Methods for injecting a consolidation fluid into a wellbore at a subterranian location
a consolidation fluid and wellbore technology, applied in the direction of fluid removal, earth drilling and mining, borehole/well accessories, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the fluid production capacity of the producing portions of the subterranean formation, insufficient bond strength, and limited use of resin consolidation methods, so as to reduce the cross-section of the lower packer
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
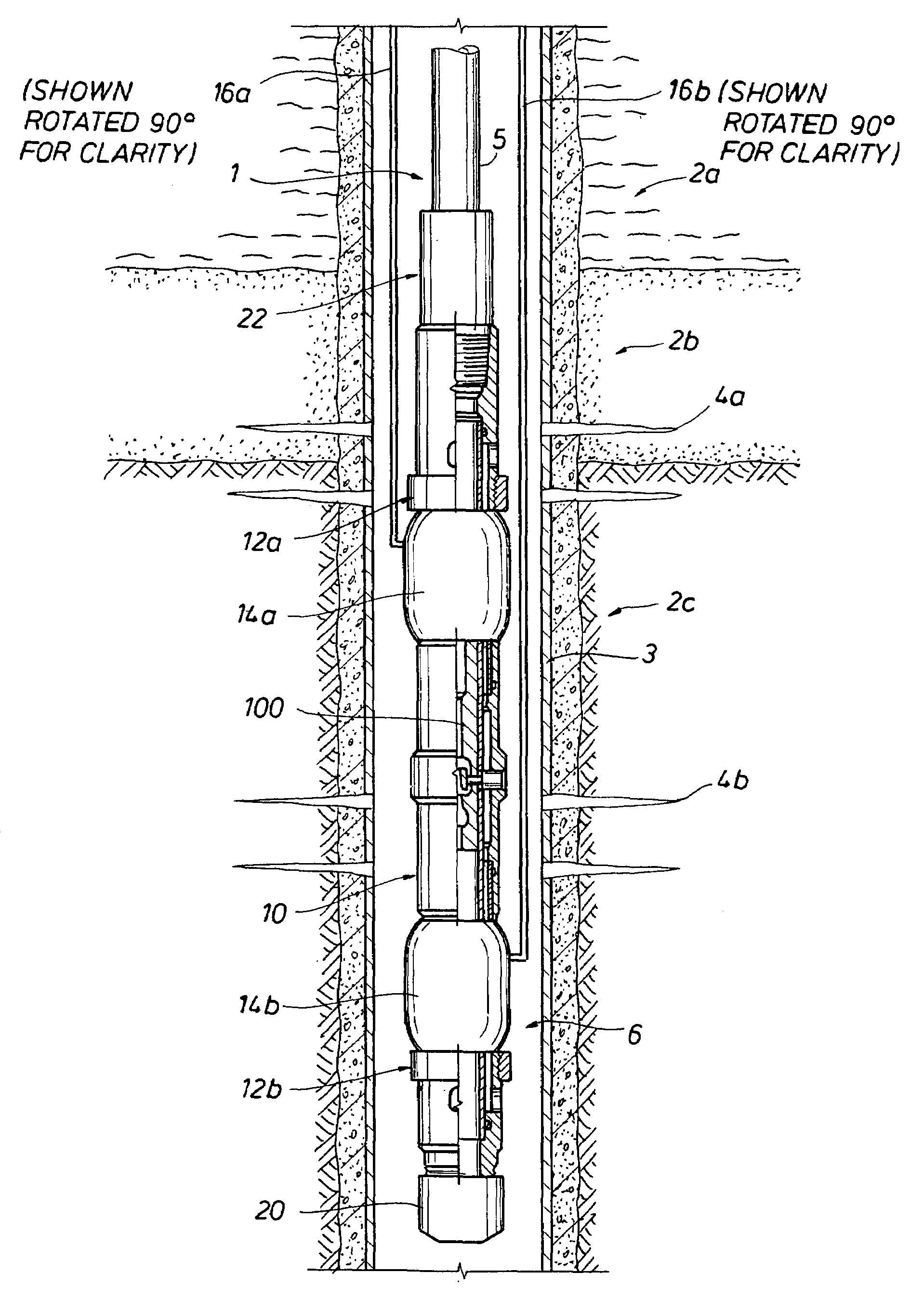
