Semiconductor Memory Device
a memory device and semiconductor technology, applied in the field of semiconductor memory devices, can solve the problems of data retention time suddenly degraded, reduced reliability of memory cells, and reduced product reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
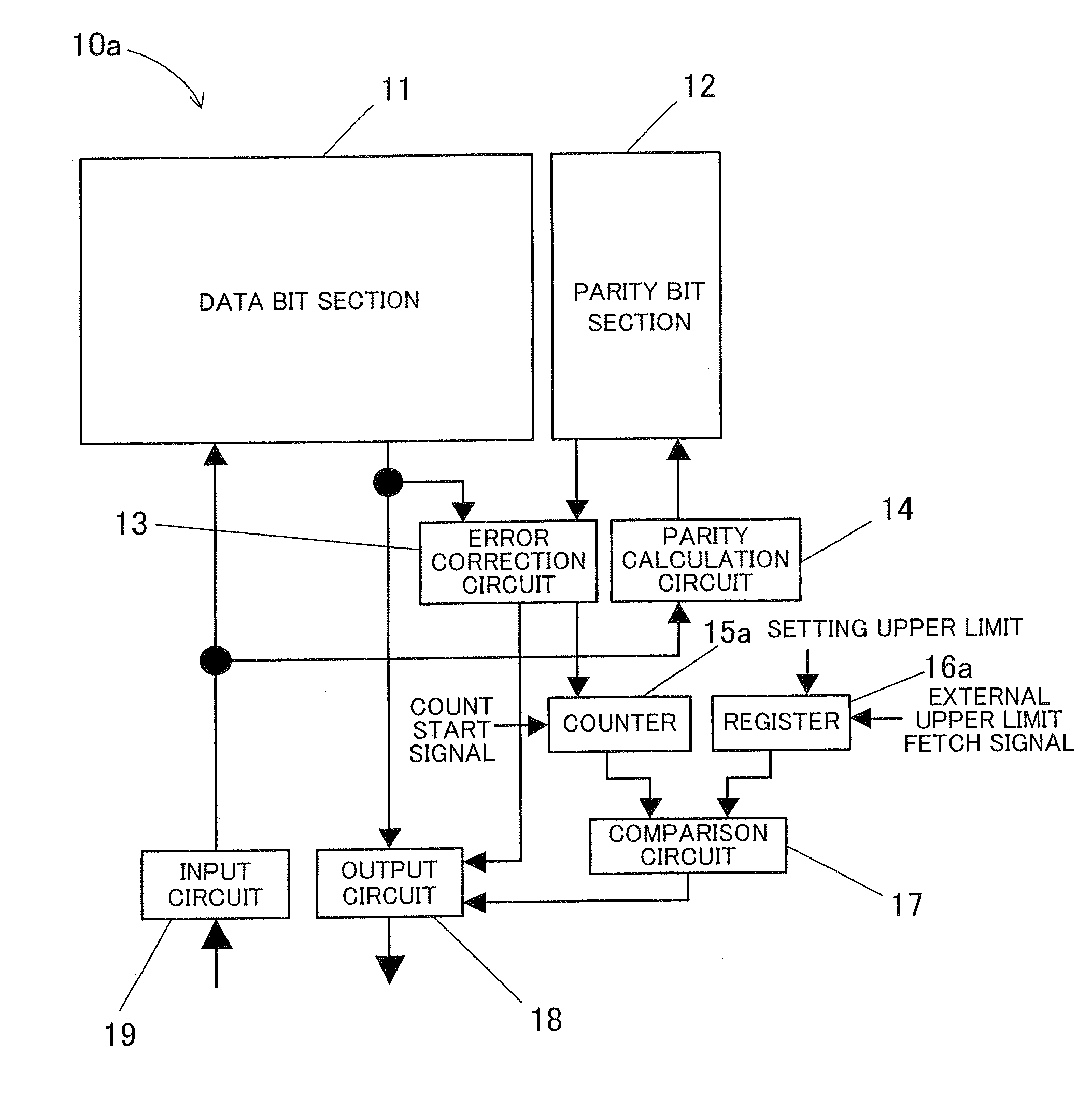
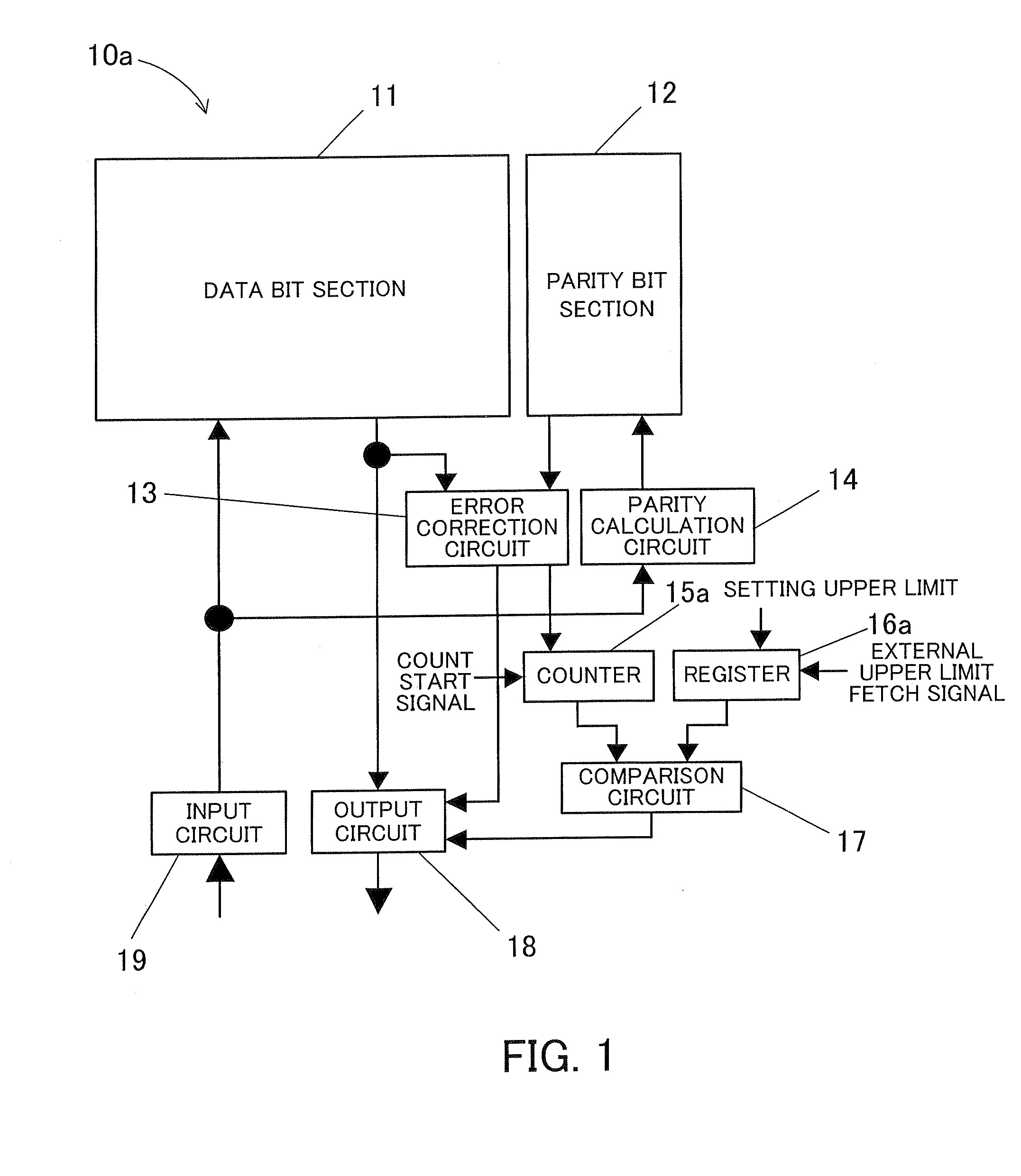
[0035]FIG. 1 shows a configuration of a semiconductor memory device according to the present invention.
[0036]The semiconductor memory device 10a of the first embodiment has the following elements: a data bit section 11 that stores a data bit; a parity bit section 12 that stores a parity bit; an error correction circuit 13 that performs an error correction with reference to the data bit and the parity bit; a parity calculation circuit 14 that generates a parity bit in response to input data by the calculation based on, for example, a hamming code; a counter 15a that counts the number of error corrections; a register 16a that sets an upper limit of the number of error corrections; a comparison circuit 17 that compares the counted number of error corrections with the upper limit of the number of error corrections stored in the register 16a; an output circuit 18; and an input circuit 19.
[0037]The data bit section 11 and the parity bit section 12 each are configured by memory cell arrays...
