Patents
Literature
6910results about "Exhaust treatment diagnostic devices" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
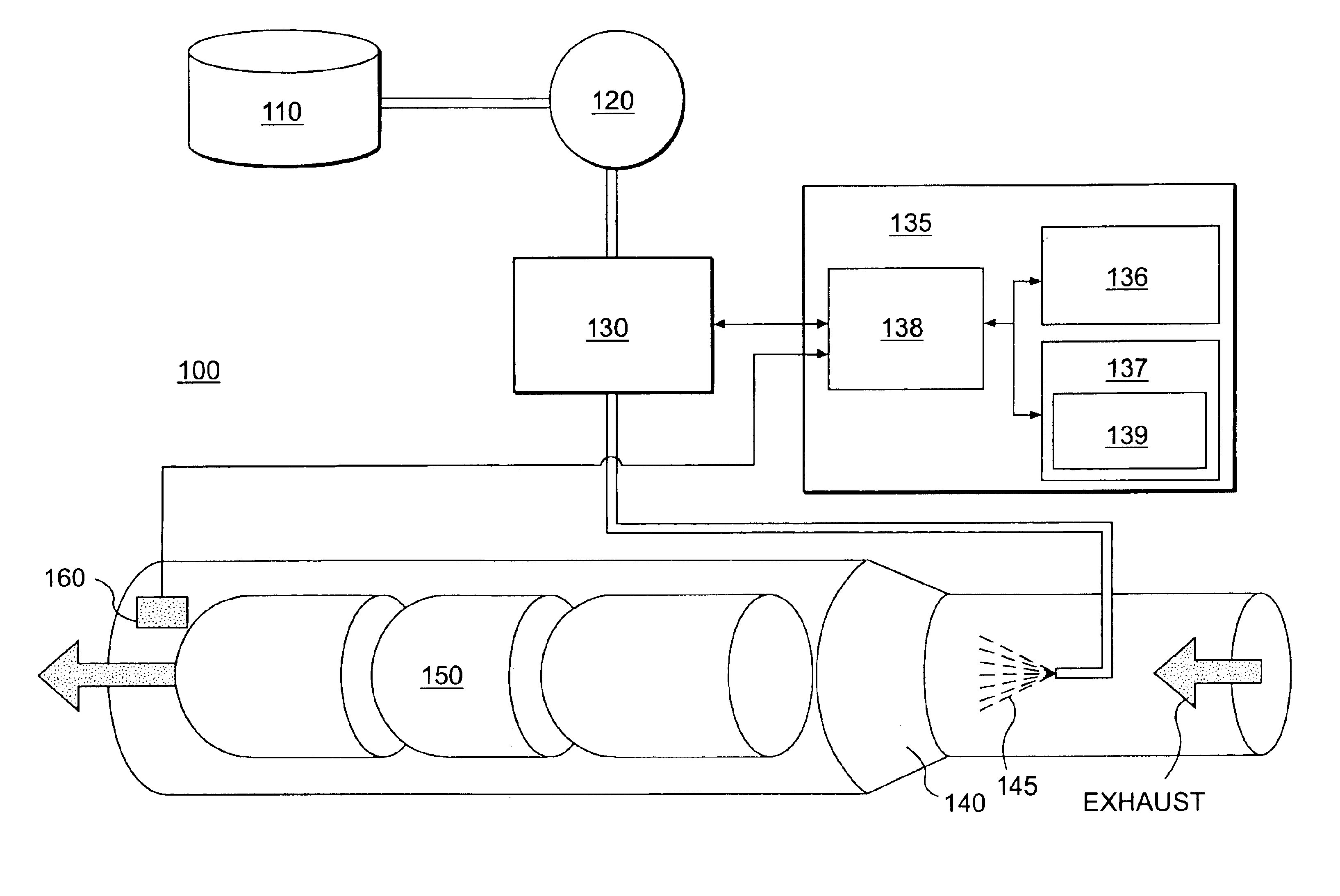
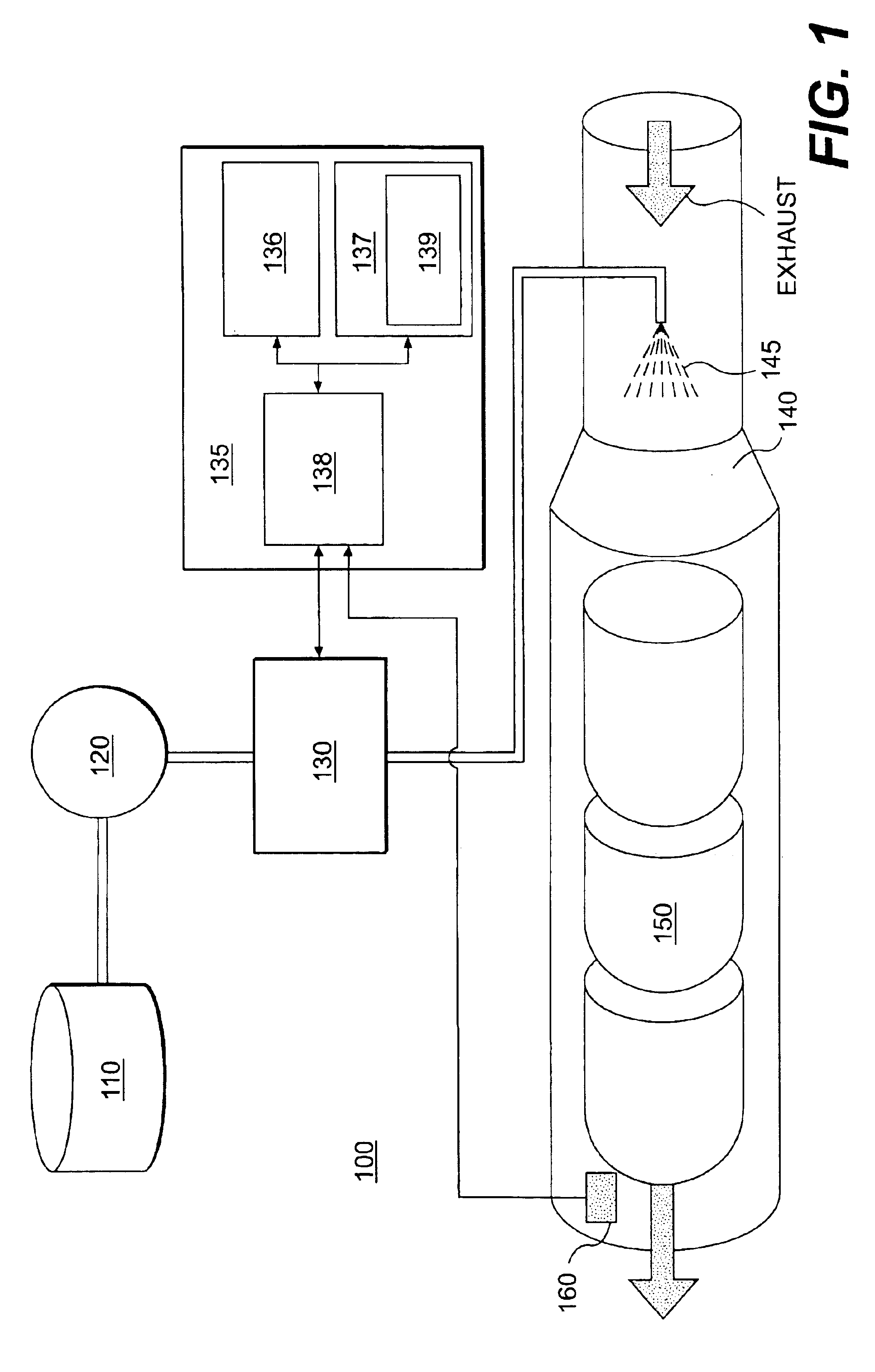
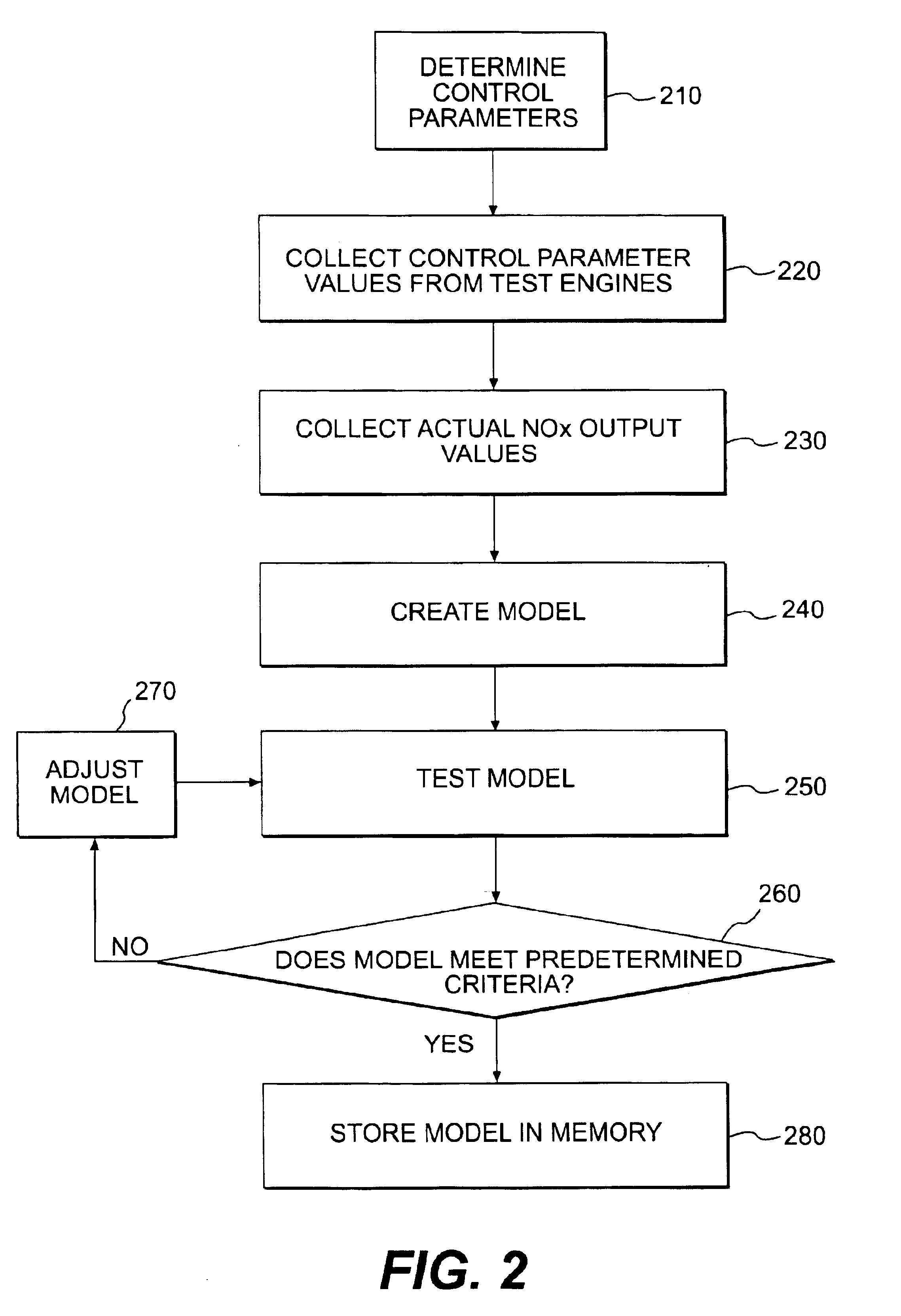
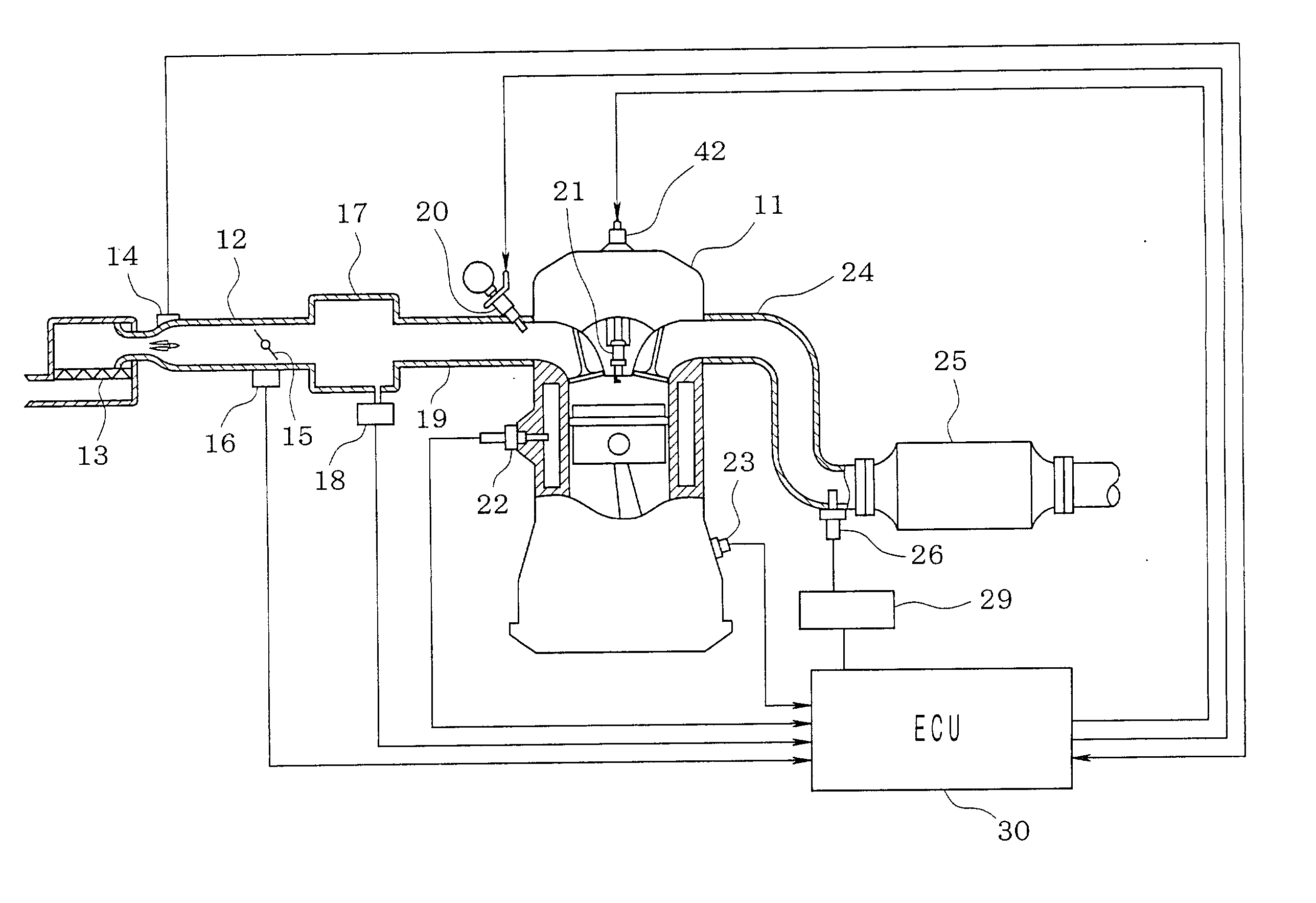
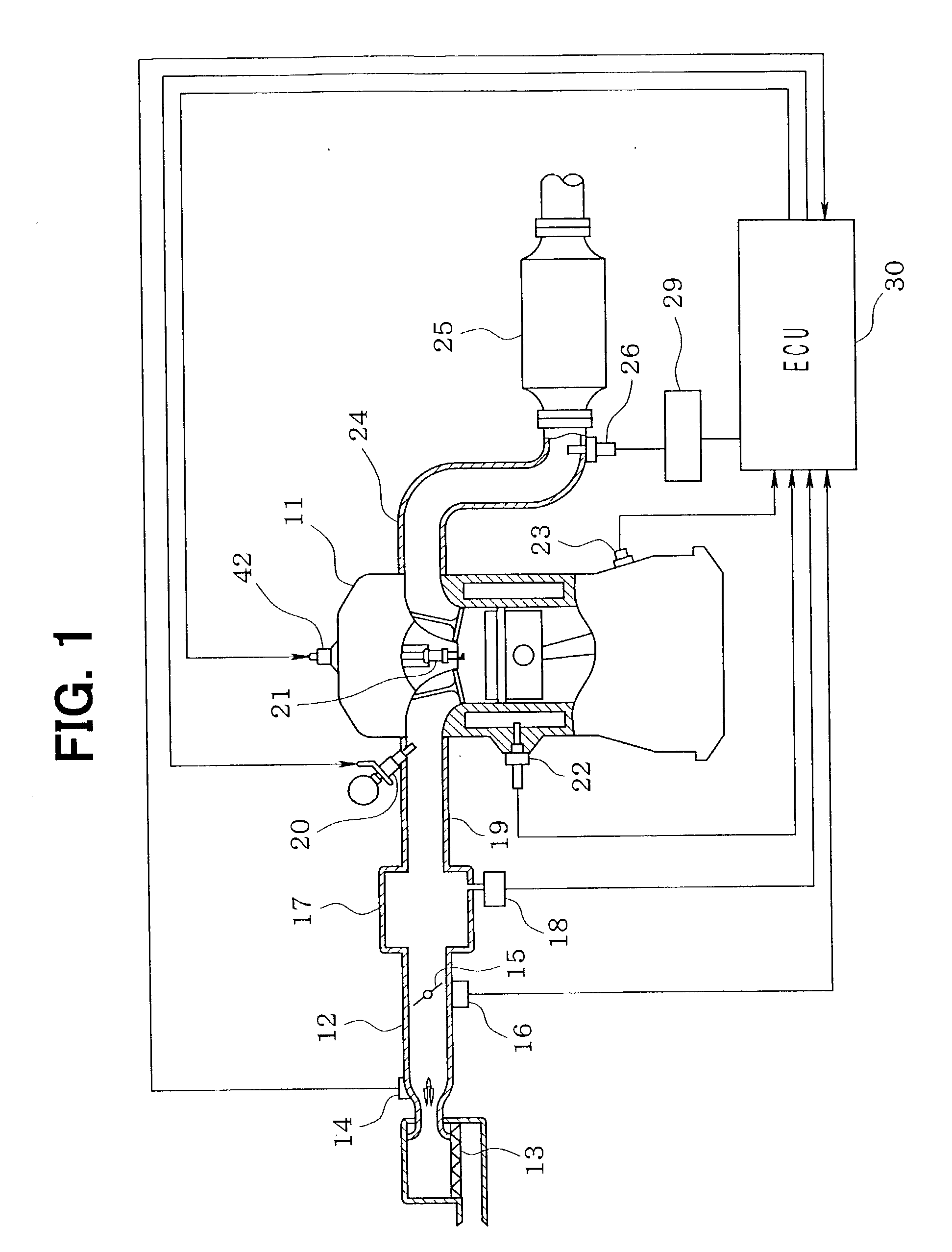
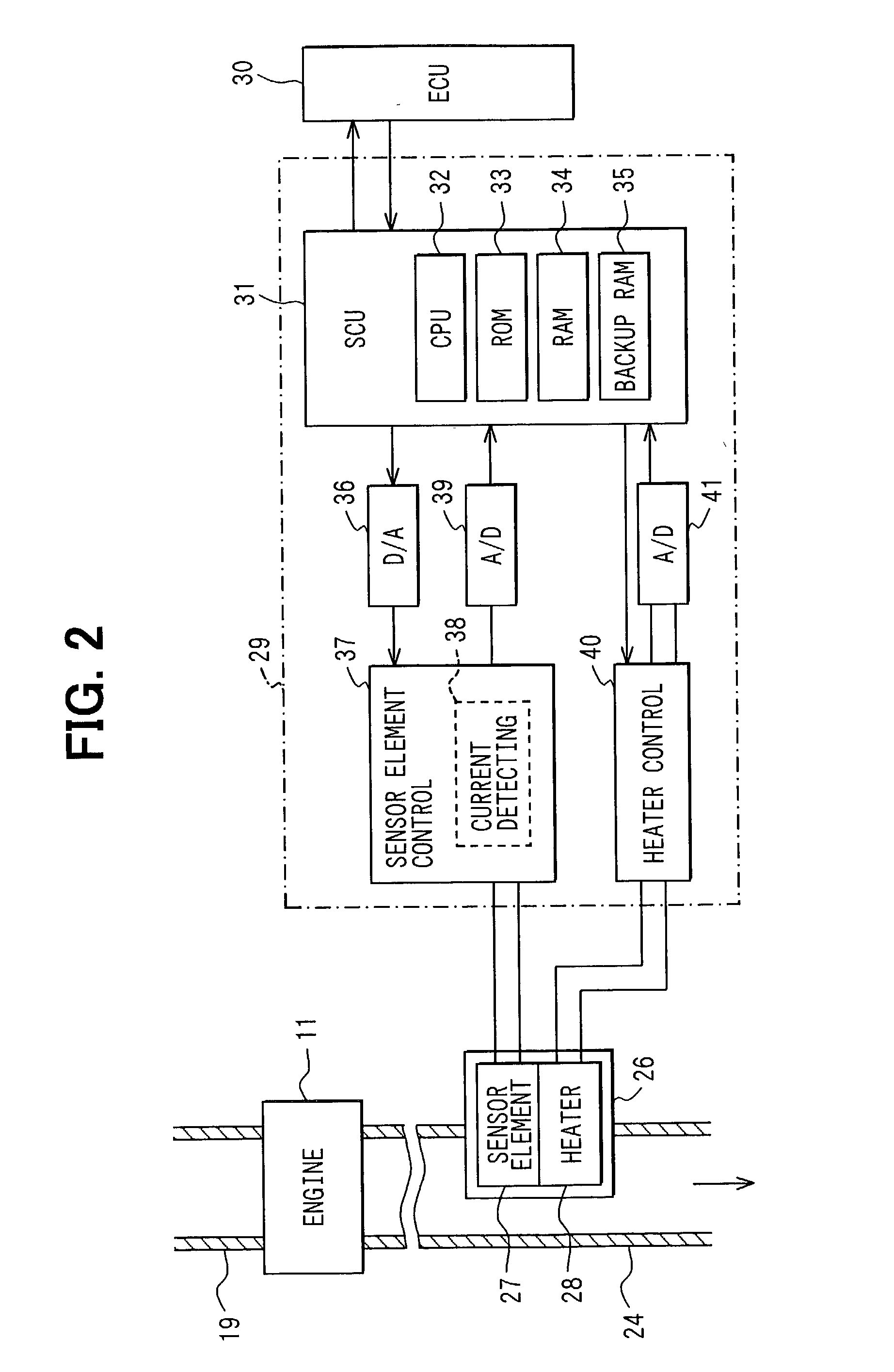
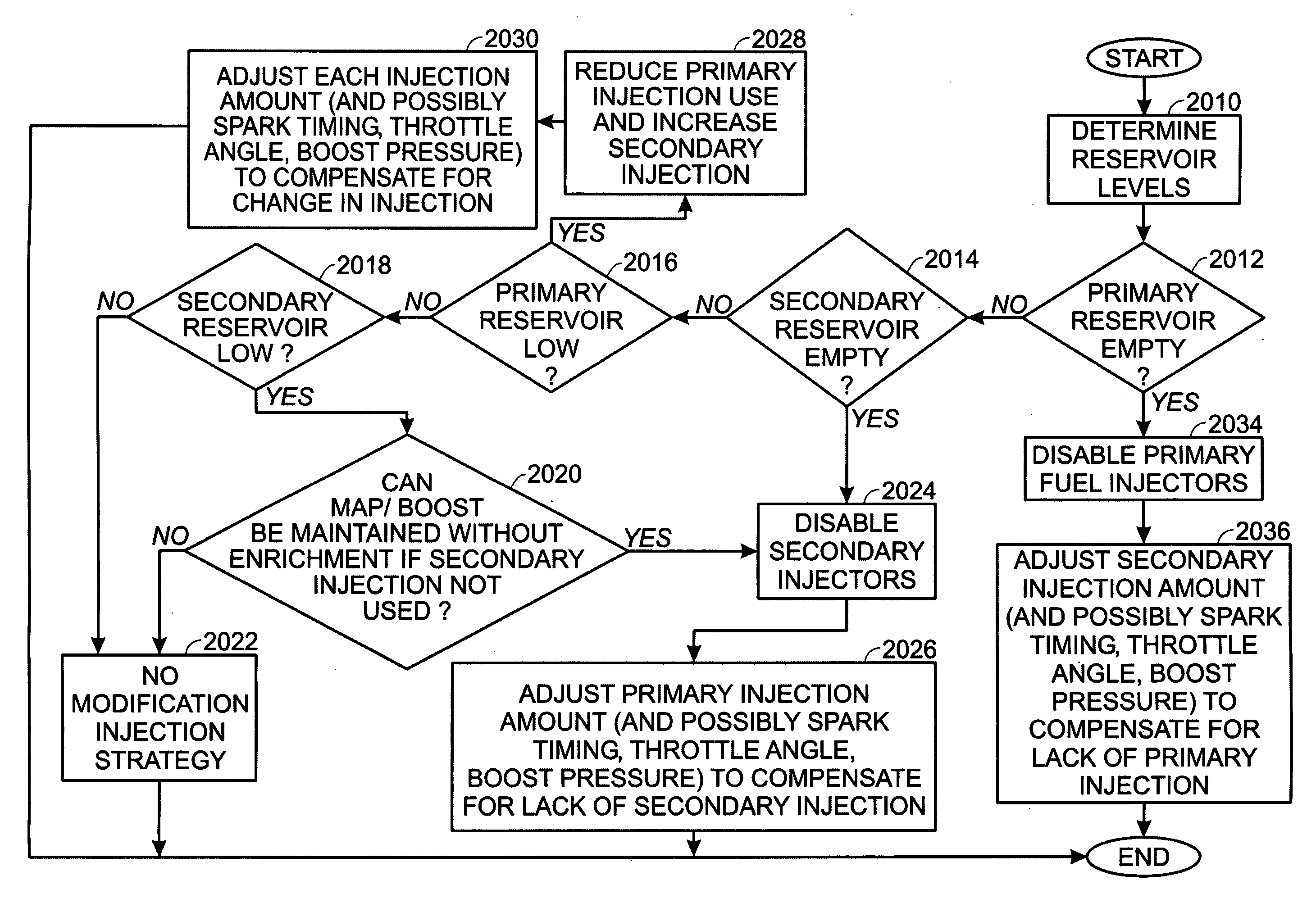
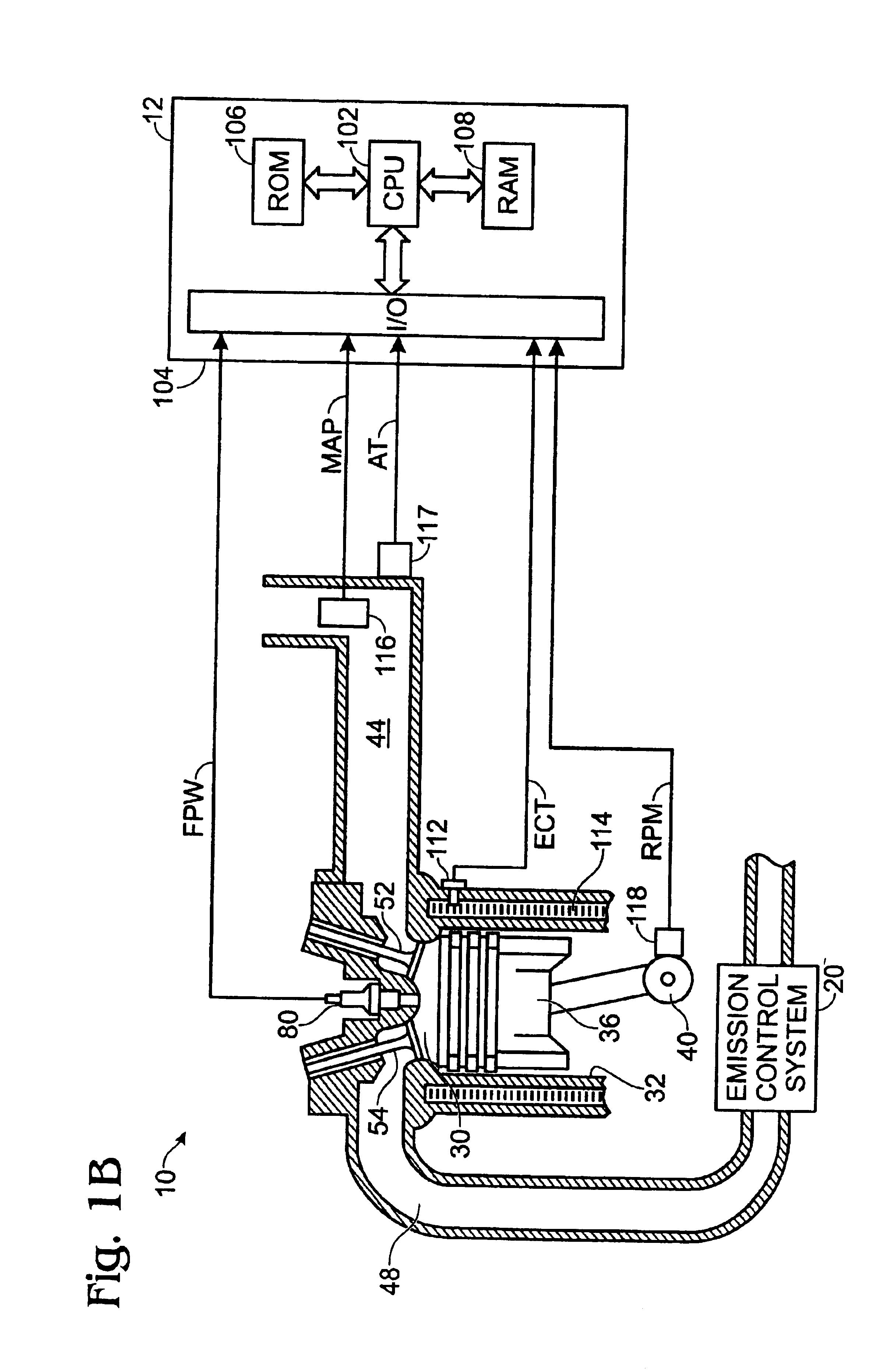
NOx emission-control system using a virtual sensor
InactiveUS6882929B2Reduce nitrogen oxide emissionsInternal combustion piston enginesDigital data processing detailsAmbient humidityControl system
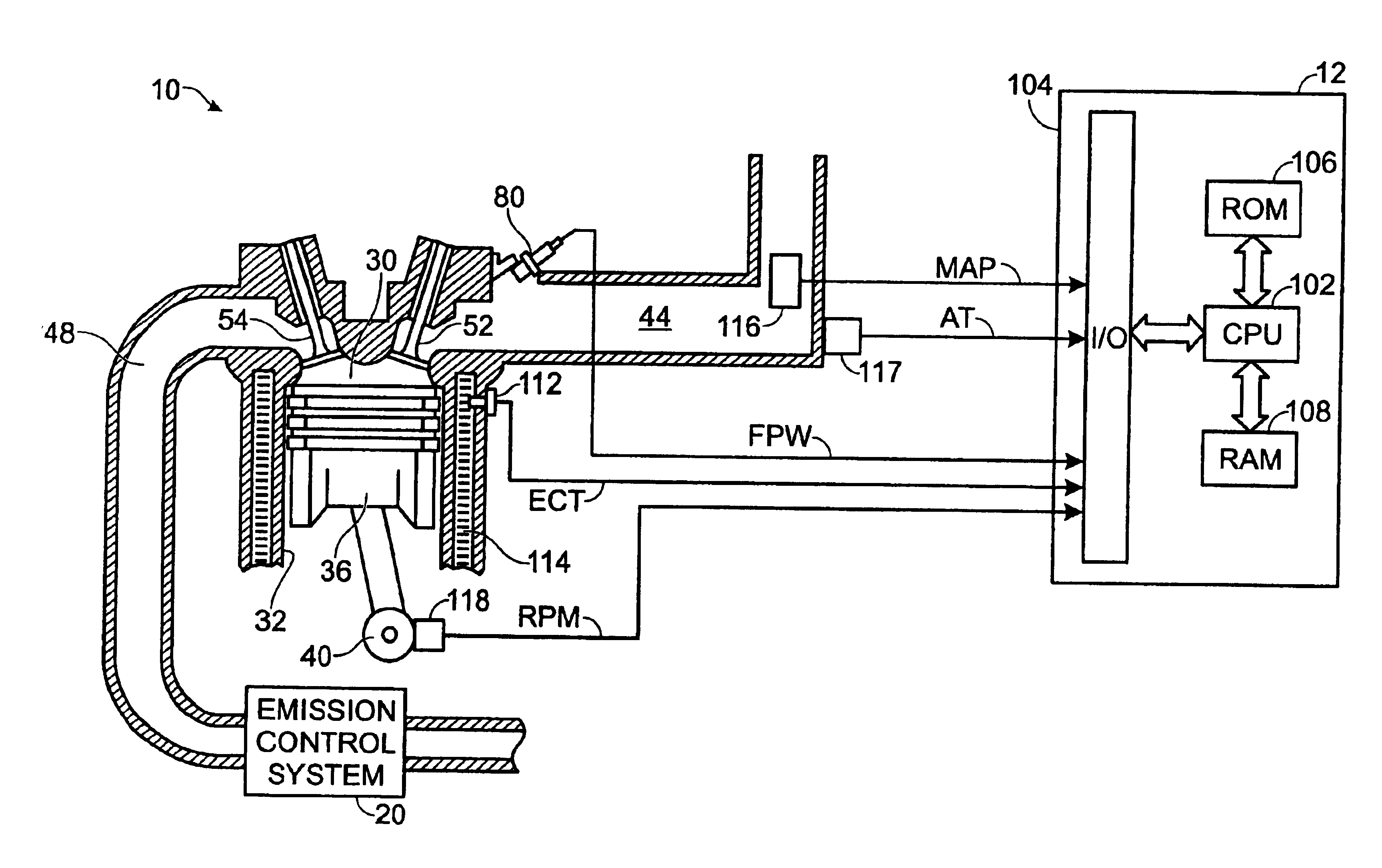
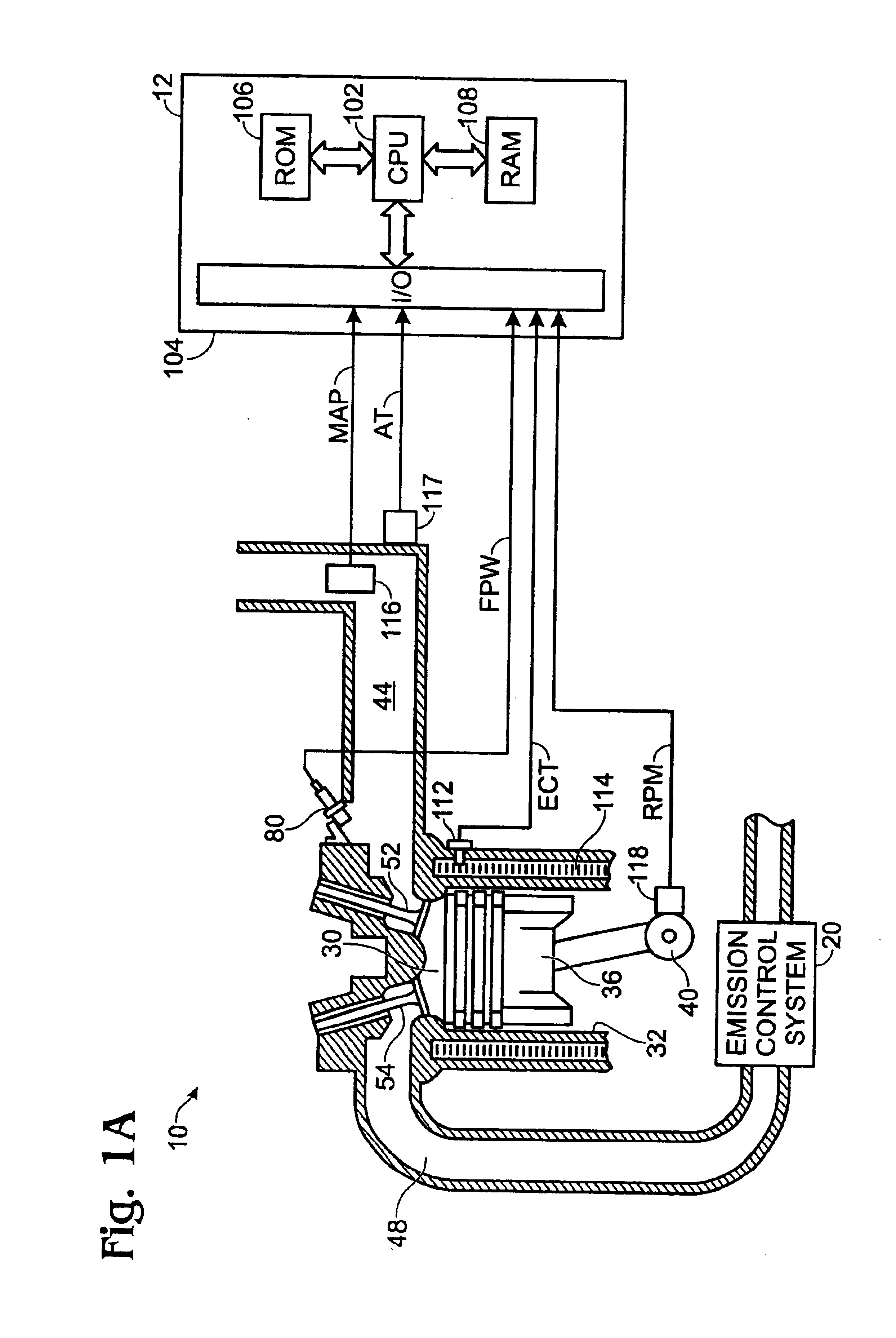
A method and system may be provided to perform a process for controlling NOx emissions of an target engine. In one embodiment of the invention, the process may include determining predicted NOx values based on a model reflecting a predetermined relationship between control parameters and NOx emissions, wherein the control parameters include ambient humidity, manifold pressure, manifold temperature, fuel rate, and engine speed associated with the engine. Further, the process may include adjusting the model based on a determination of whether the predicted NOx values meet a predetermined criteria associated with actual NOx values. The adjusted model may be stored in a memory associated with the engine whereby NOx emissions exhausted from the engine may be reduced based on virtual NOx emission values determined from the adjusted model.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Radio frequency process sensing, control, and diagnostics network and system
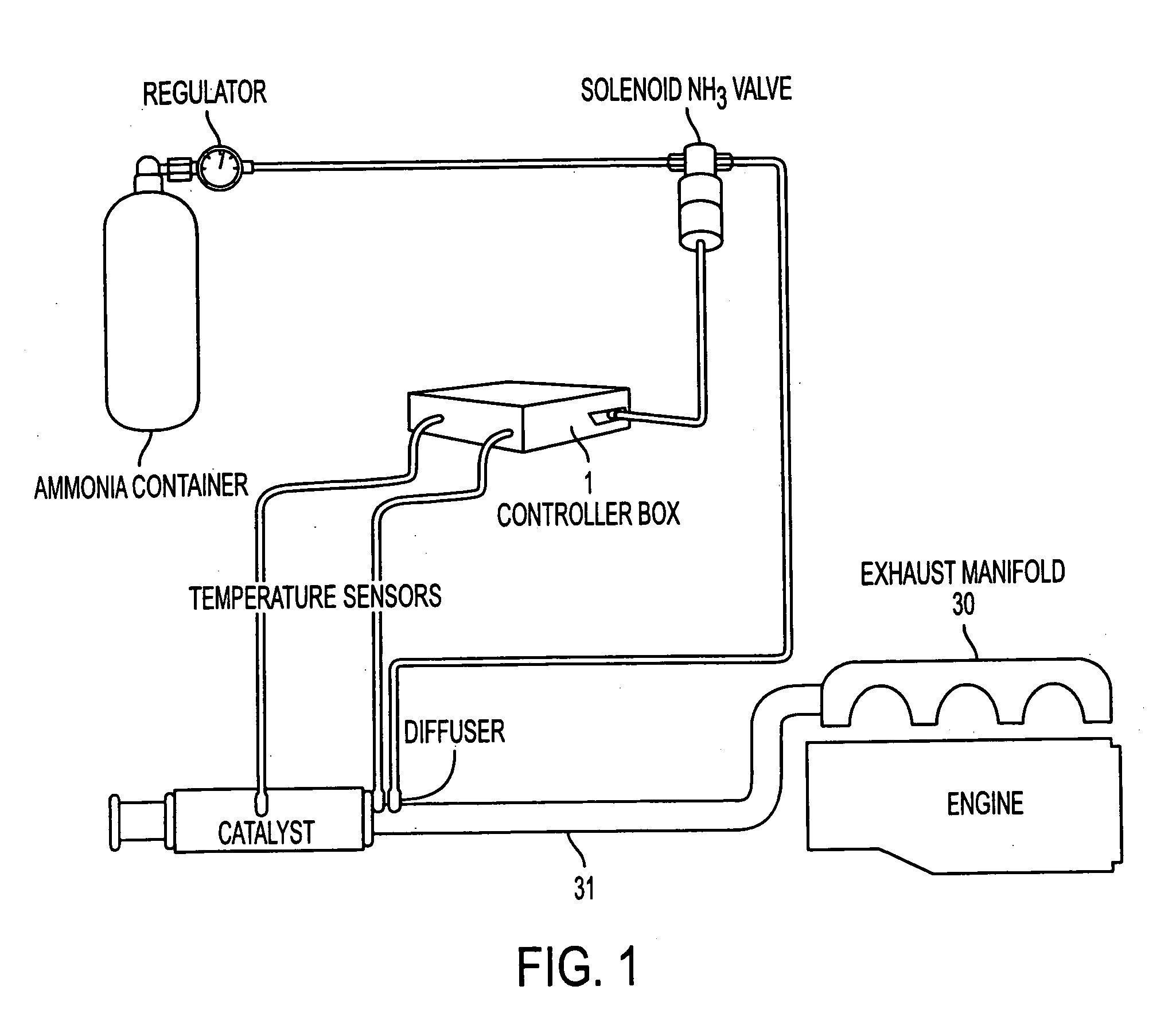
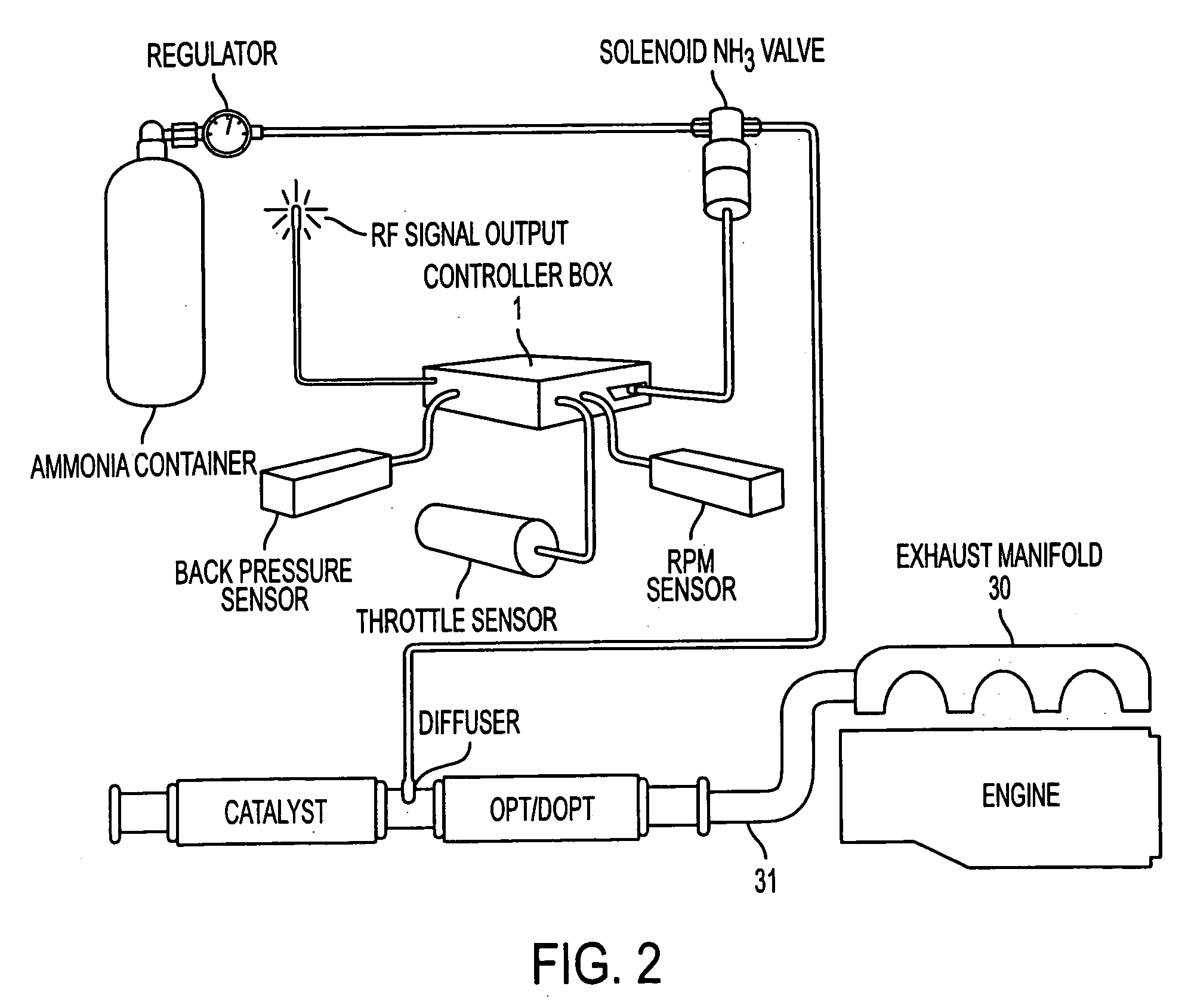
A radio frequency sensing, control, and particulate matter diagnostics network and system and method and, more specifically, a radio frequency particulate filter diagnostics system comprising a housing including an inlet connected to a source of particulate matter, a particulate filter in the housing and adapted for filtering the particulate matter, and a radio frequency sensor adapted to detect conditions of abnormal particulate filter or system operation and including at least one radio frequency probe configured to be in contact with the housing for the particulate filter housing and adapted to receive radio frequency signals and a radio frequency control unit in communication with the radio frequency probe.
Owner:CTS CORP ELKHART
Method for controlling injection timing of an internal combustion engine
InactiveUS7278396B2Reduce mixEmission reductionElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesExternal combustion engineIgnition timing
