Spring Clutch
a technology of spring and clutch, applied in the direction of mechanical actuated clutches, interengaging clutches, gearing, etc., can solve the problems of increasing belt tension, belt becoming liable to break, and decelerating quickly, so as to increase the percentage of absorption of excessive torque, not elastically deformable, and high rigidity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
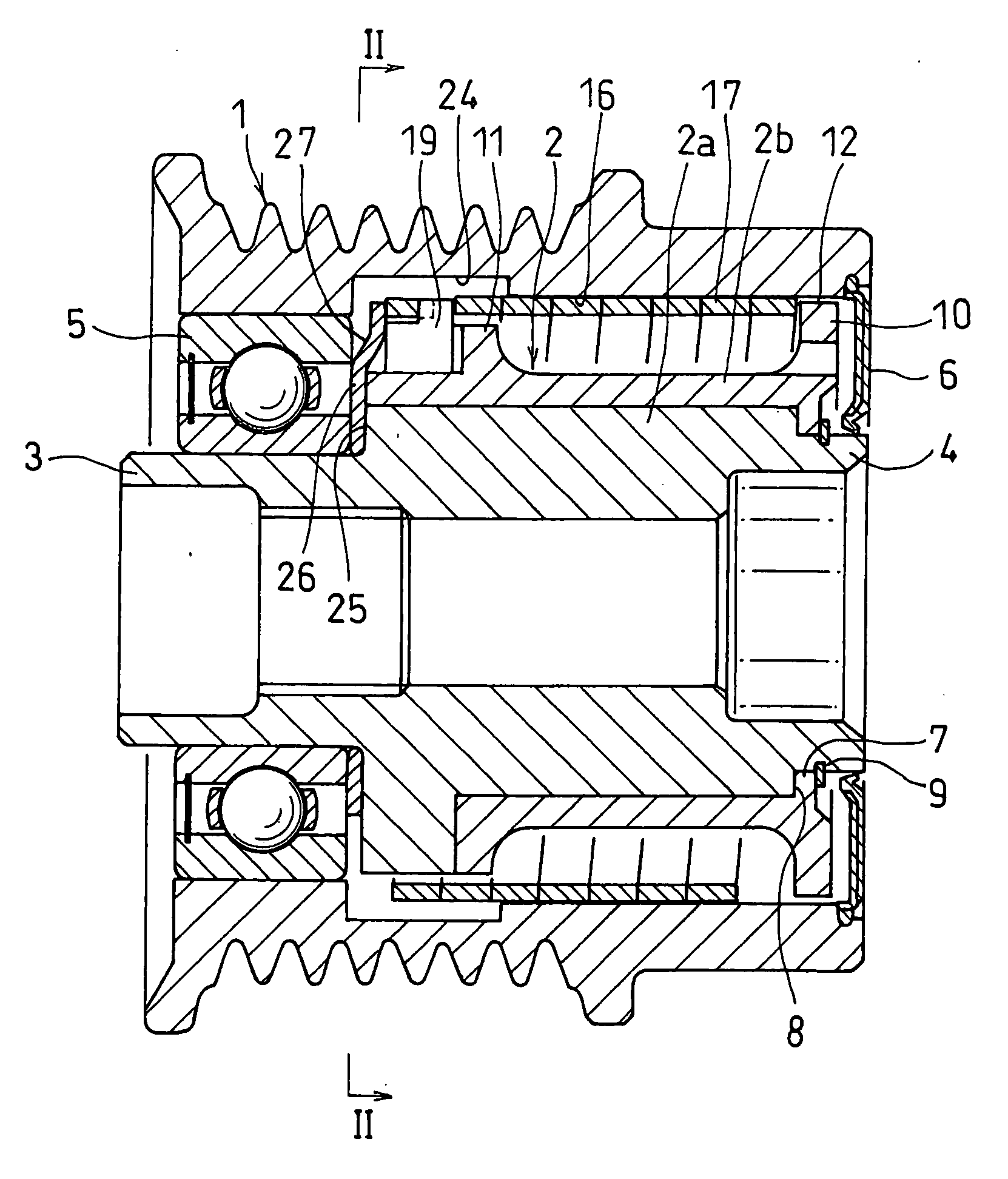
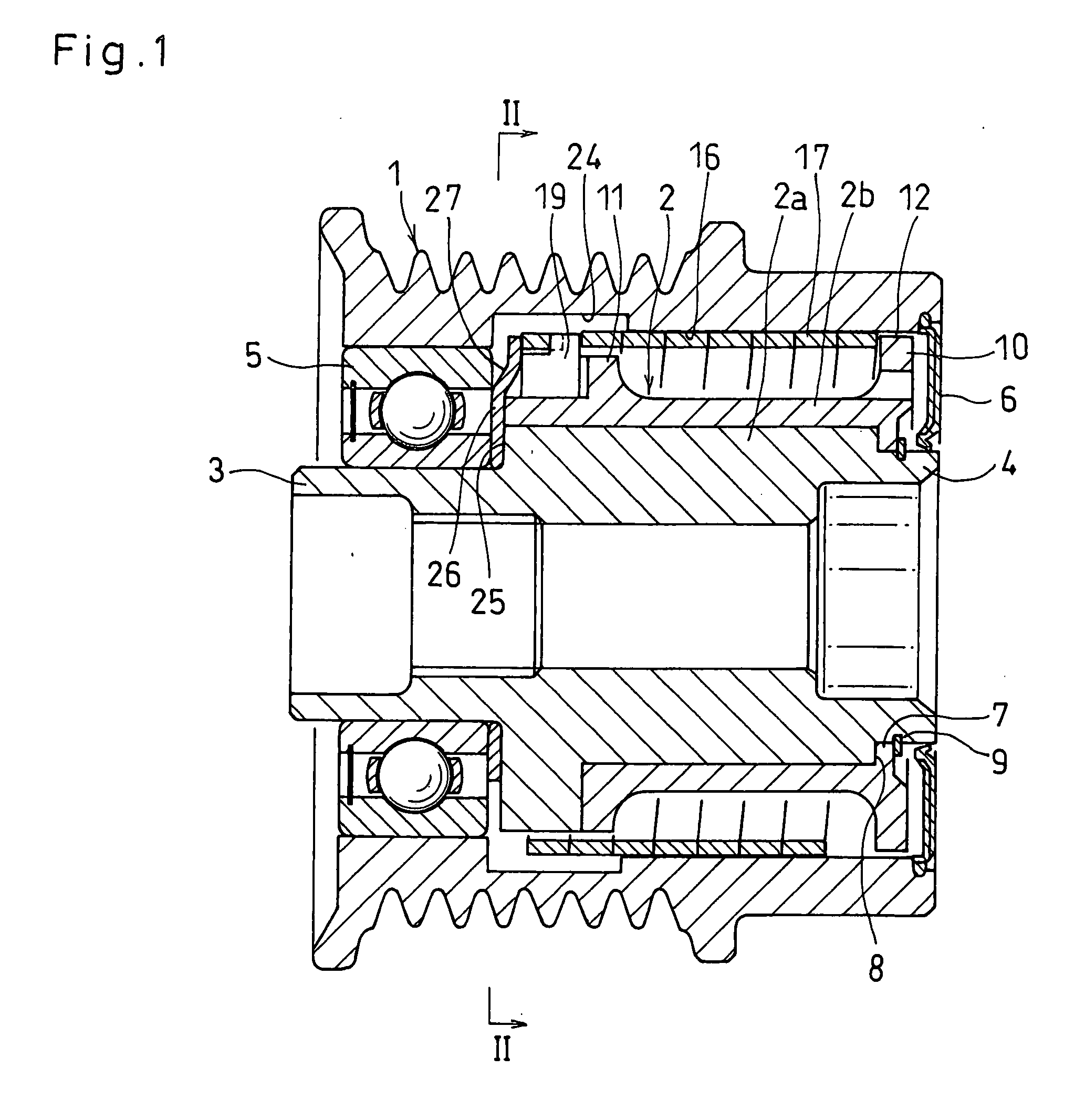
[0063]The embodiments of the present invention are described below with reference to the accompanying drawings. FIGS. 1 to 3 show a spring clutch according to the present invention. As shown in FIG. 1, the spring clutch includes a pulley 1 as an input member, and a pulley hub 2 as an output member mounted in the pulley 1.
[0064]The pulley hub 2 comprises an output shaft 2a made of a metal and a sleeve 2b mounted around the output shaft 2a. The output shaft 2a has an opposed pair of small-diameter portions 3 and 4 at both ends thereof. Between the small-diameter portion 3 at one end of the output shaft 2a and the corresponding end of the pulley 1, a single-seal bearing 5 is mounted to support the pulley 1 and the pulley hub 2 so as to be rotatable relative to each other.
[0065]At the other end of the pulley 1, a seal 6 is mounted between the pulley 1 and the output shaft 2a and has its inner periphery in elastic contact with the outer periphery of the small-diameter portion 4 at the ot...
