Method of Making an Apparatus for Forming Concrete
a concrete and making technology, applied in the field of making concrete making equipment, can solve the problems of large pavement area, large pavement area, waste of concrete, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing labor intensity, reducing labor intensity and reducing labor intensity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
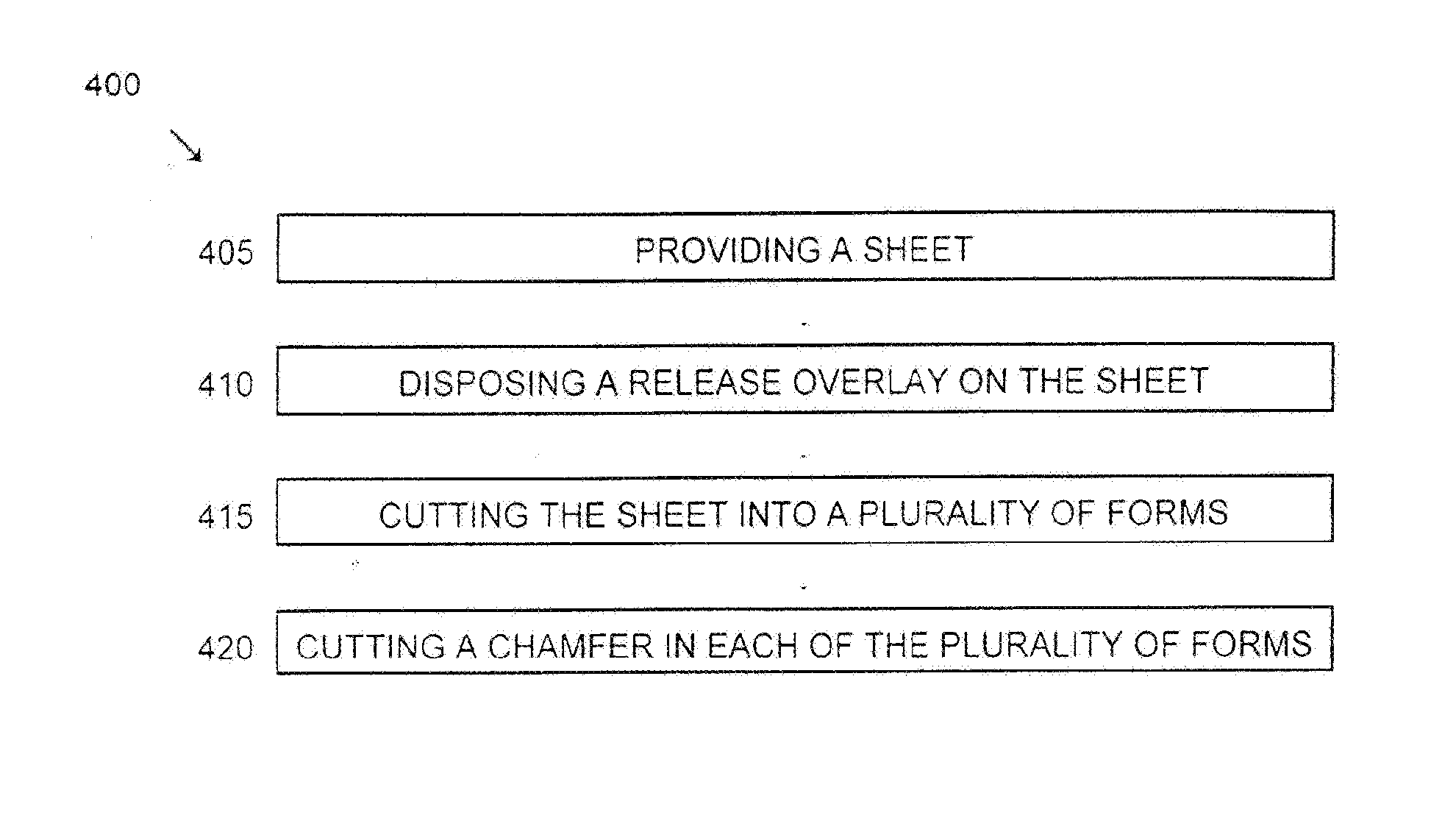
[0031] The invention is a method of forming concrete and an apparatus for same that provide partially coated load plates carried in slotted, stiff, infinitely long, pre-chamferred forms with predetermined true height.