A method to control injection timing for an internal combustion engine having a plurality of injectors in at least a cylinder, the method comprising of injecting a first fuel amount to at least a cylinder of an internal combustion engine from a first injector, injecting a second fuel amount fuel to said cylinder from a second injector, and adjusting the timing between starting or ending injection of said first fuel amount, and starting or ending of said second fuel amount in response to an operating condition of said engine.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
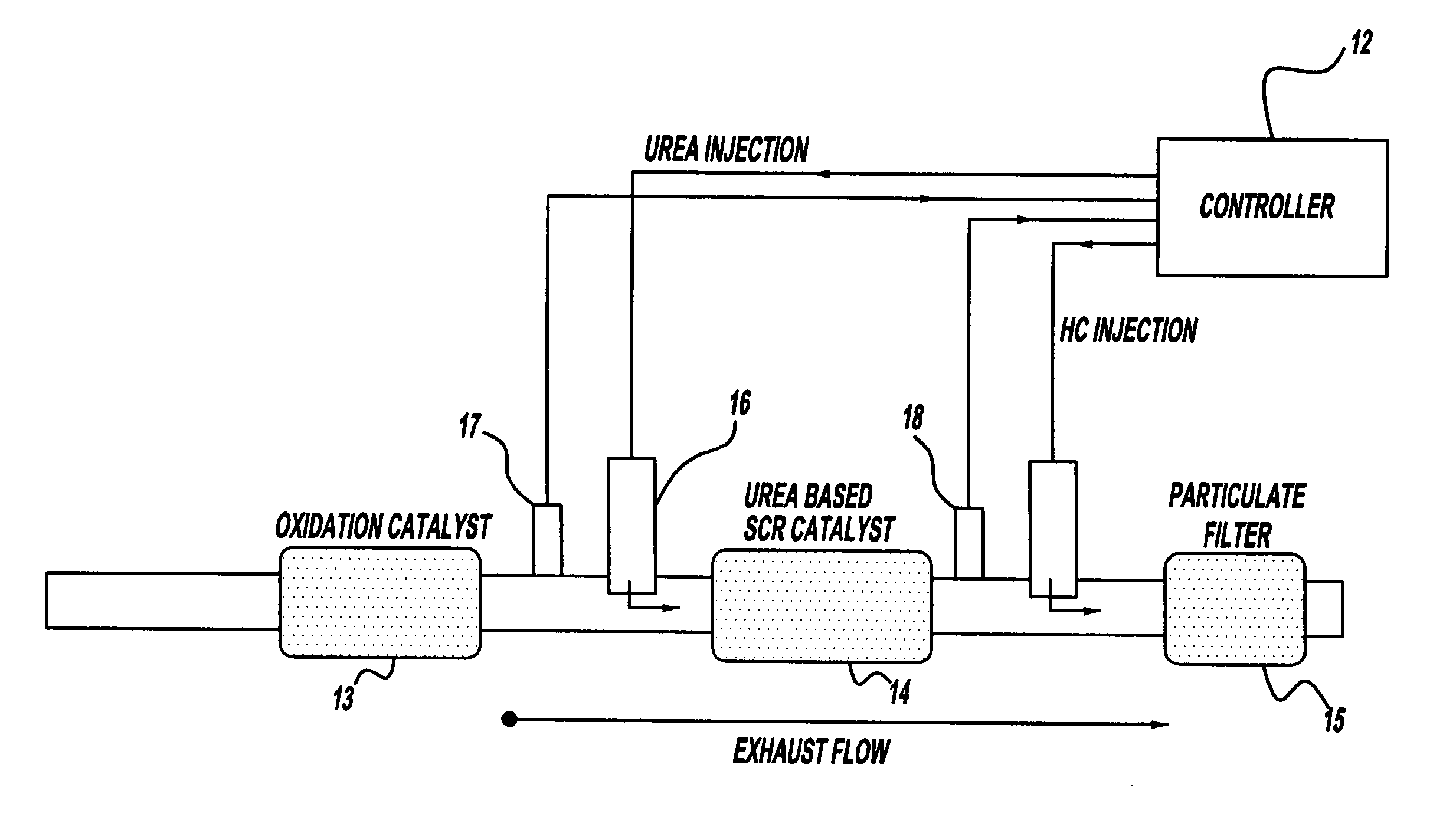
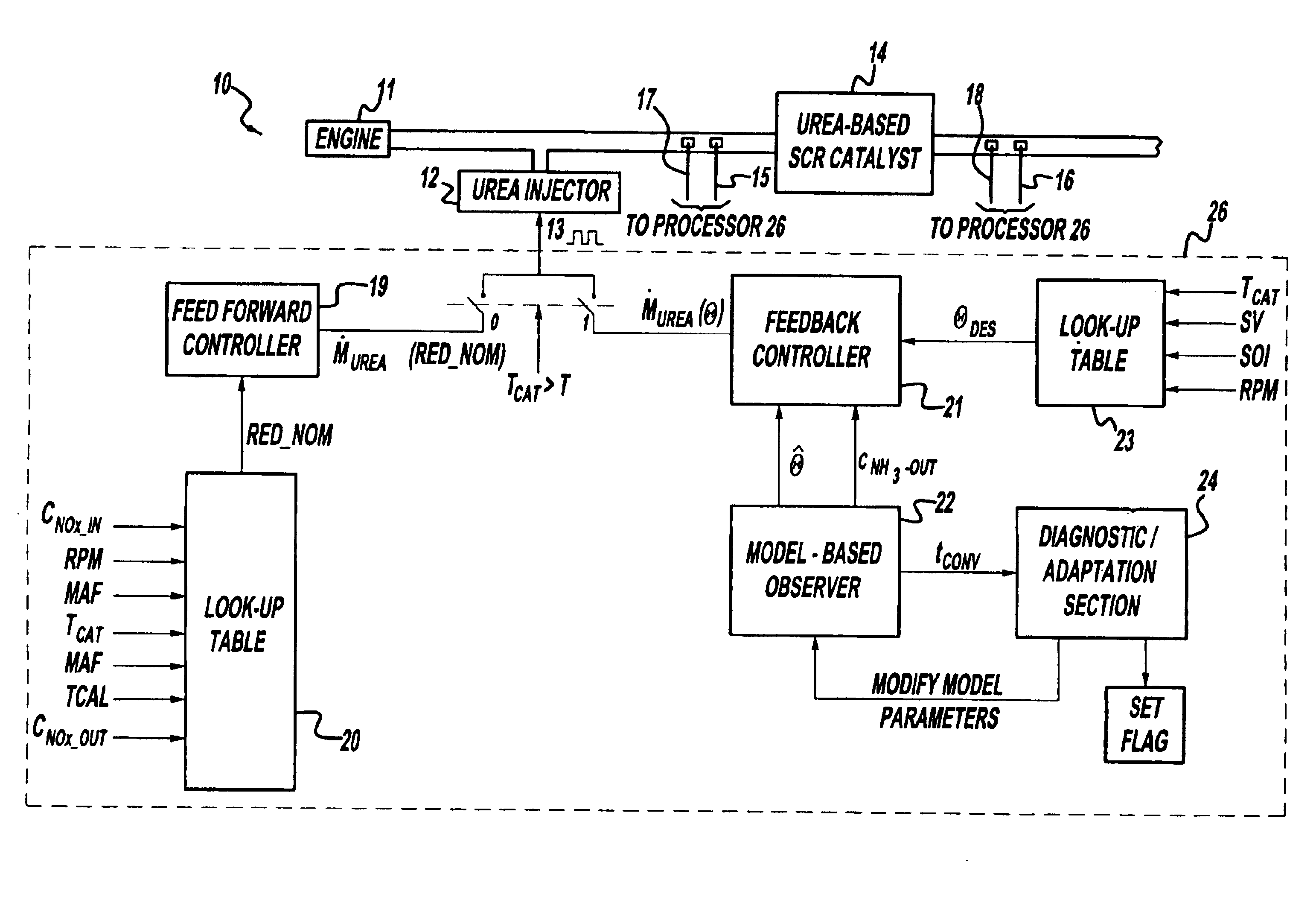
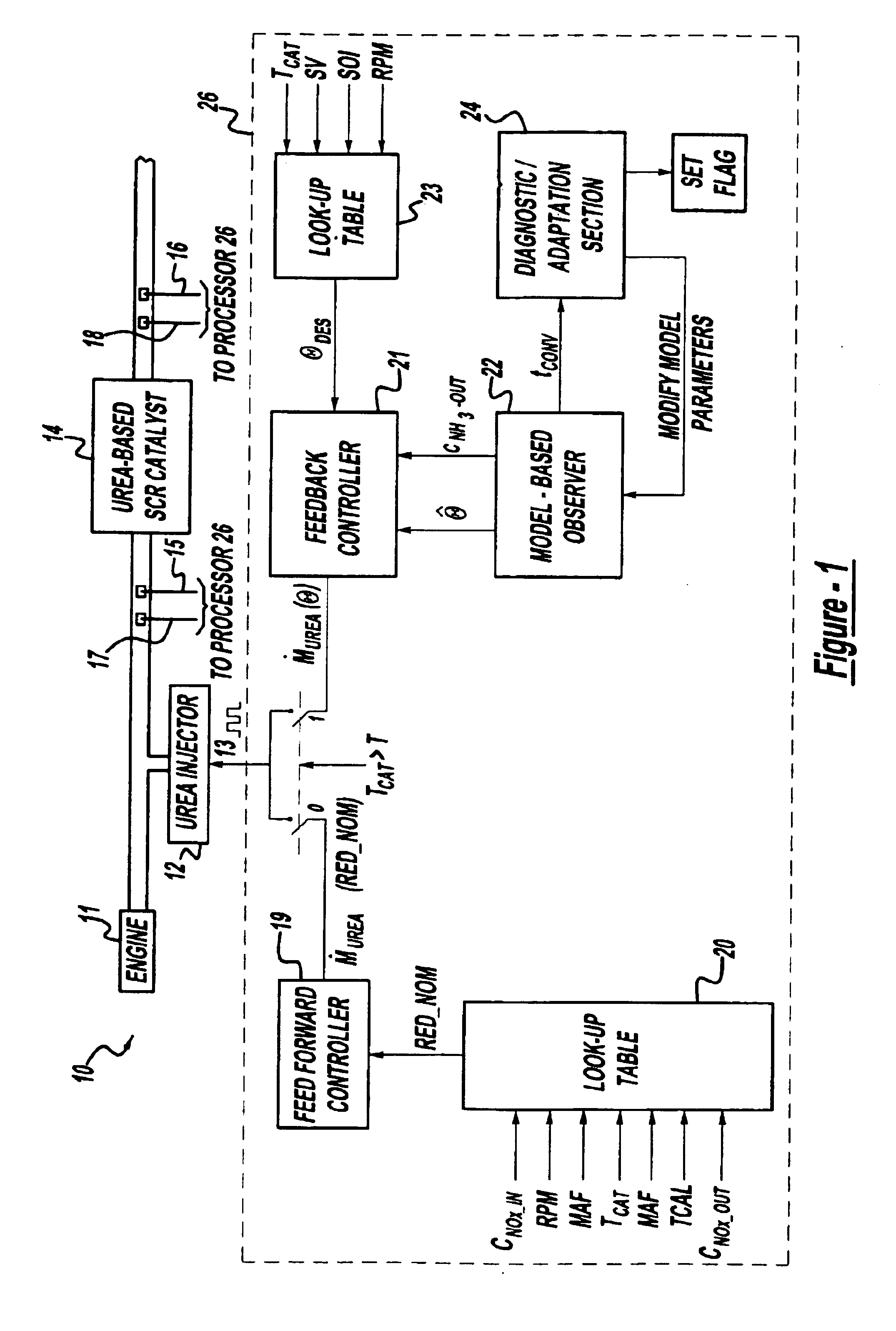
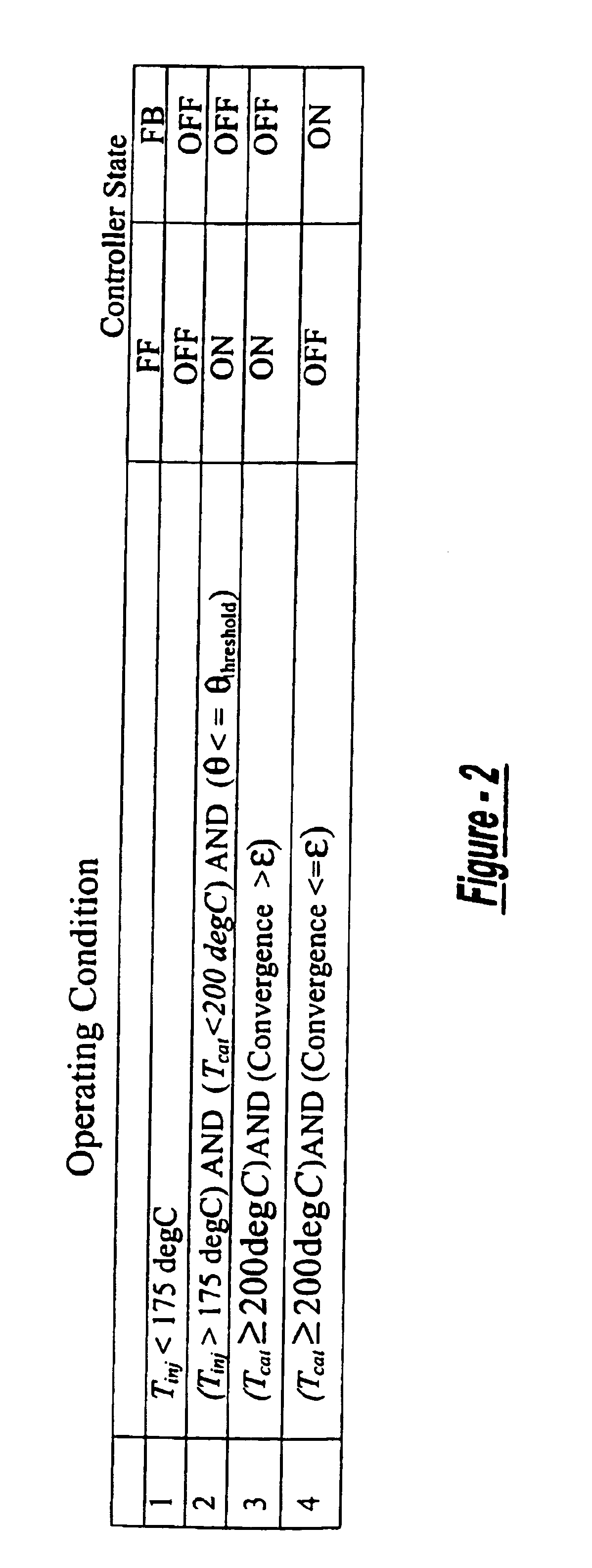
Exhaust gas aftertreatment systems
InactiveUS7093427B2Accurate estimateImprove NOx conversion efficiencyInternal combustion piston enginesAuxillariesDynamic modelsAmmonia storage
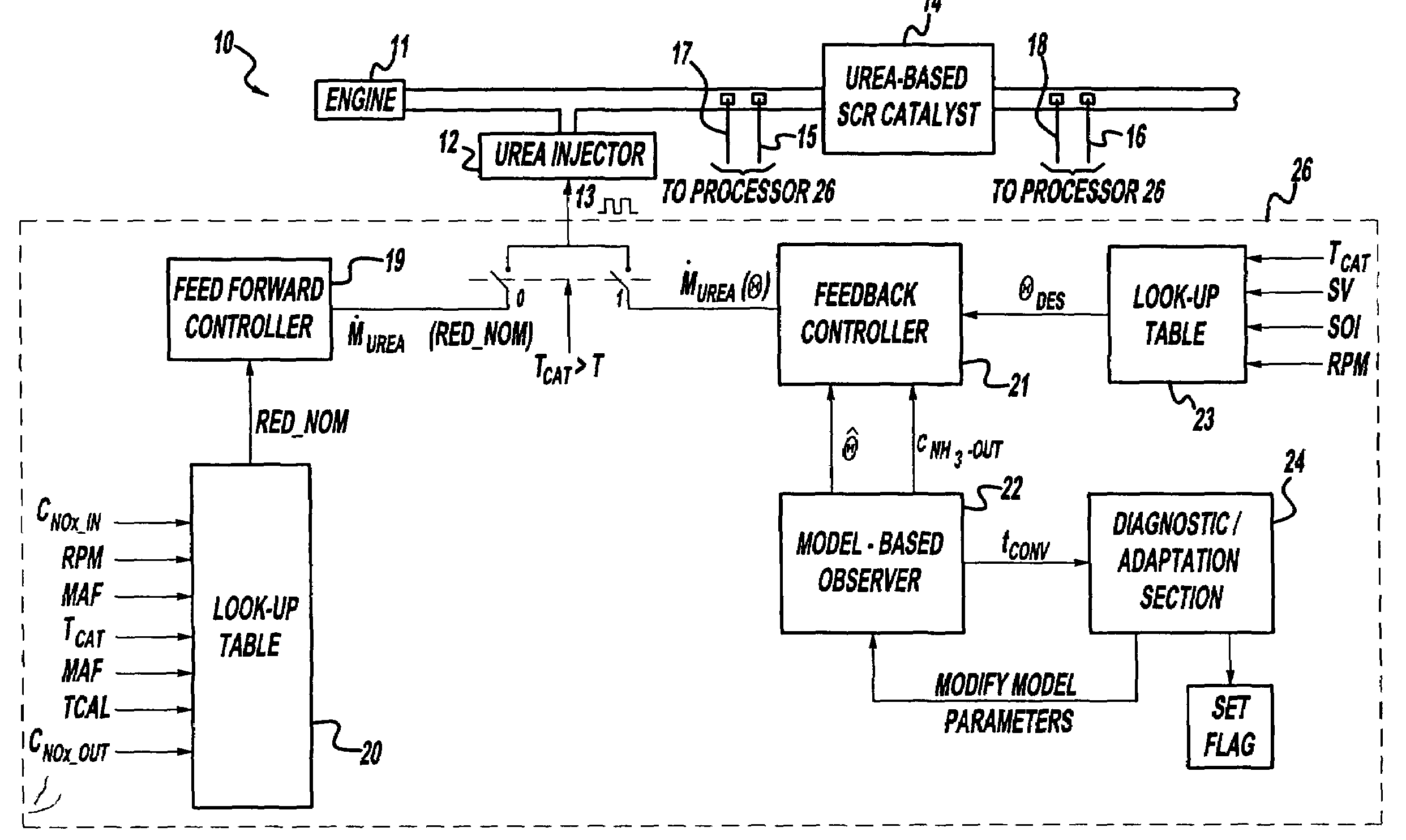
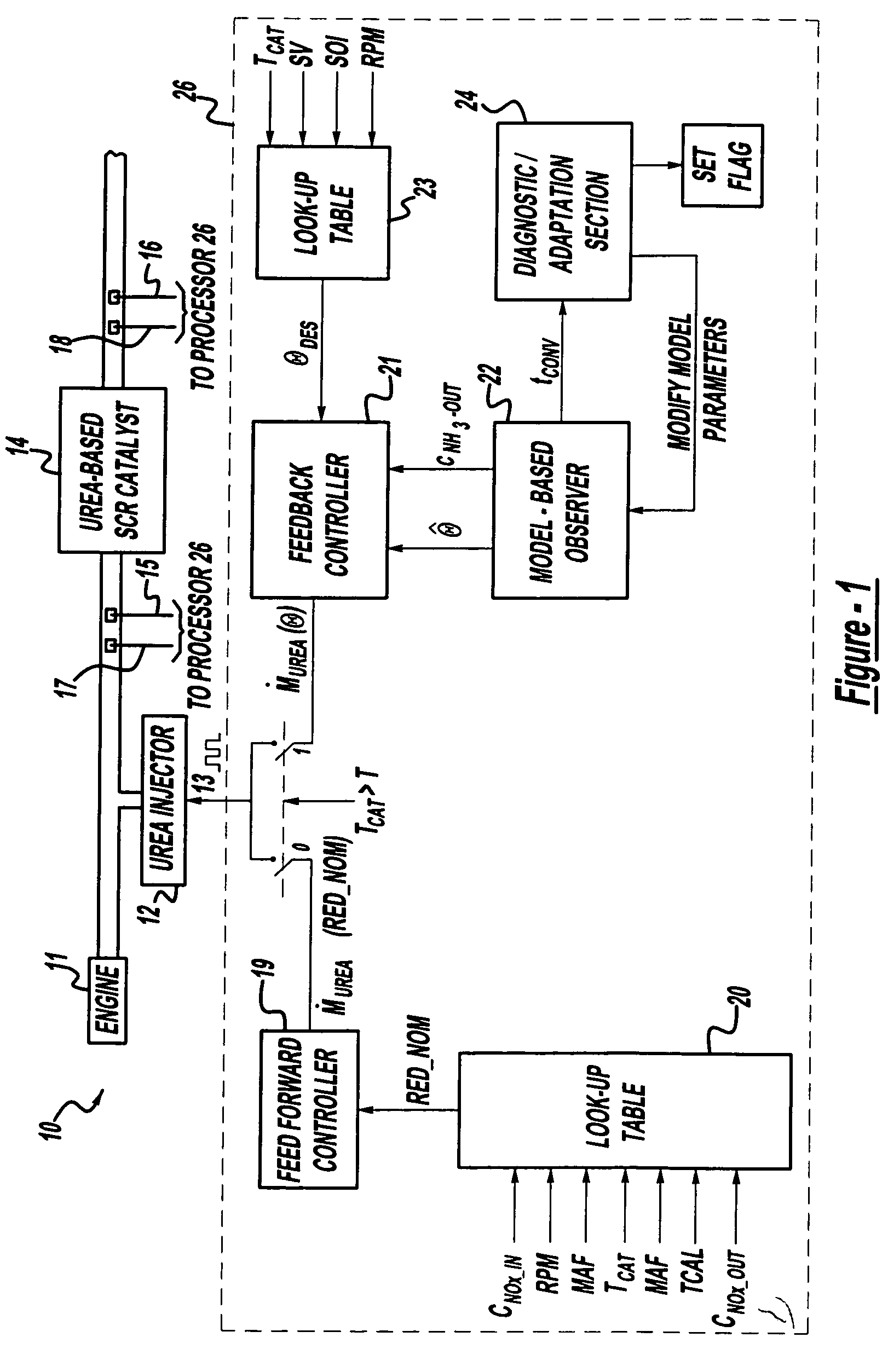
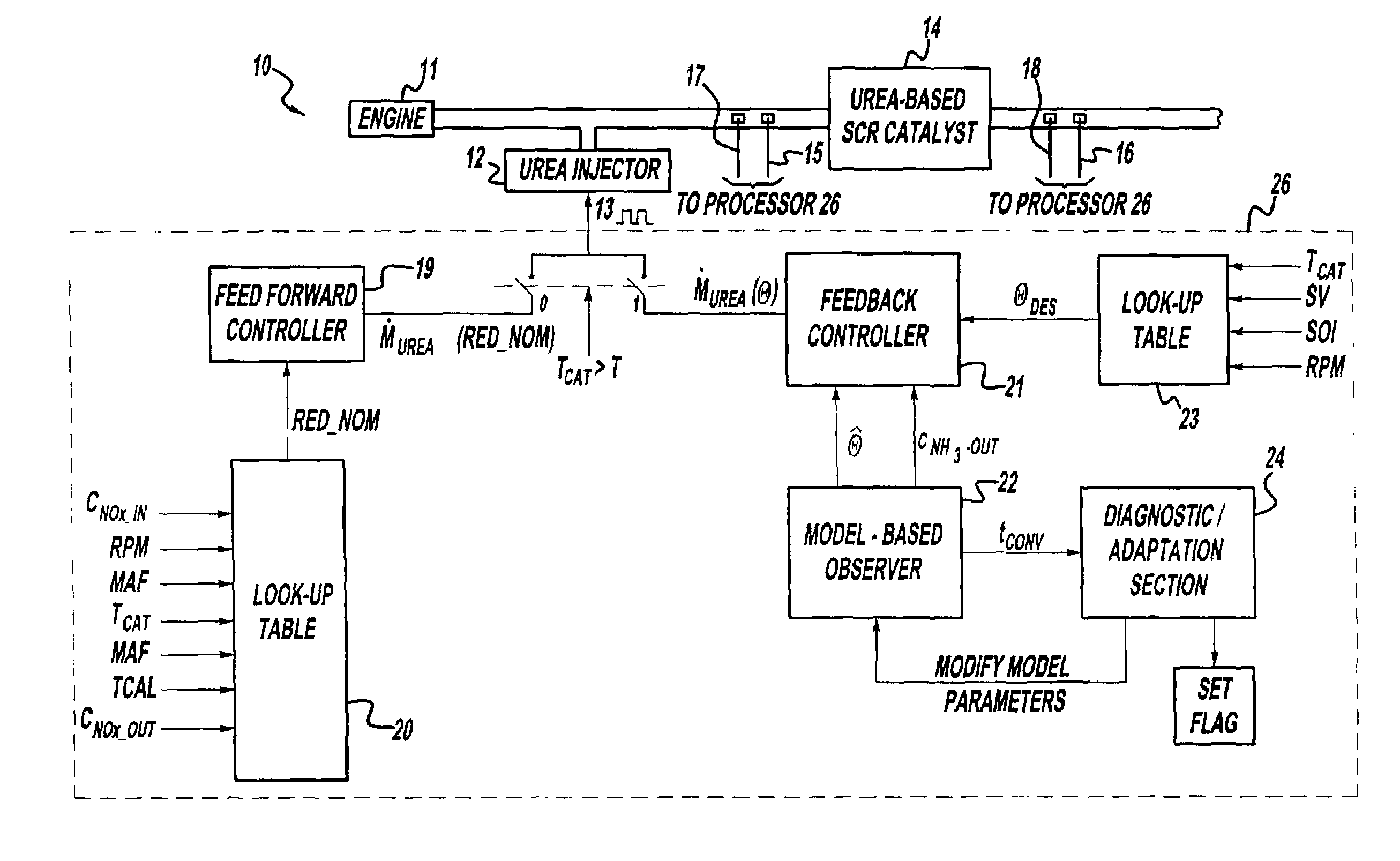
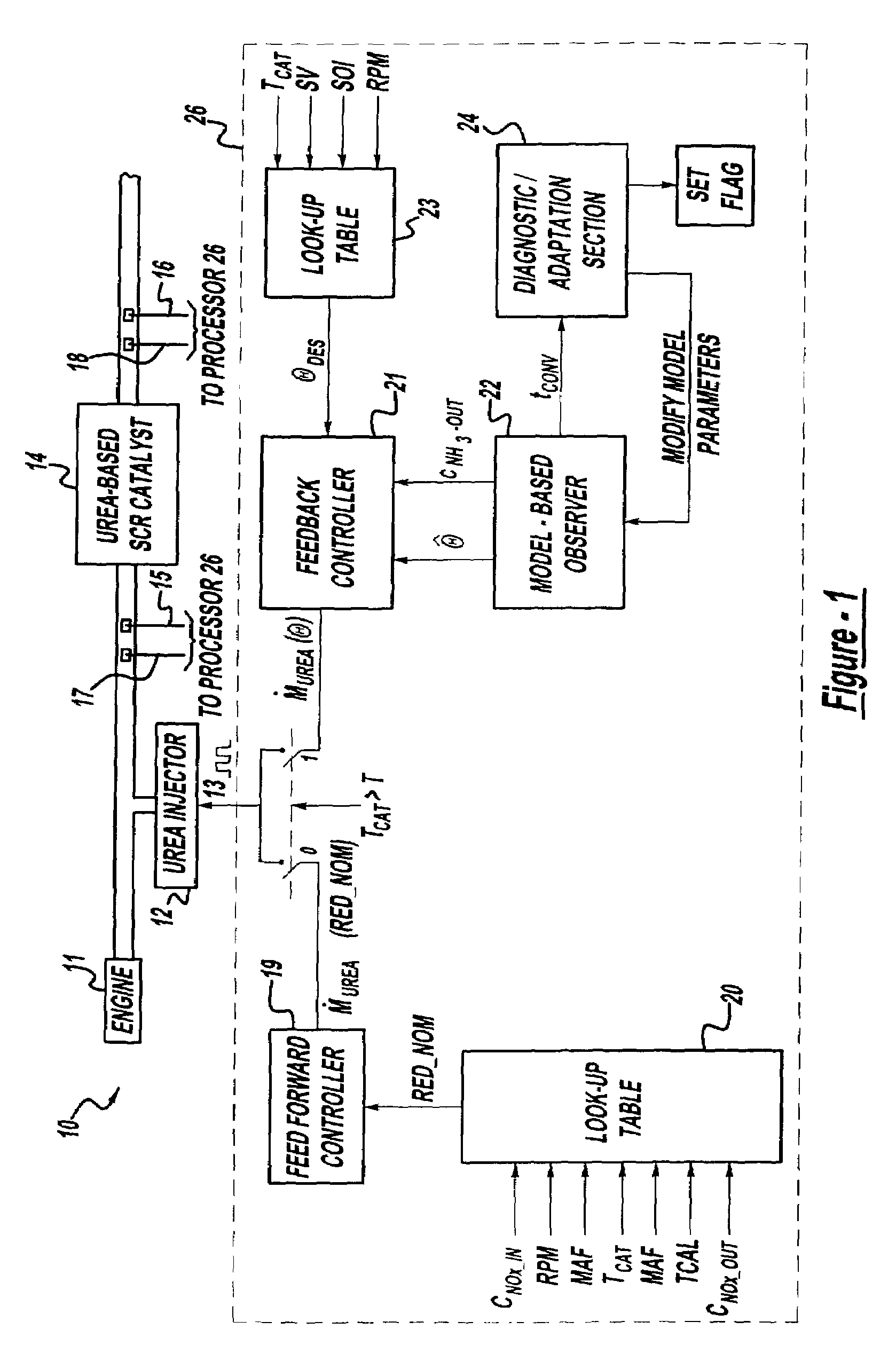
A method is presented for estimating an amount of ammonia stored in a urea-based SCR catalyst based on a dynamic model of the catalyst. The model takes into account chemical and physical properties of the catalyst, such as catalyst volume, the number of available ammonia storage cites, adsorption and desorption dynamics, as well as sulfur poisoning, thermal aging, and different catalyst operating temperatures, and generates the estimate based on a measured or estimated amount of NOx in an exhaust gas mixture upstream of the catalyst, an amount of reductant injected into the catalyst to facilitate NOx reduction, and on a measured value of NOx in an exhaust gas mixture downstream of the catalyst. The estimated ammonia storage amount is then used to control the amount of reductant injected into the catalyst to maintain desired ammonia storage amount such that maximum NOx conversion efficiency coupled with minimum ammonia slip are achieved.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Method of controlling an engine exhaust gas system and method of detecting deterioration of catalyst/adsorbing means
InactiveUS6134883AAccurate detectionElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesNitrogen oxide sensorInternal combustion engine
In a method of controlling an exhaust gas system of an internal combustion engine including a nitrogen oxide reducing catalyst capable of adsorbing nitrogen oxide under a lean atmosphere and a nitrogen oxide sensor disposed downstream of the nitrogen oxide reducing catalyst, the nitrogen oxide reducing catalyst and the nitrogen oxide sensor are disposed in the exhaust gas system operated mainly under a lean condition, respectively. An output value of the nitrogen oxide sensor is compared with a predetermined value, and an operation condition of the internal combustion engine is temporarily