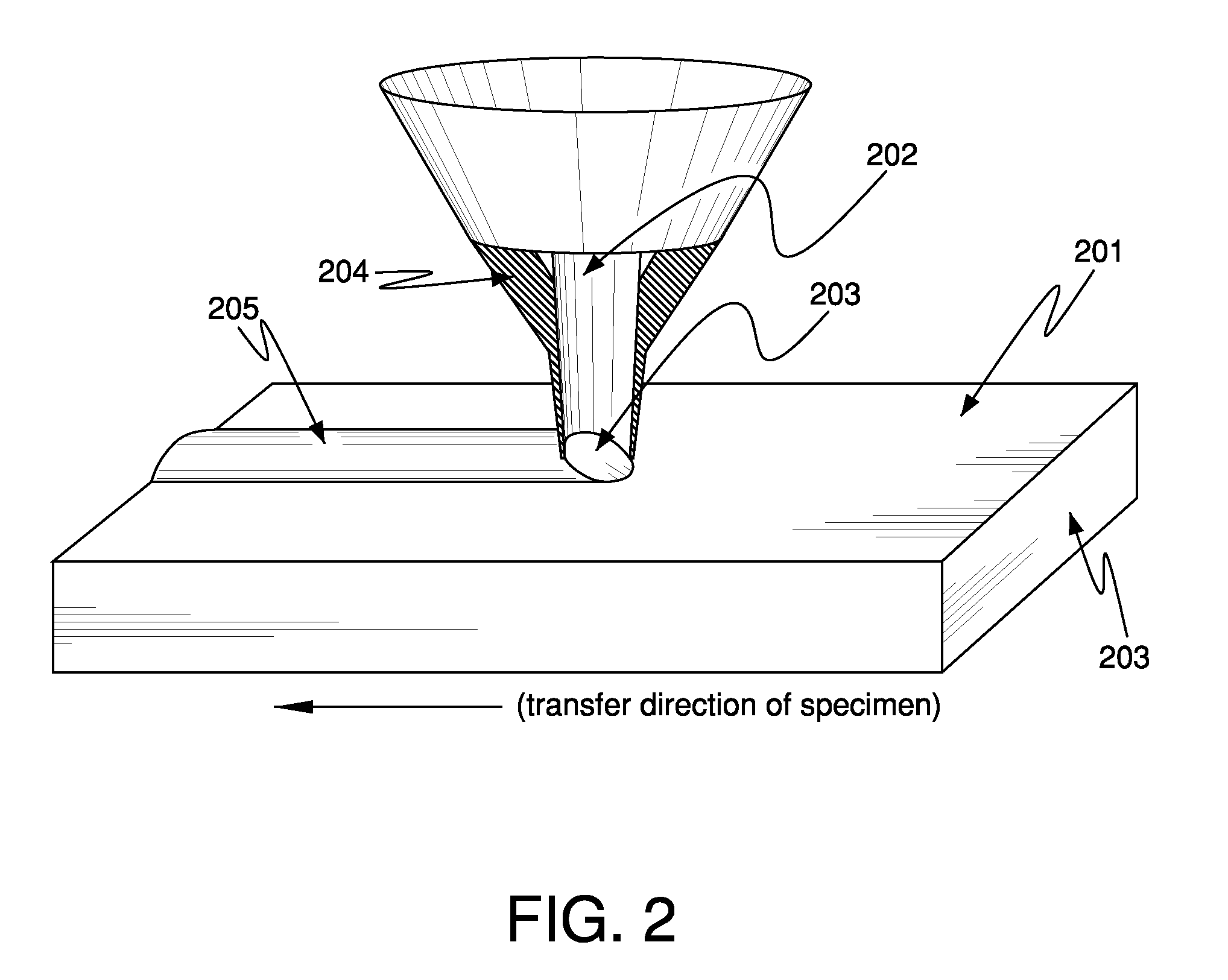
Method and system for real-time monitoring and controlling height of deposit by using image photographing and image processing technology in laser cladding and laser-aided direct metal manufacturing process
a technology of image processing technology and laser cladding, which is applied in the direction of instrumentation, programme control,foundry moulding apparatus, etc., can solve the problems of difficult 3d shape generation from cad, process parameters affecting the height of the cladding layer, and the height of the laser cladding layer
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
application example 1
[0090]FIG. 12 is a photograph showing simple metal parts manufactured by the method and apparatus of the present invention. A substrate having used in this manufacturing was stainless steel (SUS 316), and a cladding material was a chromium-molybdenum hot-work die steel, H-13 tool steel (SKD 61), which is an alloy being commonly used as a material of die casting mold. A fine structure of 100% can be obtained by the method of the present invention, and the mechanical characteristics of the product were similar or superior to those of wrought materials.
application example 2
[0091]FIG. 13 is a photograph showing a mobile phone mold part manufactured by the method and apparatus of the present invention. In this application example 2, a thickness of 250 μm was sliced using 3D CAD data, which was used as shaping information. In this case, the size of a laser beam was about 0.8 mm, and the speed of laser cladding was 0.85 m / min. The substrate was made of stainless steel (SUS 316), and a cladding material was H-13 tool steel. The laser shaping time required for manufacturing the mold was 15 hours and 37 minutes.
