Method for dewatering and a dewatering apparatus
a technology of dewatering apparatus and mesh, which is applied in the direction of machine wet end, papermaking, textiles and papermaking, etc., can solve the problems of continuous md direction decrease of the water weight of fibrous materials on the mesh, unsatisfactory formation profiles, and unacceptable cd profiles
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
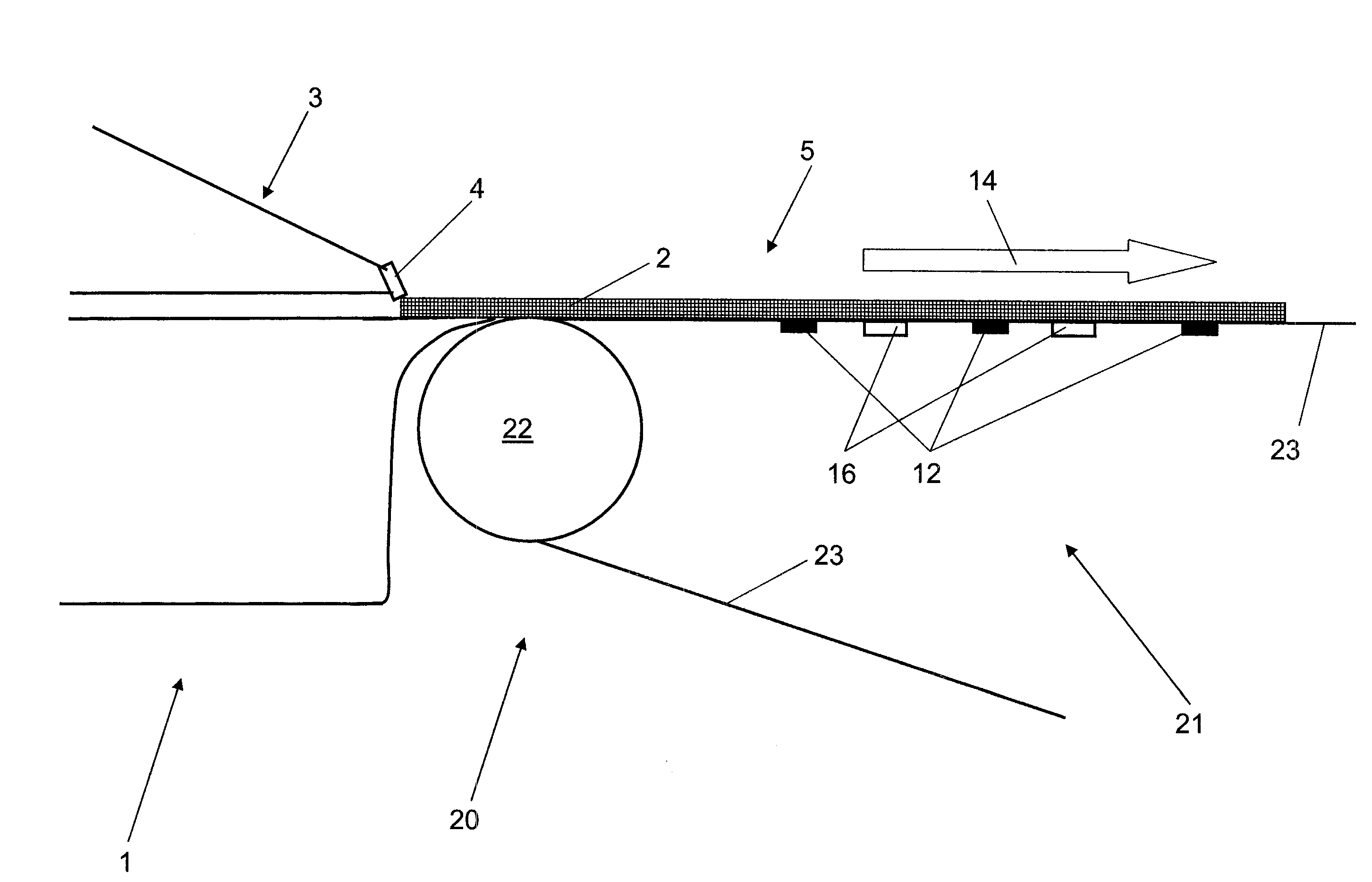
[0050]Referring now to the figures there is described below an inventive dewatering apparatus 1, which in this case is a paper machine or paperboard machine. The paper machine or paperboard machine 1 implements the inventive method.
