Feedback control of sub-atmospheric chemical vapor deposition processes
a sub-atmospheric chemical vapor and process control technology, applied in the direction of programme control, total factory control, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of sub-atmospheric chemical vapor deposition, deposited film to deviate significantly from target values, and radial and azimuthal thickness non-uniformity, both within and among wafers, to achieve the effect of improving the wafer-to-wafer and within-wafer uniformity of film
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
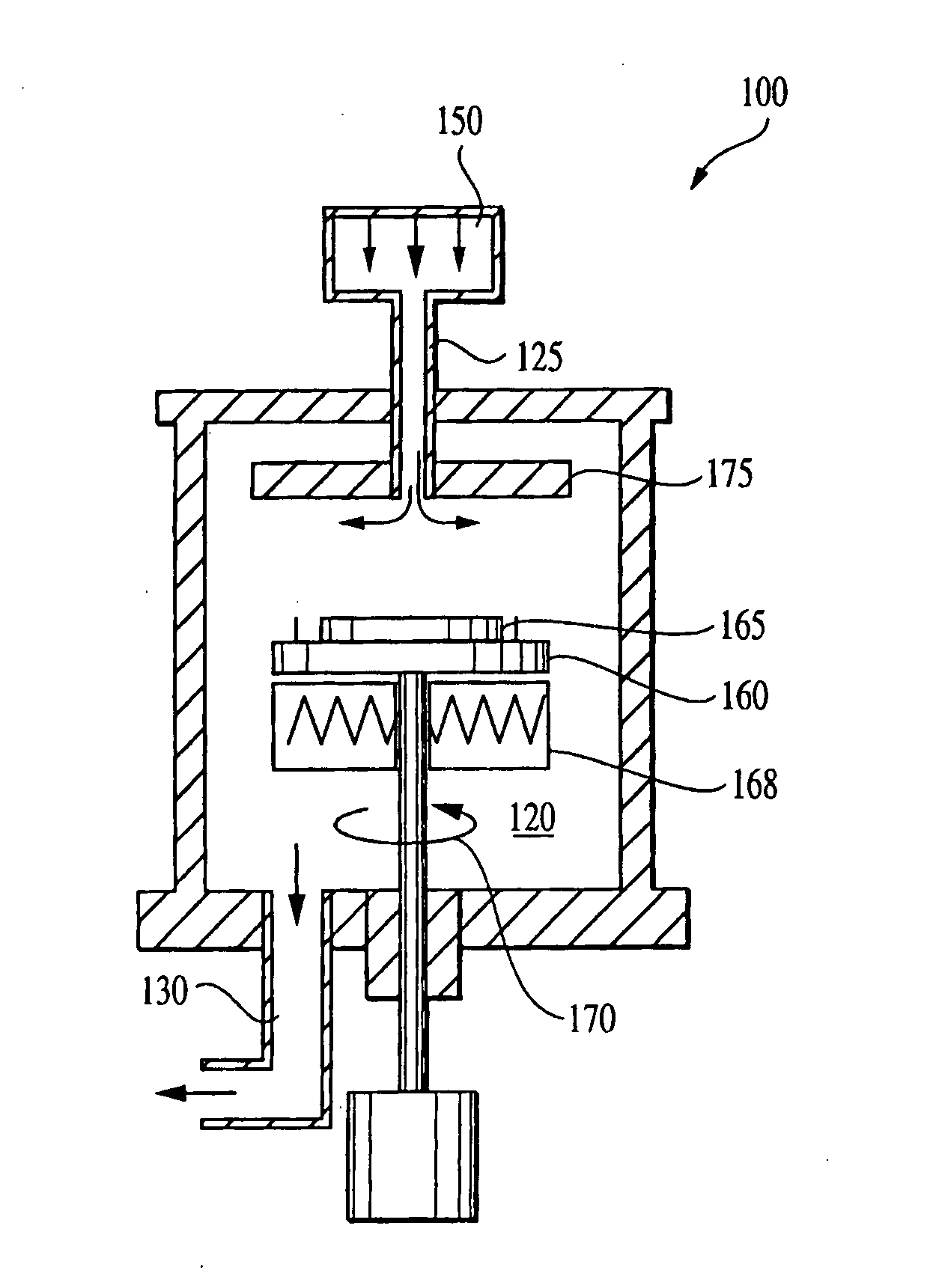
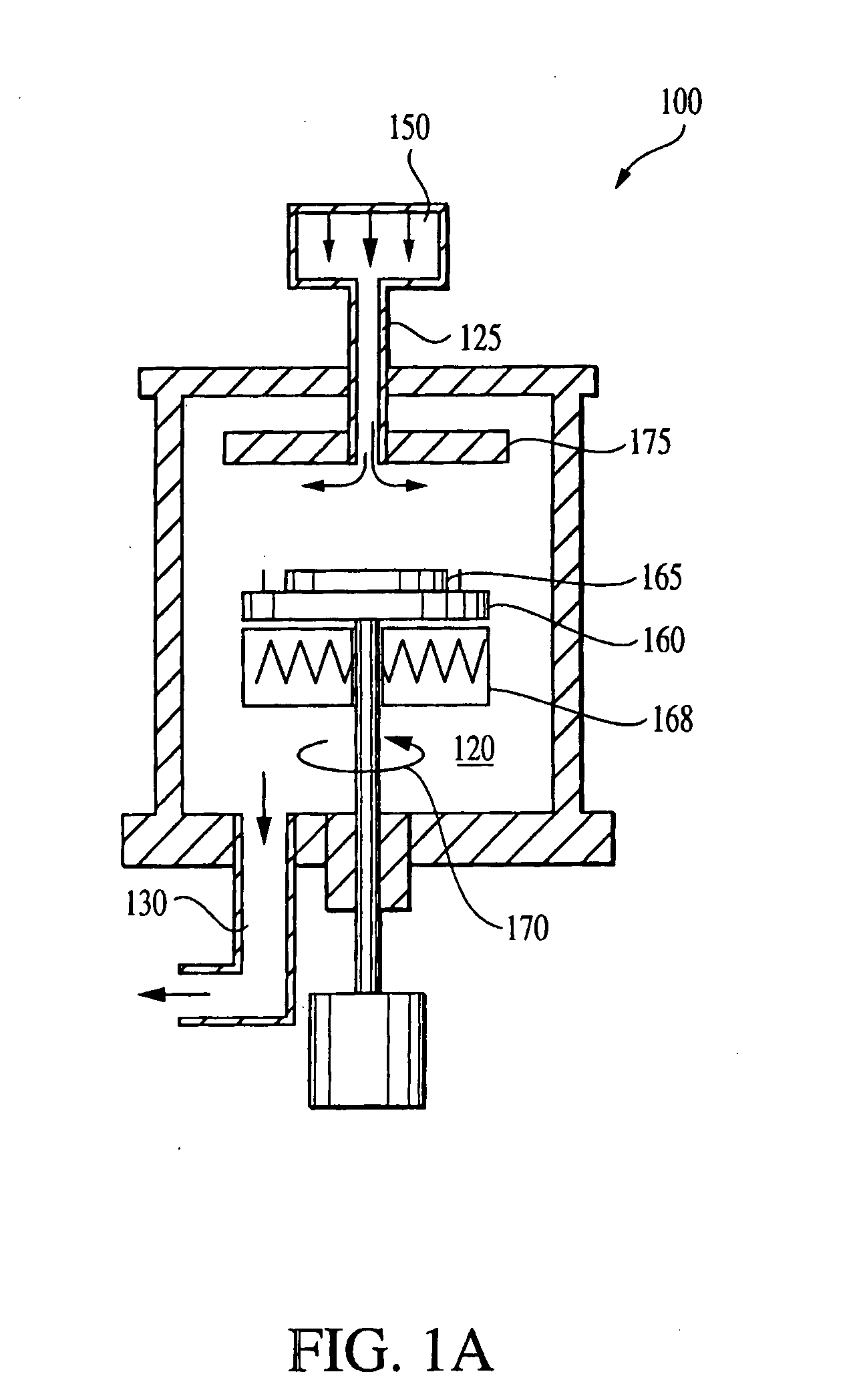
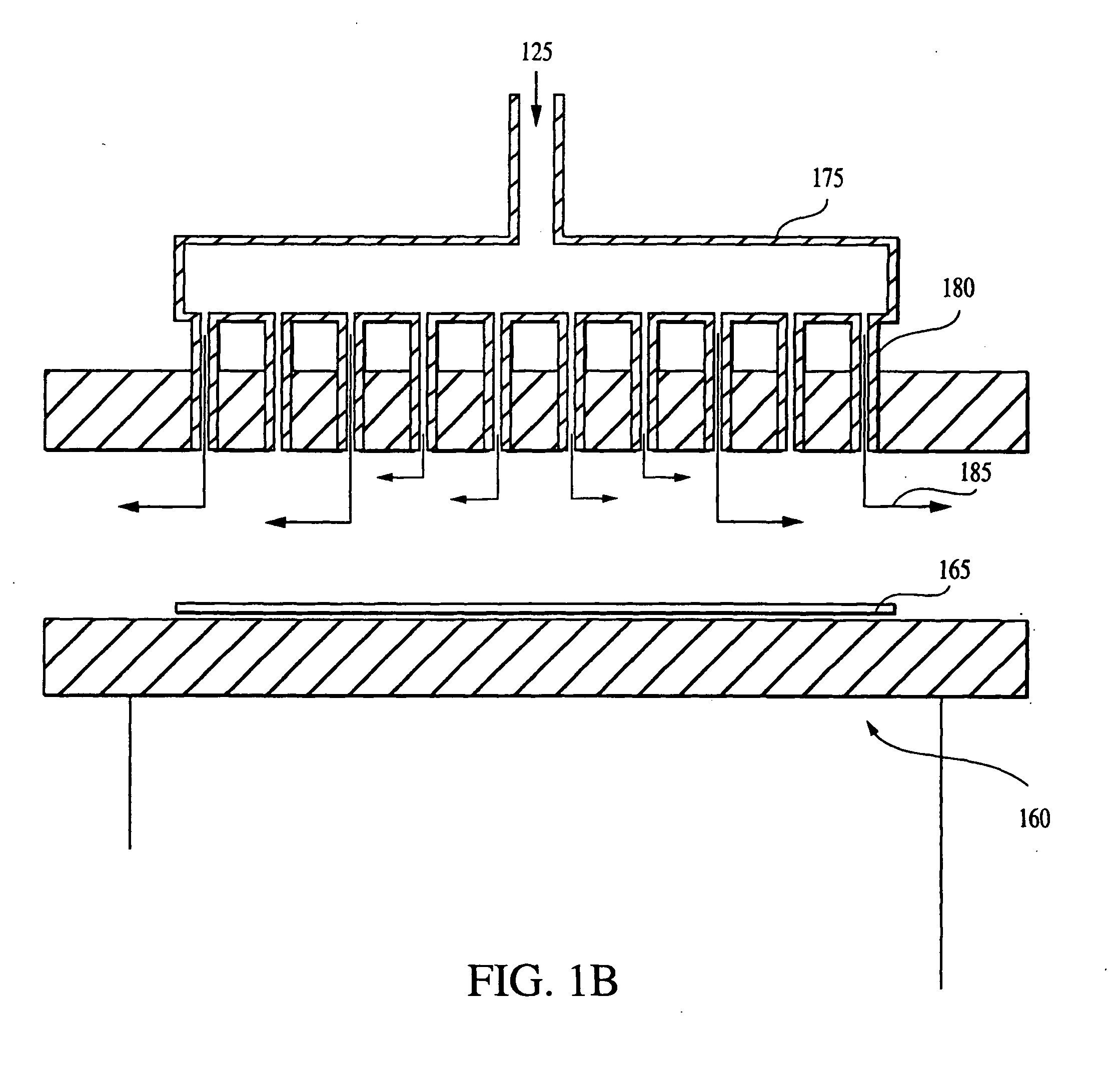
[0040] Sub-atmospheric chemical vapor deposition (SACVD) has been widely used in microelectronics fabrication to deposit films, such as a SiO2, at low temperatures. In the SACVD process, reactive gases are introduced into the reaction chamber at sub-atmospheric pressures. The reactive gases flow over a heated wafer (e.g., 300-700° C.) where the desired chemical reactions occur and the product is deposited. FIG. 1A is a schematic illustration of an exemplary SACVD system 100. The system 100 includes a chamber 120, a vacuum system 130, a wafer holder 160 for supporting wafer 165, a gas or fluid delivery system 150 for introduction of reactive gases and a heater 168 for heating the wafer holder 160. Reactive gases are introduced into a reaction chamber 120 through inlet 125 of the gas delivery system 150. In order to promote a uniform distribution, the reactive gases typically are introduced into the chamber at a source positioned opposite or a distance from the wafer 165. The heated w...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com