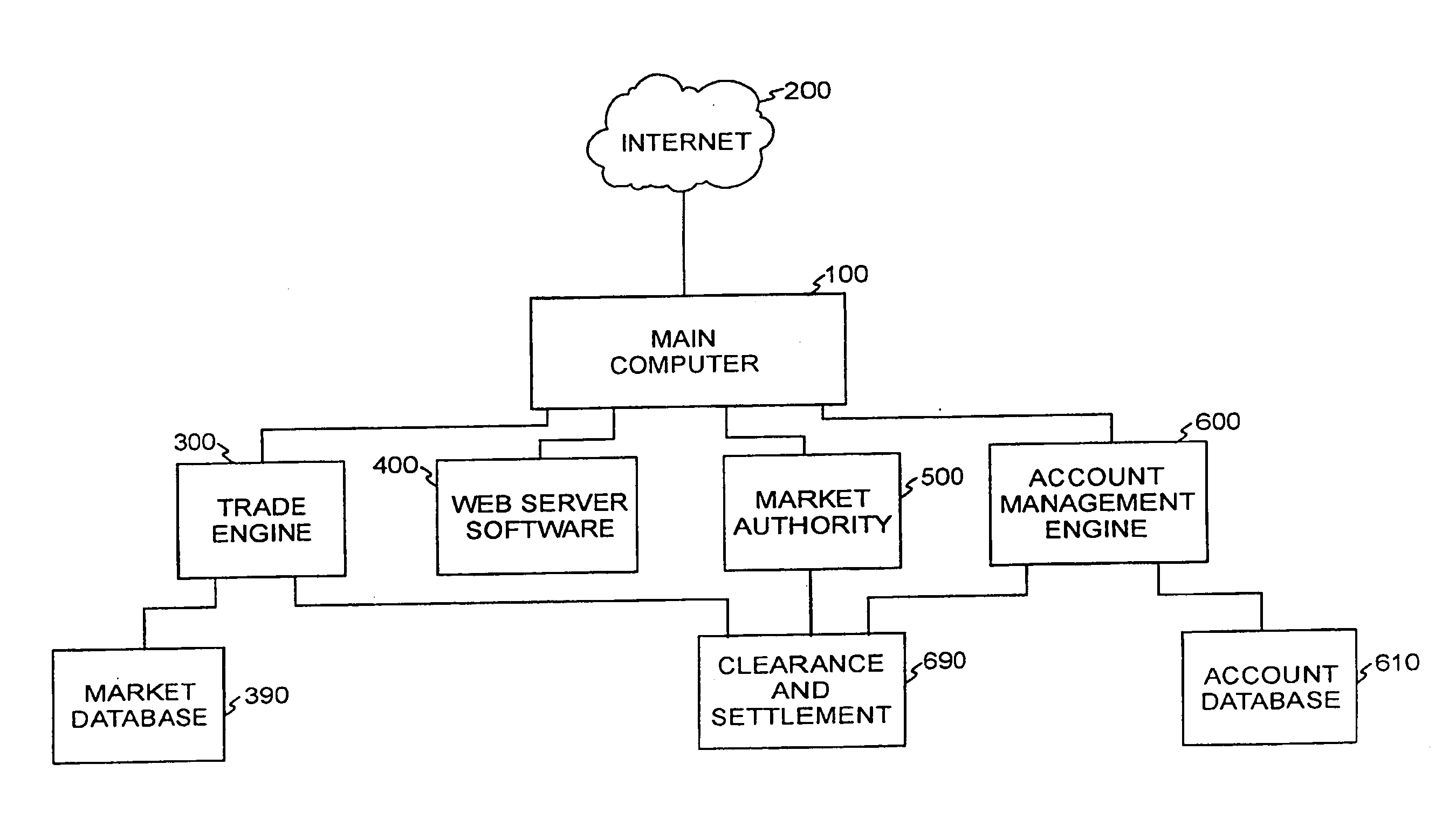
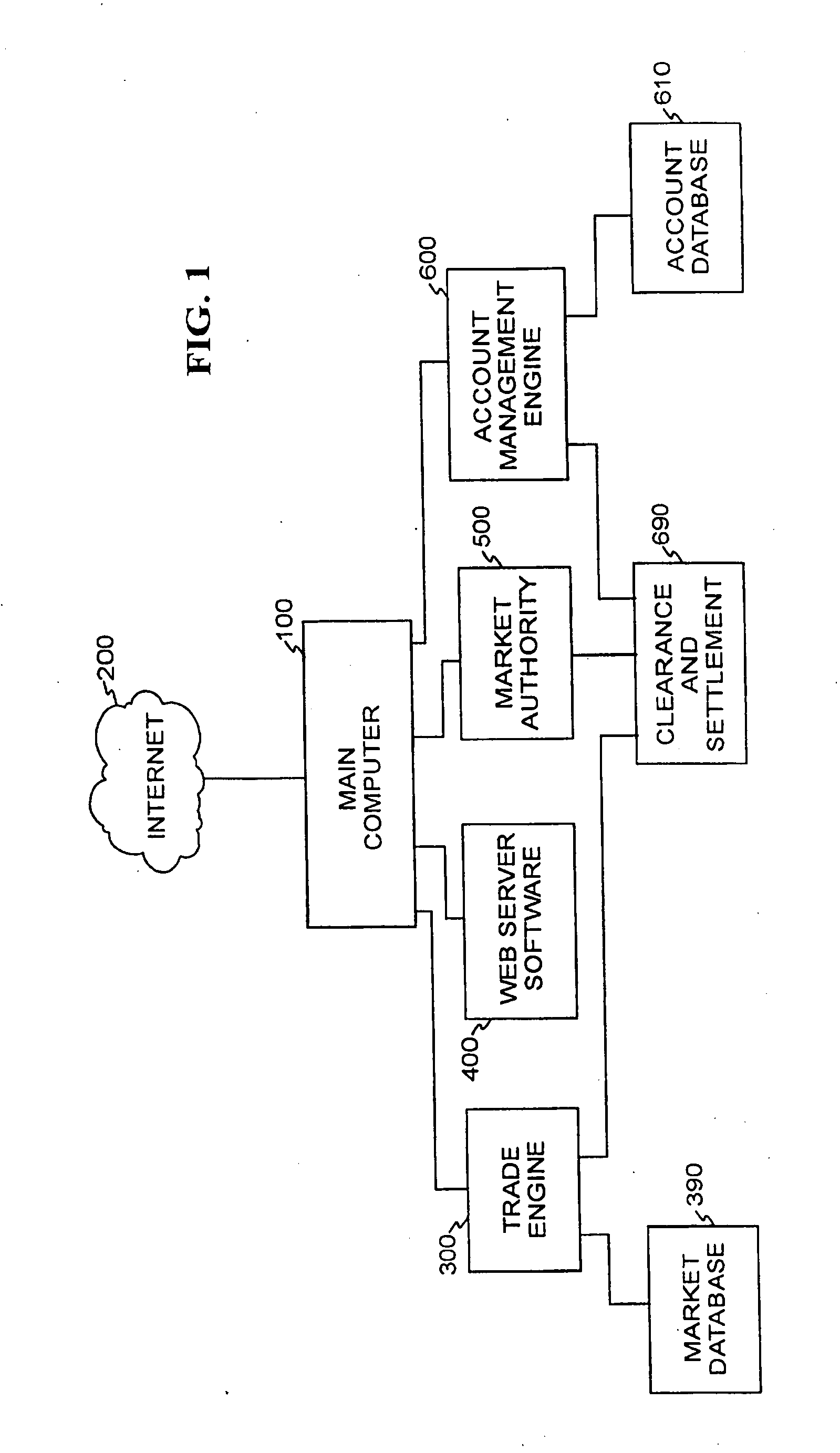
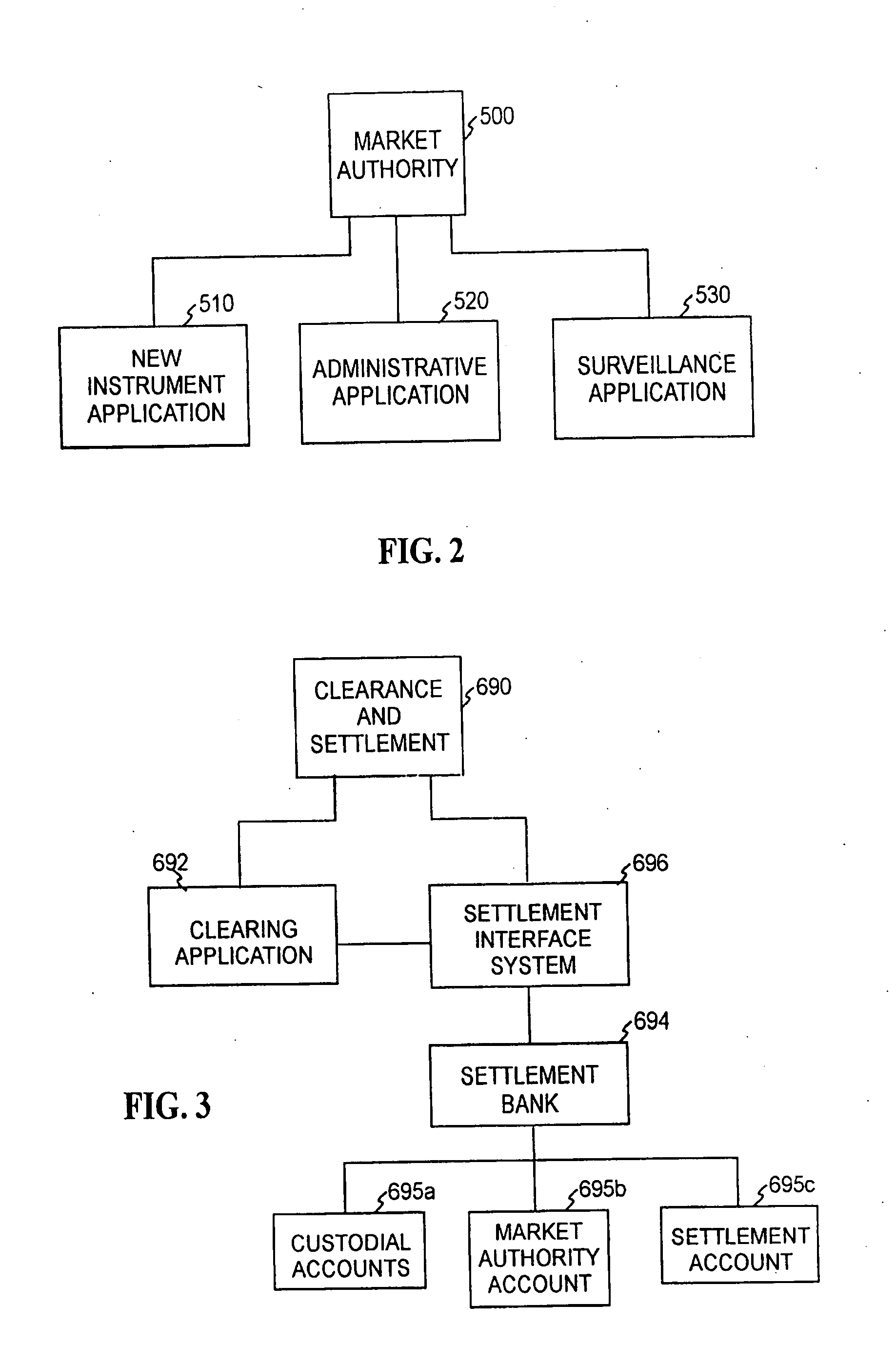
Methods and apparatus for formulation, initial public or private offering, and secondary market trading of risk management contracts
a risk management contract and market technology, applied in the field of method and apparatus for establishing and maintaining a market for initial and secondary trading in risk management instruments, to achieve the effect of zero trading volum
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Inventory Futures for Supply Chain Management
[0371] Nike faces a persistent “supply chain” problem for its designer shoes. If a shoe store in Germany orders 1000 pairs of a particular design, it takes Nike several months to buy the raw materials, manufacture that lot (usually in an Asian factory), and transport it cost effectively (usually by cargo ship) to Germany. The problem is compounded because (i)
[0372] Nike has outlets all over the world; (ii) the popularity of different designs vary greatly around the world; (iii) fads change in geographically-idiosyncratic ways in different geographical markets. For instance, a German store might believe