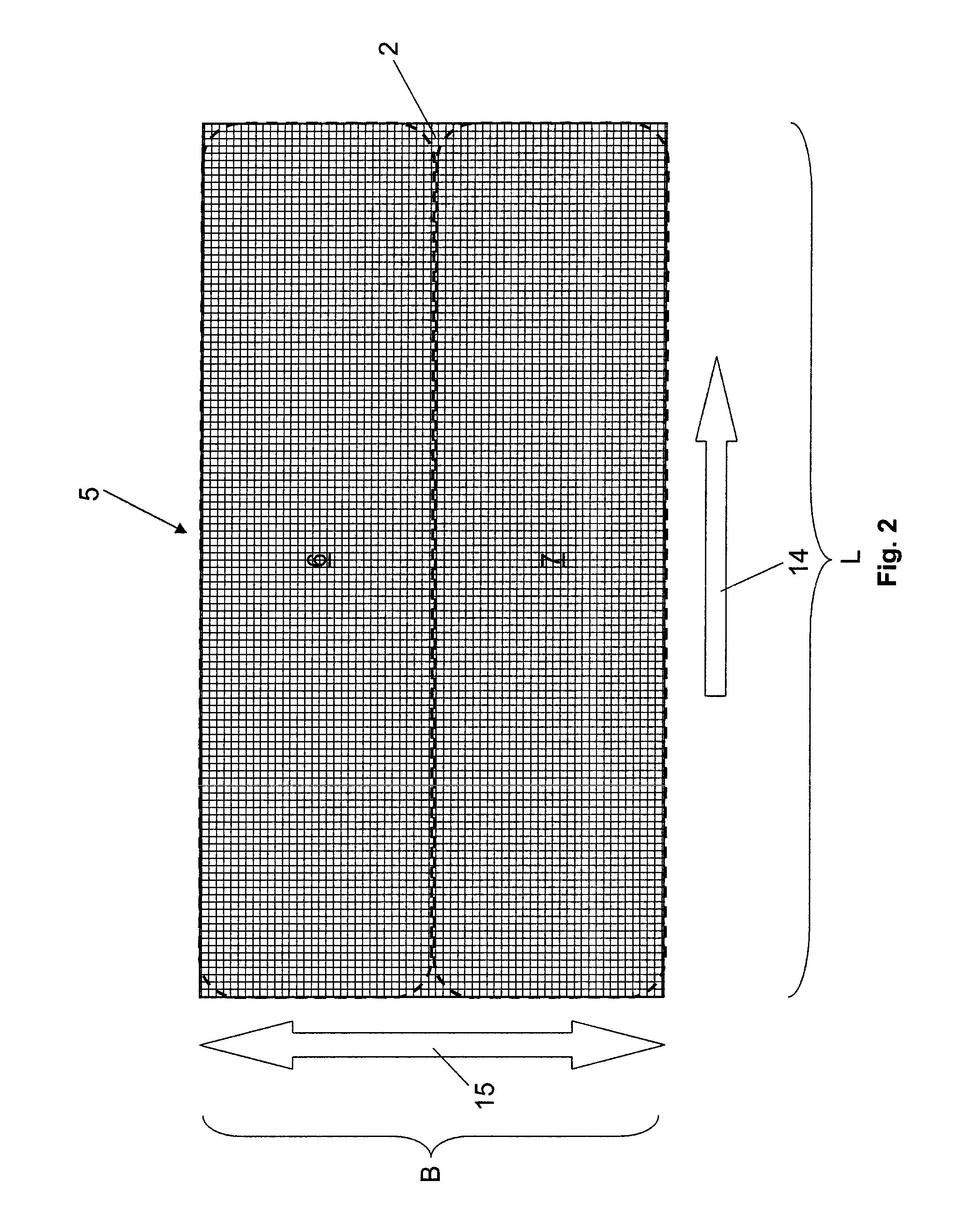
[0051]The paper machine or paperboard machine 1 has a wet section 20 with a dewatering apparatus 21, in which a fibrous material 2 is applied onto a long mesh 23 by a headbox 3. Headbox 3 is constructed as a dilution water headbox. Dilution water headbox 3 has along CD direction 15 of a fibrous web 5 a plurality of fibrous material outlet openings 4.