third embodiment
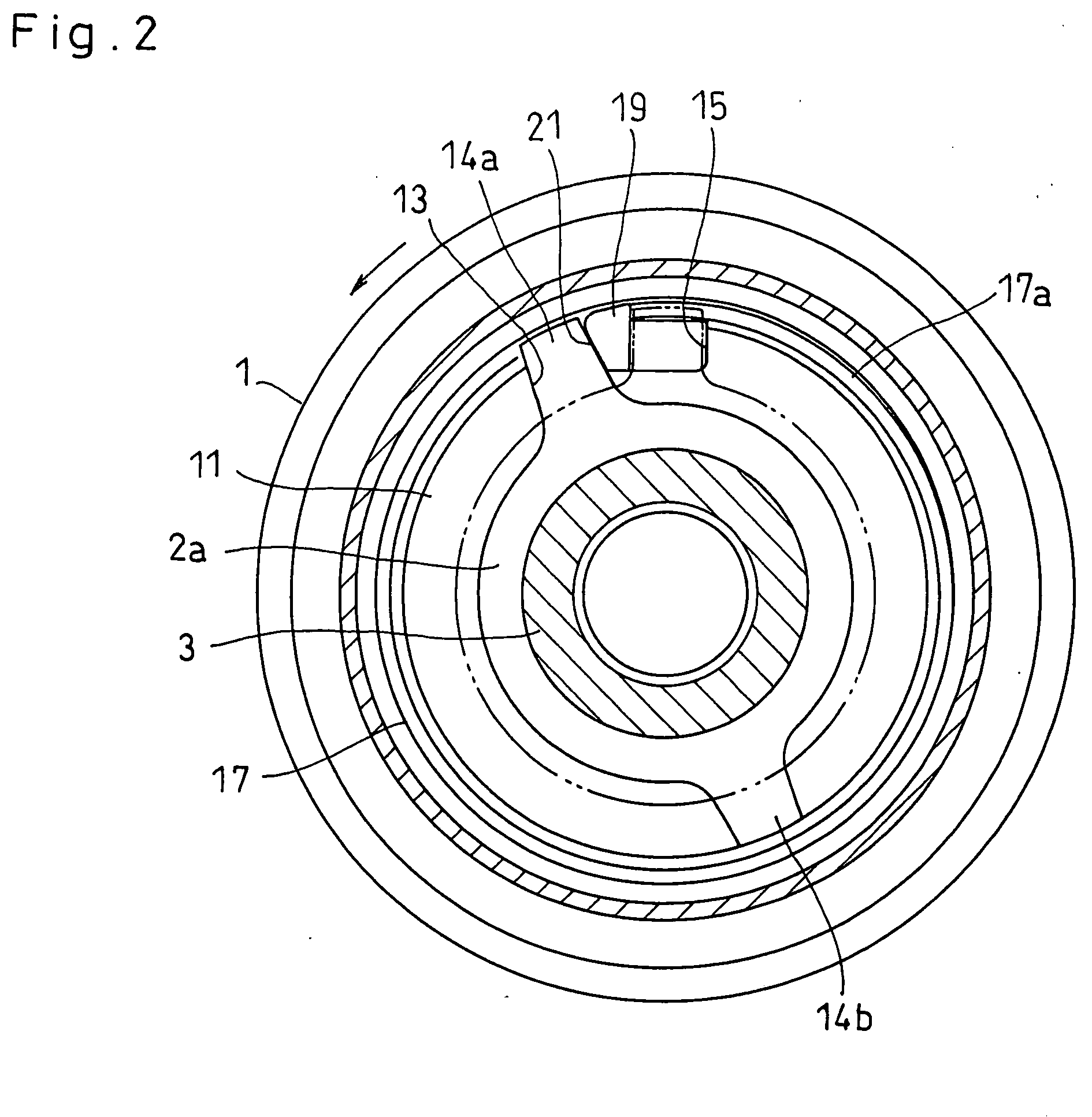
[0089]FIGS. 6 and 7 show a spring clutch according to this invention. In this embodiment, a pulley 1 as an input member and a pulley hub 2 as an output member are supported by a bearing 5 mounted at one end of the pulley 1 so as to be relatively rotatable. The pulley 1 has an radially inner cylindrical clutch surface 16 which is formed with a large-diameter recess 24 at its end near the bearing 5.
[0090]A clutch spring 17 in the form of a coil spring is mounted in a radially compressed state in the pulley 1 and has a clutch portion 17c at a position opposite to the clutch surface 16 which is in elastic contact with the clutch surface 16. The clutch spring 17 has a damper portion 17d at a position opposite to the large-diameter recess 24. The damper portion 17d has its end portion fitted on a small-diameter spring fitting surface 11a formed on a flange 11 provided at one end of the pulley hub 2 and has its extreme end inserted and engaged in a spiral groove 30 opening to the spring fi...
fifth embodiment
[0108]FIGS. 16 to 18 show a spring clutch according to the invention. In this embodiment, an elastic ring 50 is mounted in place of the cover ring 40 to supplement the spring rigidity of the portion of the clutch spring 17 near the torque transmission end.
[0109]The elastic ring 50 is formed with a cut 52 at a portion of the circumference of a cylindrical member 51. As shown in FIG. 17, between the elastic ring 50 and the large-diameter recess 24, there is formed a gap 5 of such a size that even if the pulley 1 is loaded with the maximum design torque (that is, maximum allowable torque to the spring clutch) and the elastic ring 50 expands, the outer periphery of the elastic ring 50 does not contact the-inner periphery of the large-diameter recess 24.
[0110]As shown in the fifth embodiment, by mounting the elastic ring 50 at the portion of the clutch spring 17 including the torque transmission end, the spring rigidity of this portion of the clutch spring 17 increases. This makes it pos...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com