changed into a stoichiometric condition or a rich condition, or a fuel is injected upstream of the nitrogen oxide reducing catalyst, so that the nitrogen oxide adsorbed to the nitrogen oxide reducing catalyst is detached or decomposed, and again the internal combustion engine is operated under the lean condition. Deterioration of the catalyst is determined based on Nox amount which is calculated from the sensor output, exhaust has flow amount and vehicle running distance.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
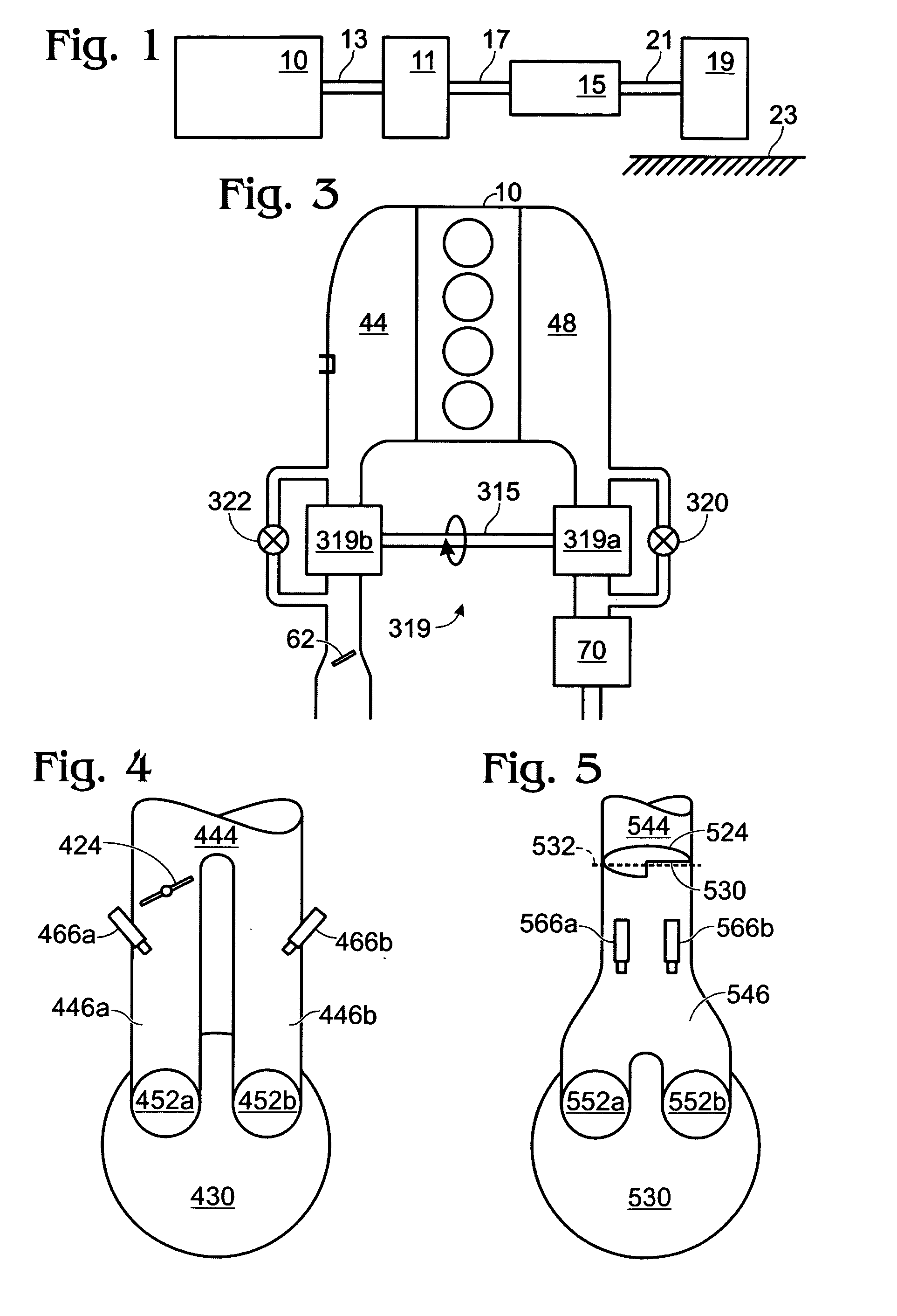
Engine with water and/or ethanol direct injection plus gas port fuel injectors
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Exhaust gas aftertreatment systems
InactiveUS20070044456A1Improved emission controlImprove diagnostic capabilitiesGas treatmentInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust fumesEngineering
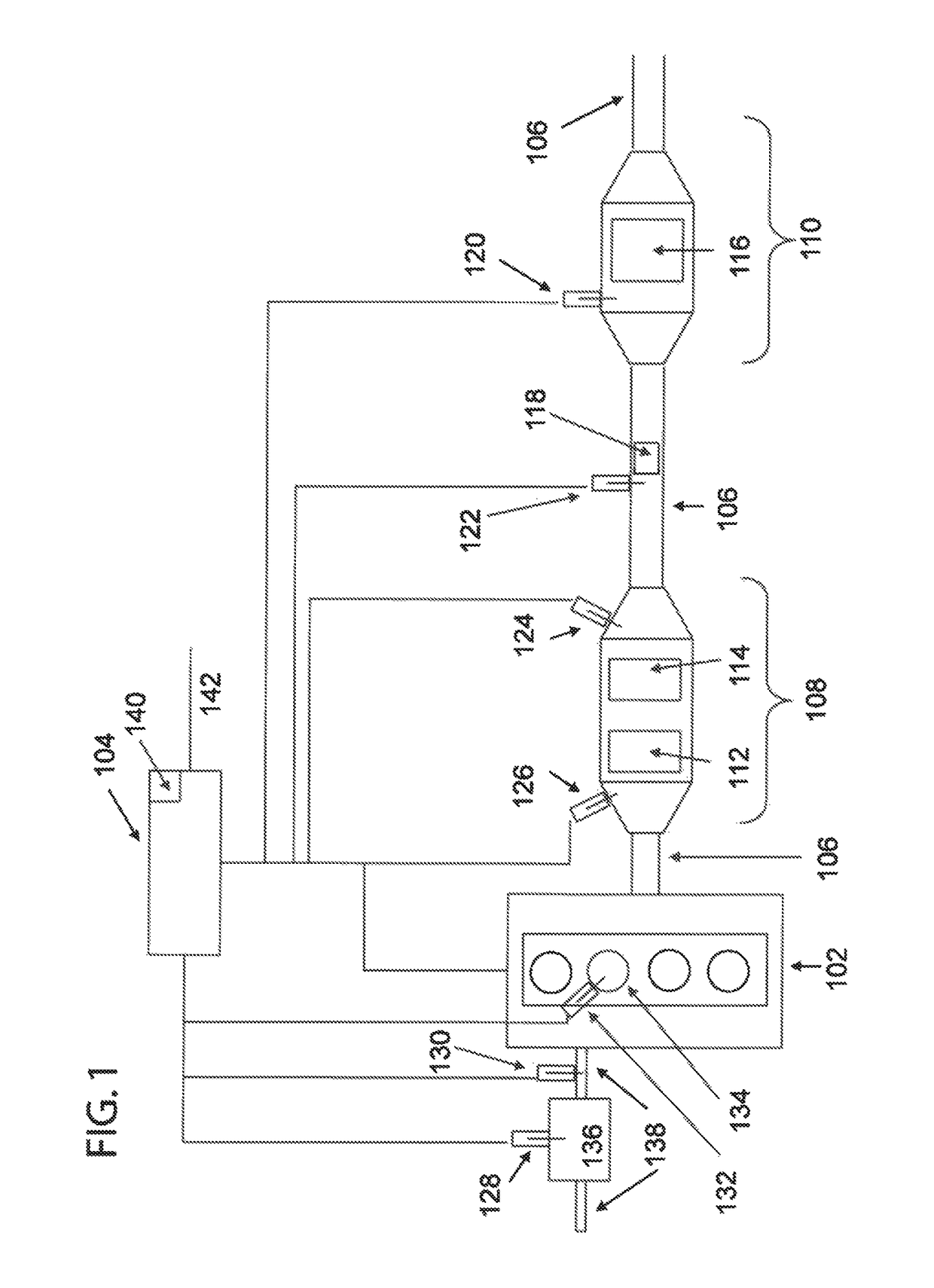
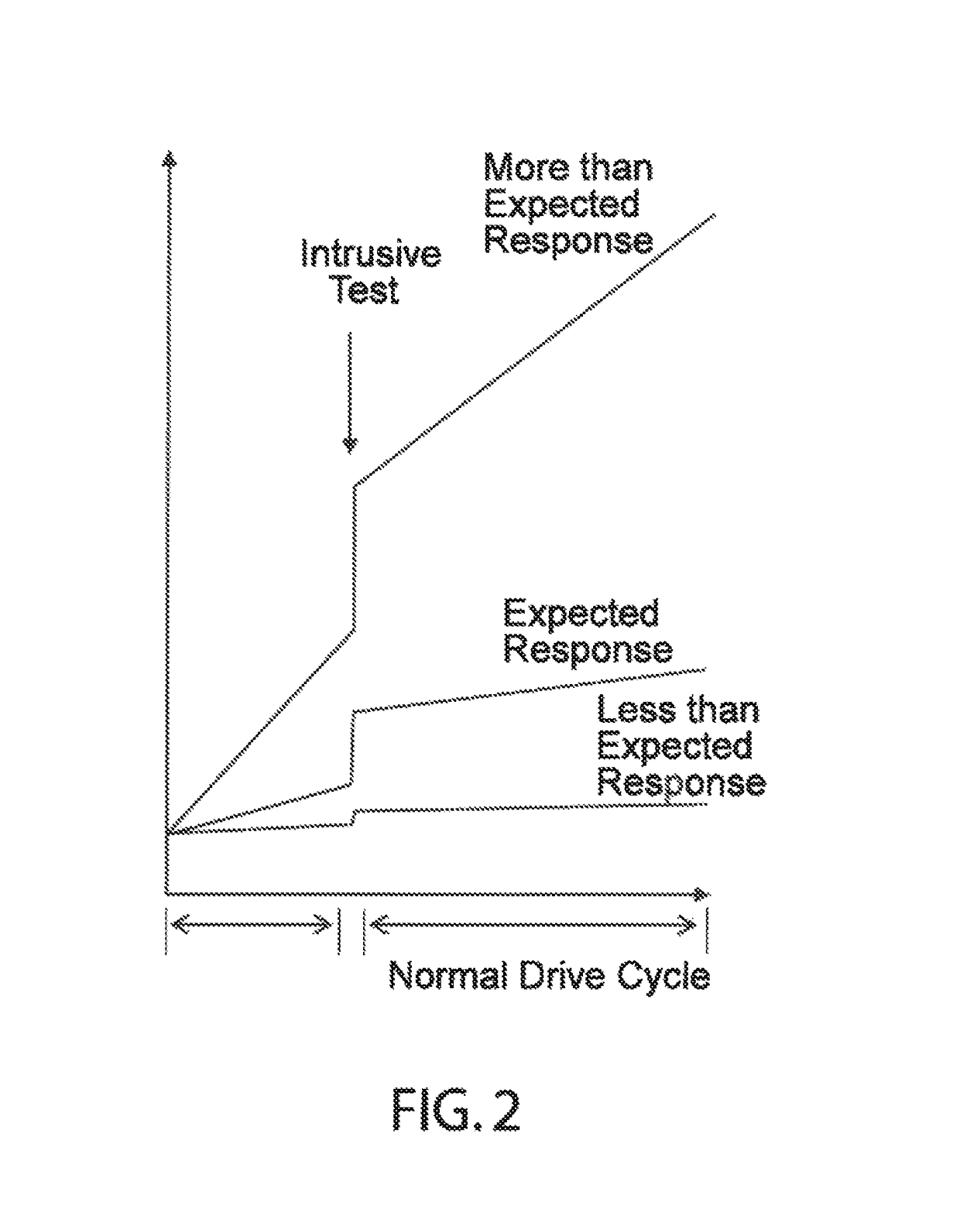
A method is presented for determining an amount of reductant stored in the catalyst by intrusively desorbing a portion of reductant and monitoring the response of an reductant sensor to the desorbed portion. The desorbtion can be performed at vehicle start-up to determine initial storage amount and to adjust reductant injection accordingly to achieve optimum storage. Additionally, a portion of reductant can be desorbed when NOx conversion efficiency of the catalyst is reduced in order to diagnose the component responsible for system degradation.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
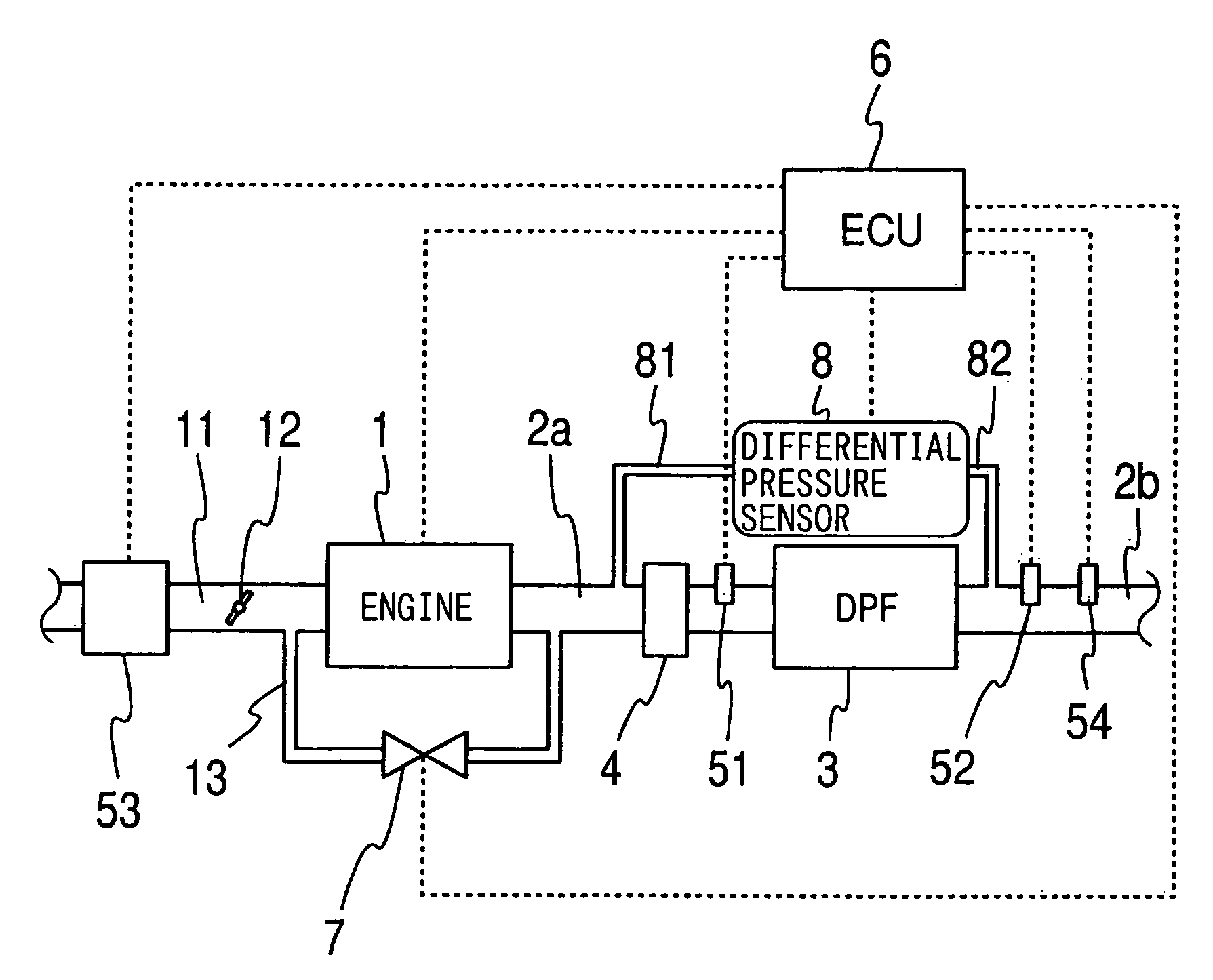
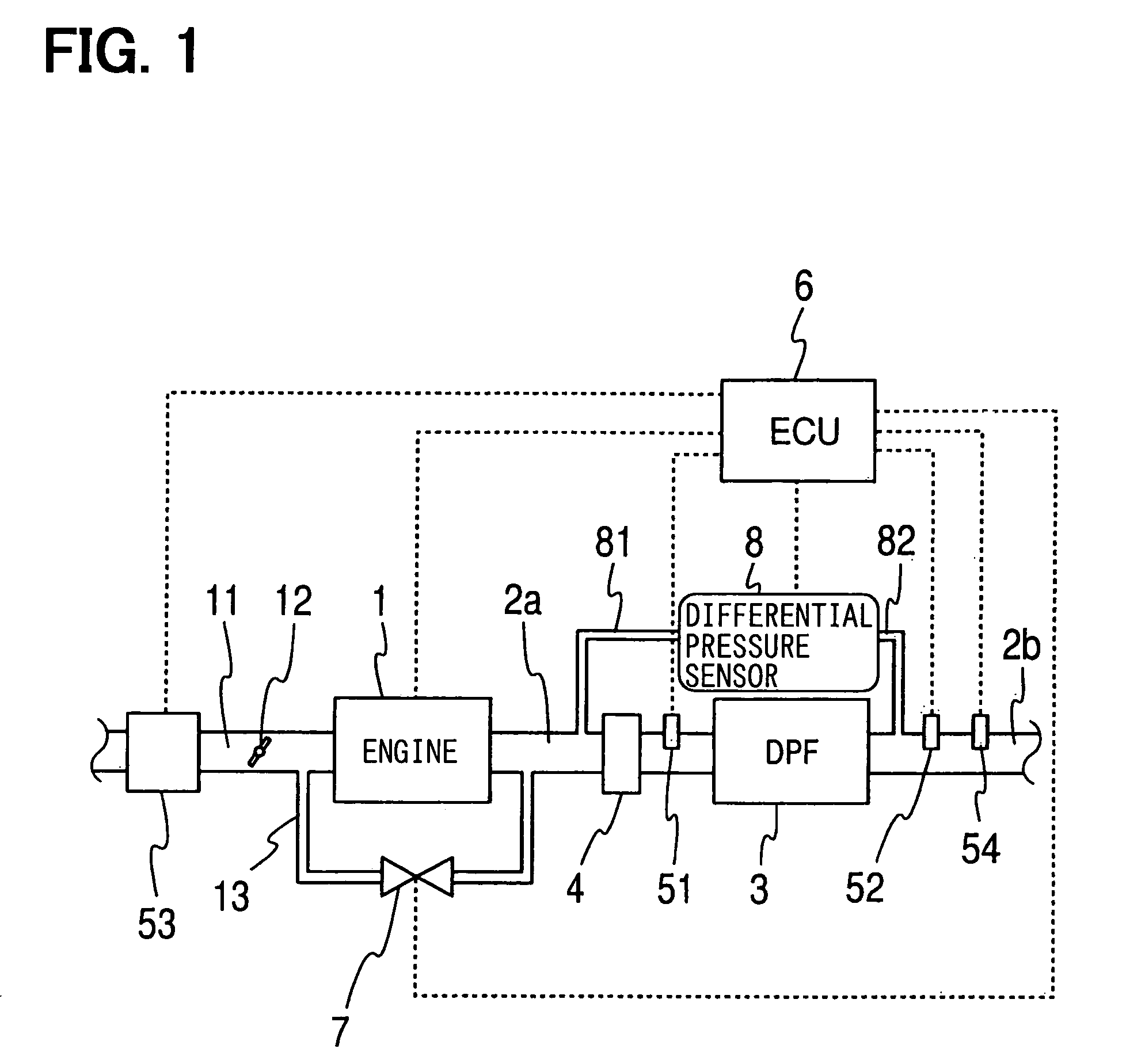
Method of determining the amount of particulate accumulated in a particulate filter
InactiveUS6941750B2Drawback can be obviatedElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesParticulatesEngineering
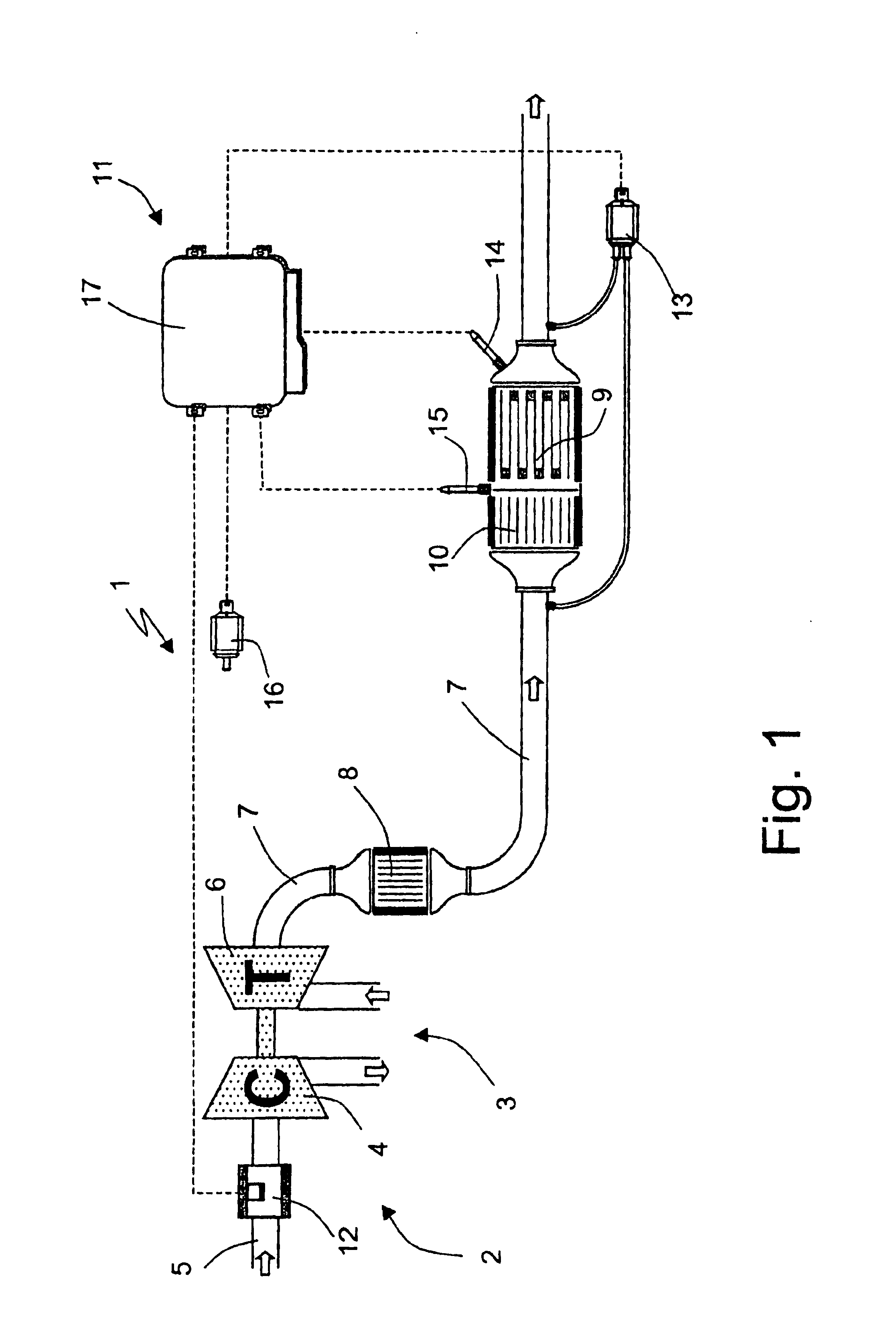
A method of determining the amount of particulate accumulated in a particulate filter, is based on determining possible variations in the spatial distribution and / or physical-chemical properties of the particulate as a function of engine operating conditions and past particulate accumulation in the particulate filter. A number of reference values defining a relationship between the amount of particulate accumulated in the particulate filter and the pressure drop across the particulate filter are mapped, each of the reference values relating to a respective steady engine operating condition in which particulate is accumulated in the particulate filter. In a given engine operating condition, an operating value of the parameter is then determined as a function of the reference value of the parameter relative to the same steady engine operating condition, and of past particulate accumulation in the particulate filter.
