Materials and methods for altering an immune response to exogenous and endogenous immunogens, including syngeneic and non-syngeneic cells, tissues or organs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
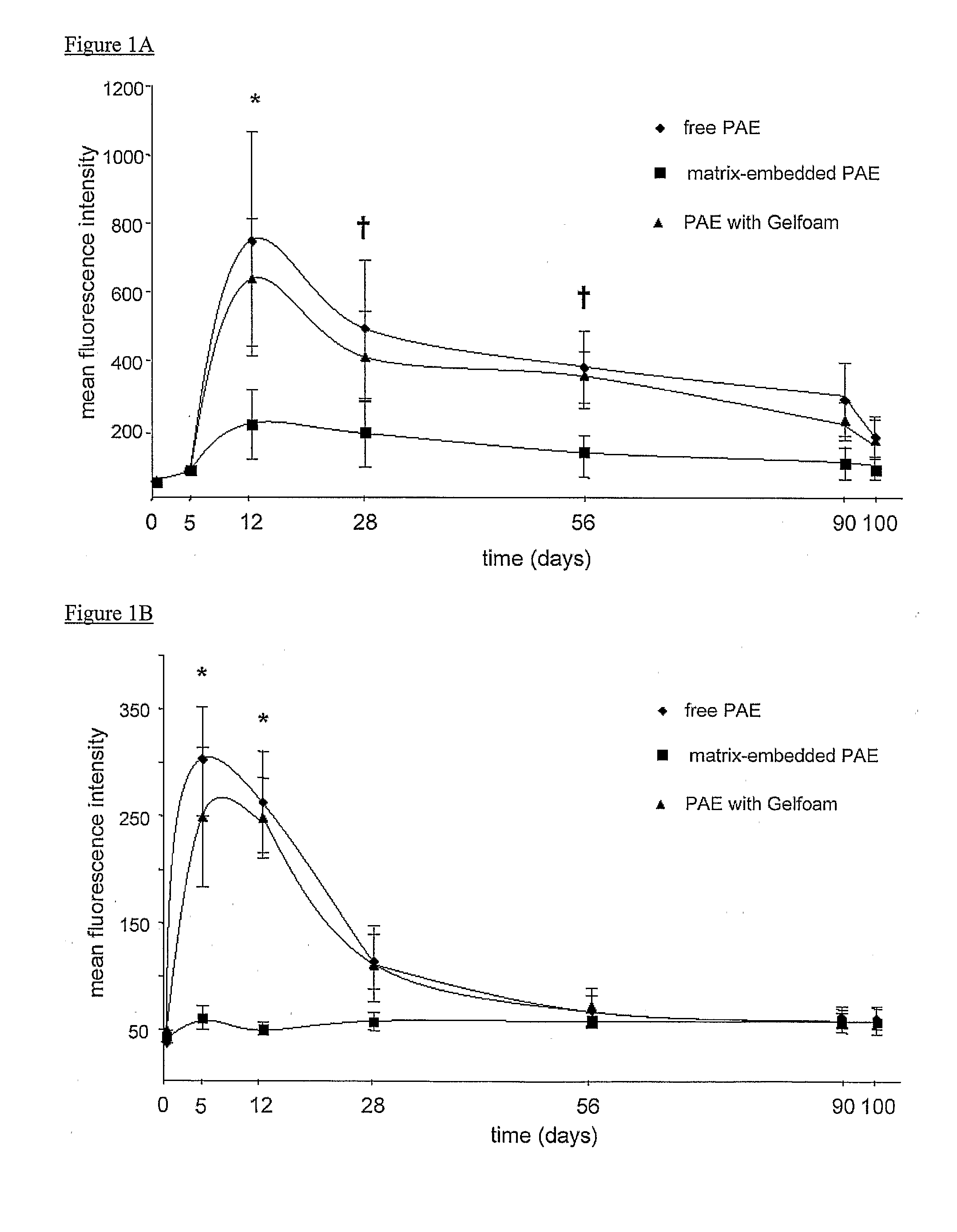
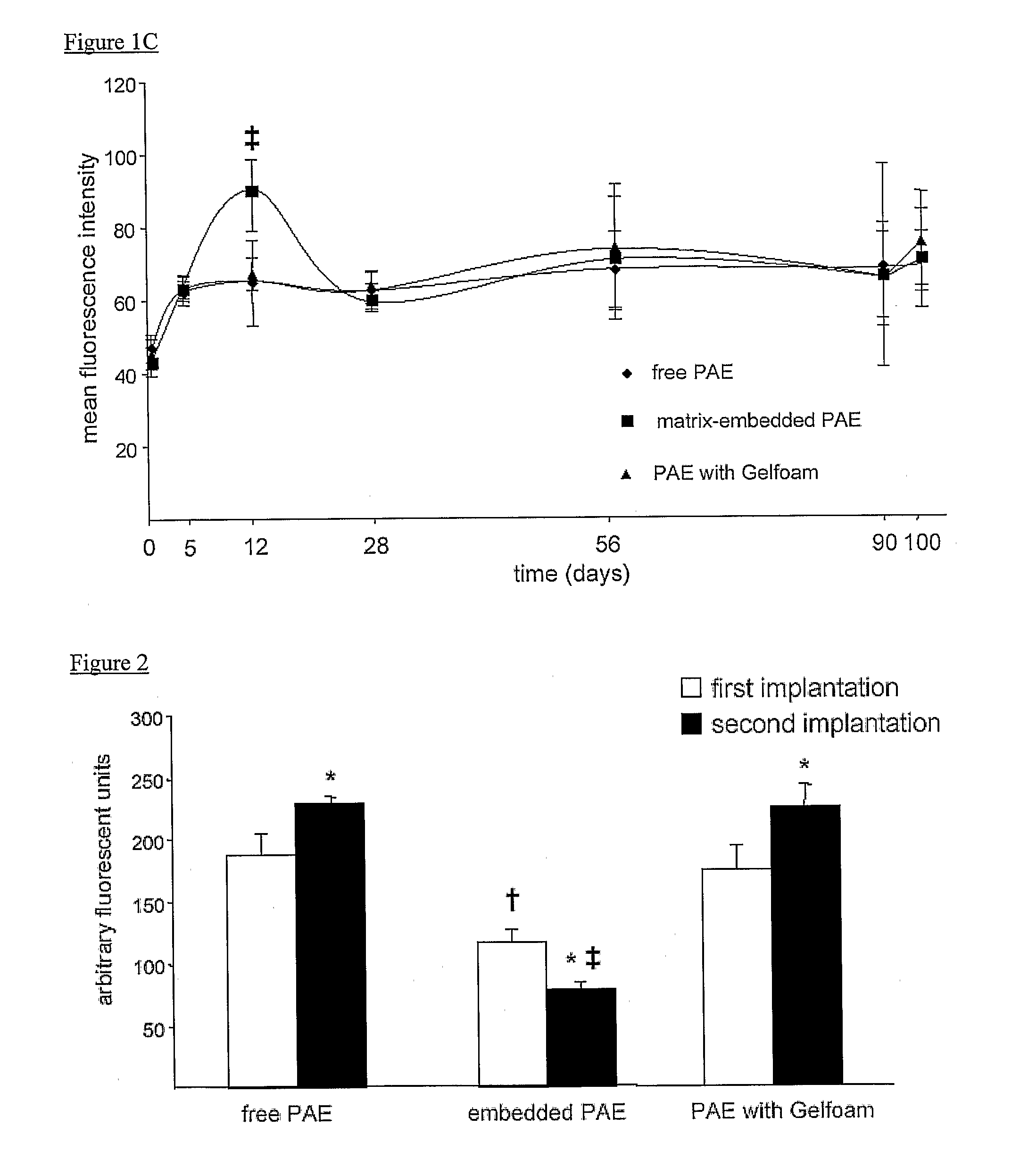
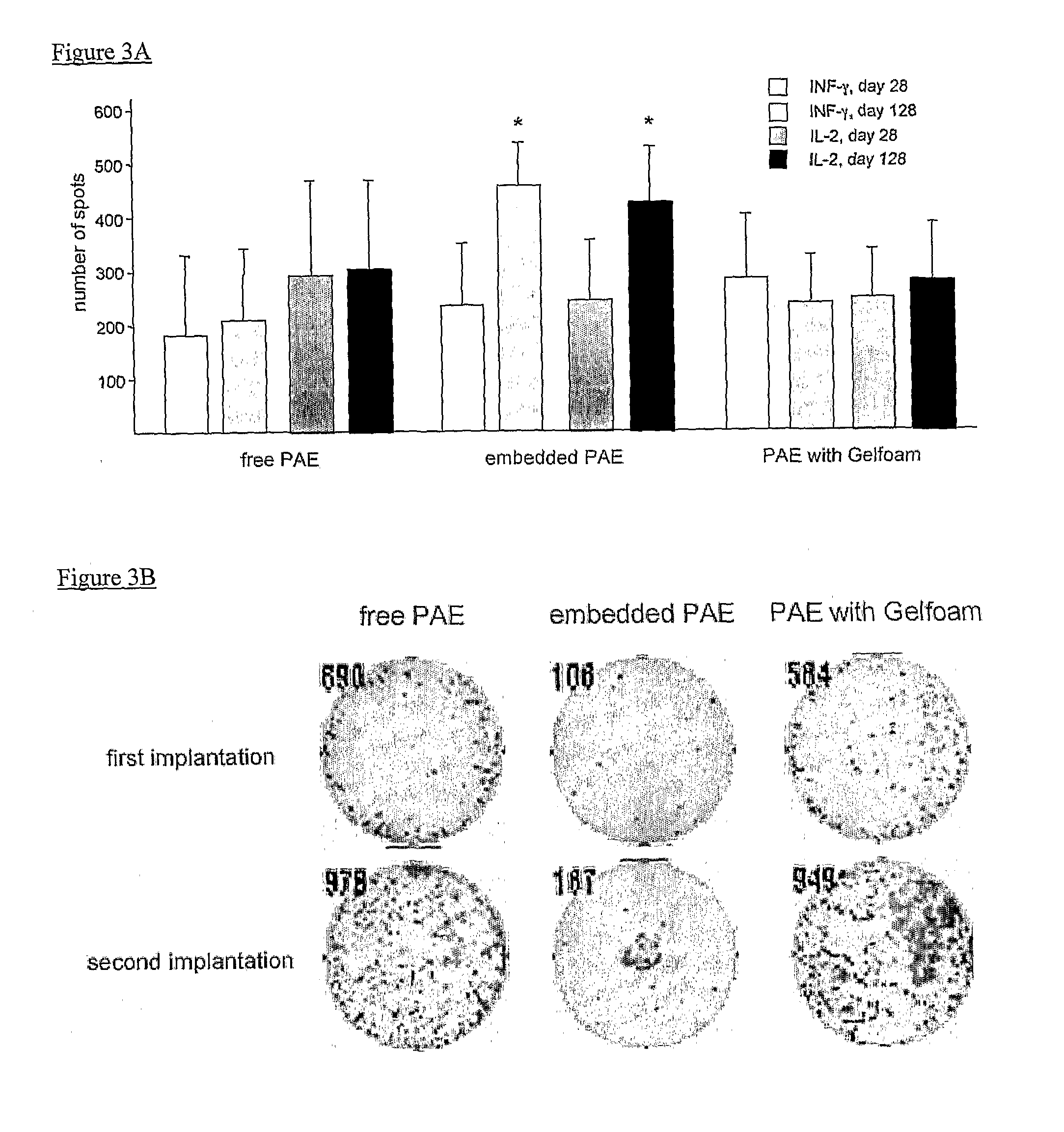
[0037]Tissue engineering is a promising approach to exploit endothelial cells, endothelial-like cells, or analogs of either as a cellular therapy for diseases accompanied by or typified by adverse immunological components. For example, certain diseases such as but not limited to vascular diseases provoke adverse immunological responses and / or inflammatory reactions. The present invention is based on the discovery that cells such as endothelial cells which are anchored to or embedded in three-dimensional matrices, secrete essential regulatory factors which can ameliorate or otherwise modulate an adverse immunological response.
[0038]The implantable material of the present invention was developed on the principals of tissue engineering and represents a novel approach to addressing the herein-described clinical needs. The implantable material of the present invention is unique in that the viable cells anchored to and / or embedded within the biocompatible matrix are able to supply to the ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Immunogenicity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Stress optical coefficient | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Biocompatibility | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com