second embodiment
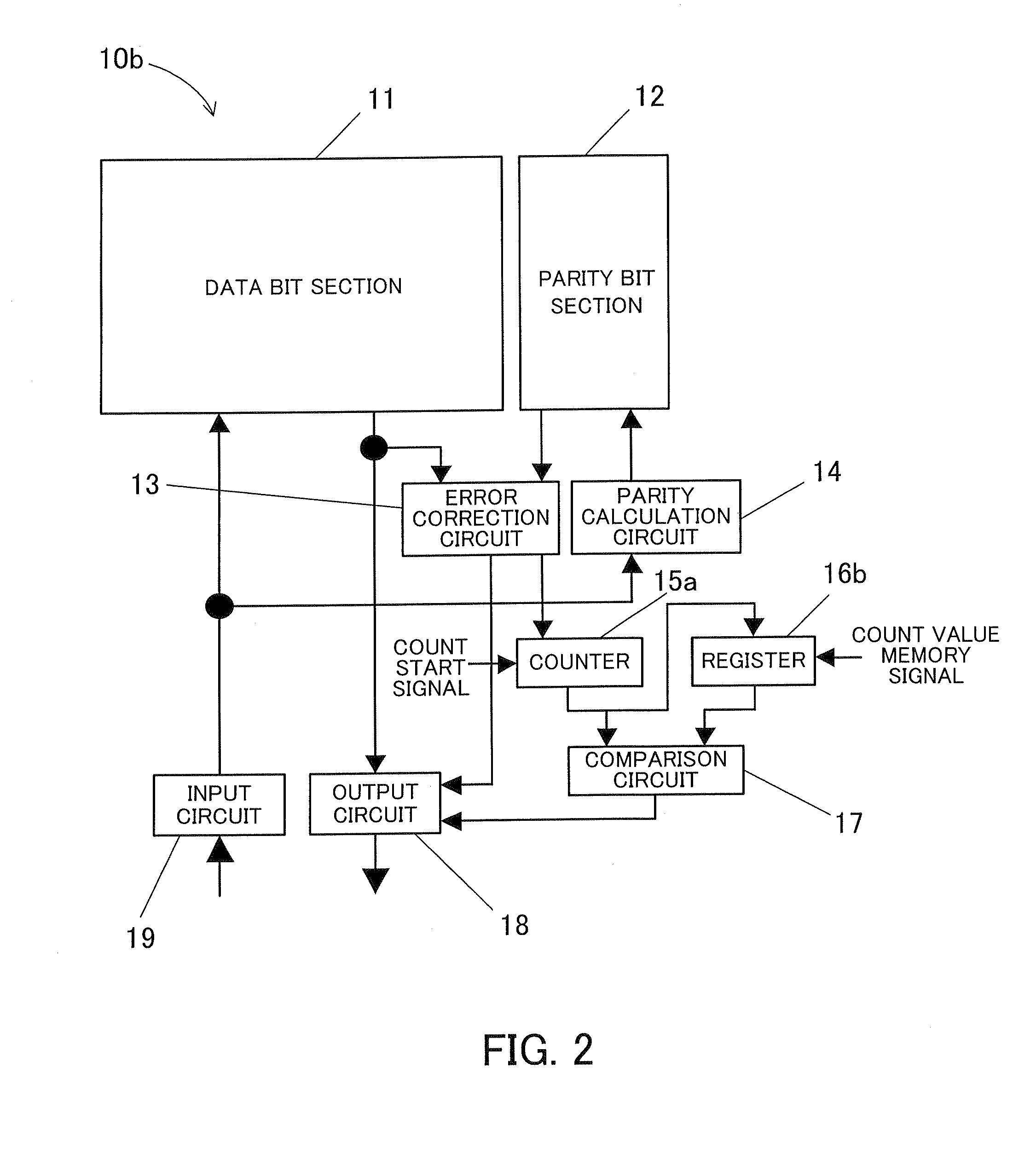
[0048]Next, the semiconductor memory device of a second embodiment is described.
[0049]FIG. 2 shows a configuration of the semiconductor memory device according to the second embodiment of the present invention.
[0050]In the diagram, the same elements as those in the semiconductor memory device 10a of the first embodiment are indicated by the same reference numerals as in the device 10a and the description is omitted.
[0051]In the semiconductor memory device 10b of the second embodiment, a register 16b that sets an upper limit is different from the register 16a in the semiconductor memory device 10a of the first embodiment. When the upper limit setting signal (referred to as a “count value memory signal” in the second embodiment) is inputted (goes to a high level) externally, the register 16b sets a count result of the number of error corrections in the counter 15a as the upper limit of the number of error corrections.
[0052]Operations of the semiconductor memory device 10b of the secon...
third embodiment
[0055]Next, a semiconductor memory device of a third embodiment is described.
[0056]FIG. 3 shows a configuration of the semiconductor memory device according to the third embodiment of the present invention.
[0057]In the diagram, the same elements as those in the semiconductor memory devices 10a and 10b of the first and second embodiments are indicated by the same reference numerals as those in the devices 10a and 10b and the description is omitted.
[0058]In the semiconductor memory device 10c of the third embodiment, the register 16c is different from the register 16a in the semiconductor memory device 10a of the first embodiment. When the upper limit setting signal (referred to as an “upper limit increment / decrement signal” in the third embodiment) is externally inputted (goes to a high level), the register 16c increments or decrements the upper limit in synchronization with a clock signal.
[0059]Operations of the semiconductor memory device 10c of the third embodiment are described b...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com