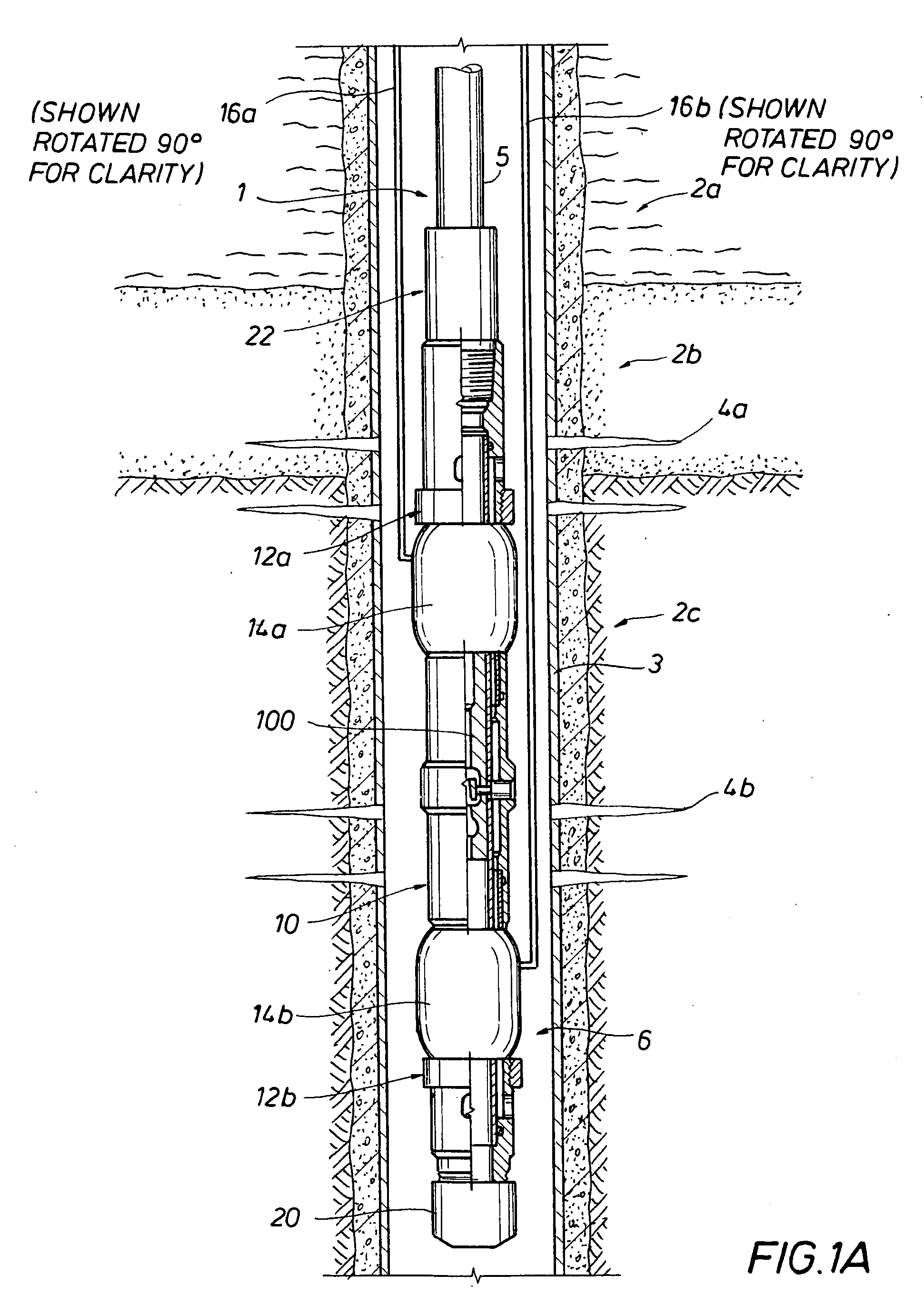
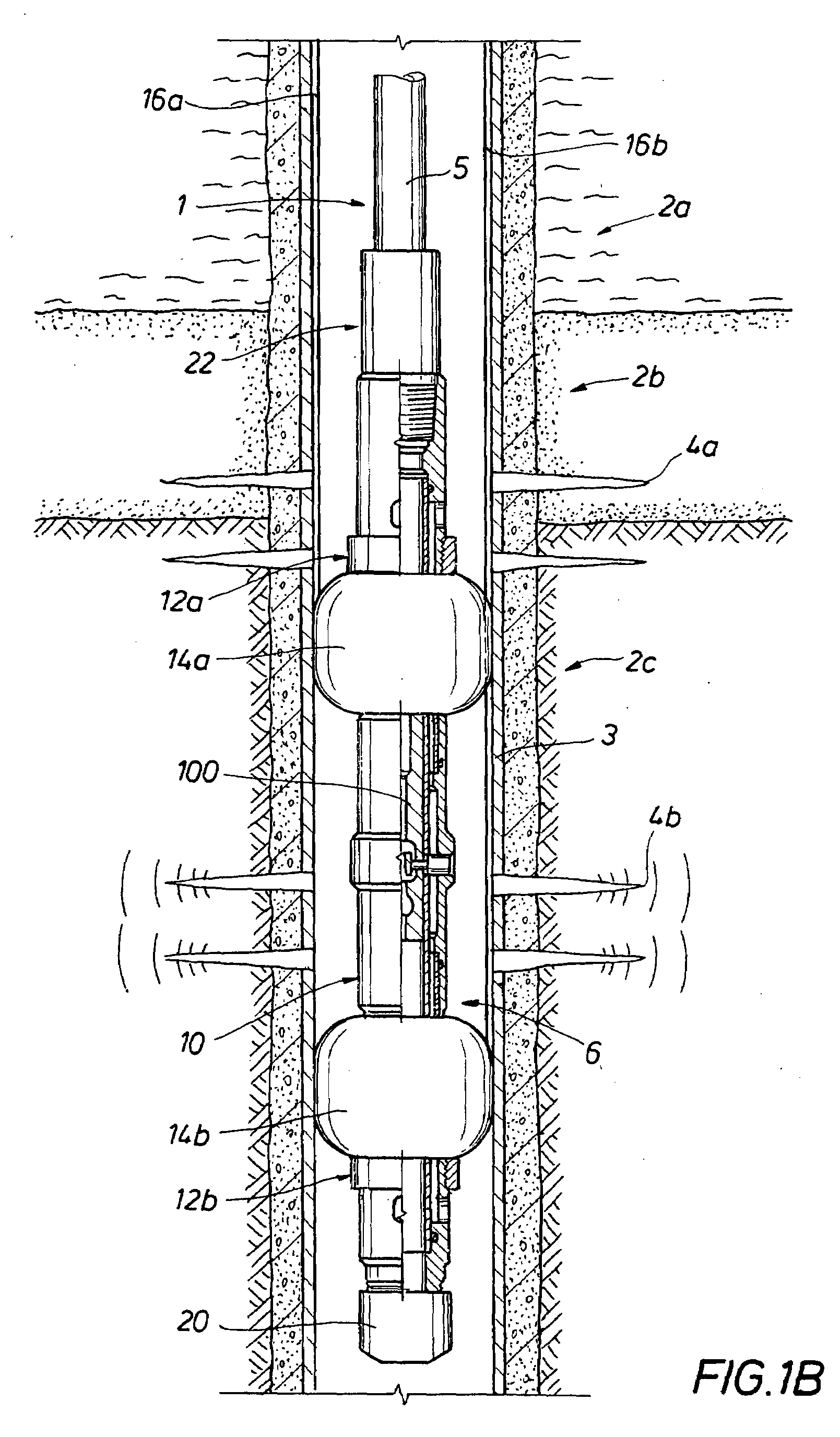
[0030]The present inventions relate to methods for controlling the migration of unconsolidated particulates in a portion of a subterranean formation, and more particularly, to the using pressure pulses to enhance the effectiveness of placement of a consolidation fluid in a portion of a subterranean formation. According to the method of the present invention, pressure pulses generated by a suitable apparatus enhance the penetration of a consolidation fluid into the portion of the subterranean formation.
[0031]The invention has particular applicability where the formation is a weakly consolidated formation. Some embodiments of the present invention provide methods for treating subterranean a formation comprising the steps of, placing a consolidation fluid into a well bore and in contact with a portion of a subterranean formation to be consolidated and then sending energy in the form of vibration or pressure pulses through the fluid and formation. Such energy changes affect the dilatanc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com