Knitted net for enveloping round bales, and method and device for the production thereof
a technology of round bales and knitted nets, applied in the field of knitted nets, can solve the problems of reducing affecting the elasticity of round bales, and affecting the elasticity of elastic marginal threads, so as to prevent the bending of round bales in the edge region
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
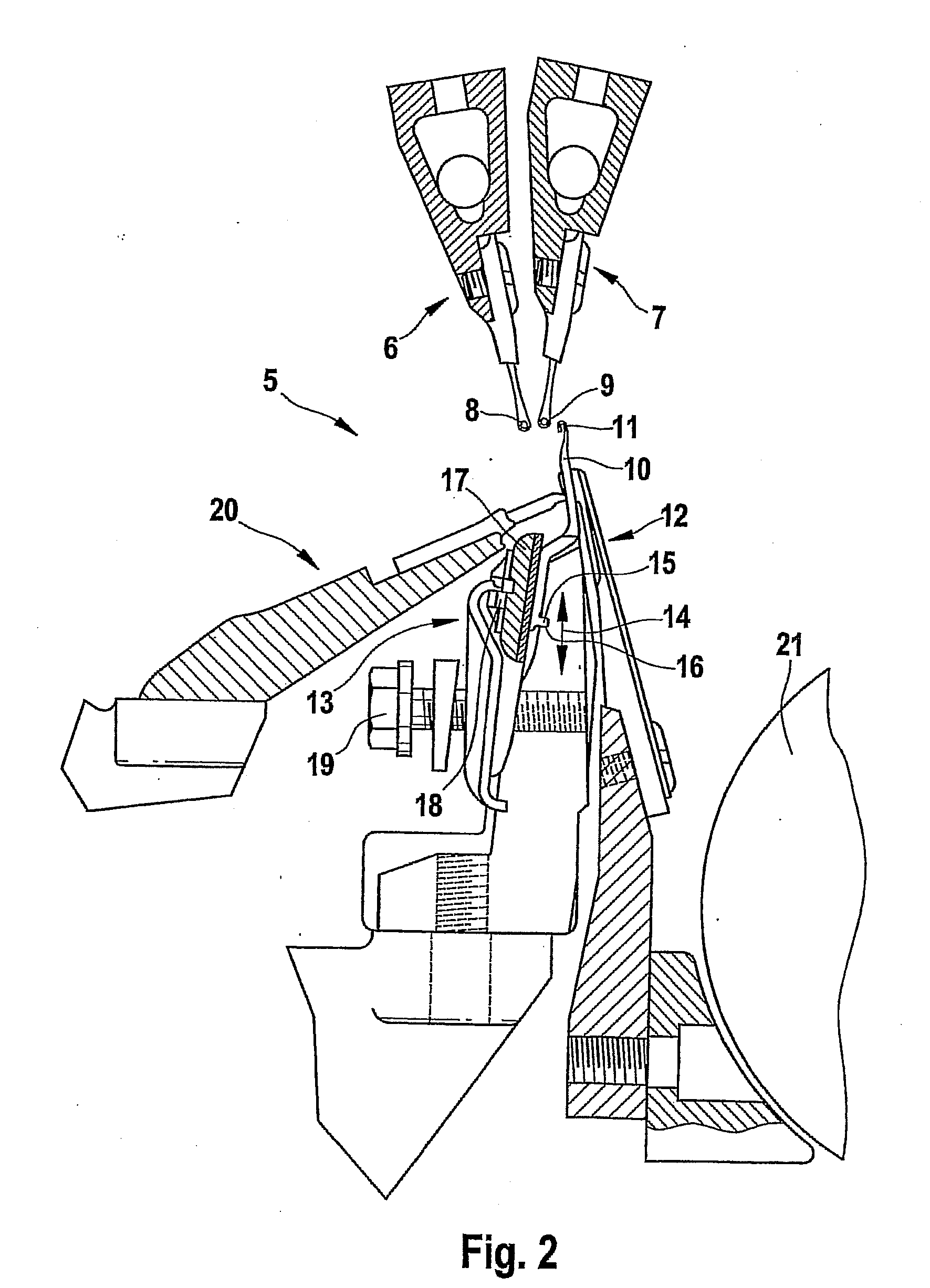
Embodiment Construction
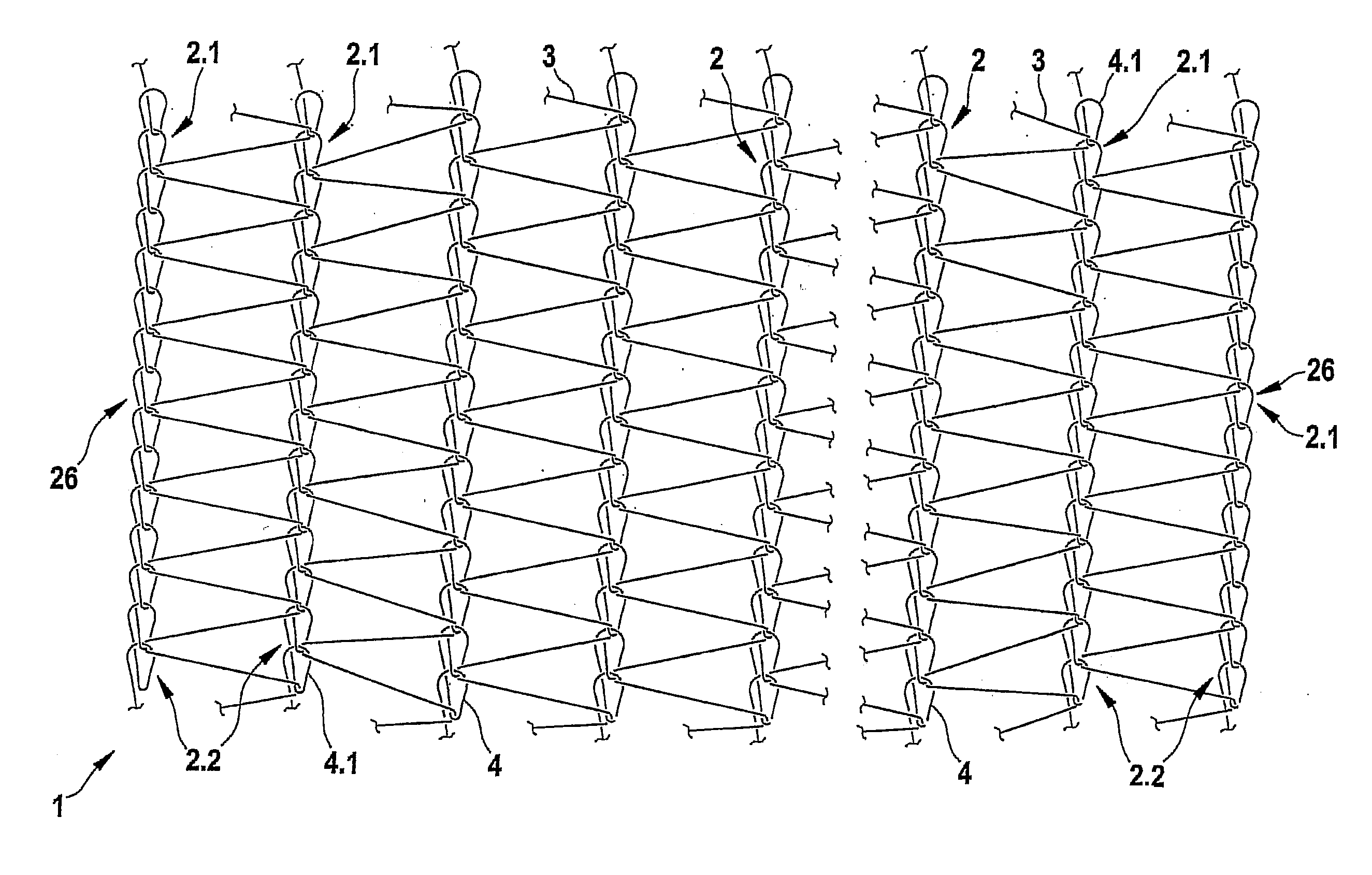
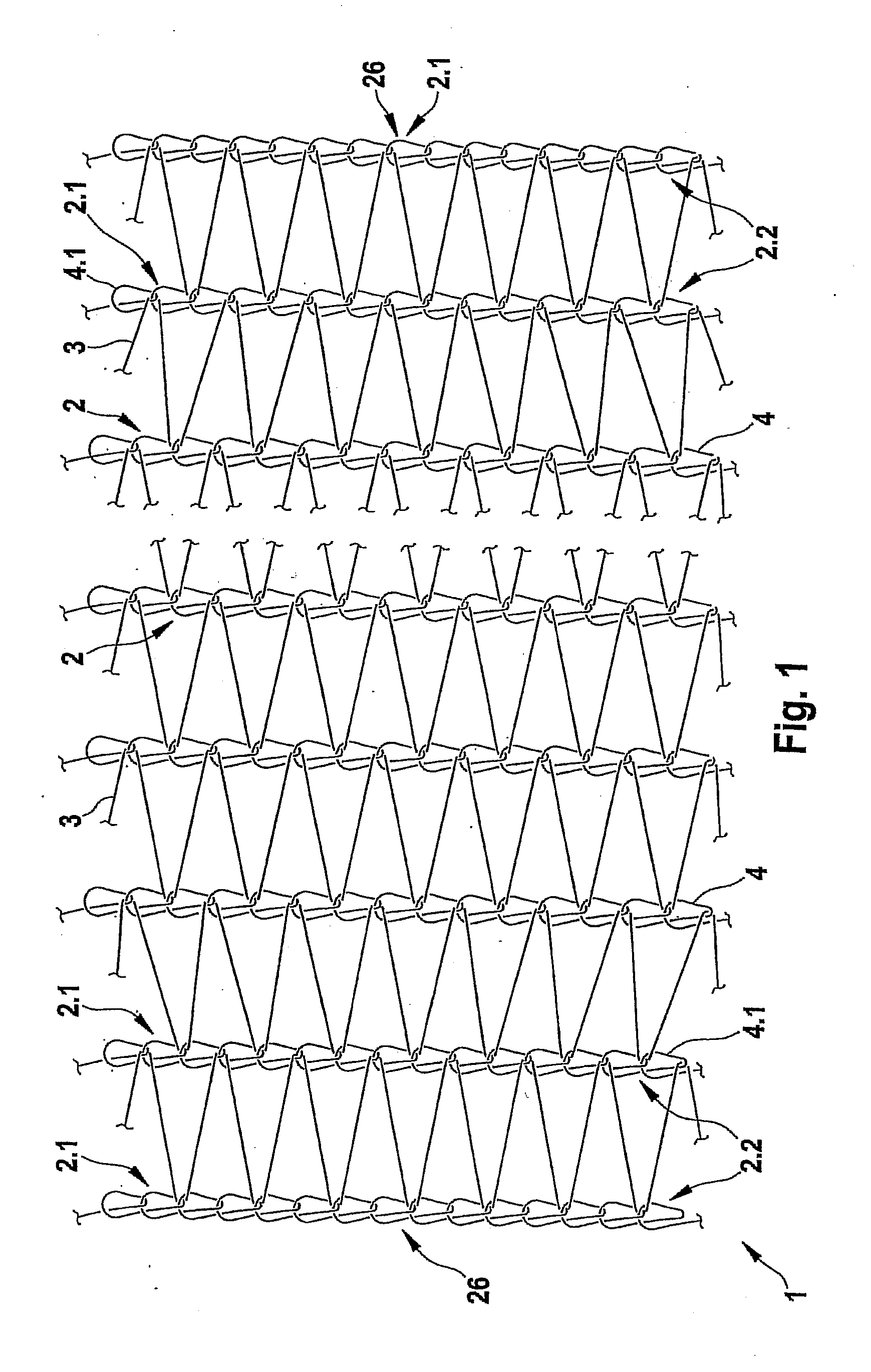
[0038]FIG. 1 shows a knitted netting having shorter fringes in a knitting region.
[0039] A knitted netting 1 comprises fringes 2 and weft threads 3. The fringes 2 are in this instance knitted in each case from a longitudinal thread. In a preferred embodiment, the longitudinal threads from which the fringes 2 are knitted and the weft threads 3 are polyolefin strips which are cut from a polyolefin film and subsequently drafted.
[0040] To produce the fringes 2, loops 4 are formed from the longitudinal thread, through which loops the longitudinal thread is drawn so as to form a new loop. A loop through which the longitudinal thread is drawn so as to form a further loop is designated in general as a stitch.
[0041] The netting 1 illustrated in FIG. 1 is what is known as a Raschel netting in which the weft threads 3 run in each case in a “zigzag” manner between two fringes 2. A fastening of the weft thread 3 and the fringe 2 takes place in that the weft thread 3 is drawn through a stitch o...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Distance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com