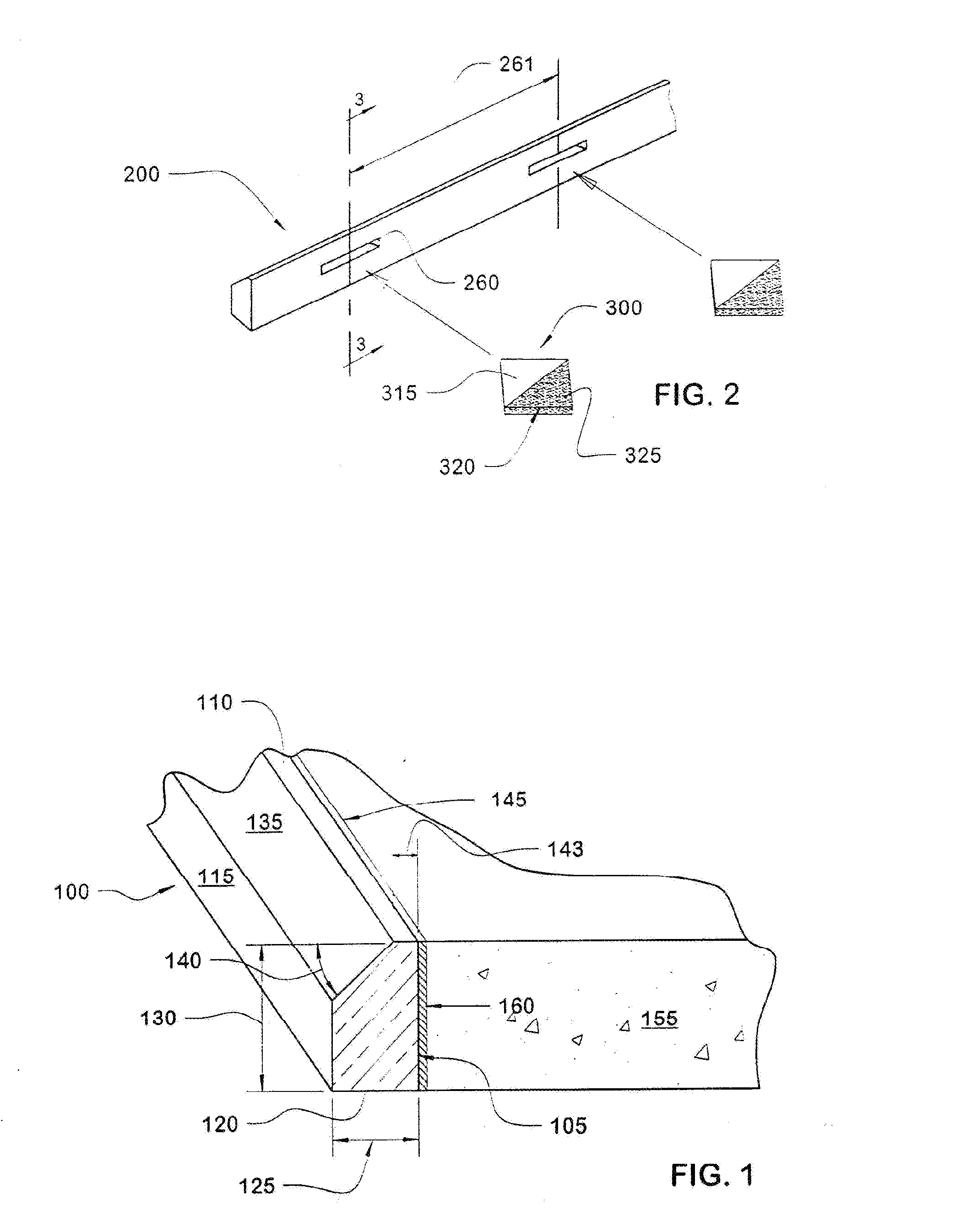
[0032] Referring to FIG. 1, an embodiment of an apparatus for forming concrete configured according to principles of the invention includes a form 100. Form 100 has a side surface 105, a top surface 110, a back surface 115 and a bottom surface 120. Side surface 105 and back surface 115 define a width 125 ranging from 0.875 to 2.500 inches. Top surface 110 and bottom surface 120 define a height 130 ranging from 3 to 18 inches or more, depending on the thickness required for pavement.