in March that red Michael Jordan designs will become popular next Christmas and order 1000 pairs. However, in September it turns out that white shoes are the rage in Germany, and the German store can no longer sell the red shoes. However, suppose a red shoe fad takes hold in Brazil, and a Canadian outlet is willing to cancel its order of ...
example 2
Mutual Fund Cash Flow Management
[0378] Open end mutual funds have problems with cash flow. In such funds, investors have the right to buy or redeem more shares at will. Therefore, depending on market sentiment, these funds face either mass redemptions (and thus a cash shortage) or mass purchases (and thus cash surpluses due to excess inflows of investor cash). These wide swings in cash force mutual funds to alter their investment behavior. When they have a cash shortage, they are forced to sell shares. When there is a cash surplus, funds are pressured to making additional investments. However, these forced sales and purchases may be suboptimal. For instance, when the market crashes, investors tend to redeem their shares, which forces mutual funds with long positions to sell equity at lower prices that they otherwise would want to.
[0379] There are widely publicized indices which measure net cash inflow (NCI) or redemptions each month. Based on these indices, A Market Authority acti...
example 3
Risk-Sharing Management
[0385] Firms A, B, and C are insurance companies that are liable for $1.0 billion of housing reconstruction in event of an earthquake in Los Angeles and firms X, Y, and Z are housing construction companies in Los Angeles.
[0386] Firms A, B, and C are risk complements to X, Y, and Z in the following sense. While an earthquake is financially devastating for A, B, and C, they create windfall profits for X, Y, and Z. A, B, and C and X, Y, and Z could reduce their financial volatility by pooling their risks so that, regardless of whether an earthquake occurs or not, each are guaranteed of a medium outcome.
[0387] These six firms can hedge each other's risk by forming a private market to trade the following two contracts: [0388] Contract I which pays $10 if there is a 7.0 or greater earthquake in Los Angeles during year 2002, and $0 otherwise. [0389] Contract II which pays $10 if there is not a 7.0 or greater earthquake in Los Angeles during year 2002, and $0 other...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com