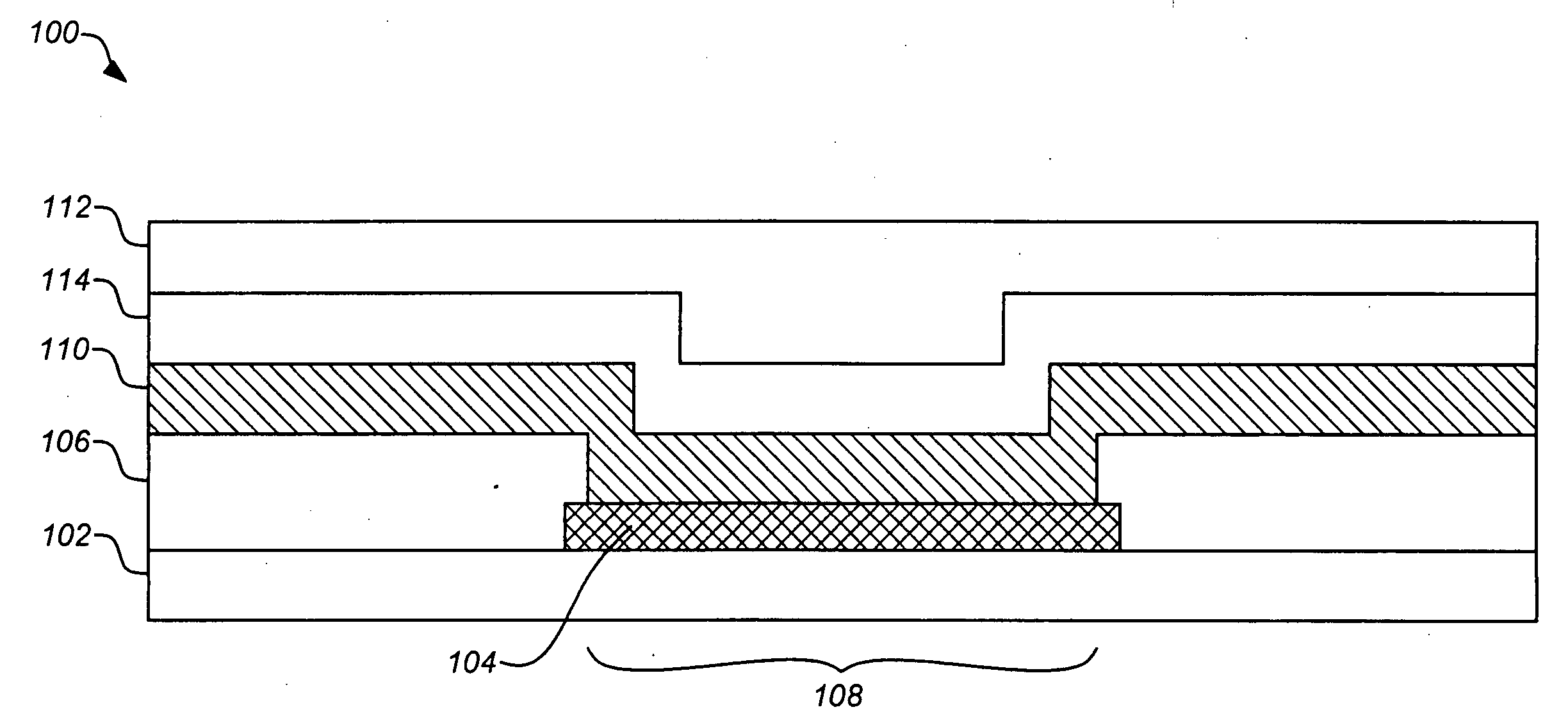
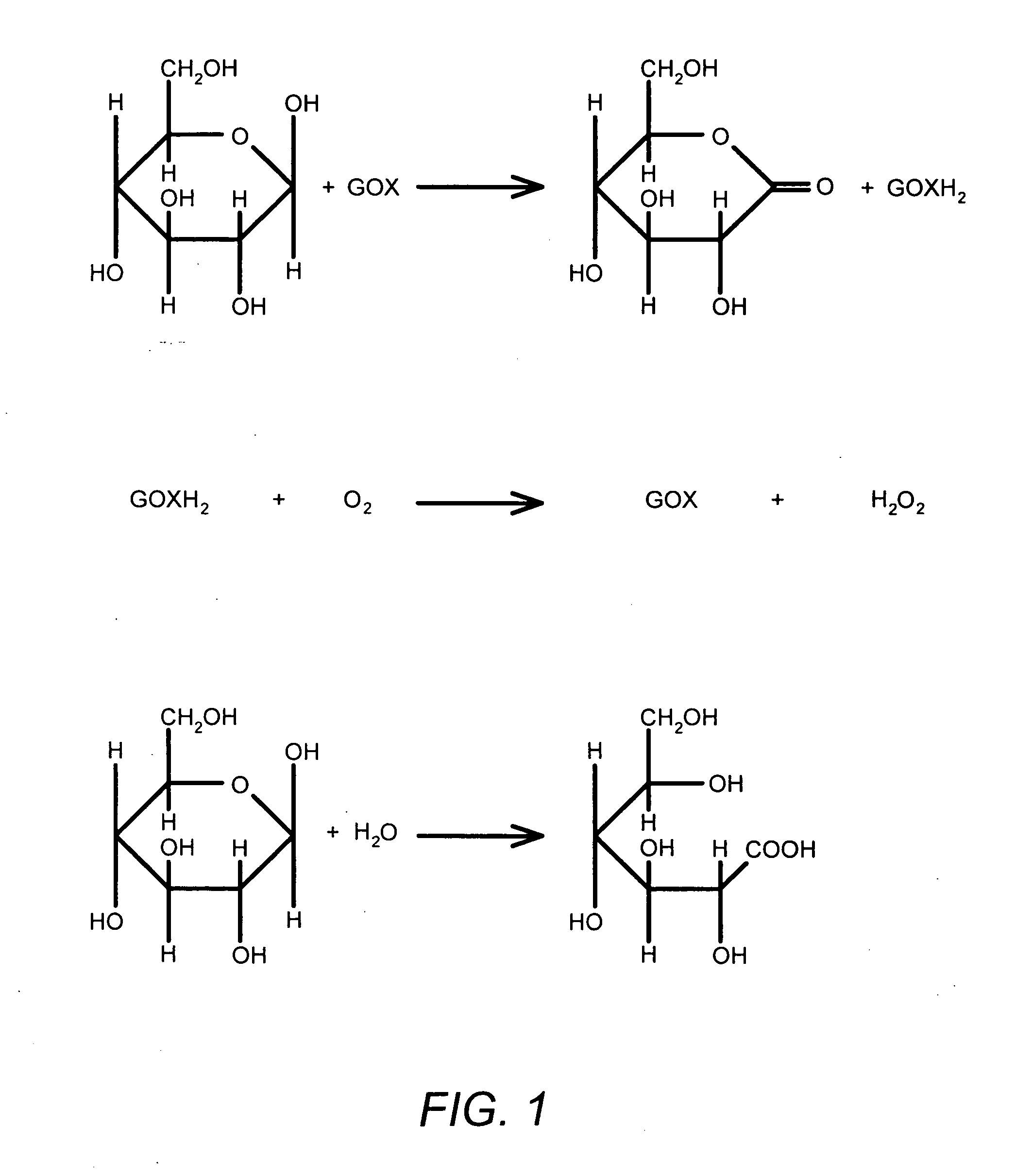
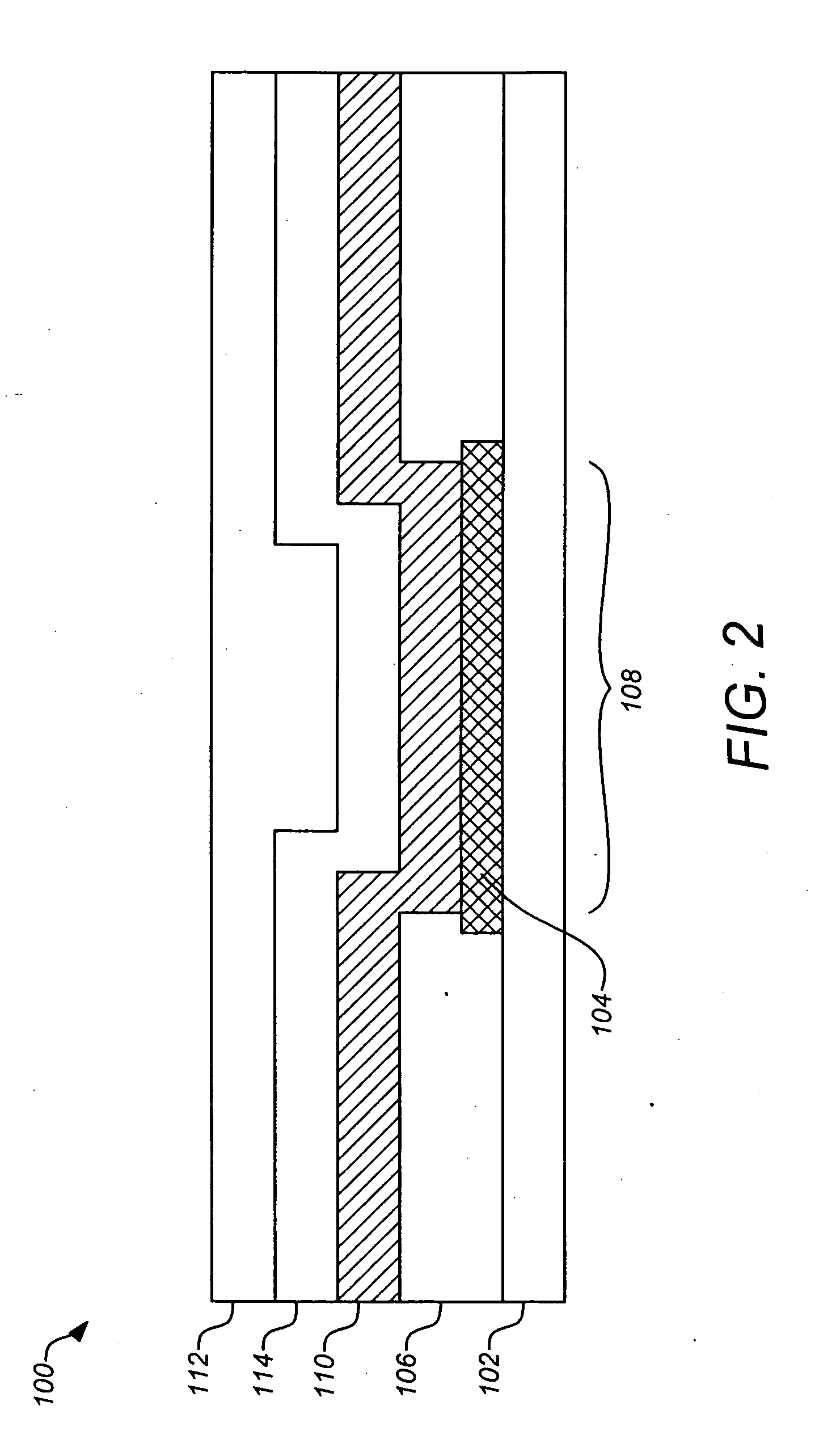
Methods and materials for controlling the electrochemistry of analyte sensors
a technology of electrochemistry and sensors, applied in the field of devices and methods for controlling the electrochemistry of analyte sensors, can solve the problems of lowering blood pressure, reproducibility, speed of response, and/or the detection range,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0021]Unless otherwise defined, all terms of art, notations and other scientific terms or terminology used herein are intended to have the meanings commonly understood by those of skill in the art to which this invention pertains. In some cases, terms with commonly understood meanings are defined herein for clarity and / or for ready reference, and the inclusion of such definitions herein should not necessarily be construed to represent a substantial difference over what is generally understood in the art. Many of the techniques and procedures described or referenced herein are well understood and commonly employed using conventional methodology by those skilled in the art. As appropriate, procedures involving the use of commercially available kits and reagents are generally carried out in accordance with manufacturer defined protocols and / or parameters unless otherwise noted. A number of terms are defined below.
[0022]The term “analyte” as used herein is a broad term and is used in it...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com