Owner:CENT RICERCHE FIAT SCPA
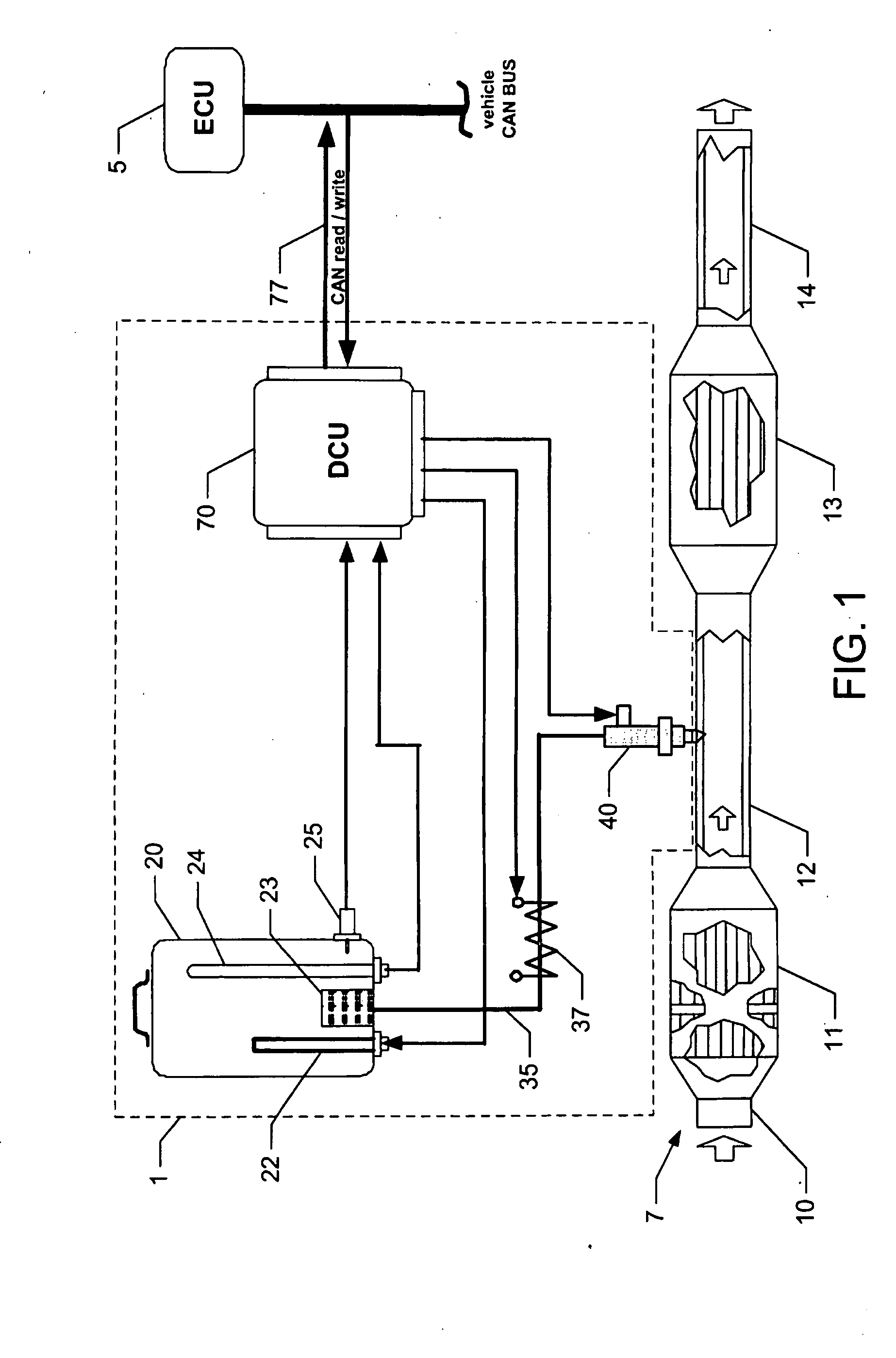
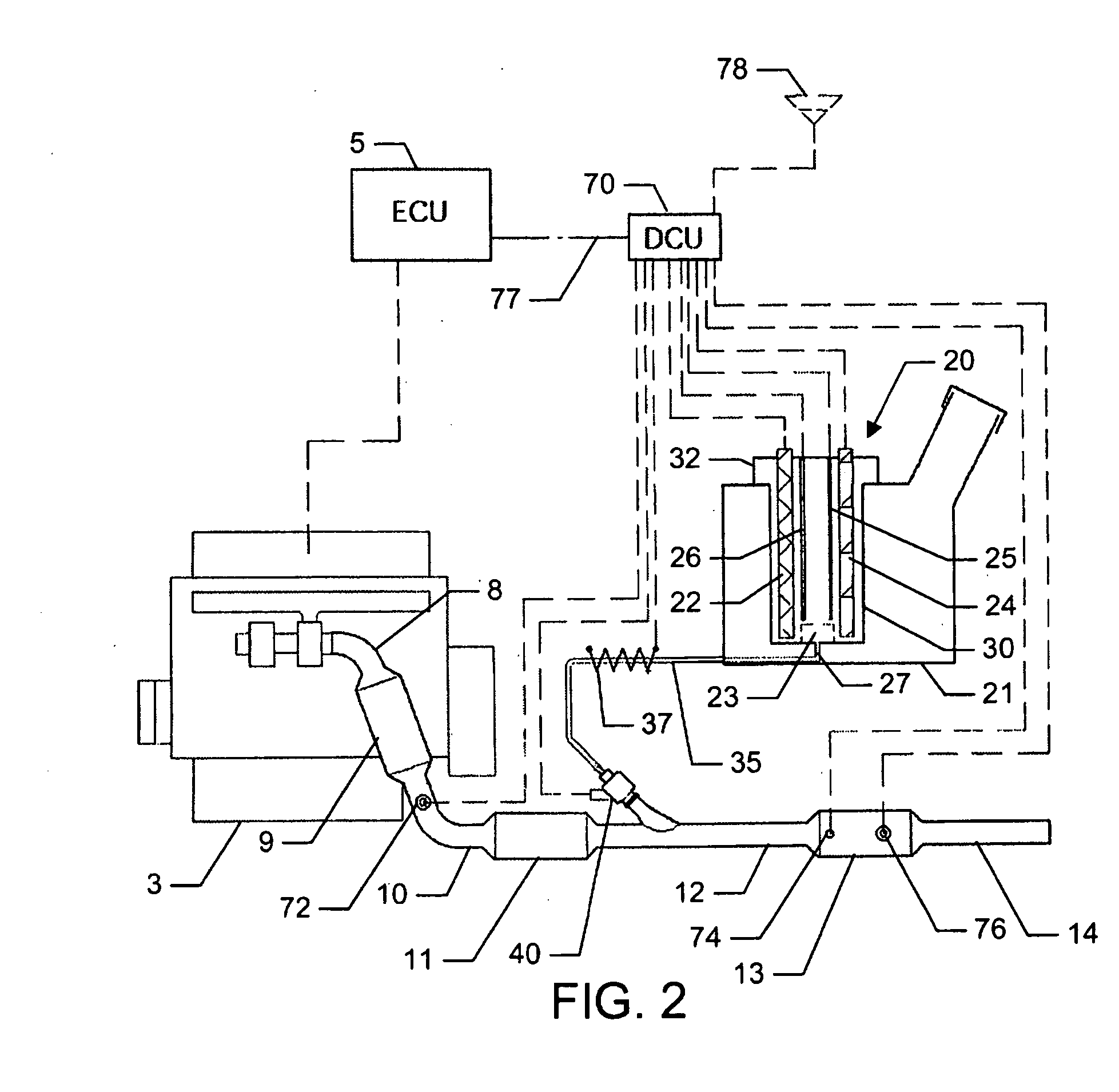
Emission control system
InactiveUS7065958B2Emission reductionEfficientlyInternal combustion piston enginesFlow mixersNitrogen oxidesControl system
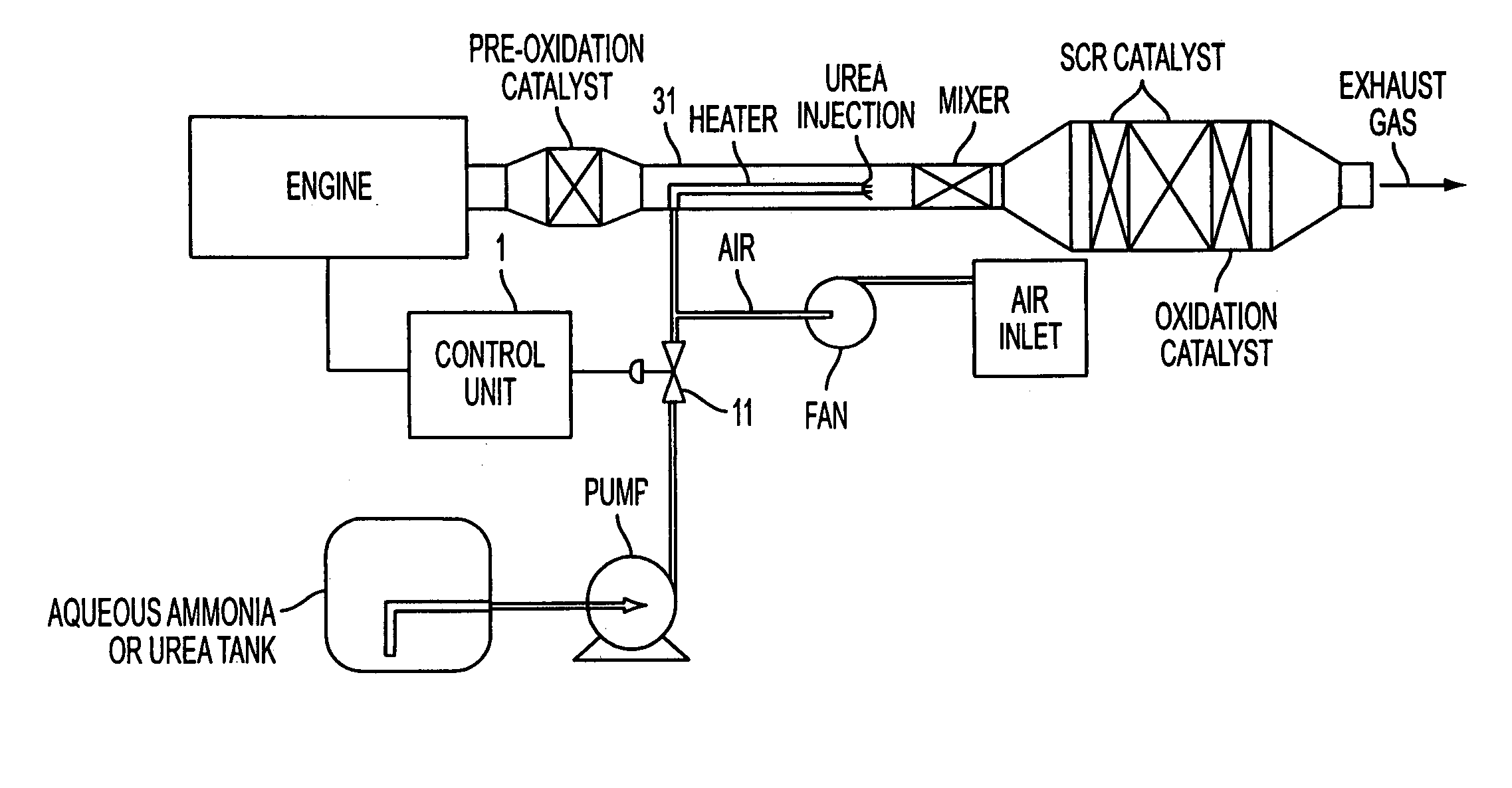
A method and apparatus to reduce the emissions of an exhaust stream is provided. One feature of the present invention includes a control unit for metering a reagent into the exhaust stream. The control unit adjusts a quantity of the reagent to be metered into the exhaust stream. One embodiment of the present invention concerns a method of removing nitrogen oxides in exhaust gases from a diesel engine by introducing ammonia into the exhaust stream. This Abstract is provided for the sole purpose of complying with the Abstract requirement rules that allow a reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the disclosure contained herein. This Abstract is submitted with the explicit understanding that it will not be used to interpret or to limit the scope or the meaning of the claims.
Owner:EXTENGINE TRANSPORT SYST
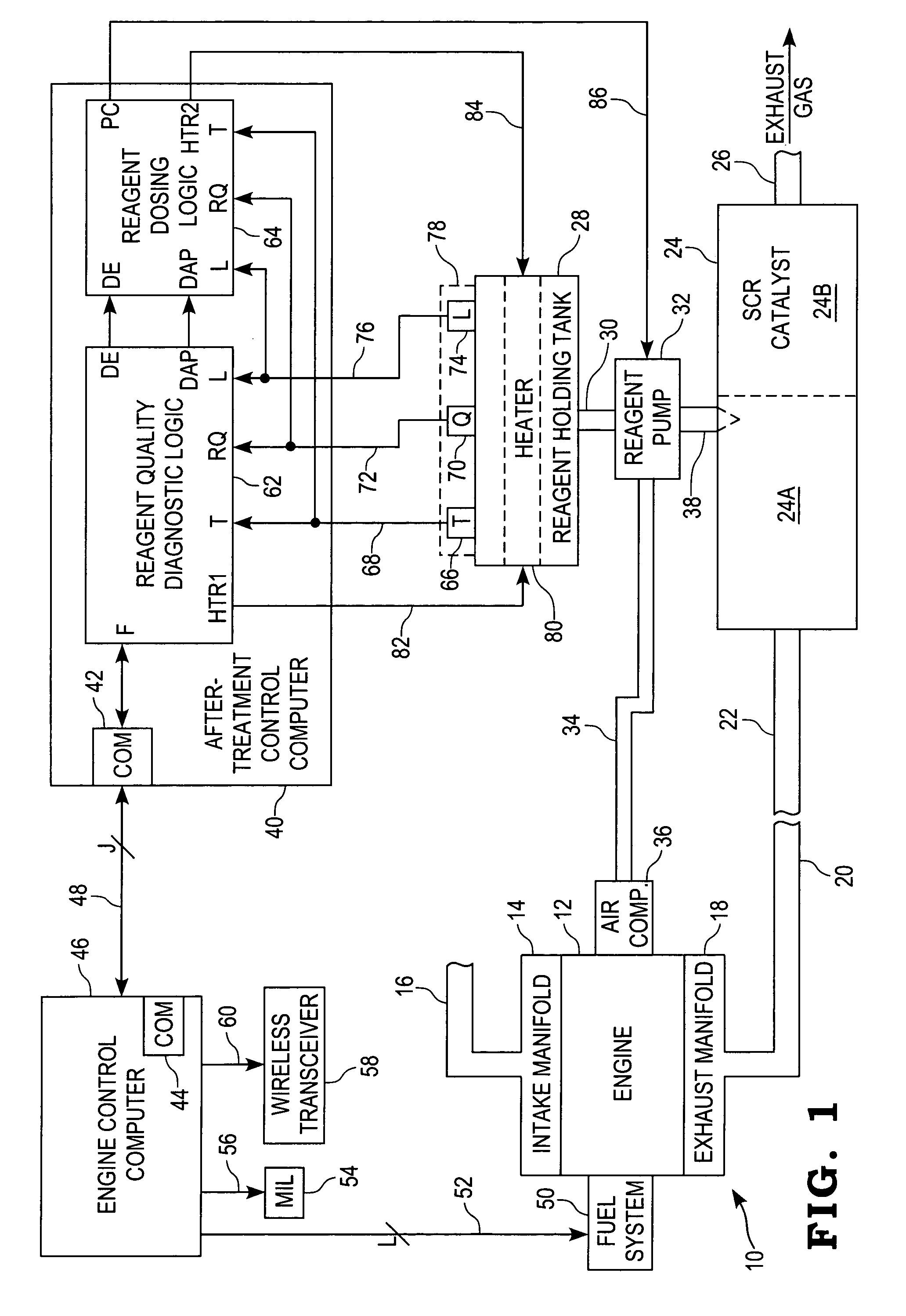
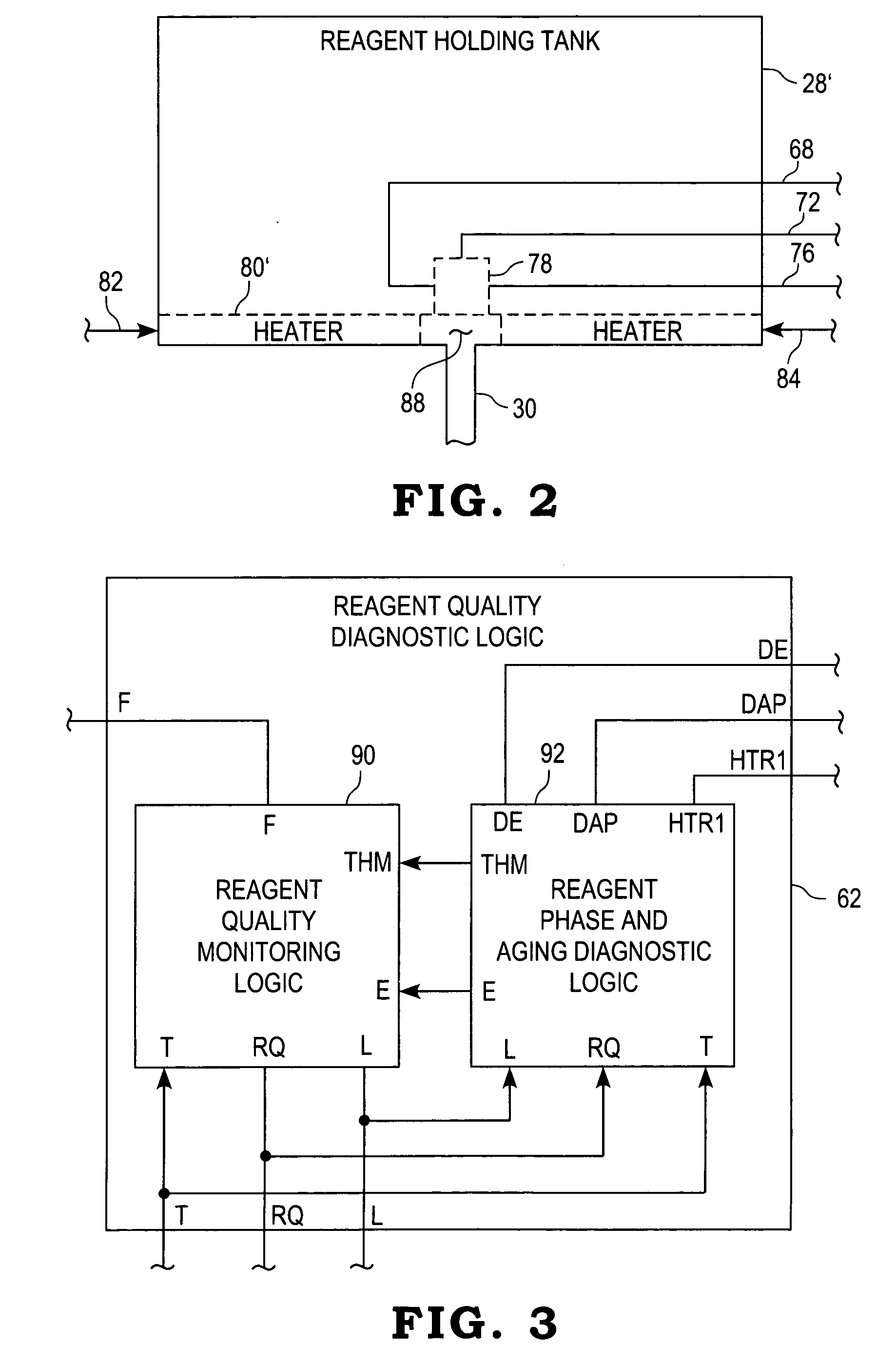
System for diagnosing reagent solution quality
ActiveUS20050207936A1Electrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesInternal combustion engineComparator
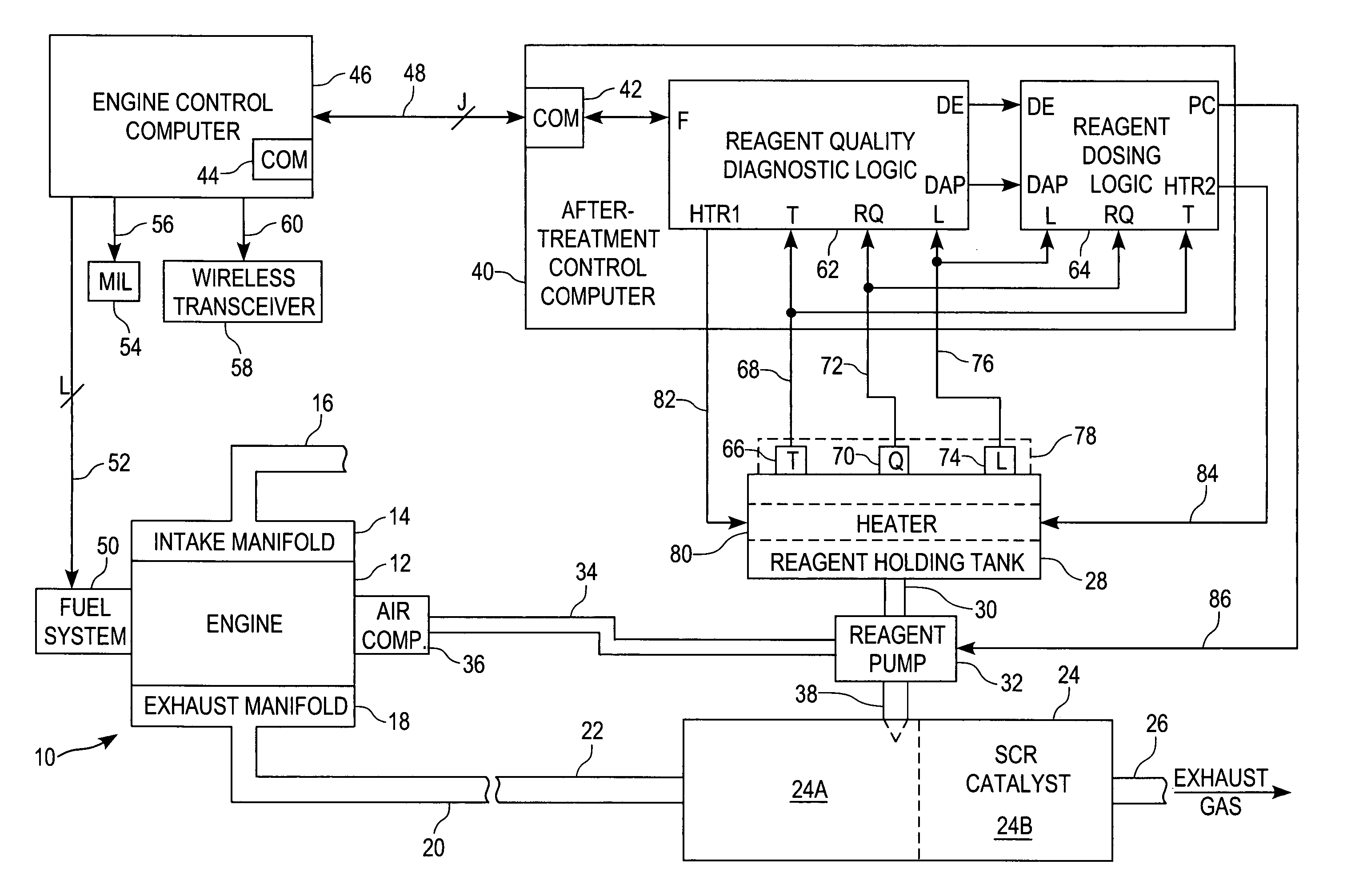
A system for diagnosing the quality of a reagent solution may comprise a reagent solution source for supplying the reagent solution to an emissions catalyst of an internal combustion engine. Means may be provided for determining a quality value corresponding to the quality of the reagent solution. A first filter may receive the quality value and produce a first filtered quality value, and a first comparator may compare the filtered quality value to a threshold and produce a fault value if the first filtered quality value crosses the threshold. Alternatively or additionally, a second filter may receive the quality value and produce a second filtered quality value. A second comparator may compare a difference between the first and second filtered quality values to another threshold and produce another fault value if the difference crosses that threshold.
