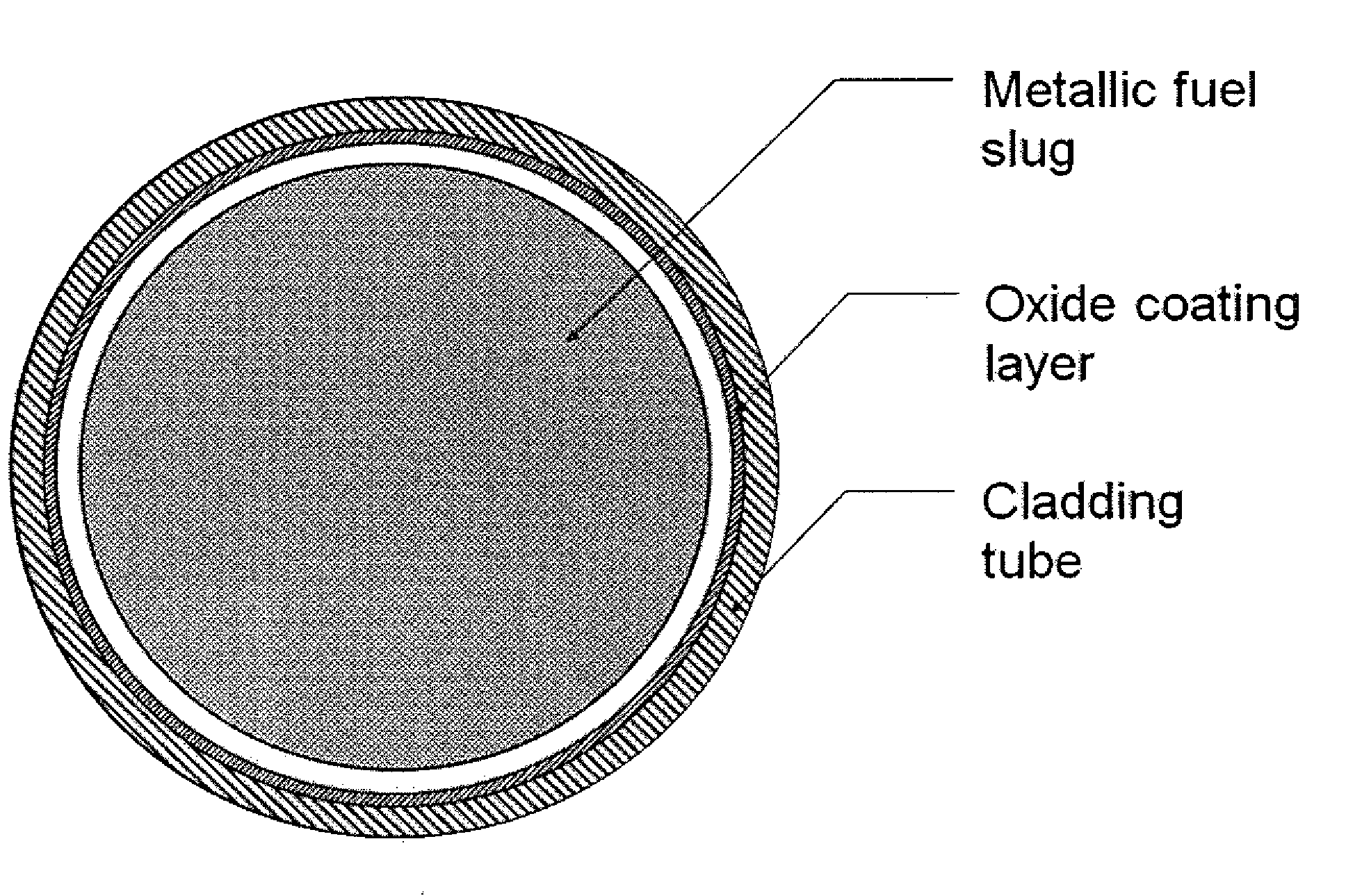
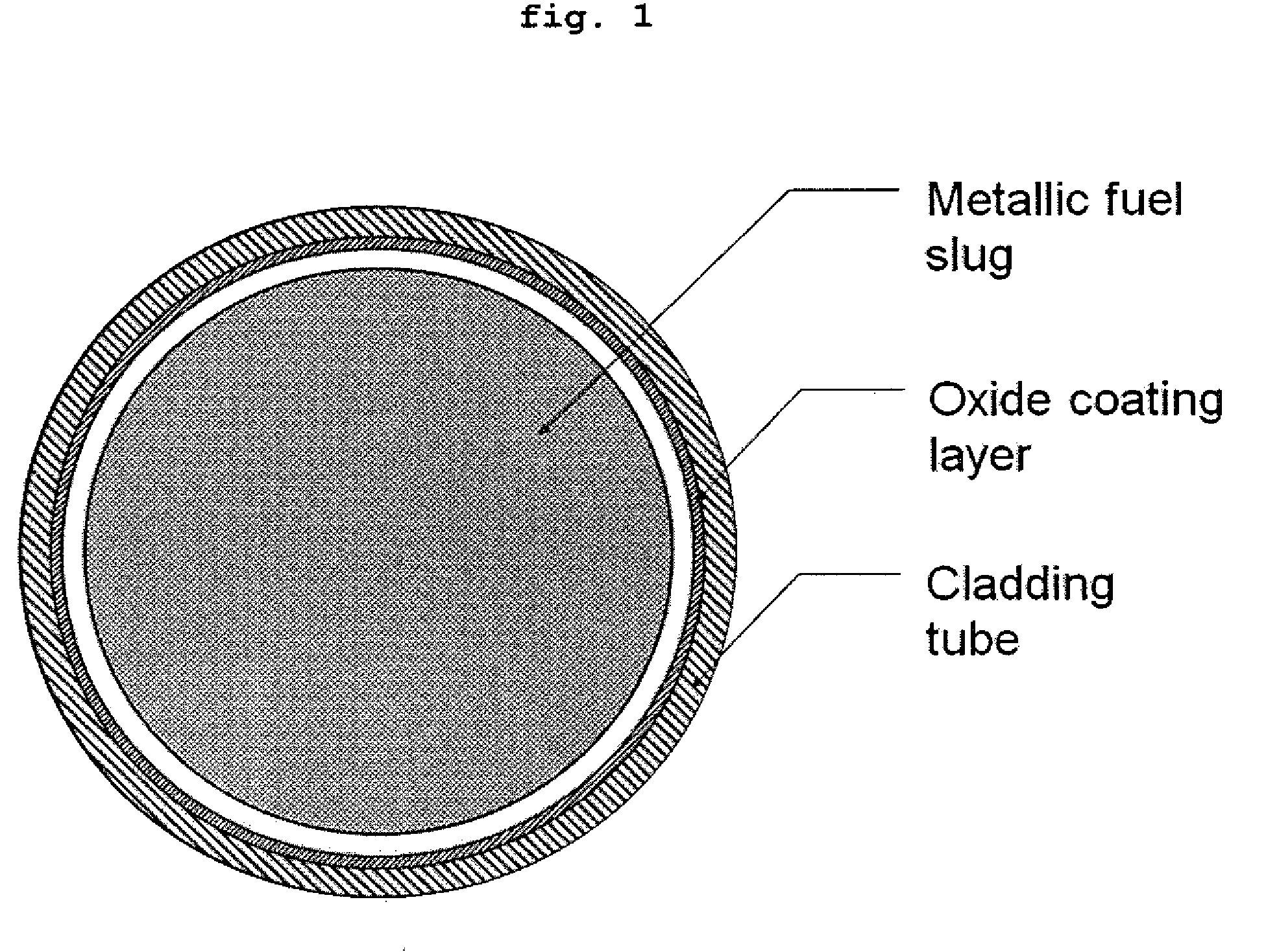
Nuclear fuel rod for fast reactors with oxide coating layer on inner surface of cladding, and manufacturing method thereof
a technology of oxide coating layer and nuclear fuel rod, which is applied in the direction of distance measurement, greenhouse gas reduction, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of cracks in zirconium tubes, significant additional costs, and complicated production of nuclear fuel rods, so as to prolong the fuel life cycle of the fast reactor, increase the maximum permissible burnup, and increase the economic efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Manufacture 1 of Nuclear Fuel Rod for Fast Reactors, which has Oxide Coating Layer Formed by Oxidation in Acid Solution
[0032]A stainless steel (SS316L or SS316LN) or ferrite / martensite steel (ASTM Gr. 91 or ASTM Gr. 92) tube for prior nuclear fuel claddings for fast reactors was cut to a length of 100 mm to make a tube sample. Then, the inner surface of the tube was mechanically or chemically polished to have a roughness (Rmax) of less than 1 μm.
[0033]The inner surface of the sample was dipped in a 45-55 vol % nitric acid solution using a specifically designed device at 54° C. for at least 30 minutes according to test procedures specified in ASTM standards (ASTM A967-01, ASTM A380-99, and ASTM B912-00). Then, the sample was washed with distilled water having an impurity concentration of less than 200 ppm, thus manufacturing a nuclear fuel rod for fast reactors having an oxide coating layer formed on the inner surface thereof.
example 2
Manufacture 2 of Nuclear Fuel Rod for Fast Reactors, which has Oxide Coating Layer Formed by Oxidation in Acid Solution
[0034]The procedure of Example 1 was repeated, except that the dipping process was carried out in a 49-60 vol % nitric acid solution at a temperature of 49-60° C. for at least 20 minutes.
example 3
Manufacture 3 of Nuclear Fuel Rod for Fast Reactors, which has Oxide Coating Layer Formed by Oxidation in Acid Solution
[0035]The procedure of Example 1 was repeated, except that the dipping process was carried out in a 20-45 vol % nitric acid solution at a temperature of 21-32° C. for at least 30 minutes.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com