Catalyst deterioration detecting system and catalyst deterioration detecting method of internal combustion engine
a technology of catalyst deterioration and detection system, which is applied in the direction of engines, machines/engines, mechanical equipment, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the oxygen storage capacity of the catalyst, and affecting the performance of the catalys
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
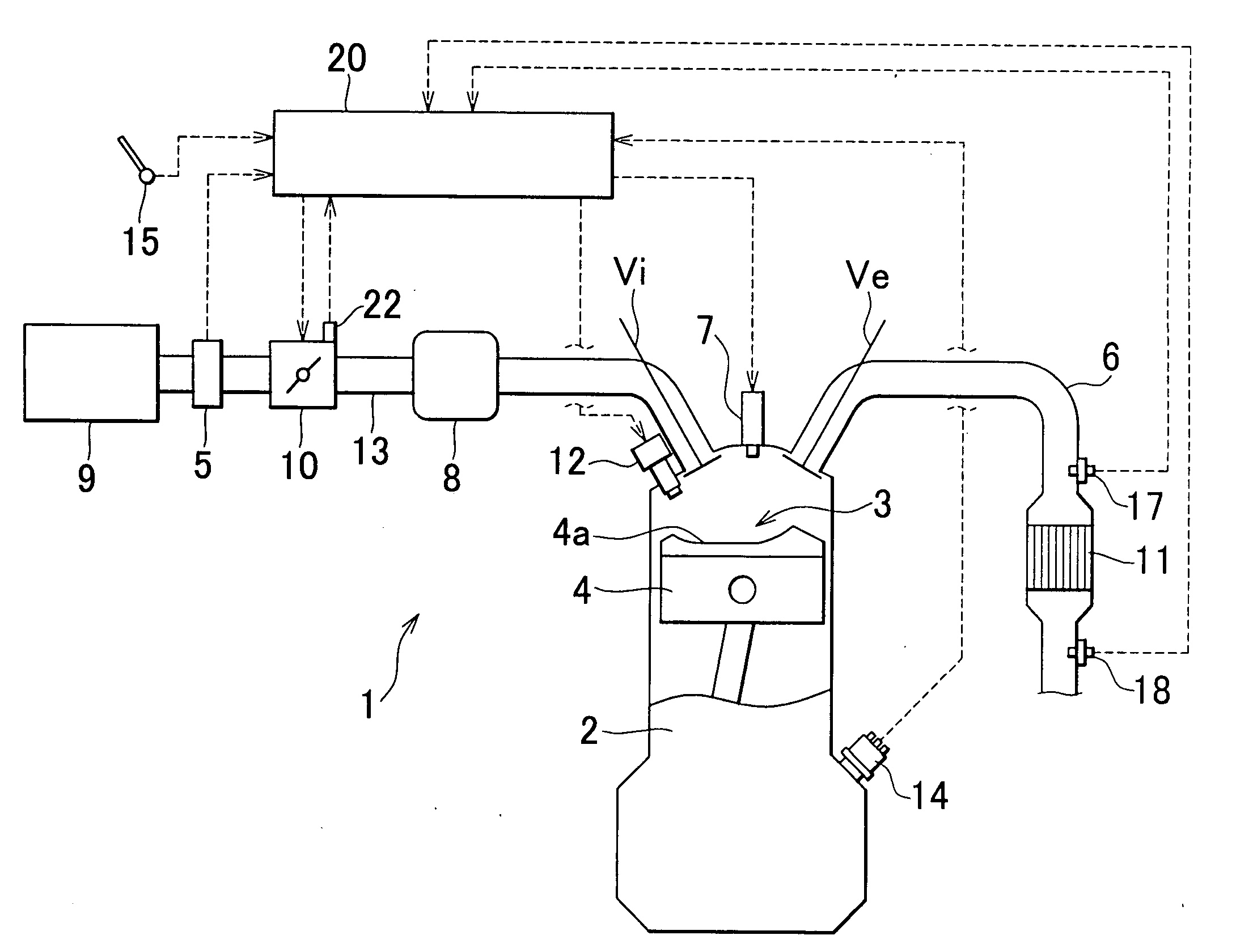
[0074]In the following, detection of catalyst poisoning will be explained with reference to FIG. 6. The ECU 20 repeatedly executes the routine of the process illustrated in FIG. 6 at certain time intervals.
[0075]Initially, it is determined in step S101 whether preconditions for measurement of the oxygen storage capacity along with execution of the active air / fuel ratio control are satisfied. The preconditions, which are similar to the above-described preconditions for execution of catalyst deterioration detection, are satisfied if the engine 1 is in normal (or steady-state) operating conditions and the catalyst temperature is in a certain activation temperature range. If the conditions are not satisfied, the process of FIG. 6 is finished. If the conditions are satisfied, on the other hand, the ECU 20 proceeds to step S102.
[0076]In step S102, an estimated value of the catalyst temperature Tc is acquired. In step S103, it is determined whether the estimated value of the catalyst temp...
third embodiment
[0090]In the third embodiment, therefore, poisoning of the catalyst is detected from the relationship between a change in the rich amplitude Ar and a change in the oxygen storage capacity OSC corresponding to the change in the rich amplitude Ar. More specifically, poisoning of the catalyst is detected based on the amount of change of the oxygen storage capacity between at least two points of rich amplitudes Ar.
[0091]Referring to FIG. 8, for example, when the rich amplitude Ar is equal to a relatively small first amplitude Ara, the same oxygen storage capacity OSCa is obtained in the case where the catalyst suffer poisoning and the case where the catalyst is free from poisoning. On the other hand, when the rich amplitude Ar is equal to a relatively large second amplitude Arb, the oxygen storage capacity is equal to OSCb1 where the catalyst is free from poisoning, while it is equal to OSCb2 that is smaller than OSCb1 where the catalyst suffers poisoning. Thus, the presence or absence ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com