Owner:CUMMINS FILTRATION IP INC
Engine exhaust gas cleaning method and system
InactiveUS20060086080A1Emission reductionReduce cleaning rateElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelExhaust fumesEnvironmental engineering
An engine exhaust gas cleaning method and system, which can effectively reduce emission amounts of particular components, such as NOx, contained in exhaust gas by adding an additive, such as urea water or light oil, into an exhaust passage, which is adaptable for a reduction of the cleaning rate caused by deterioration of a catalyst, which can always maintain a high cleaning rate during acceleration and deceleration as well, and which can minimize environmental pollution with use of the additive in the least necessary amount. The engine exhaust gas cleaning system comprises a catalyst for removing a particular component, represented by NOx, contained in exhaust gas of an engine, an additive adding unit for adding, to the exhaust gas, an additive for reducing the particular component represented by NOx, and an EGR amount adjusting unit for adjusting an EGR amount. An addition amount of the additive and the EGR amount are set depending on an operating state and deterioration of the catalyst with time. The catalyst is regenerated when a cleaning capability of the catalyst has reduced to a predetermined value or below.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
OBDII readiness status notification device
InactiveUS20060030980A1Vehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesEngineeringControl logic
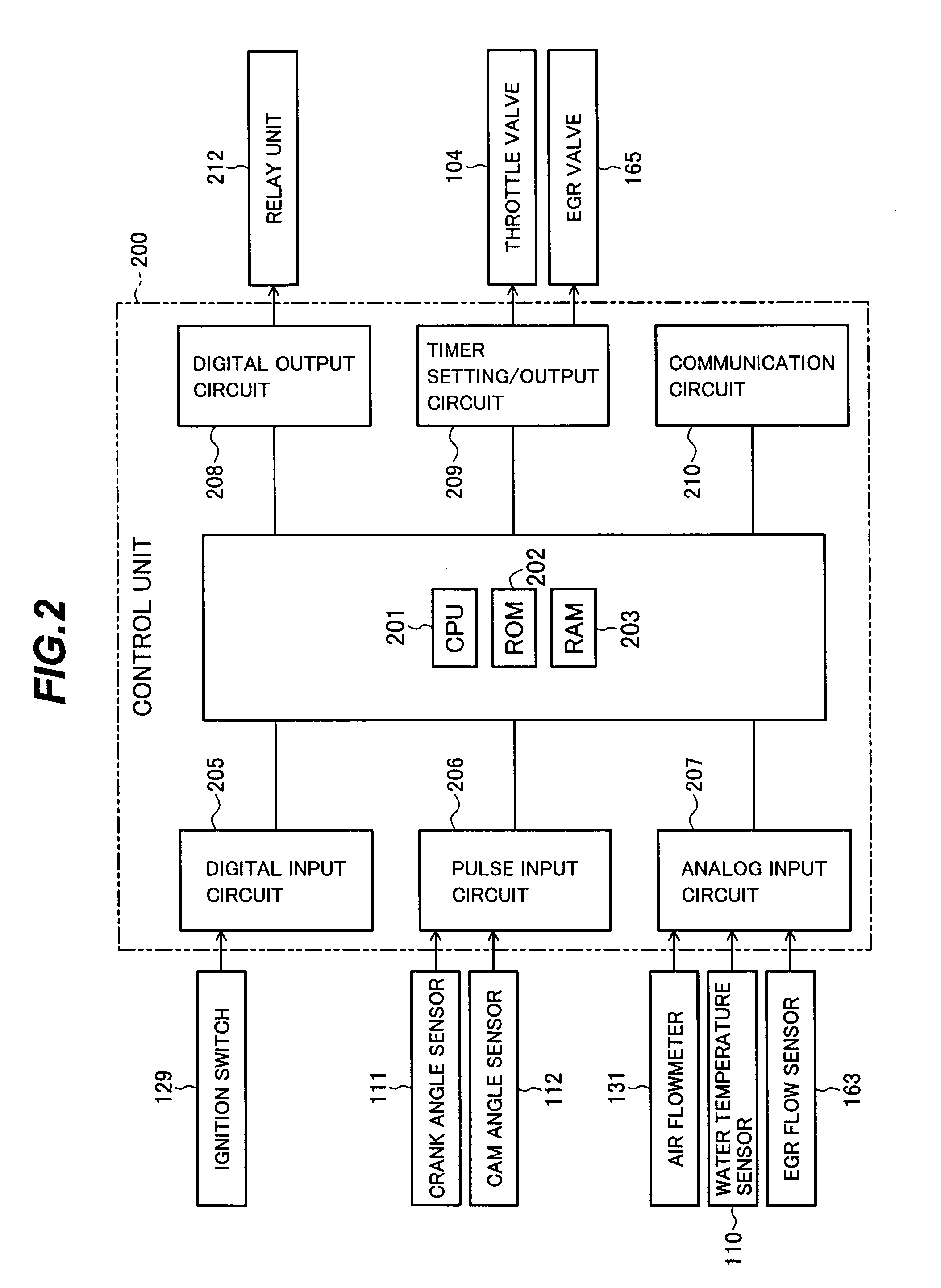
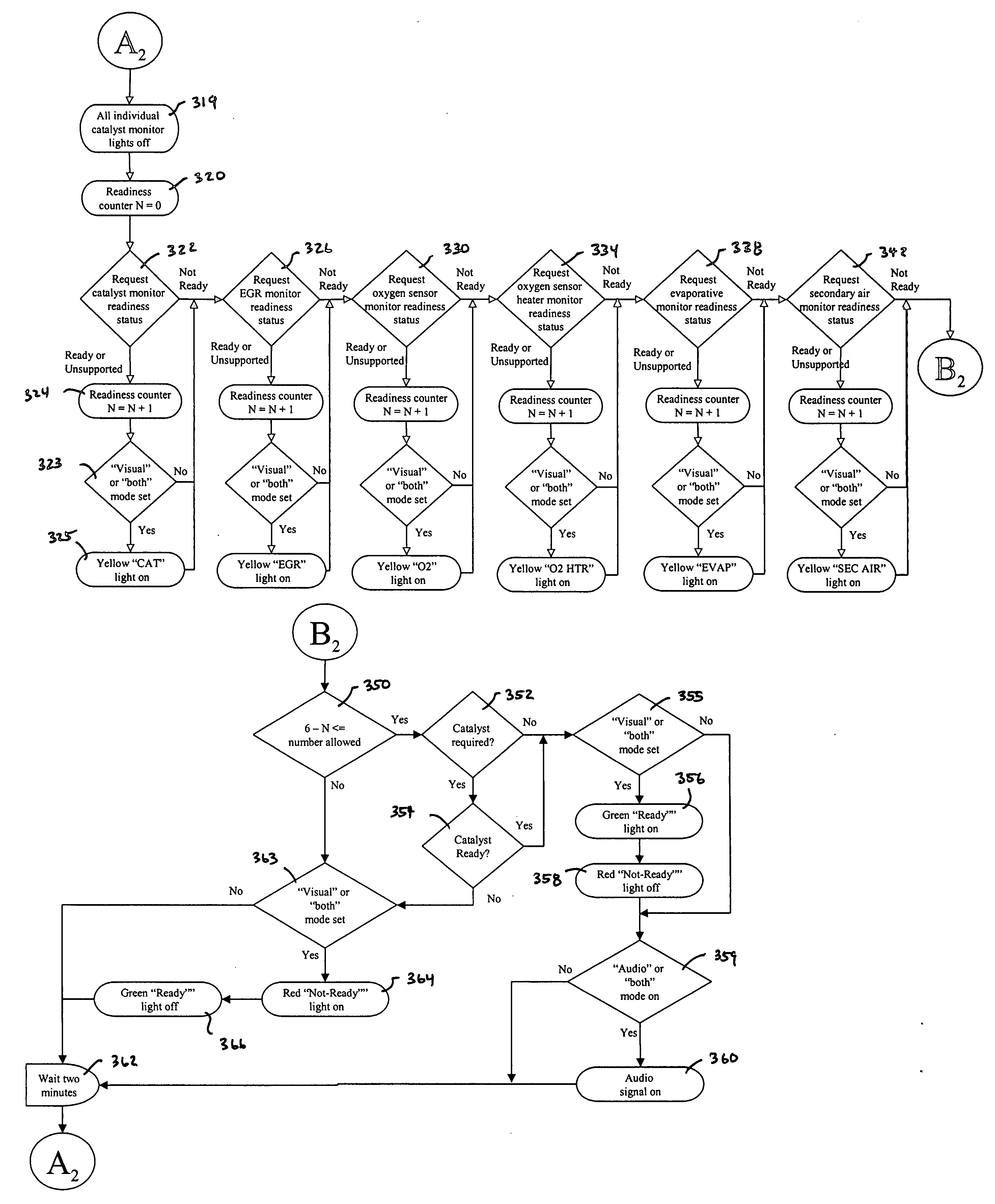
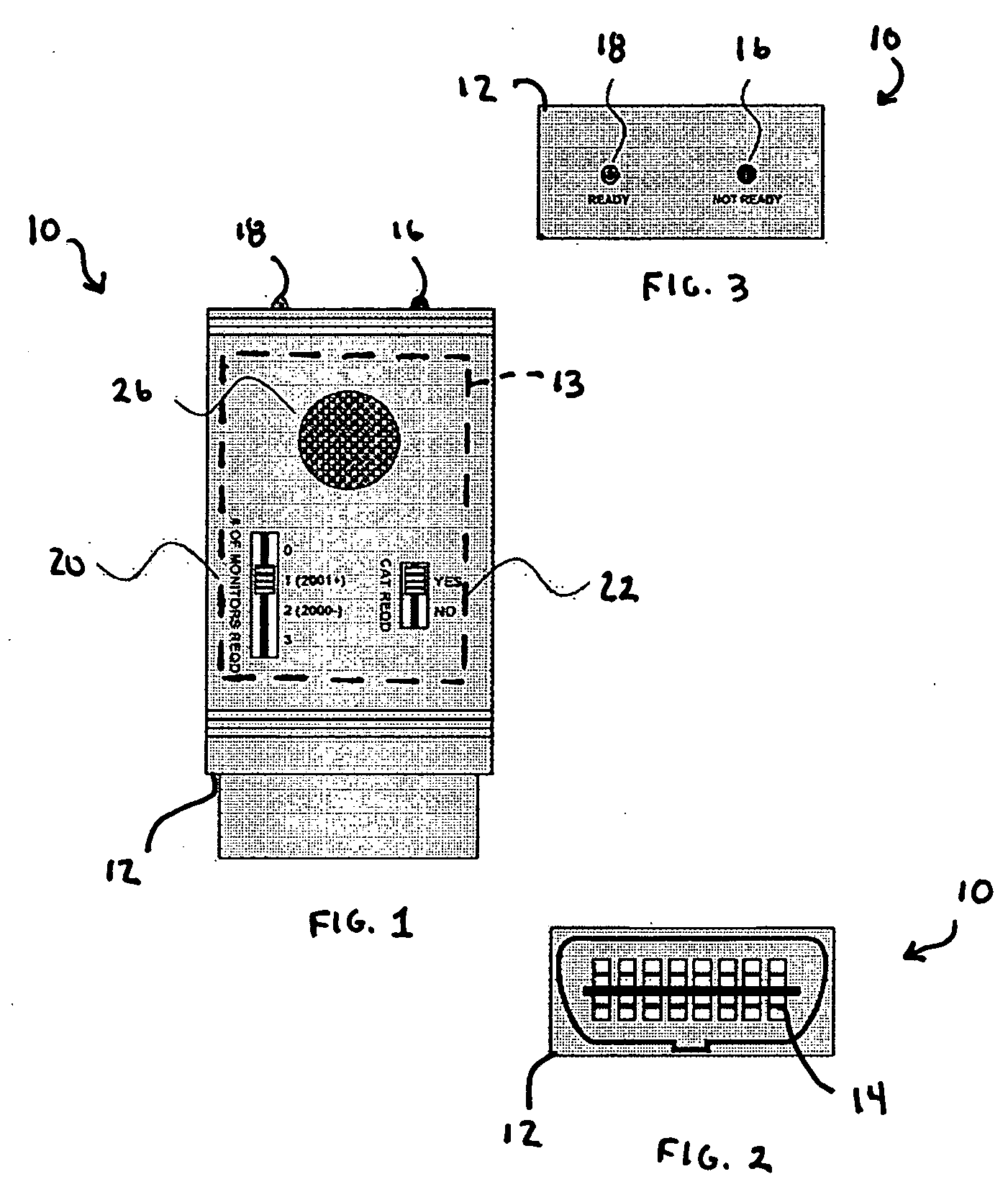
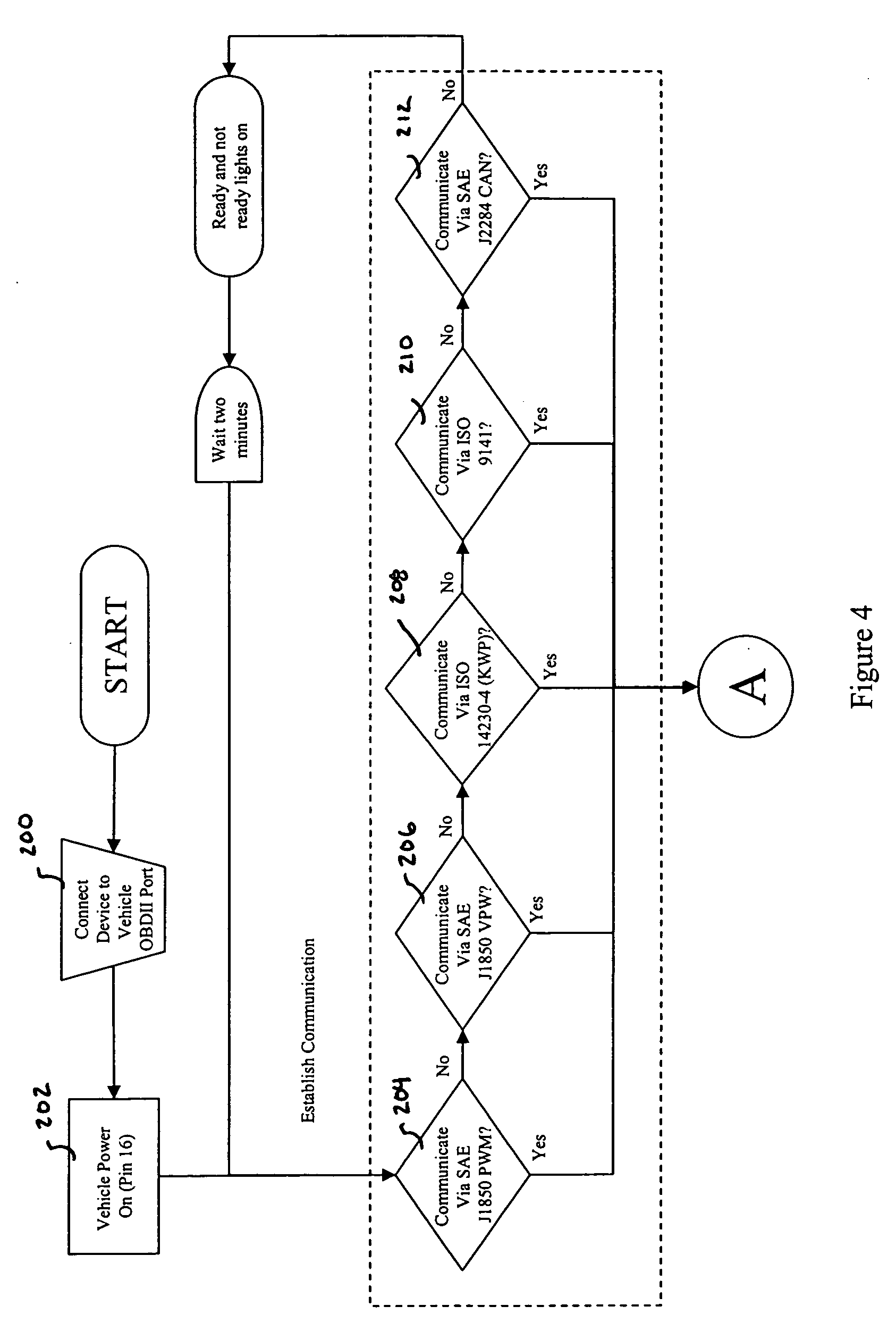
A device for notifying an operator of the readiness of a vehicle for emissions testing includes a control logic for evaluating the status of each of a plurality of the monitors of an on-board diagnostics (OBDII) system of the vehicle. Once the vehicle is determined to be ready for emissions testing based on the status of each evaluated monitor of the OBDII system, an indicator light is illuminated and / or an audio signal is emitted to notify the operator.
Owner:ST DENIS INNOVATIONS
Emission control system with catalyst warm-up speeding control
InactiveUS20030070423A1High precisionElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesAir volumeControl system
An emission control system has a catalyst and a sensor responding to a component of exhaust gas. In order to speed warming up the catalyst, the emission control system increases the amount of heat dissipated by exhaust gas. A diagnosis of the emission control system is carried out by determining whether the amount of heat dissipated by exhaust gas is sufficient or insufficient. The amount of heat dissipated by exhaust gas is represented by the length of time to an activated state of the sensor. In the diagnosis, the amount of heat generated by a heater provided in the sensor is taken into consideration. The diagnosis can also be carried out before and after the warming up the catalyst. The heater can also be deactivated. Detection of an abnormality of a secondary air control system can be based on a component of exhaust gas. If the amount of heat dissipated by exhaust gas is found insufficient, additional control can be executed. The amount of heat dissipated by exhaust gas can also be represented by an intake air volume and an air-fuel ratio.
Owner:DENSO CORP
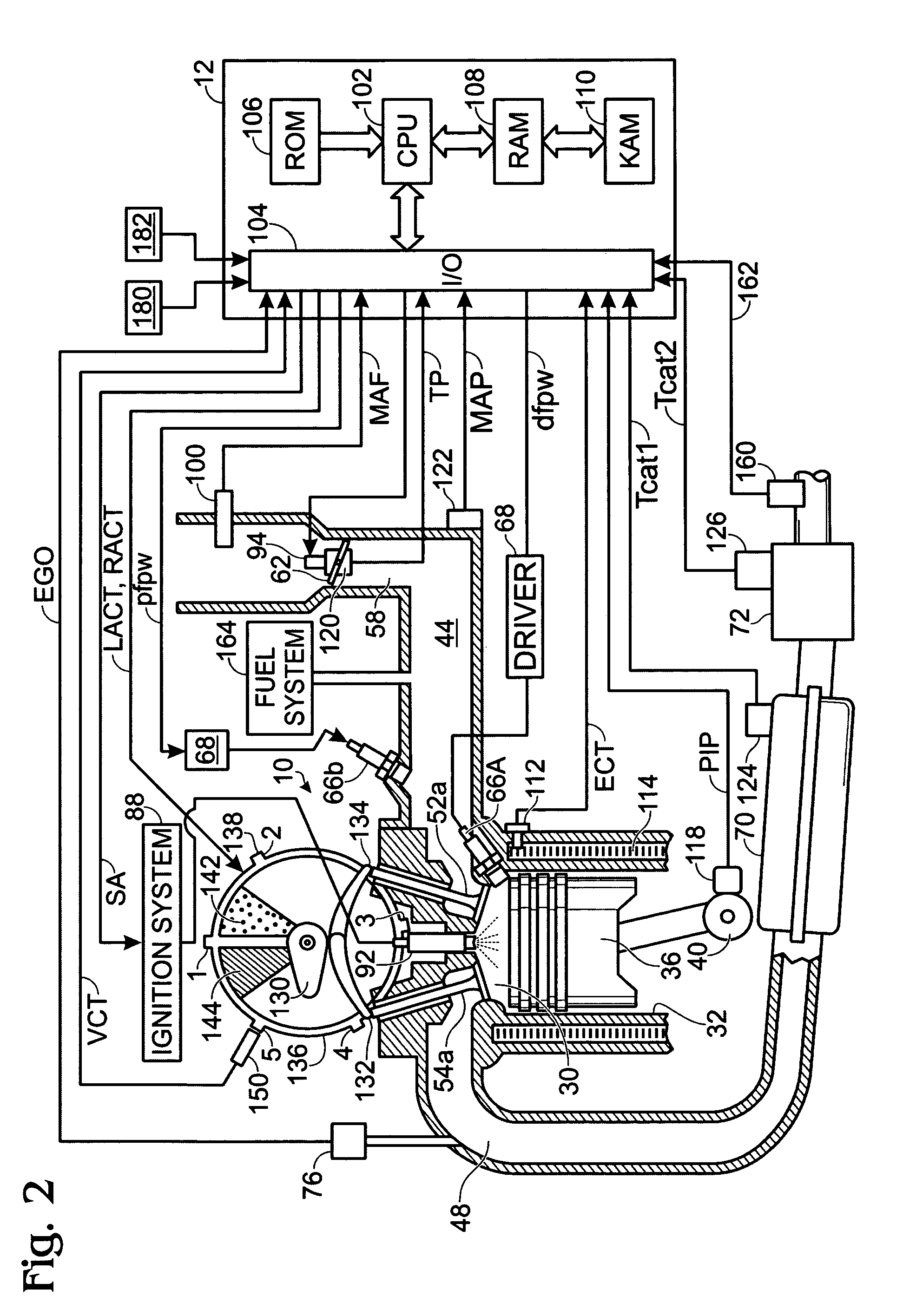
System and method for engine air-fuel ratio control
InactiveUS20070119415A1Improve engine performanceLow costElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelOxygen sensorOperant conditioning
A method for operating an engine having a first injector for injecting a first fuel into a cylinder of the engine and a second injector for injection a second fuel into said cylinder of the engine, the engine further having at least an exhaust gas oxygen sensor, the method comprising of varying an amount of said first fuel injection in response to said sensor under a first operating condition, and varying an amount of said second fuel injection in response to said sensor under a second operating condition.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
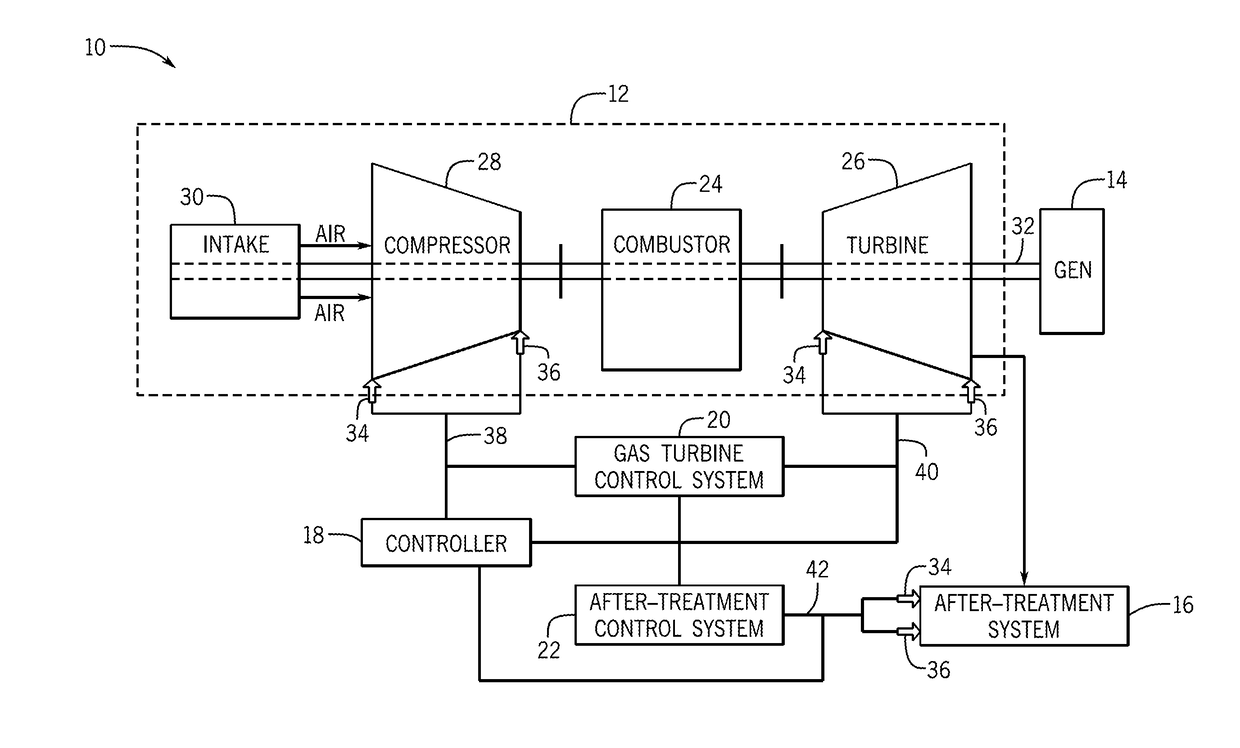
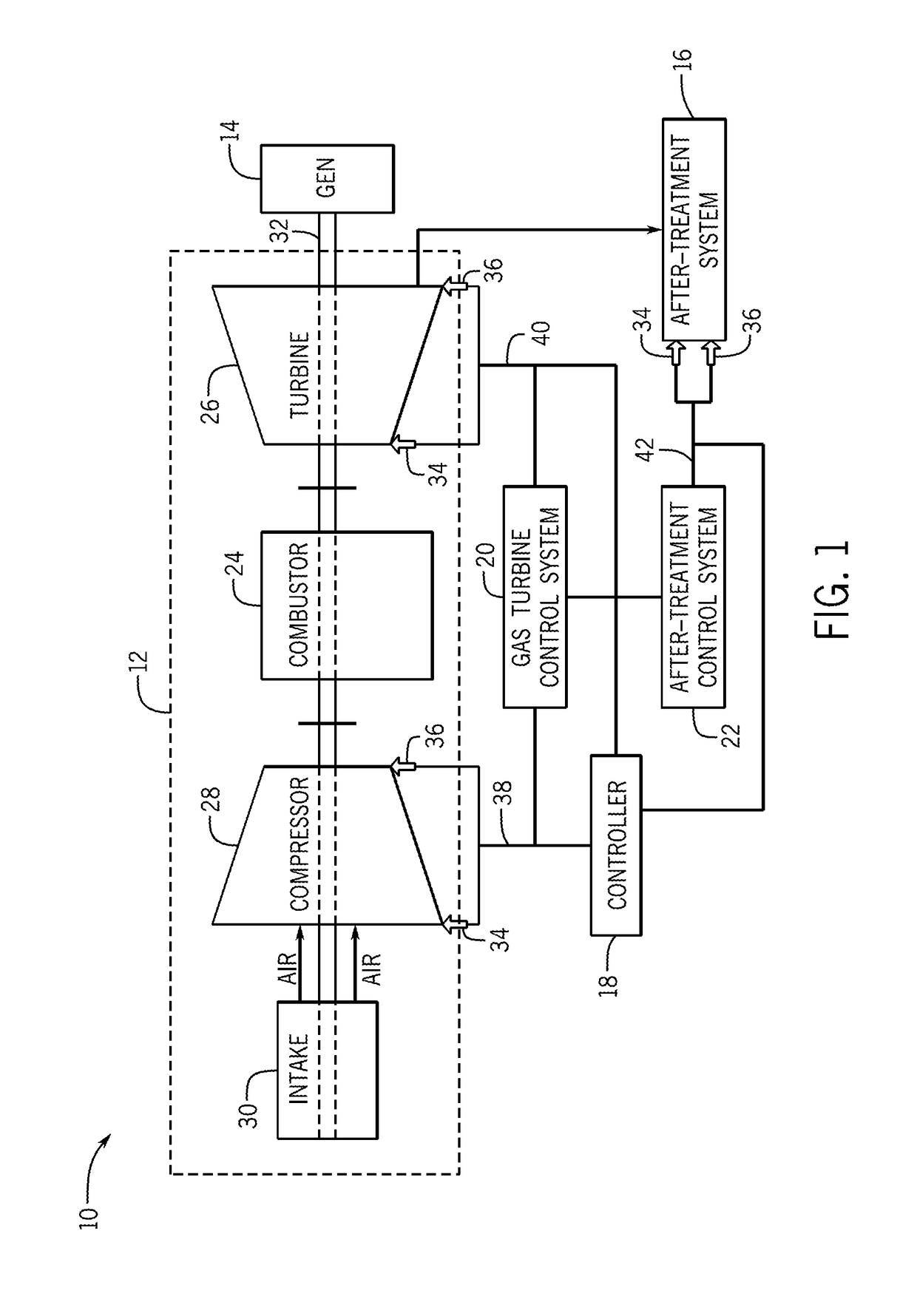
Enhanced performance of a gas turbine
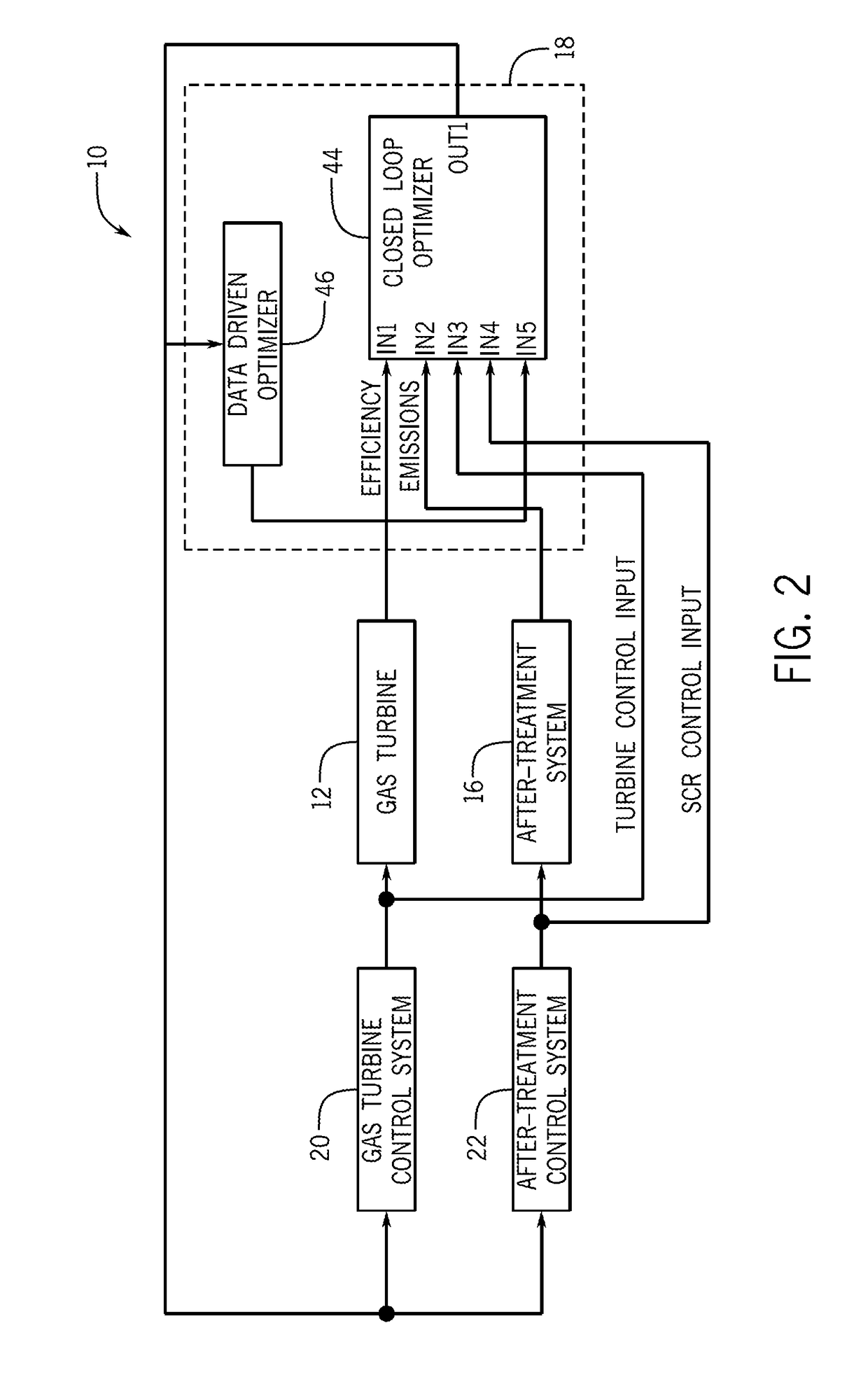
ActiveUS20170175645A1Reduce outputMinimizes outputExhaust apparatusEngine fuctionsAfter treatmentOperational behavior
