of the present invention. In this embodiment, thermally isolating structure 120 includes thermoelectric device 150 that provides selective heating or cooling of device substrate 130. In addition, thermally isolating structure 120 reduces the thermal conductivity between device substrate 130 and support structure 140 while also providing mechanical support. Device substrate 130 is disposed, within aperture 142 formed in support structure 140.
[0022] In this embodiment, active device 134 is disposed on device substrate 130. Active device 134 includes, for example, various transistors (including thin-film-transistor (TFT) technology using polysilicon on glass substrates), diodes, logic cells, as well as sensors, transducers, electron emitters, bolometers, and superconductoring high Q RF filters to name just a few of the many active devices that may be utilized in the present invention eithe...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com