[0052]With the help of dewatering elements 16 there takes place a first dewatering step for fibrous material 2 in fibrous web 5 conveyed on long mesh 23. Dewatering elements 16 are constructed here as suction boxes 16. The embodiment shown includes two suction boxes 16, whose dewatering performance is zonally adjustable. The paper machine or paperboard machine 1 has further sections such as a drying section, a...
second embodiment
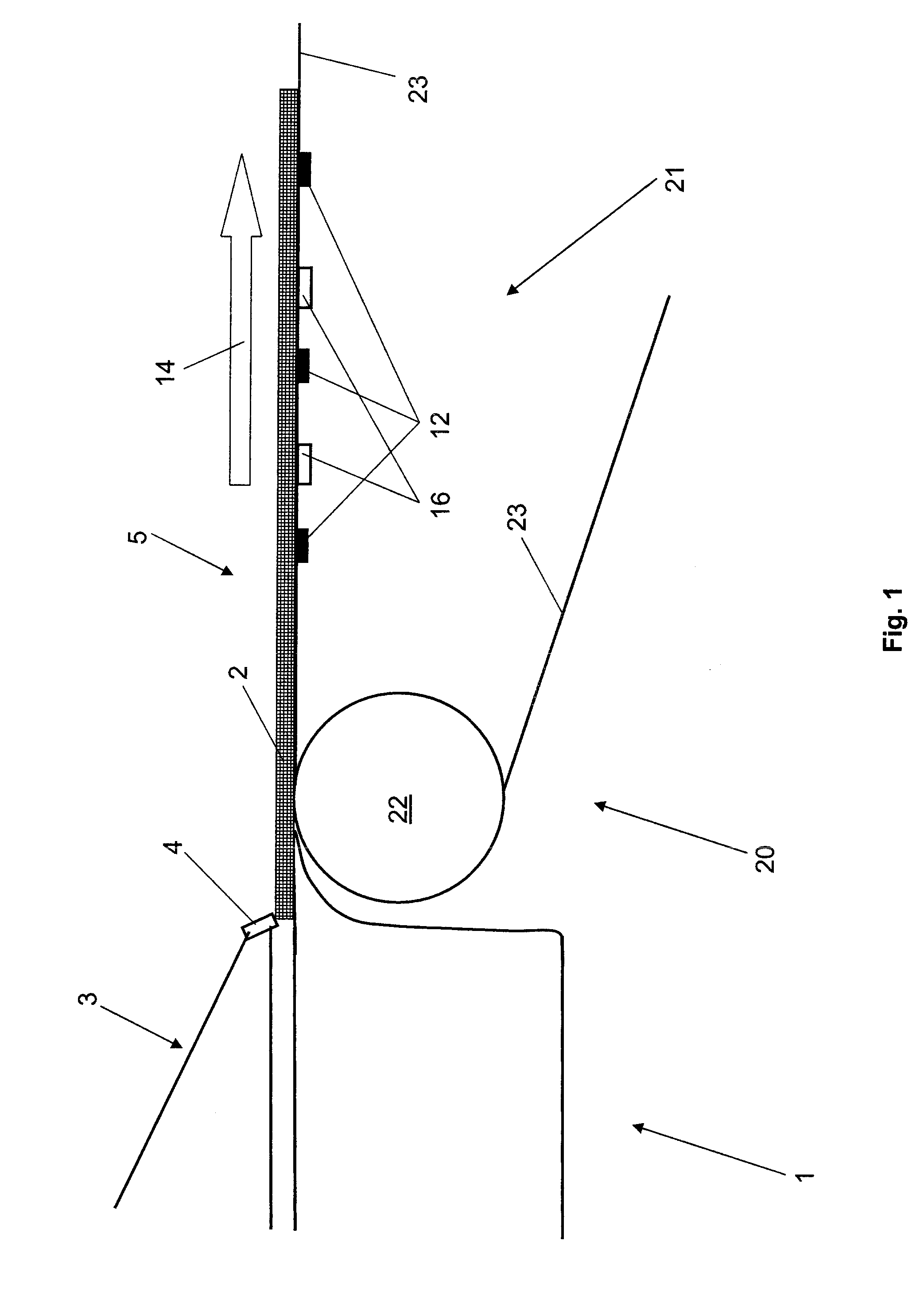
[0063]Inventive features not presented in FIG. 3 are shown in FIG. 4, which presents the present invention.
[0064]Dewatering elements 16 are available in both embodiments only in, or in the region of, wet section 20. However, dewatering elements 16 could also be arranged, in particular respectively in addition or solely, in at least one additional section of dewatering apparatus 1, such as in a steam blower box or in a press or in a headbox 3, in particular in a dilution water headbox 3.
[0065]The first embodiment has three one-dimensional sensor arrangements 13 which are offset in pairs in CD direction 15 and have five water weight sensors 12 each. Sensor arrangements 13 and hence their sensors 12 are also set apart from each other in MD direction 14. The result is therefore a very regular periodicity as a pattern of sensors 12. A different pattern or different periodicity of sensors 12 is implemented on the second embodiment, which is presented in FIG. 4.
[0066]On the second embodime...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com