In one embodiment, a system may include a gas turbine system. the gas turbine system includes a gas turbine, an after-treatment system that may receive exhaust gases from the gas turbine system, and a controller that may receive inputs and model operational behavior of an industrial plant based on the inputs. The industrial plant may include the gas turbine and the after-treatment system. The controller may also determine one or more operational parameter setpoints for the industrial plant, select the one or more operational parameter setpoints that reduce an output of a cost function, and apply the one or more operational parameter setpoints to control the industrial plant.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
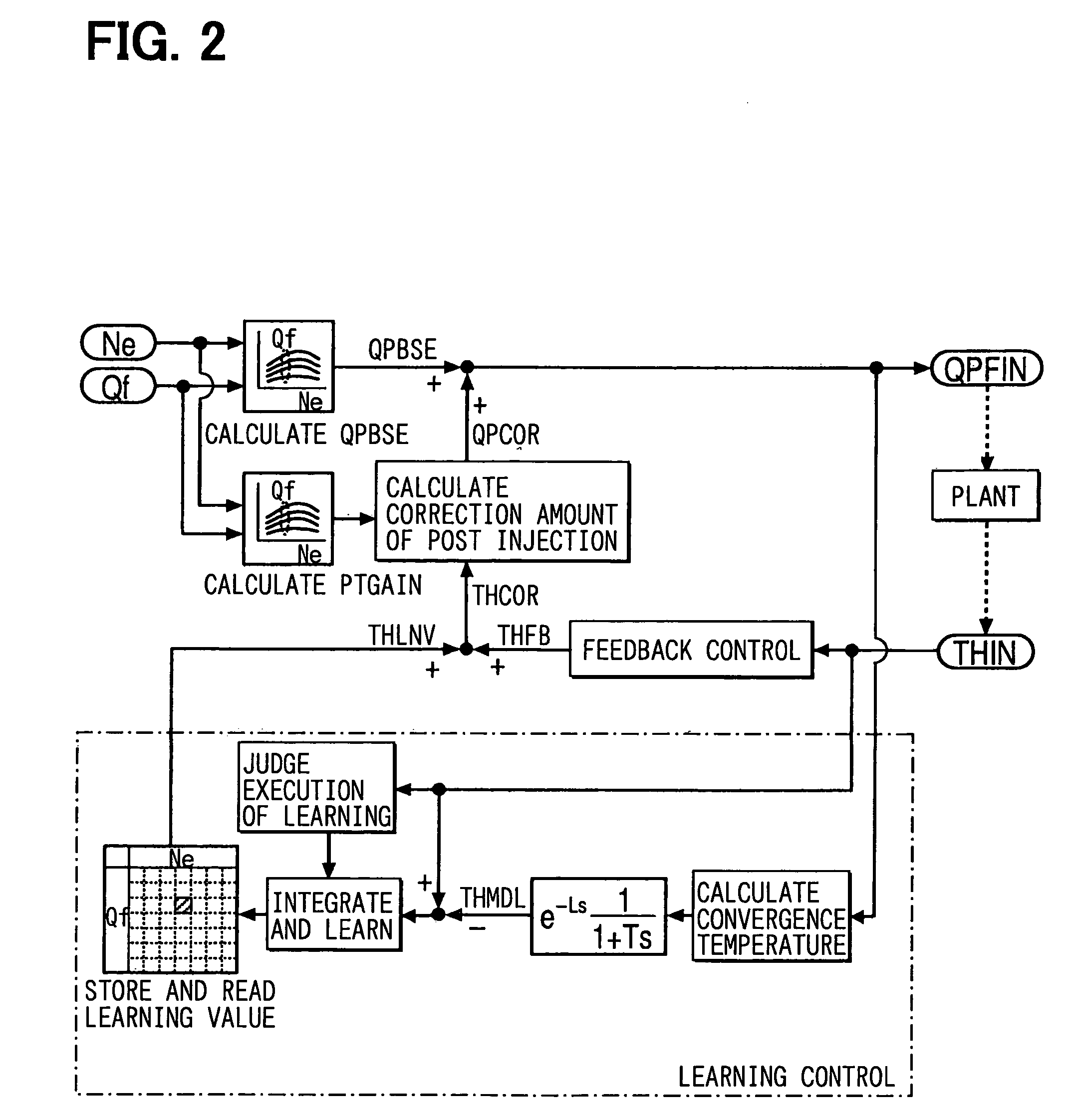
Exhaust cleaning device of internal combustion engine
ActiveUS7111455B2Sufficient learning frequencyEasy to controlElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesParticulatesEngineering
An exhaust cleaning device of an internal combustion engine includes a particulate filter disposed in an exhaust duct of the internal combustion engine. A regeneration control increases the temperature of the particulate filter to approximately a predetermined target temperature but the amount of the temperature increase controllably corrected by the regeneration control.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Engine exhaust emission control system providing on-board ammonia generation
InactiveUS20070271908A1Calculation amountHydrogenInternal combustion piston enginesControl systemOn board
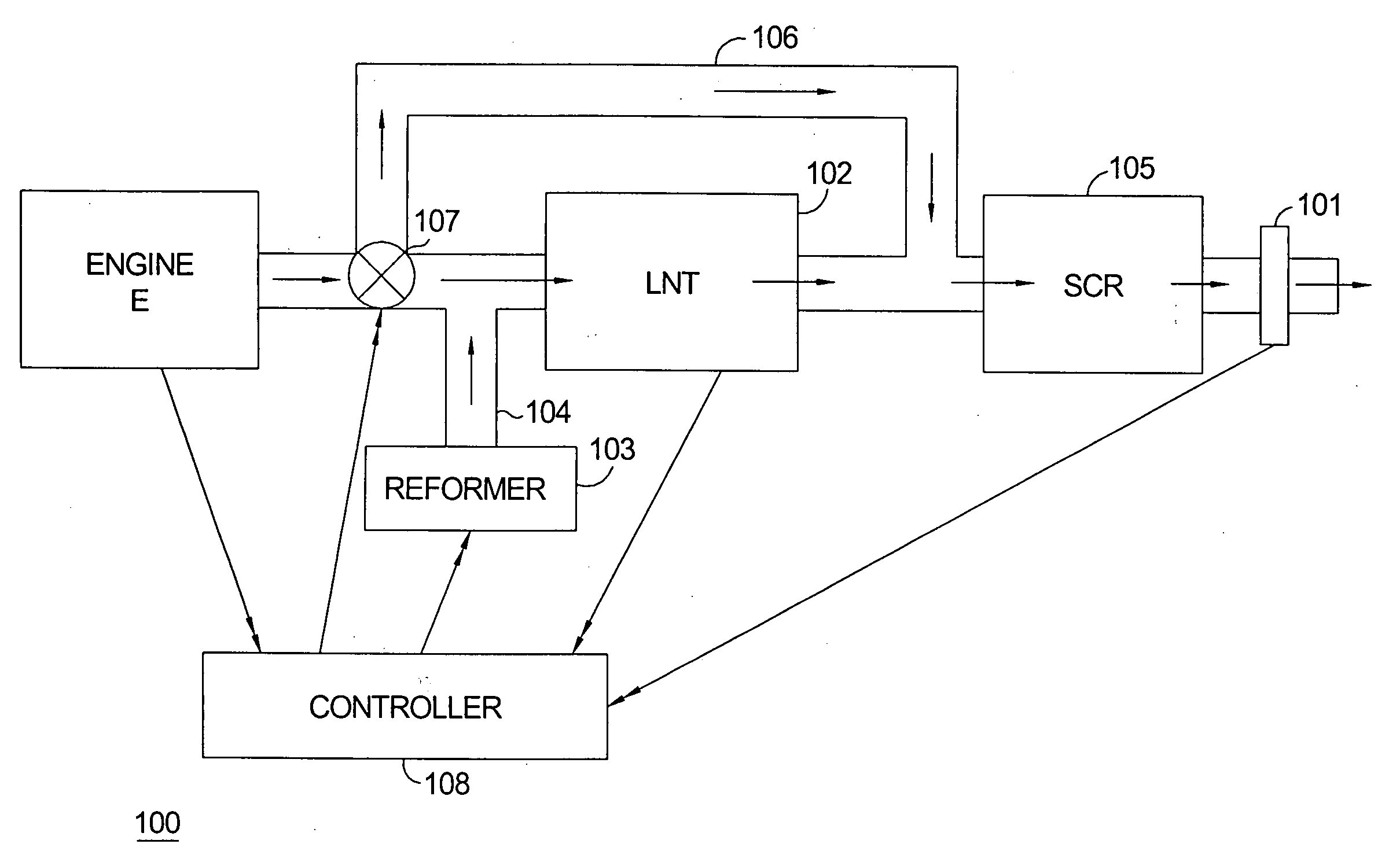
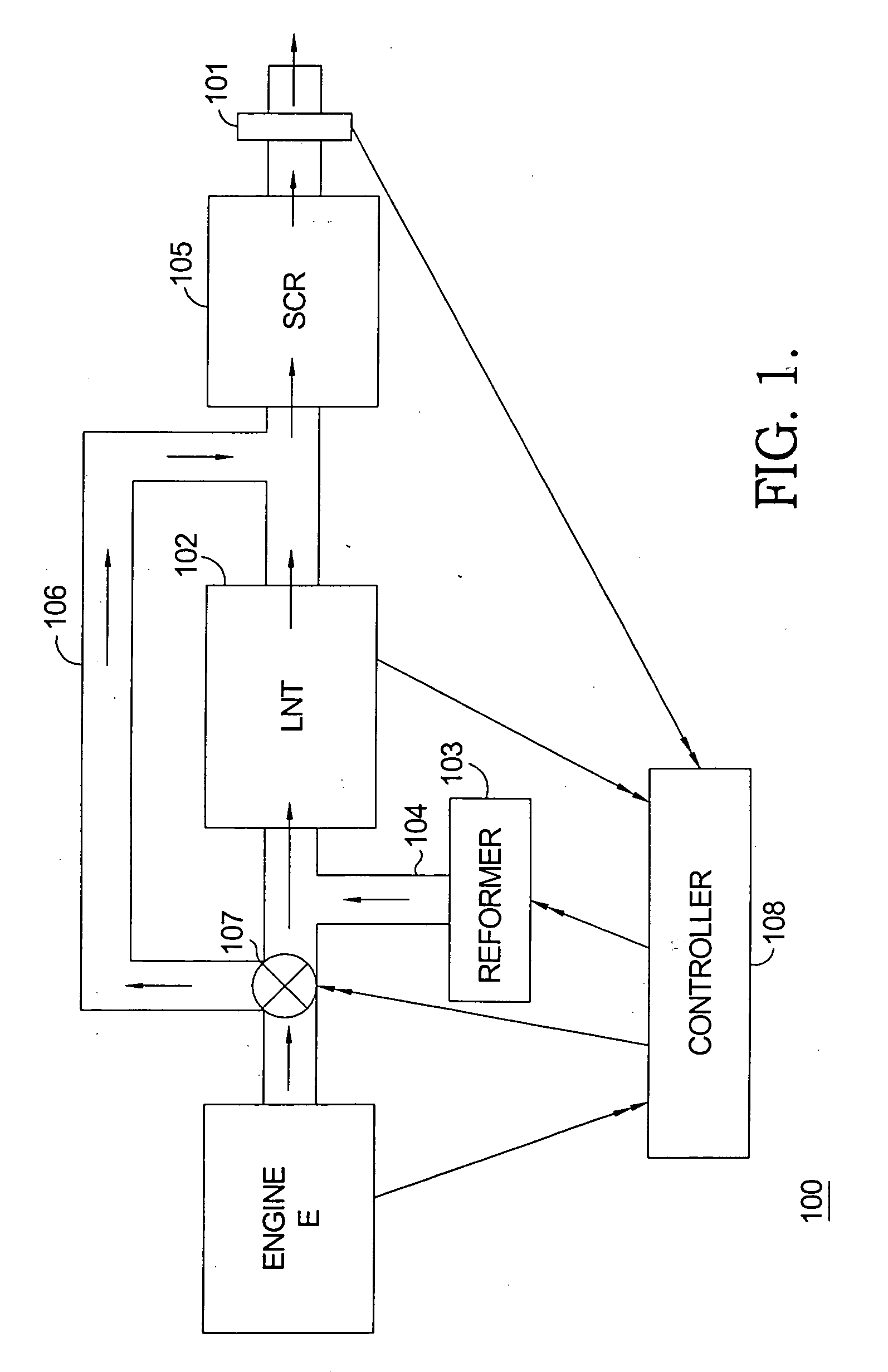
An exhaust emission control system that provides on-board ammonia generation includes a valve disposed upstream of the LNT and SCR catalyst that operates to selectively control the flow of engine exhaust gas to an LNT and / or an SCR catalyst; while reformate fuel is being conveyed from a reformer to the LNT, the valve operates to cause the exhaust gas to bypass the LNT and flow directly to the SCR catalyst. The exhaust emission control system further includes a controller provided with an algorithm that monitors engine operating conditions and exhaust gas conditions, estimates the cumulative amount of exhaust gas created by the engine and the amount of NOx stored in the LNT, and calculates the amount of NOx required to be converted to NH3.
Owner:DELPHI TECH INC
System for controlling particulate filter temperature
InactiveUS6901751B2Increase flow rateProtection from damageInternal combustion piston enginesDispersed particle filtrationParticulatesElectricity
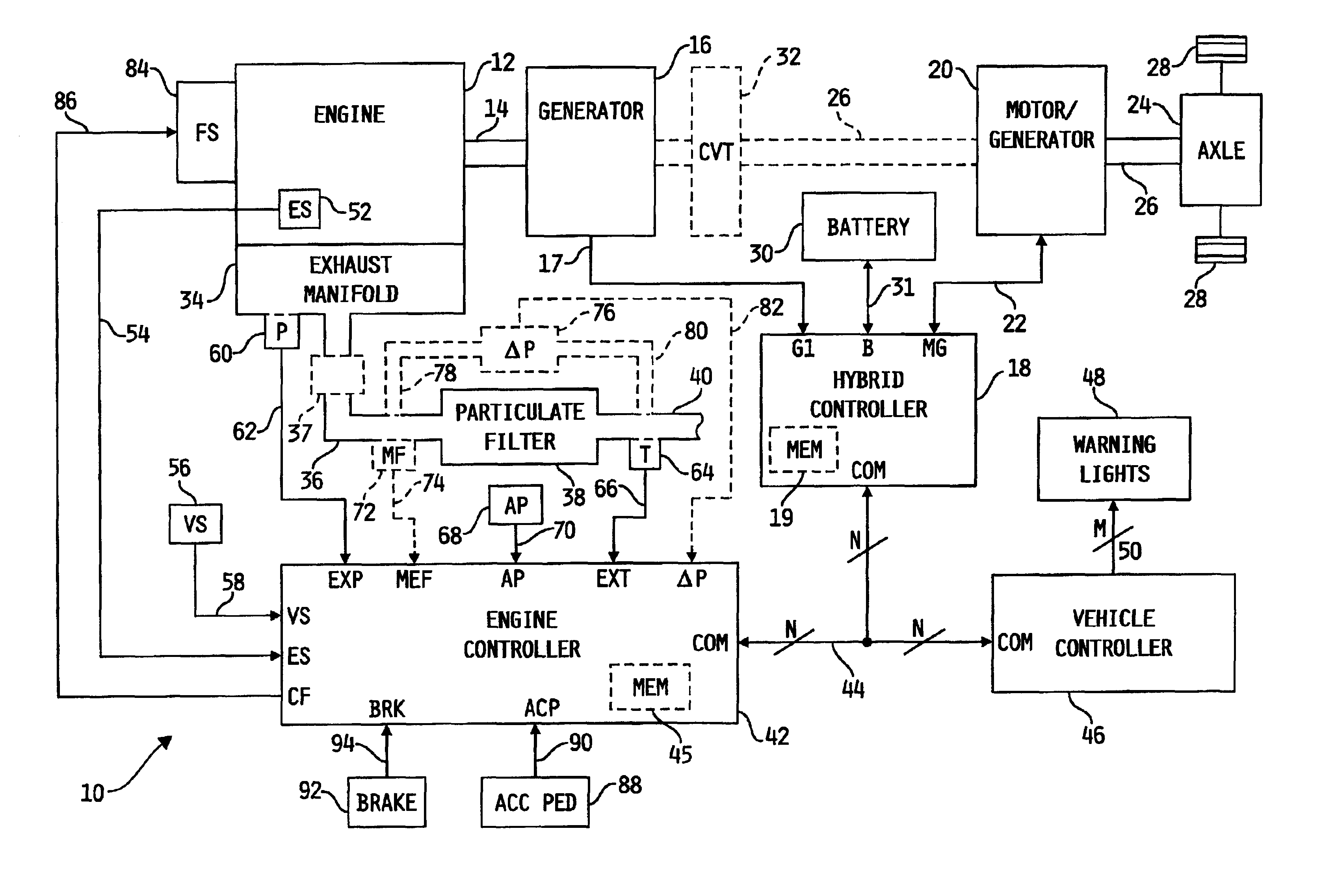
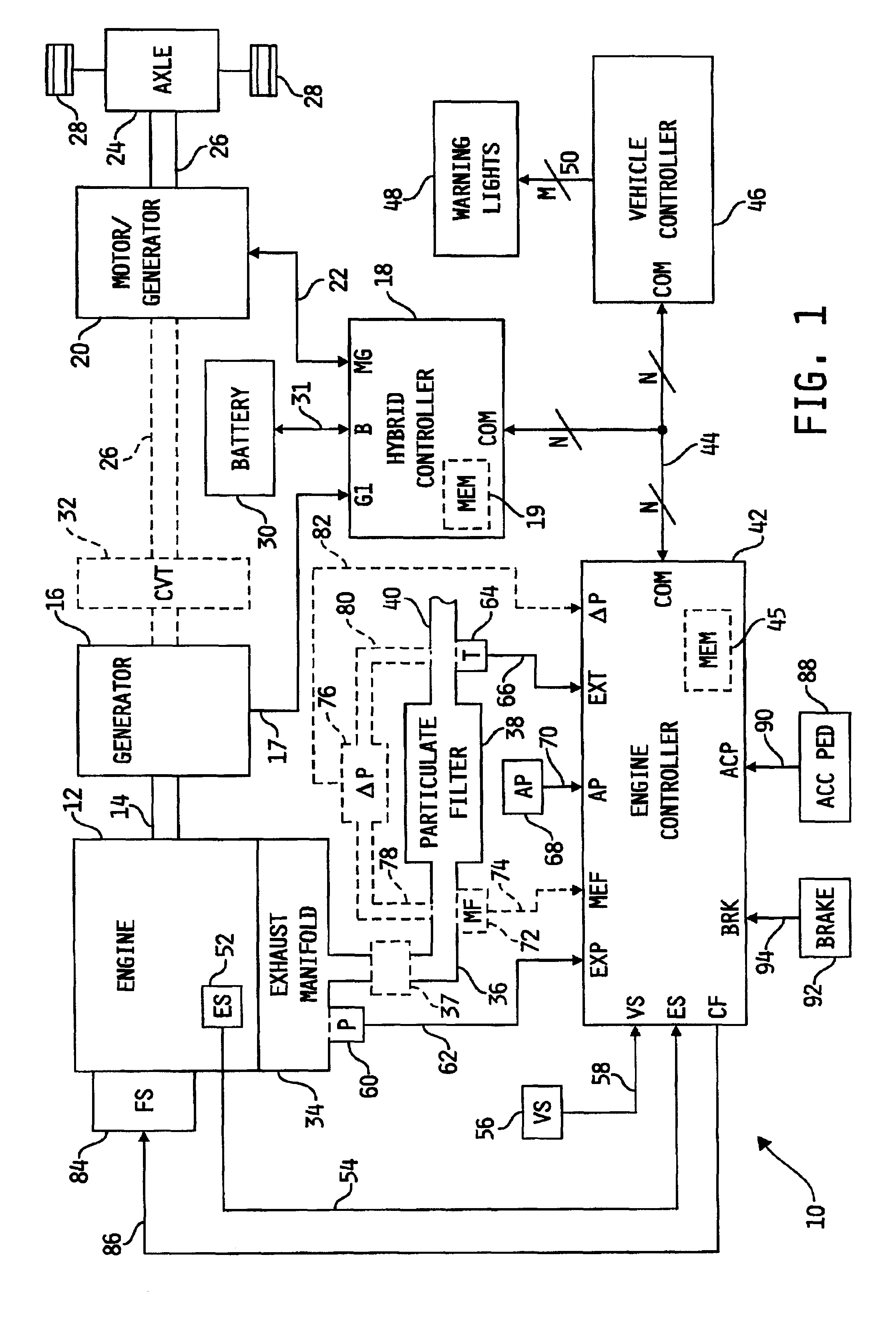
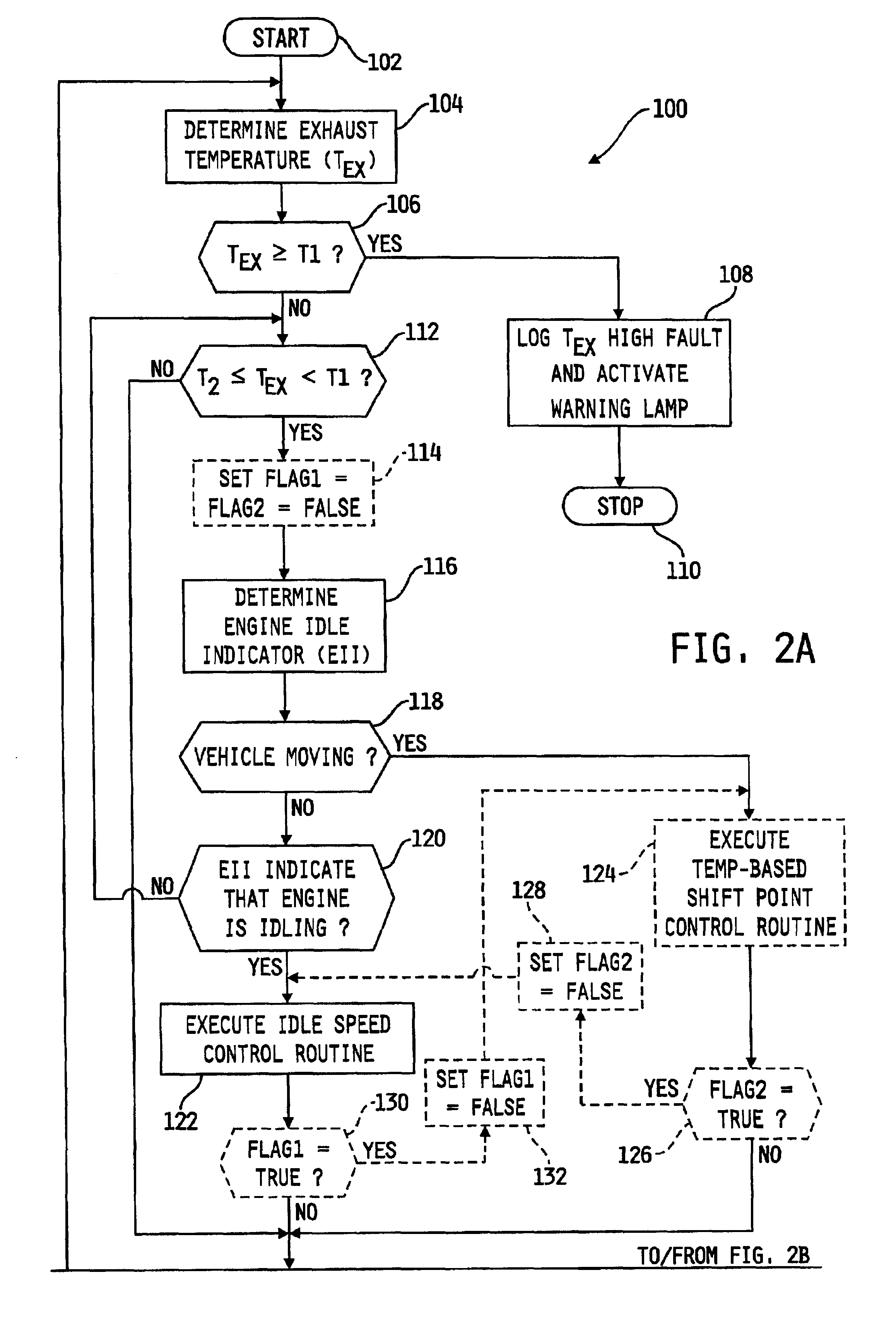
A system for controlling the temperature of a particulate filter coupled to an exhaust outlet of an internal combustion engine includes a controller responsive to volumetric flow and temperature of exhaust gas to determine a filter regeneration parameter. In a hybrid electric-engine vehicle application, various control strategies are implemented as a function of the regeneration parameter to control exhaust gas temperature suitably for proper regeneration of the particulate filter. Such strategies include shifting the duty cycle of the engine toward lower engine speed operation along lines of constant power output, modifying the ratio of electrical power and engine power and controlling recharging of the battery supplying electrical energy to the vehicle's electric drive motor under vehicle deceleration conditions. In vehicle applications including a transmission coupled directly to the engine, shift points of the transmission are modified as a function of the regeneration parameter to control exhaust gas temperature.
Owner:CUMMINS INC
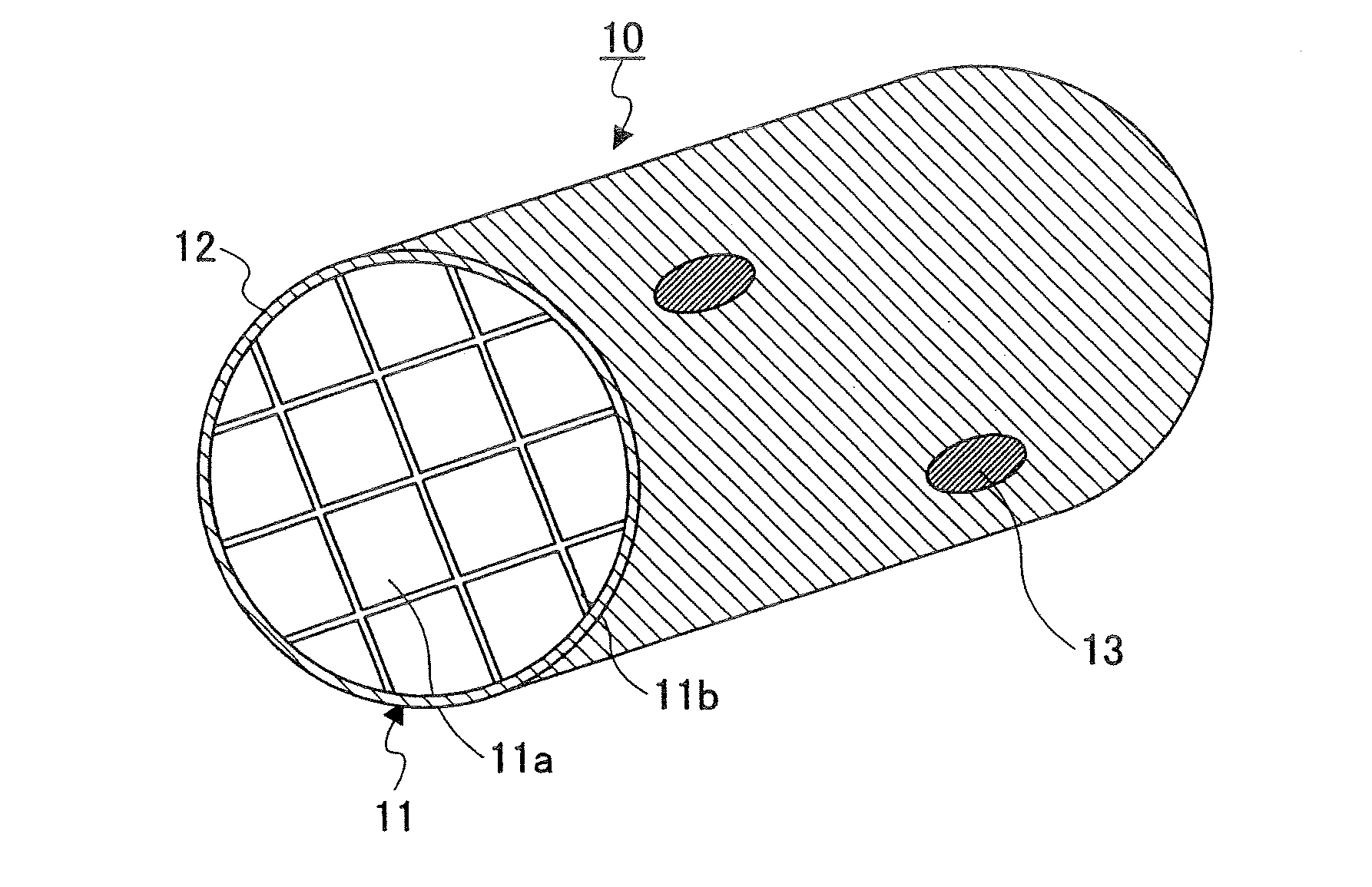
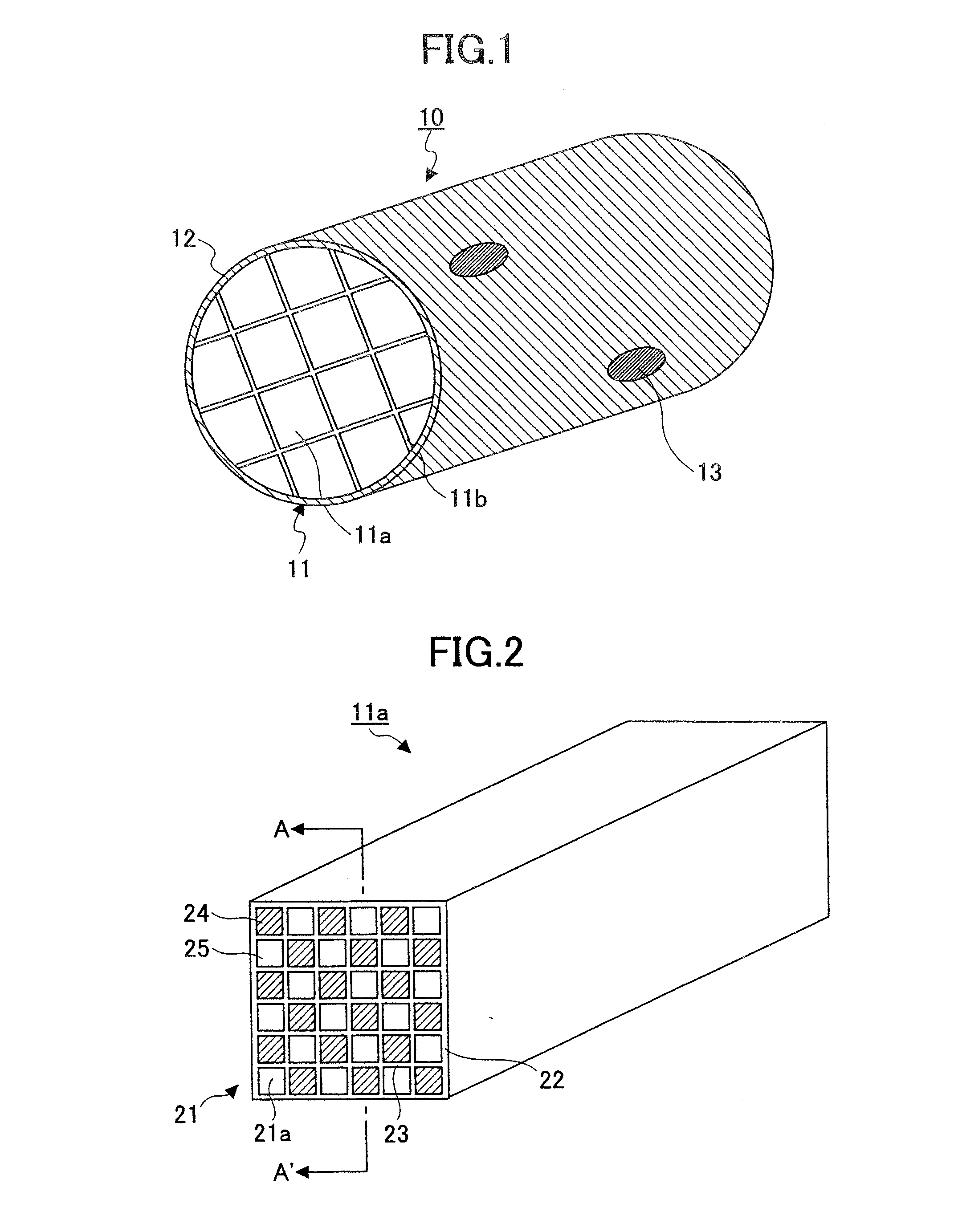
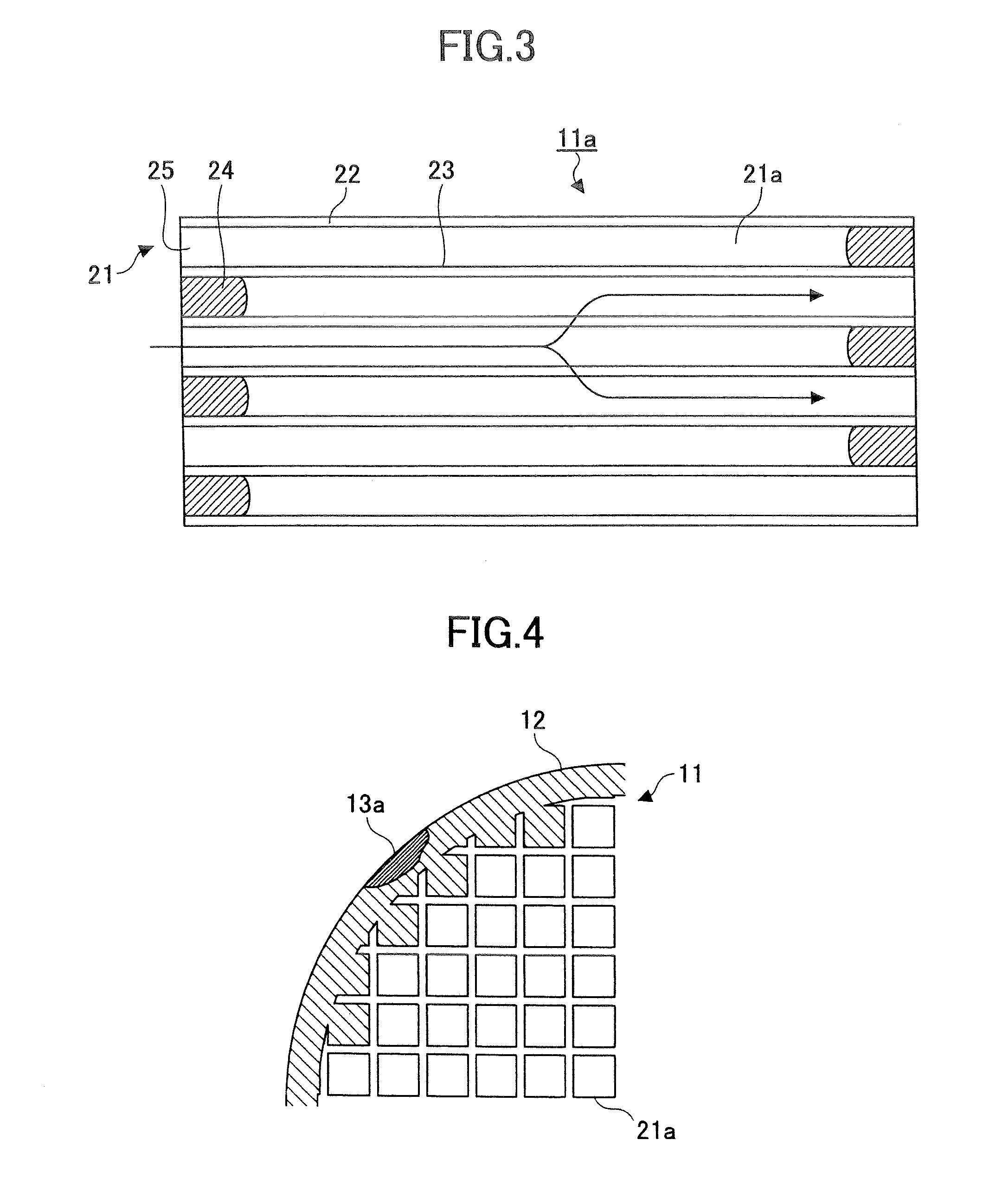
Honeycomb structure, method of manufacturing honeycomb structure, exhaust gas treating apparatus, and method of manufacturing exhaust gas treating apparatus
A honeycomb structure including plural cells with holes arranged in a longitudinal direction, a peripheral wall, and a defective portion formed on the peripheral wall that is mended with a mending material that is in a color different from the color of the peripheral wall. Also, a method is provided for manufacturing a honeycomb structure including plural cells with holes arranged in a longitudinal direction and a peripheral wall which method involves mending a defective portion formed on the peripheral wall of the honeycomb structure with a mending material in a color different from the color of the peripheral wall.