application example 3
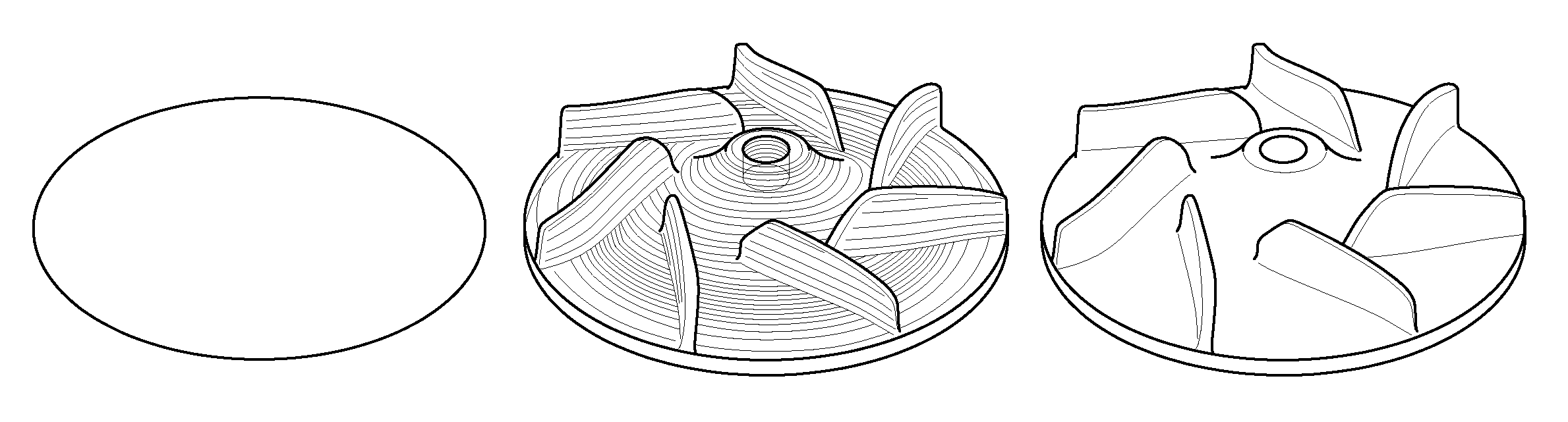
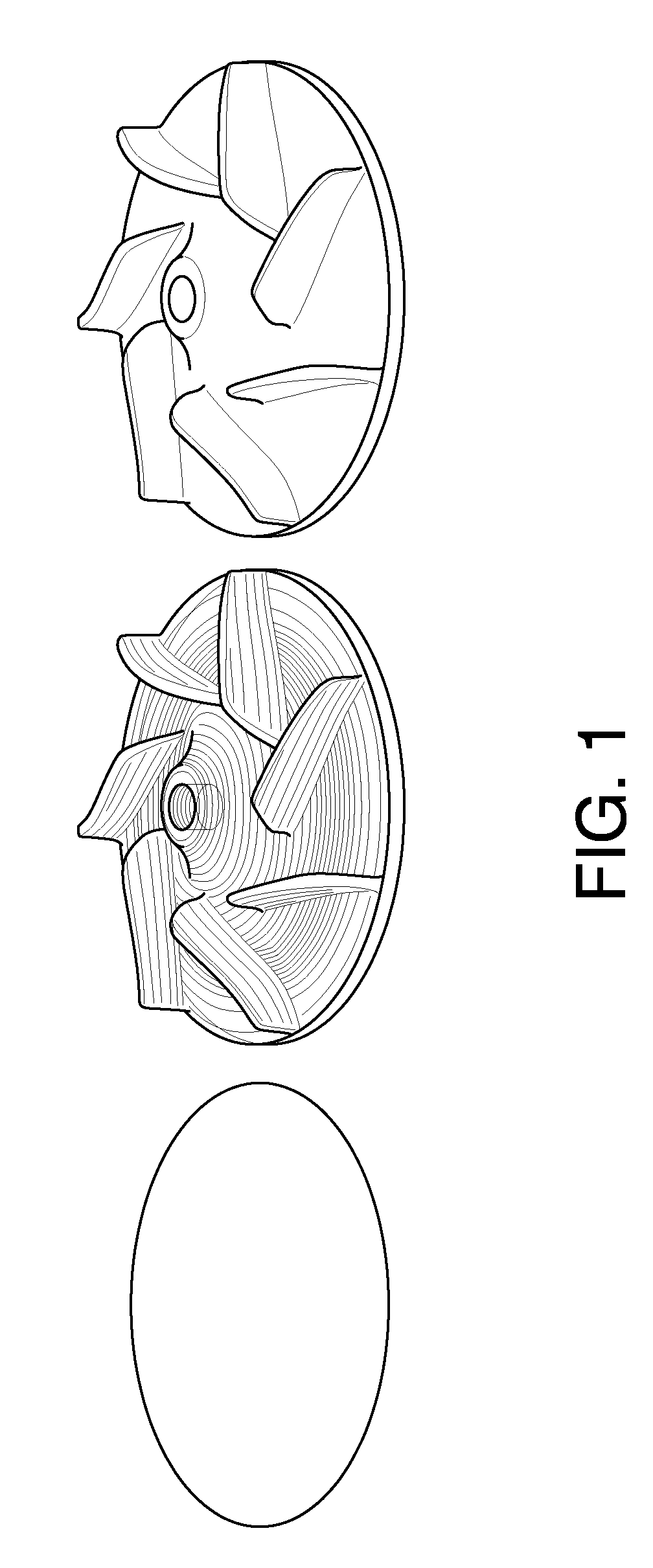
[0092]FIG. 14 is a photograph showing an impeller part manufactured by the laser-aided direct metal manufacturing technology of the present invention. The material of a substrate and a cladding was H-13 tool steel. The other conditions are the same as those of application 2. The laser shaping time required for manufacturing the mold was 12 hours and 8 minutes.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com