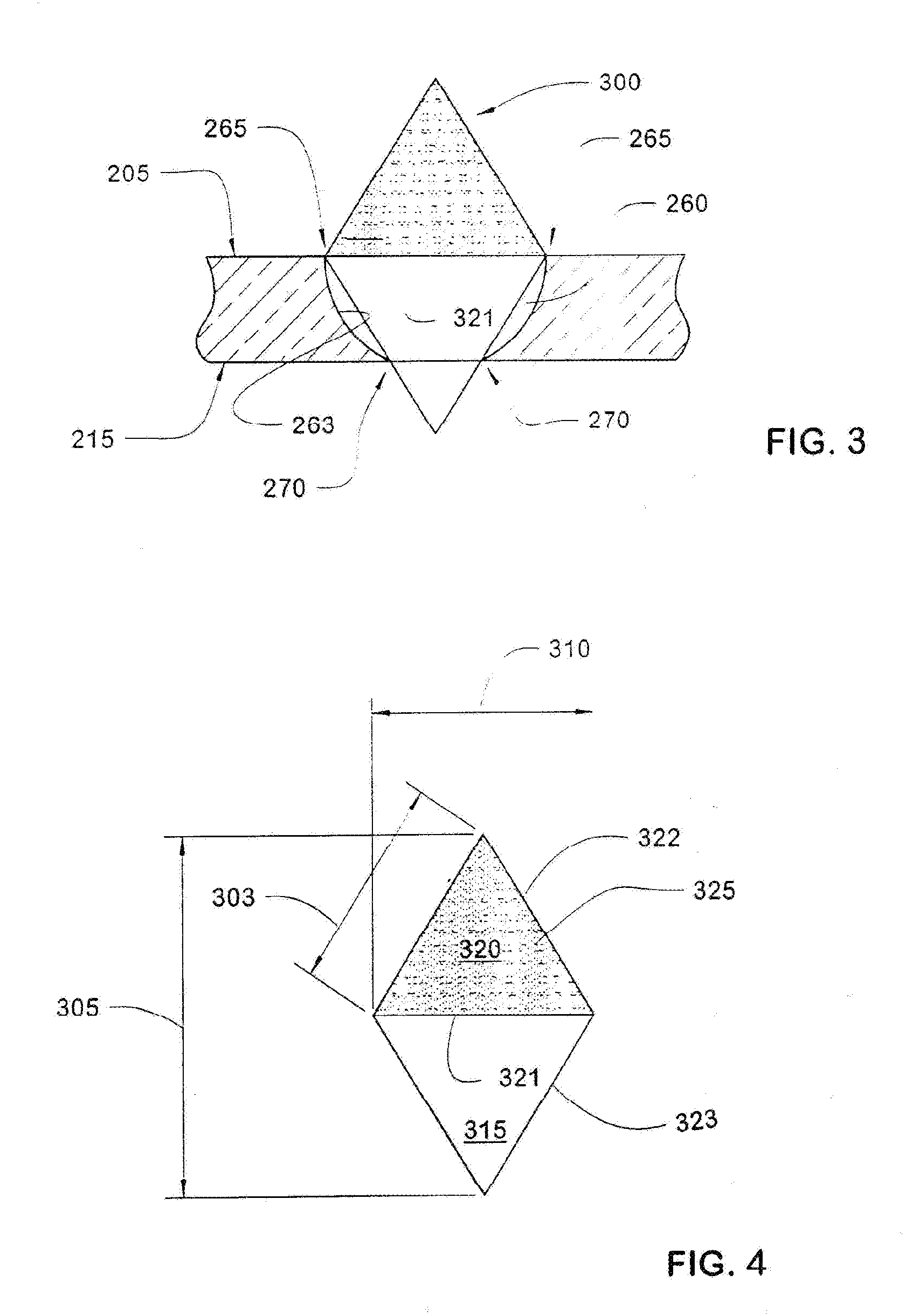
[0033] Form 100 has a chamfer 135 between top surface 110 and back surface 115. Chamfer 135 defines an angle 140 relative to top surface 110 ranging from 10° to 89°, preferably 22.5° to 45°. Side surface 105 and chamfer 135 define a top surface width 143 ranging from 0.125 to 0.875 inch. Ch...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com