Owner:IBIDEN CO LTD
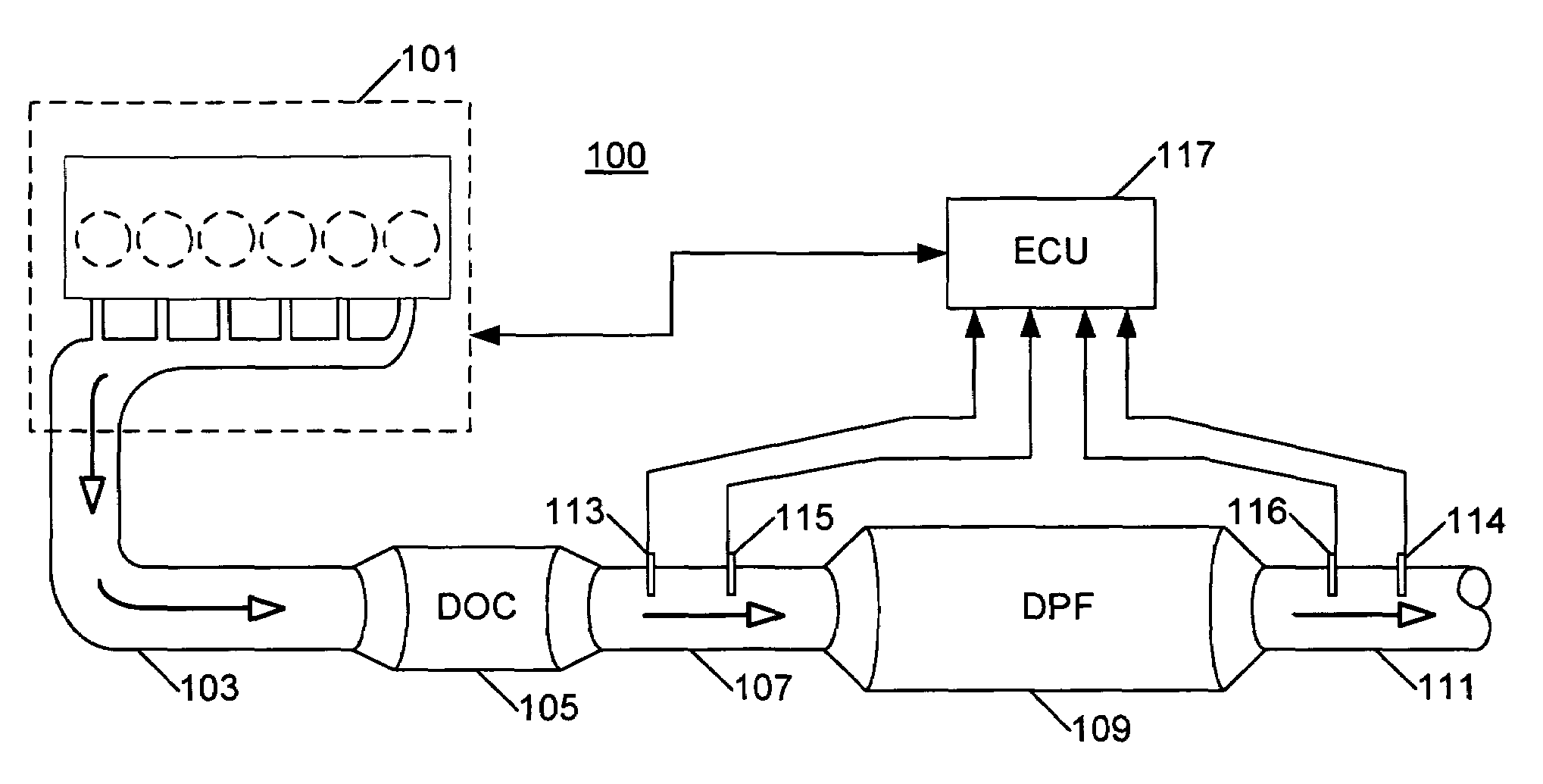
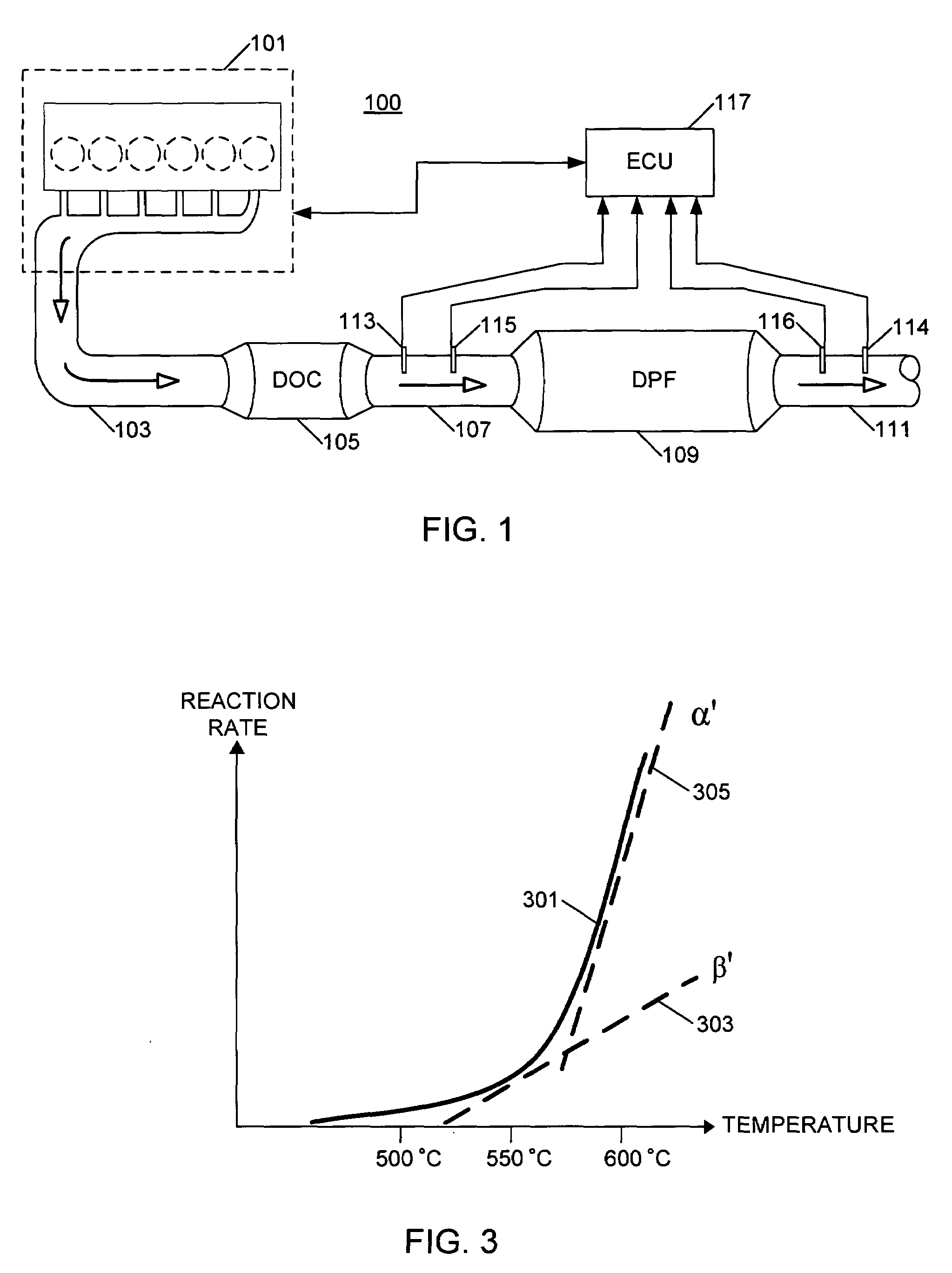
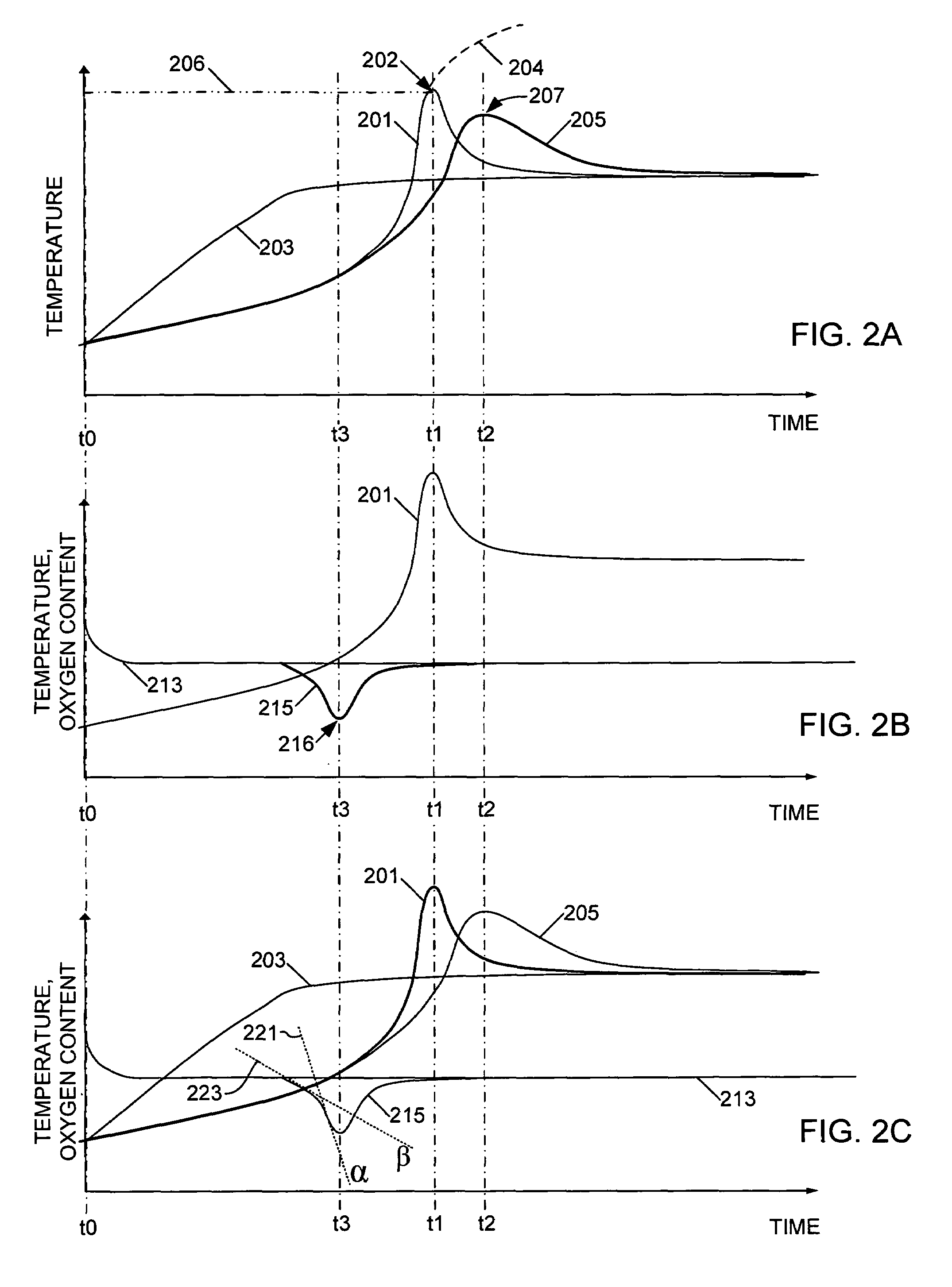
DPF regeneration monitoring method
A method for operating an internal combustion engine (100) and exhaust system therefor includes the step of initiating a regeneration event in a diesel particulate filter (DPF 109) (401). A first oxygen concentration (213) of a gas upstream of the DPF 109, and a second oxygen concentration (215) of the gas downstream of the DPF 109 are sensed (403) to infer a rate of combustion of material in the DPF (405) based on the difference between the first (213) and the second (215) oxygen concentrations. The rate of combustion is compared to a threshold value (409) and the regeneration event in the DPF 109 is terminated (411) if the rate of combustion is above the threshold.
Owner:INT ENGINE INTPROP CO LLC
Emission control system with catalyst warm-up speeding control
InactiveUS6898927B2High precisionLow costElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesControl systemExhaust fumes
An emission control system has a catalyst and a sensor responding to a component of exhaust gas. In order to speed warming up the catalyst, the emission control system increases the amount of heat dissipated by exhaust gas. A diagnosis of the emission control system is carried out by determining whether the amount of heat dissipated by exhaust gas is sufficient or insufficient. The amount of heat dissipated by exhaust gas is represented by the length of time to an activated state of the sensor. In the diagnosis, the amount of heat generated by a heater provided in the sensor is taken into consideration.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Sensor Element for Gas Sensors and Method for Operating Same
ActiveUS20090217737A1Simple structureCost-effectiveInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusElectrical resistance and conductanceScreen printing
A sensor element is provided for gas sensors, in particular to determine particles in gas mixtures, the sensor element including at least one electrochemical measuring element exposed to the gas mixture to be determined, and at least one temperature-measuring element integrated into the sensor element. The temperature-measuring element includes a resistor track, which has an electric resistance of less than 180 Ohm at 0° C. The resistor track may thus be produced by thin-foil technology, such as screen printing, for example.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Catalyst deterioration detecting apparatus and method
InactiveUS20030017603A1Electrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesOxygen sensorEnvironmental engineering
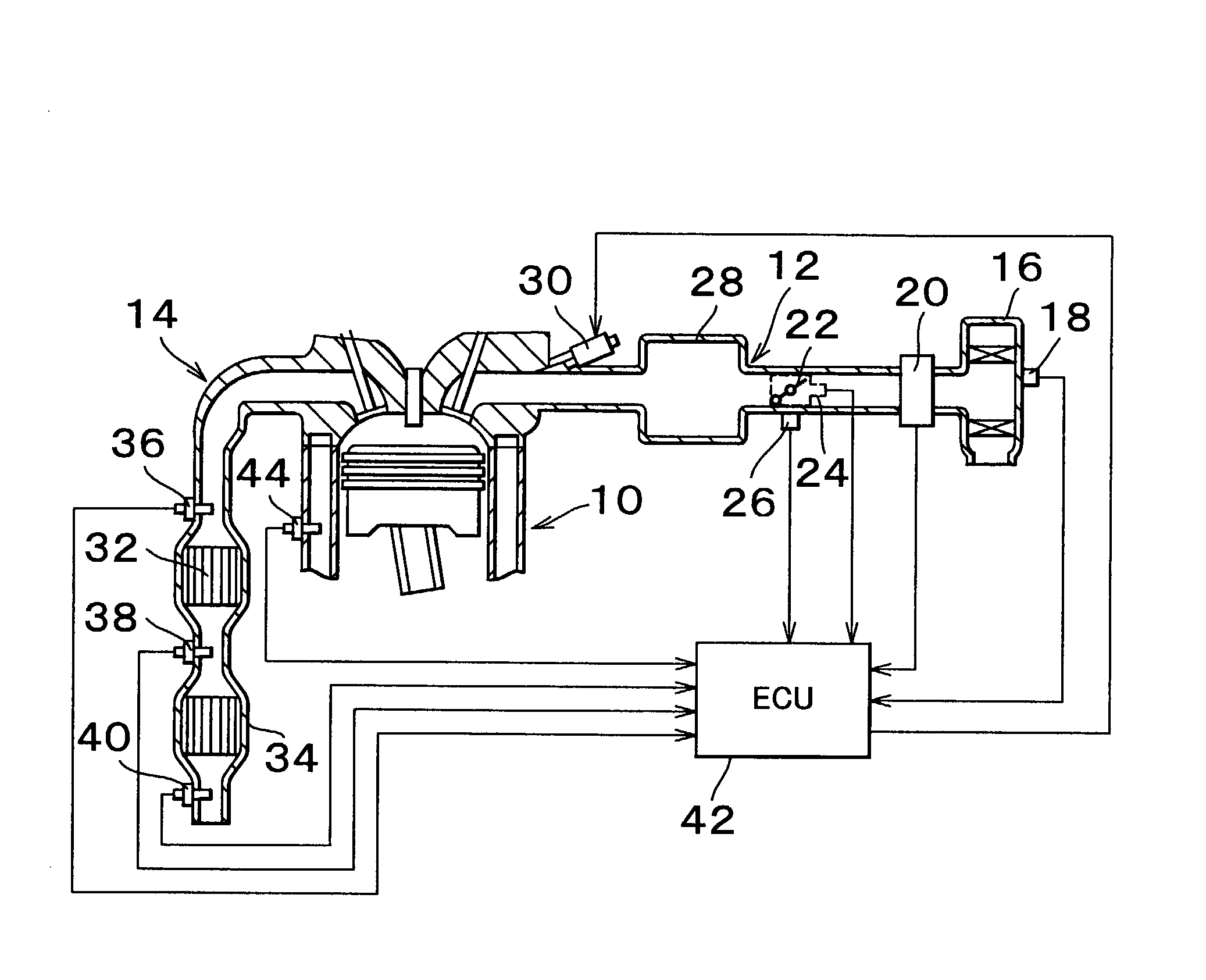
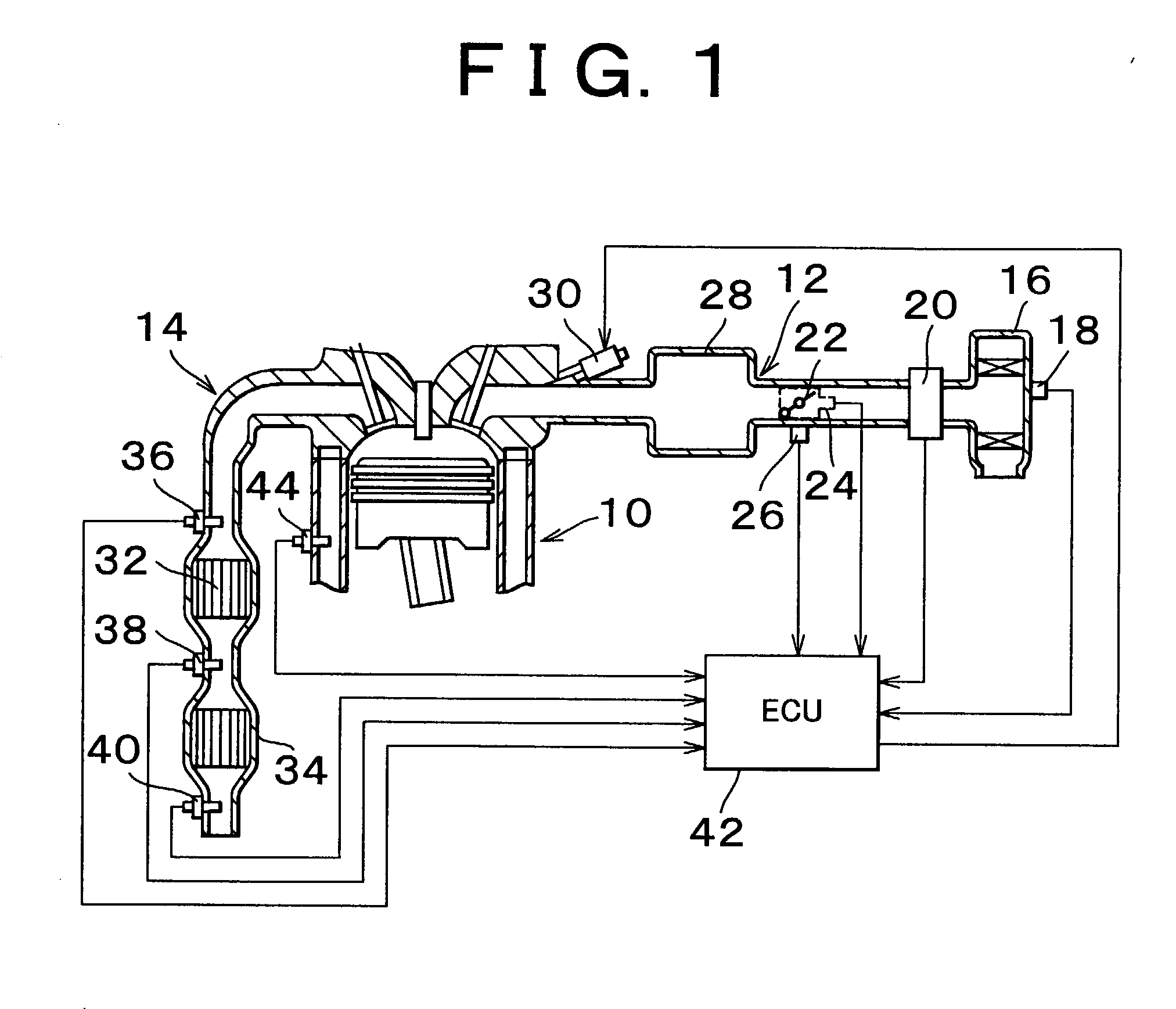
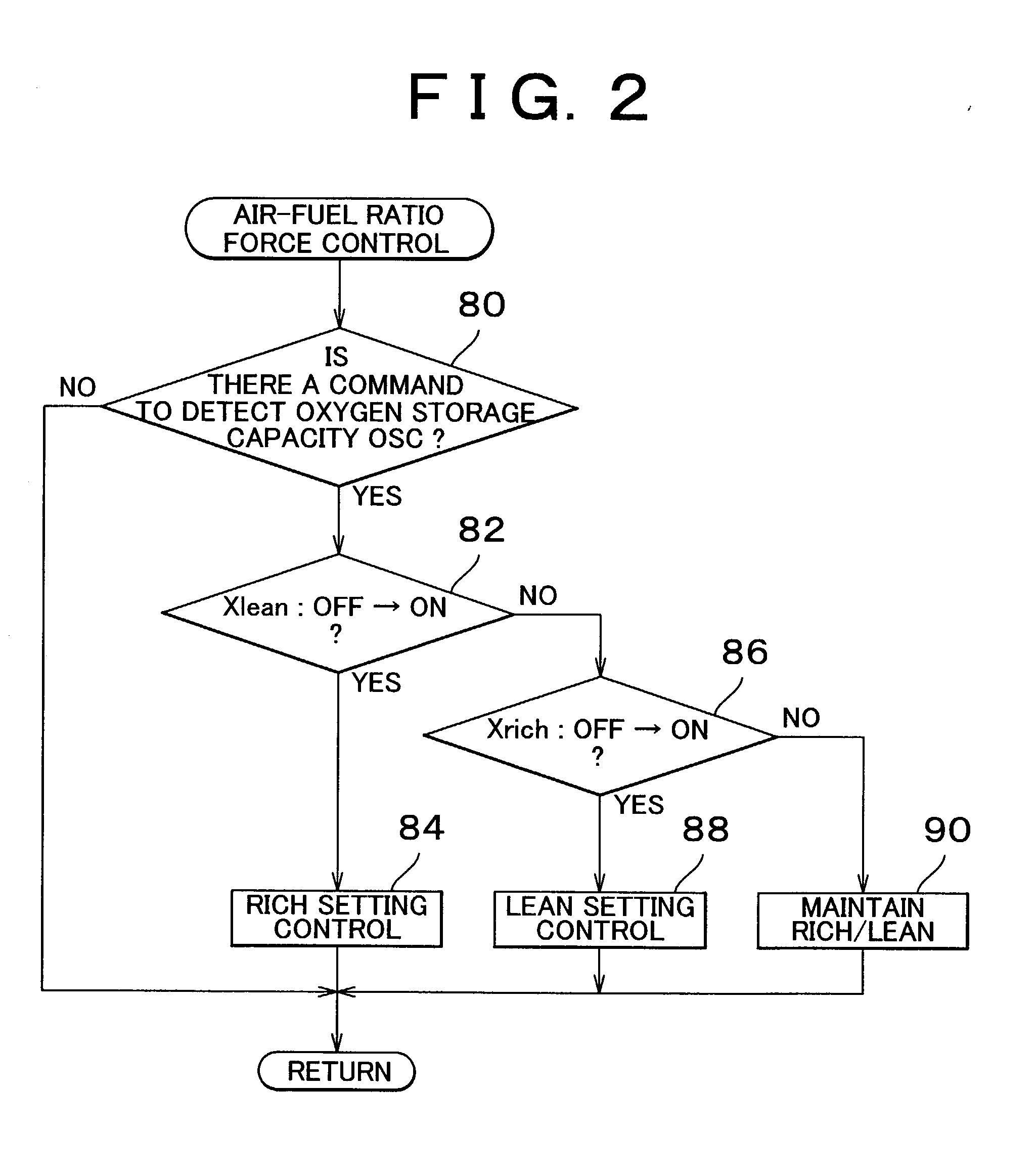
An upstream side catalyst and a downstream side catalyst are disposed in an exhaust passage. A first oxygen sensor is disposed between these two catalysts and a second oxygen sensor is disposed downstream of the downstream side catalyst. The air-fuel ratio is forcibly oscillated and the oxygen storage capacity of the upstream side catalyst is detected. Deterioration of the upstream side catalyst is then detected based on whether this oxygen storage capacity is larger than a predetermined value. The forced oscillation of the air-fuel ratio is performed only when the oxygen storage state of the downstream side catalyst is appropriate.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
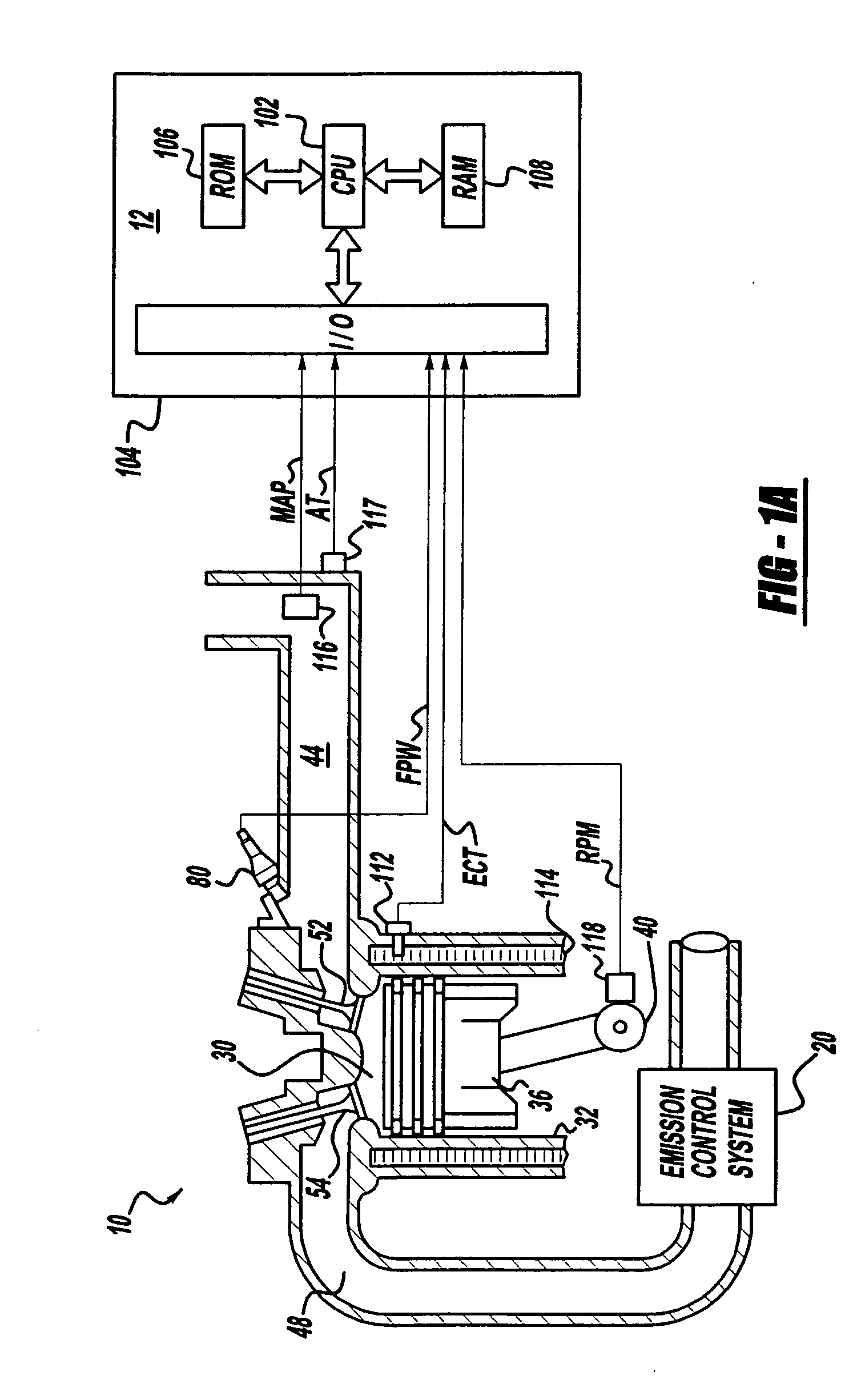
System for controlling valve timing of an engine with cylinder deactivation
InactiveUS7249583B2Sufficient NOx reduction and fuel economy benefitsEasy to operateValve arrangementsElectrical controlSystems designEngineering
Various systems and methods are disclosed for carrying out combustion in a fuel-cut operation in some or all of the engine cylinders of a vehicle. Further, various subsystems are considered, such as fuel vapor purging, air-fuel ratio control, engine torque control, catalyst design, and exhaust system design.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
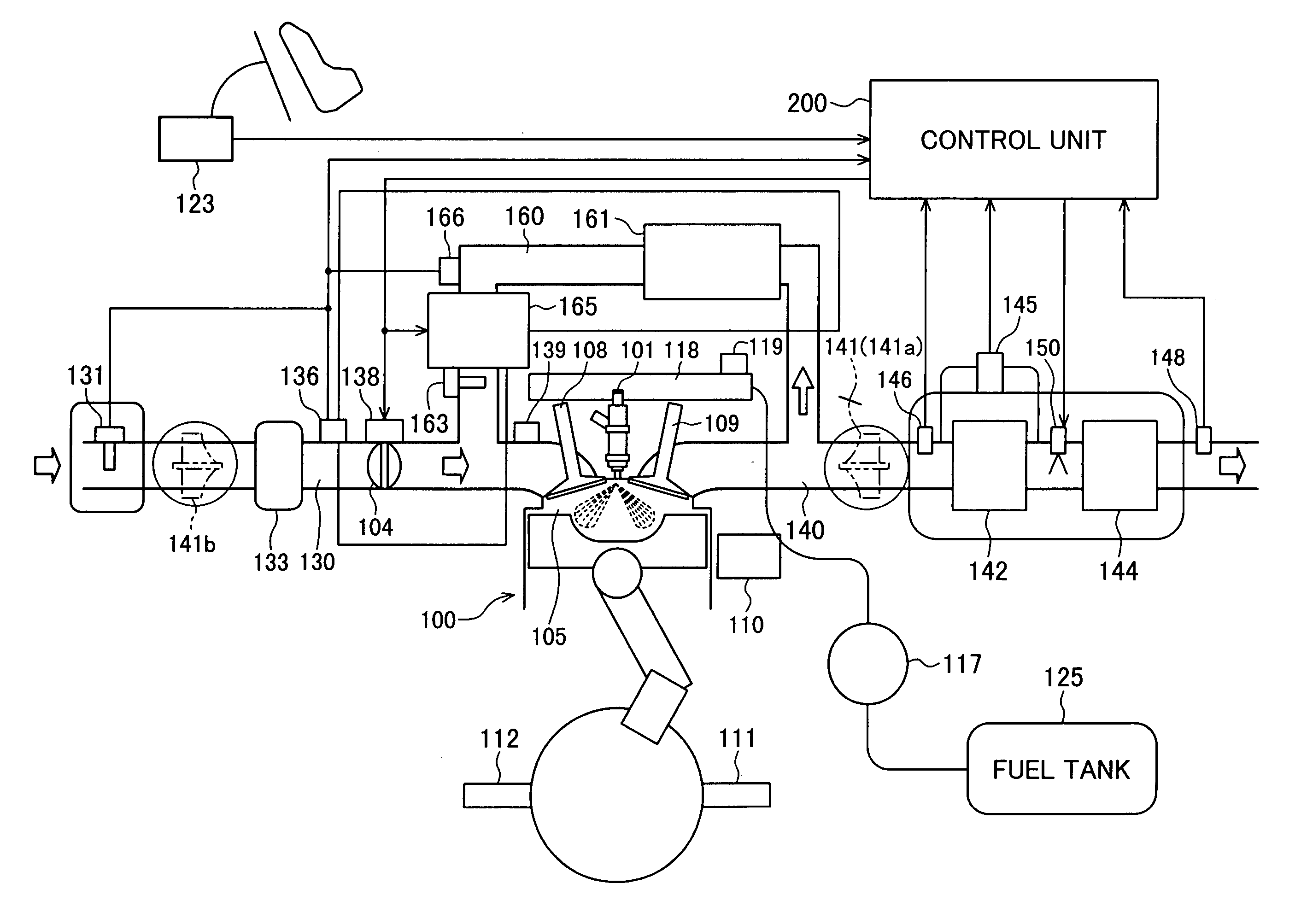
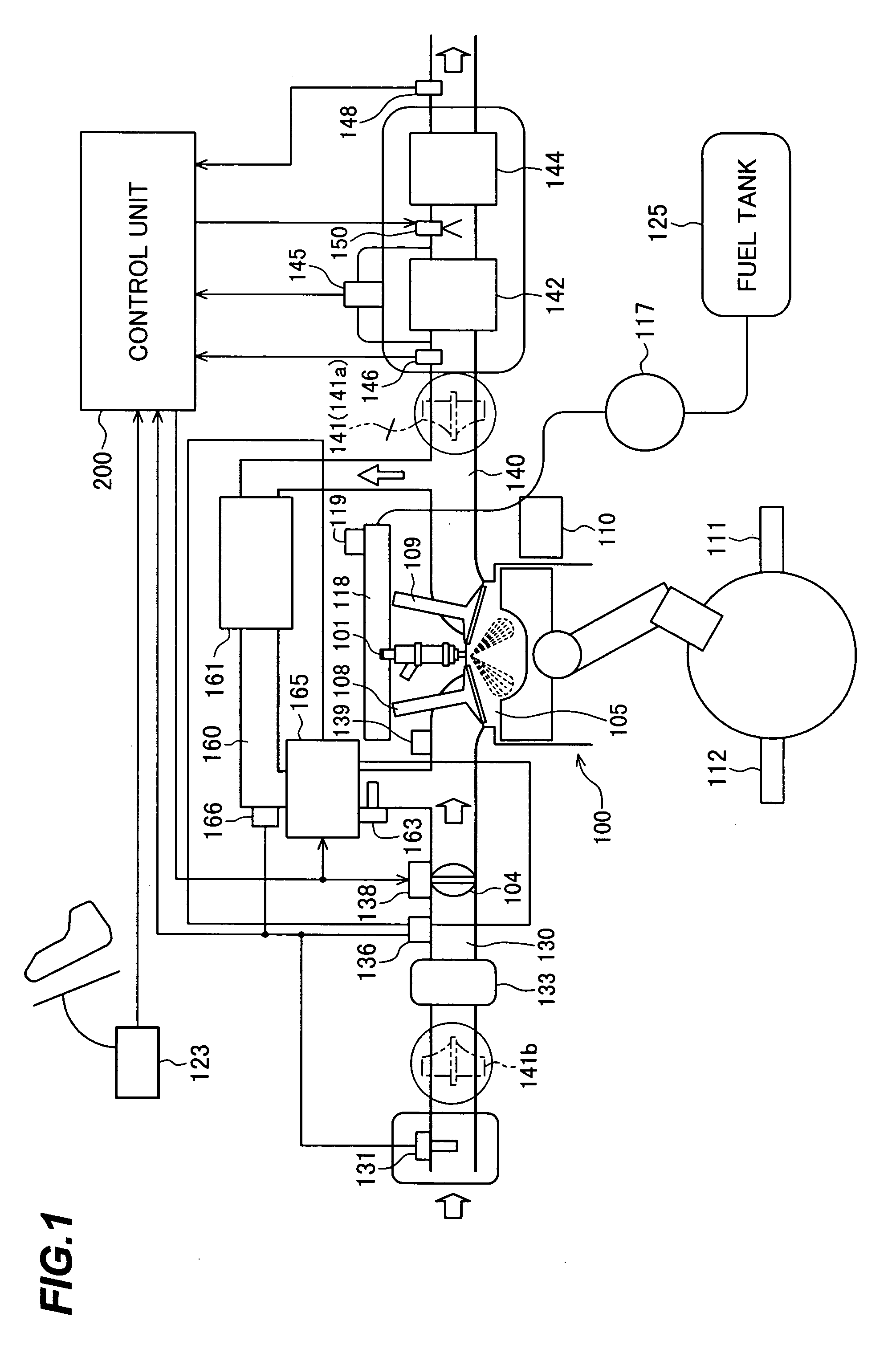
Reagent dosing system and method of dosing reagent
InactiveUS20090301067A1Well mixedInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusEngineeringInternal combustion engine
A method of dosing a reagent into an exhaust gas stream of an internal combustion engine having an SCR catalyst, the method comprising injecting reagent from a reagent tank into the exhaust gas stream at a position upstream of the SCR catalyst using a reagent injector in accordance with a first dosing schedule in order to remediate a predetermined proportion of NOx in the exhaust gas stream, the first dosing schedule being associated with a first range of engine operating conditions; and injecting reagent from the reagent tank into the exhaust gas stream at a position upstream of the SCR catalyst using a reagent injector in accordance with a second dosing schedule in order to enable heat transfer between the reagent injector and said injected reagent, the second dosing schedule being associated with a second range of engine operating conditions.Dosing in accordance with said first or said second dosing schedule is carried out in dependence on whether engine operating conditions lie within said first or said second range of engine operating conditions, and the proportion of NOx in the exhaust gas stream which is remediated by dosing using said second dosing schedule is less than said predetermined portion. A reagent dosing system is also provided for dosing a reagent into the exhaust gas stream of an internal combustion engine, comprising a reagent tank for storing a supply of reagent, an injector module comprising an atomising dispenser and a positive-displacement metering pump which draws reagent from the reagent tank and delivers it to the dispenser a supply line coupling the reagent tank to the injector module, and a dosing control unit operable to control the injector module to inject reagent into the exhaust gas stream. A priming pump is provided to urge reagent along the supply line toward the injector module under selected conditions.
Owner:DELPHI TECH IP LTD
Pressure sensor diagnosis via a computer
InactiveUS6947831B2Reduce stepsLower regenerationAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlParticulatesDifferential pressure
A method is described for controlling regeneration of a particulate filter based on at least a sensor, such as a differential pressure sensor. Degradation of the sensor is then detected in a variety of ways. One approach takes advantage of the slowly varying flow resistance of the filter compared with the more rapid variations in flow caused by changing engine conditions. Default operation is then taken when a degraded sensor is detected.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Exhaust gas aftertreatment systems
InactiveUS6993900B2Accurate estimateImprove NOx conversion efficiencyInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusAmmonia storageDynamic models
A method is presented for estimating an amount of ammonia stored in a urea-based SCR catalyst based on a dynamic model of the catalyst. The model takes into account chemical and physical properties of the catalyst, such as catalyst volume, the number of available ammonia storage cites, adsorption and desorption dynamics, as well as poisoning, thermal aging, and different catalyst operating temperatures, and generates the estimate based on a measured or estimated amount of NOx in an exhaust gas mixture upstream of the catalyst, an amount of reductant injected into the catalyst to facilitate NOx reduction, and on a measured value of NOx in an exhaust gas mixture downstream of the catalyst. The estimated ammonia storage amount is then used to control the amount of reductant injected into the catalyst to maintain desired ammonia storage amount such that maximum NOx conversion efficiency coupled with minimum ammonia slip are achieved.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Emission amount report device, system for charge for exhaust gas from vehicle, management unit and inspection device making up the system
InactiveUS20050173523A1Sure easyIncrease volumeTicket-issuing apparatusInternal combustion piston enginesHydrocotyle bowlesioidesHazardous substance
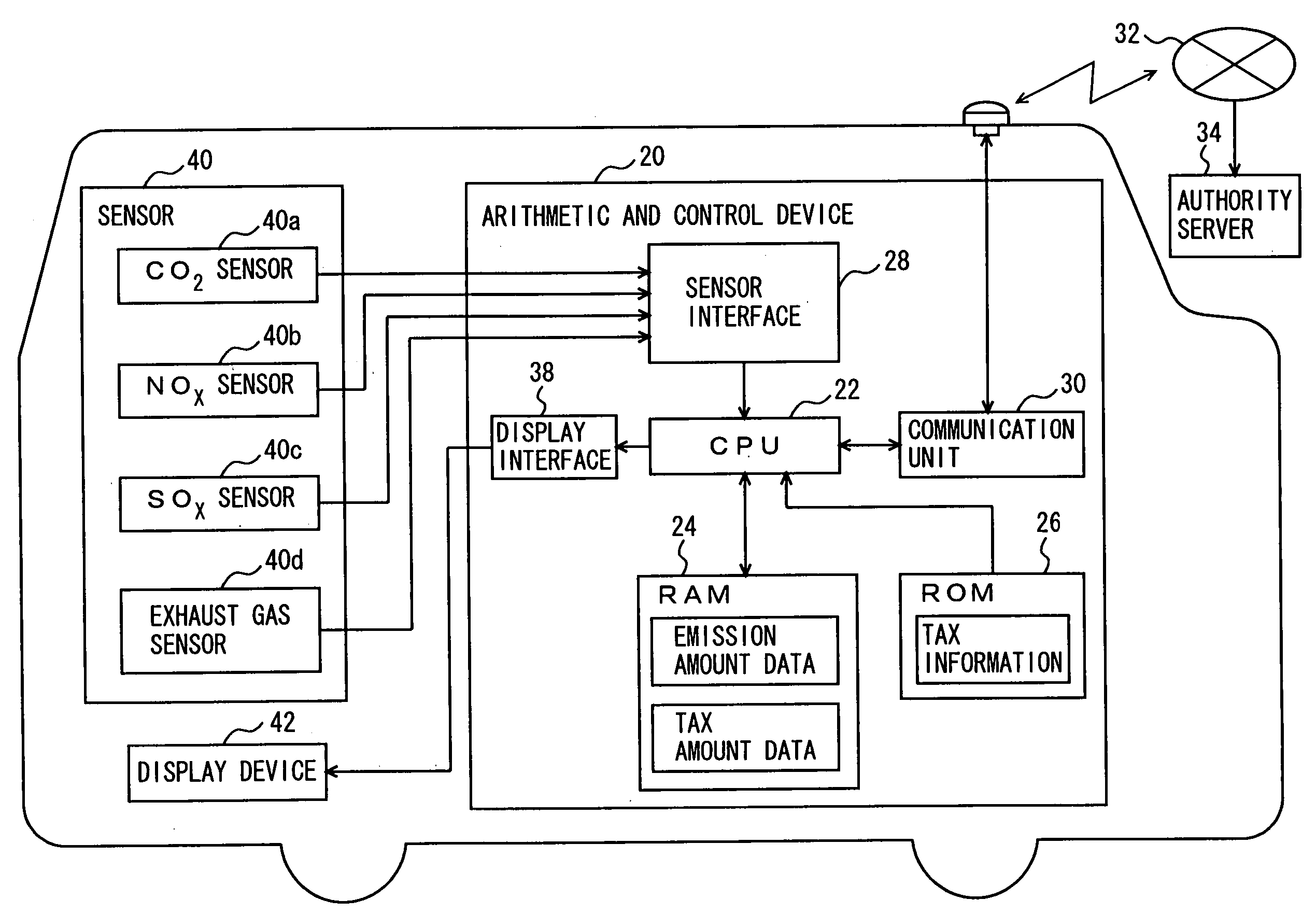
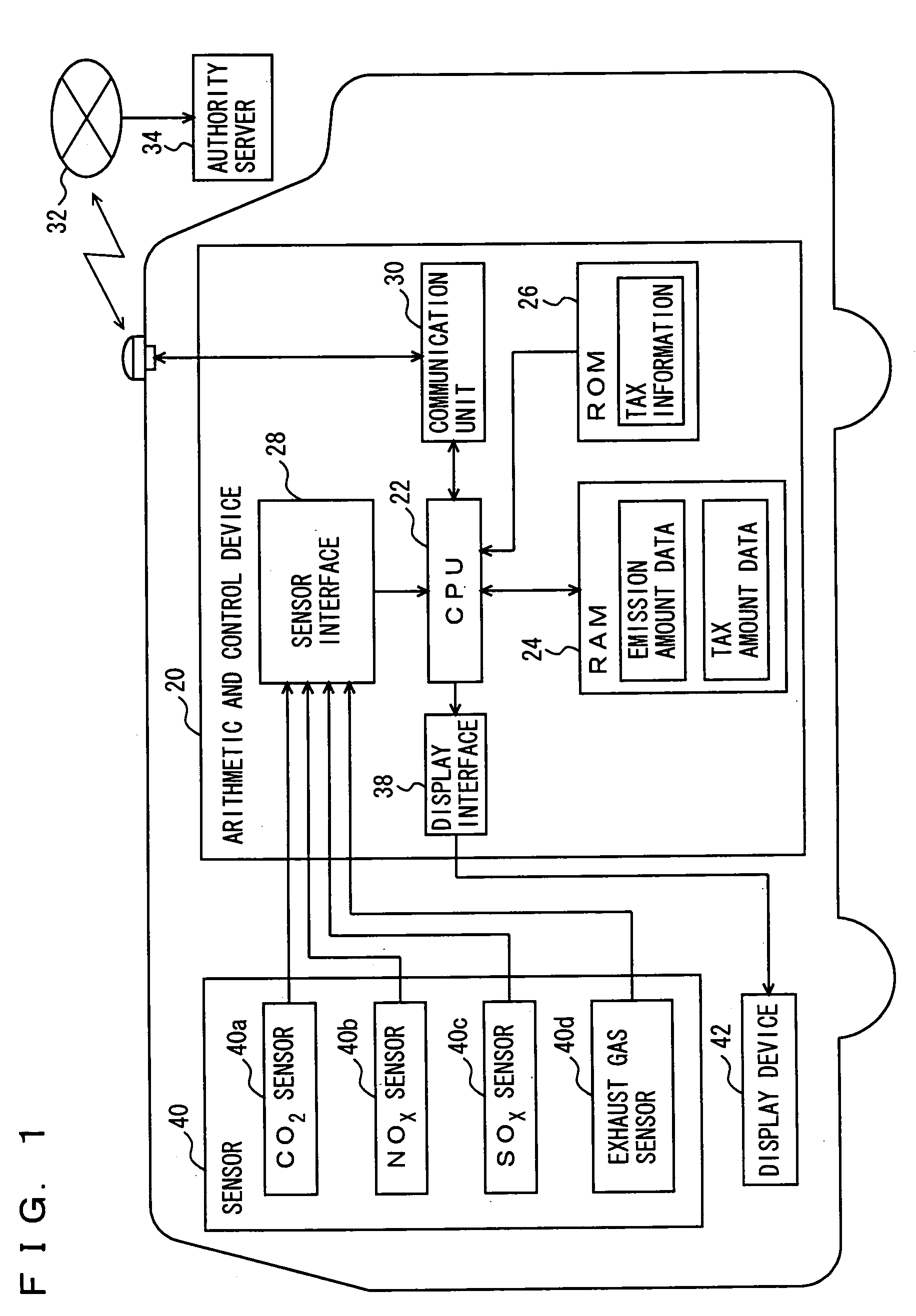
For improving driver's awareness about emissions and promoting environmental protection, an emission amount notifying device is provided. When such a taxation system becomes effective that a tax is imposed in accordance with an amount of one or more kinds of harmful substances, which include a carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides, sulphur oxides and hydrocarbons emitted from a vehicle, a sensor determines the emission amounts of respective harmful substances, and a CPU obtains the amount of tax corresponding to the determined emission amounts from a ROM storing tax information related to the tax amounts corresponding to respective displacements, and displays the obtained tax amount on a display device. Further, the CPU sends the information relating to the determined emission amount to a server of authorities from a communication unit for performing tax payment procedures.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
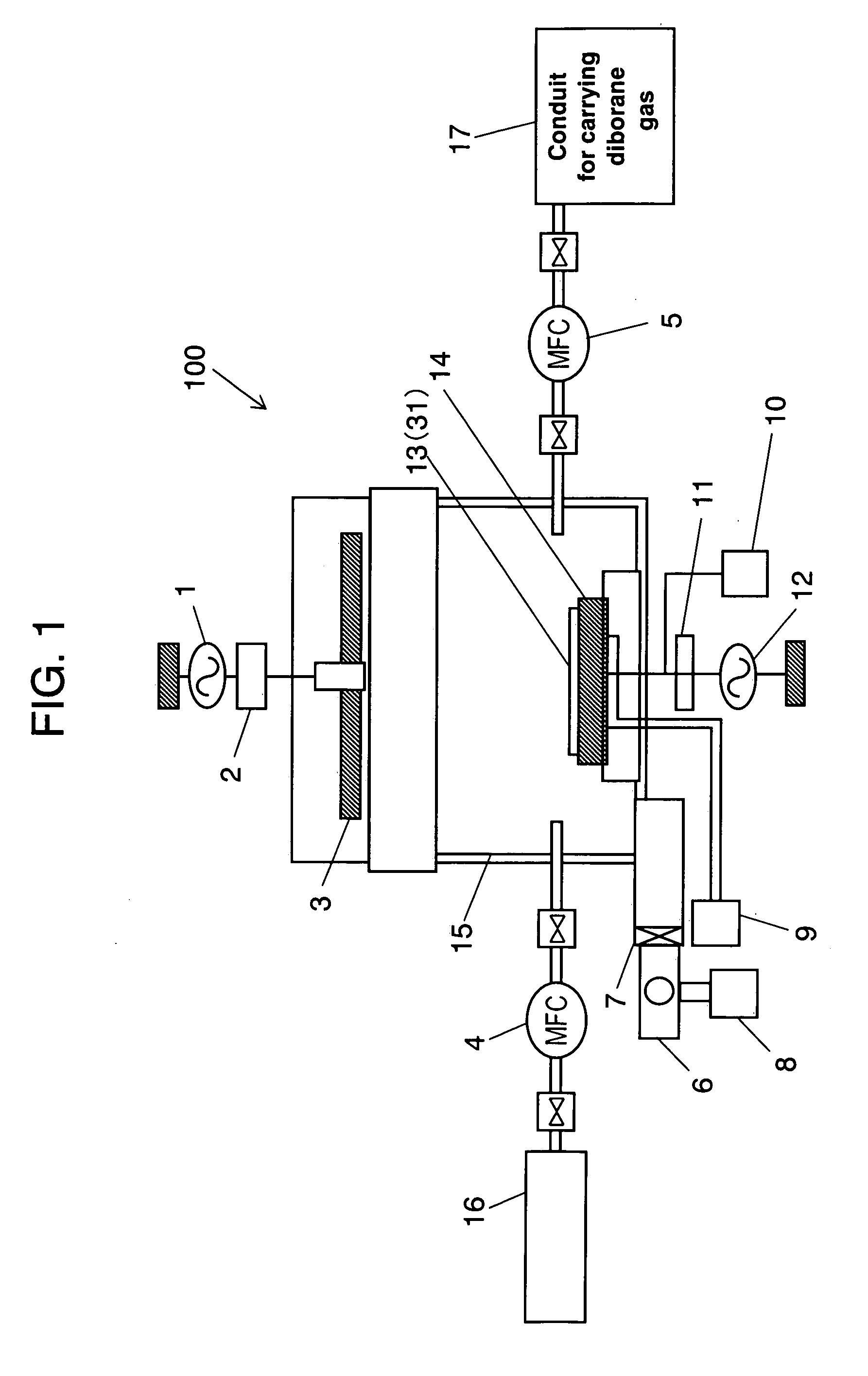
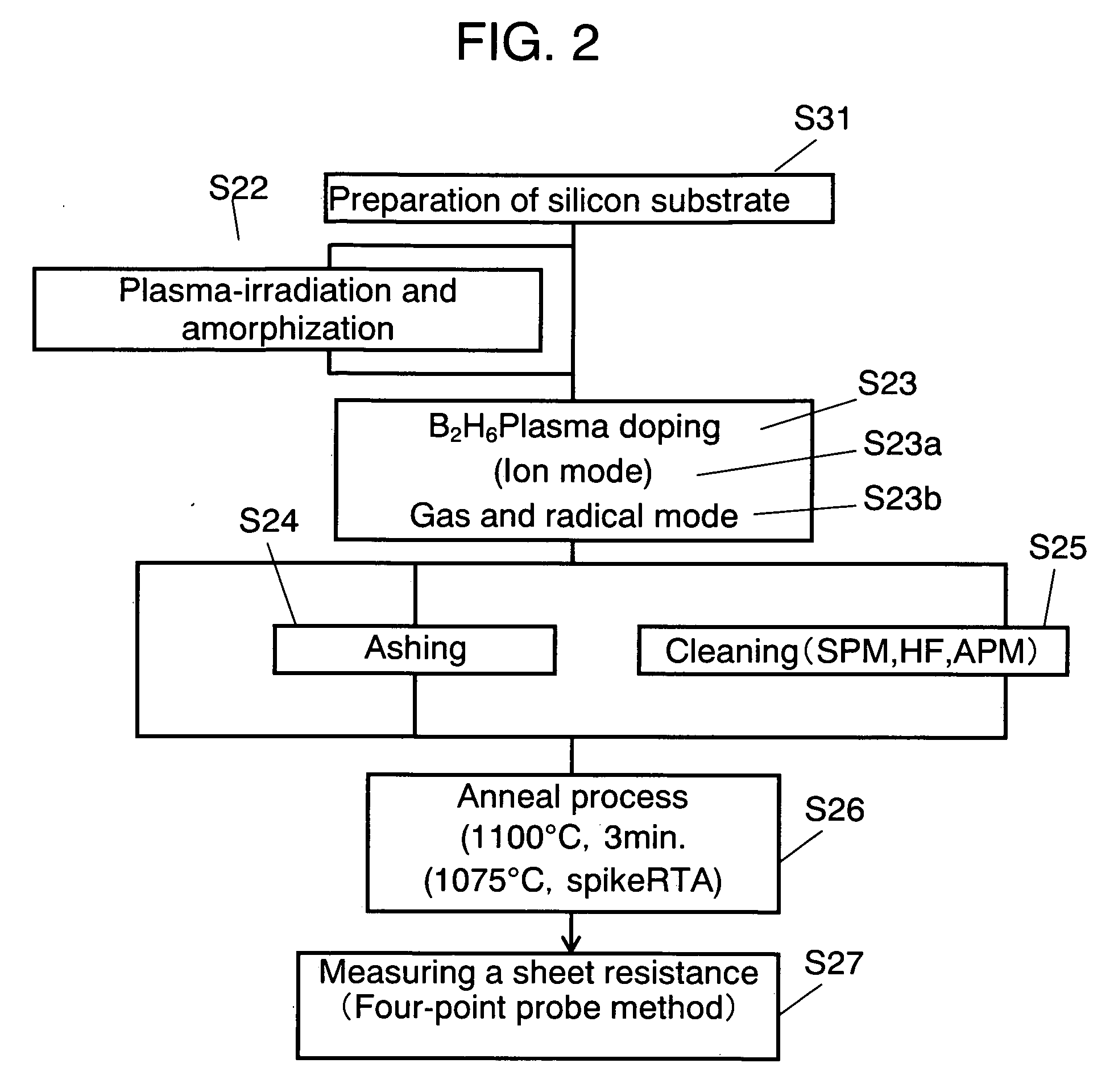
Method for formng impurity-introduced layer, method for cleaning object to be processed apparatus for introducing impurity and method for producing device
A method of forming an impurity-introduced layer is disclosed. The method includes at least a step of forming a resist pattern on a principal face of a solid substrate such as a silicon substrate (S27); a step of introducing impurity into the solid substrate through plasma-doping in ion mode (S23), a step of removing a resist (S28), a step of cleaning metal contamination and particles attached to a surface of the solid substrate (S25a); a step of anneal (S26). The step of removing a resist (S28) irradiates the resist with oxygen-plasma or brings mixed solution of sulfuric acid and hydrogen peroxide water, or mixed solution of NH4OH, H2O2 and H2O into contact with the resist. The step of cleaning (S25a) brings mixed solution of sulfuric acid and hydrogen peroxide water, or mixed solution of NH4OH, H2O2 and H2O into contact with the principal face of the solid substrate. The step of removing a resist (S28) and the step of cleaning (S25a) can be conducted simultaneously by bringing mixed solution of sulfuric acid and hydrogen peroxide water, or mixed solution of NH4OH, H2O2 and H2O into contact with the principal face of the solid substrate.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Exhaust gas aftertreatment systems
InactiveUS6981368B2Accurate estimateImprove NOx conversion efficiencyGas treatmentInternal combustion piston enginesDynamic modelsAmmonia storage
A method is presented for estimating an amount of ammonia stored in a urea-based SCR catalyst based on a dynamic model of the catalyst. The model takes into account chemical and physical properties of the catalyst, such as catalyst volume, the number of available ammonia storage cites, adsorption and desorption dynamics, as well as poisoning, thermal aging, and different catalyst operating temperatures, and generates the estimate based on a measured or estimated amount of NOx in an exhaust gas mixture upstream of the catalyst, an amount of reductant injected into the catalyst to facilitate NOx reduction, and on a measured value of NOx in an exhaust gas mixture downstream of the catalyst. The estimated ammonia storage amount is then used to control the amount of reductant injected into the catalyst to maintain desired ammonia storage amount such that maximum NOx conversion efficiency coupled with minimum ammonia slip are achieved.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com