Method for source-related risk detection and alert generation
a source-related risk and alert generation technology, applied in the field of source-related risk detection, can solve the problems of code contamination, pre-existing code, and the introduction of source-related risks in software development, and achieve the effects of reducing the burden of code, reducing the risk of code contamination, and reducing the difficulty of sharing and reusing the cod
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
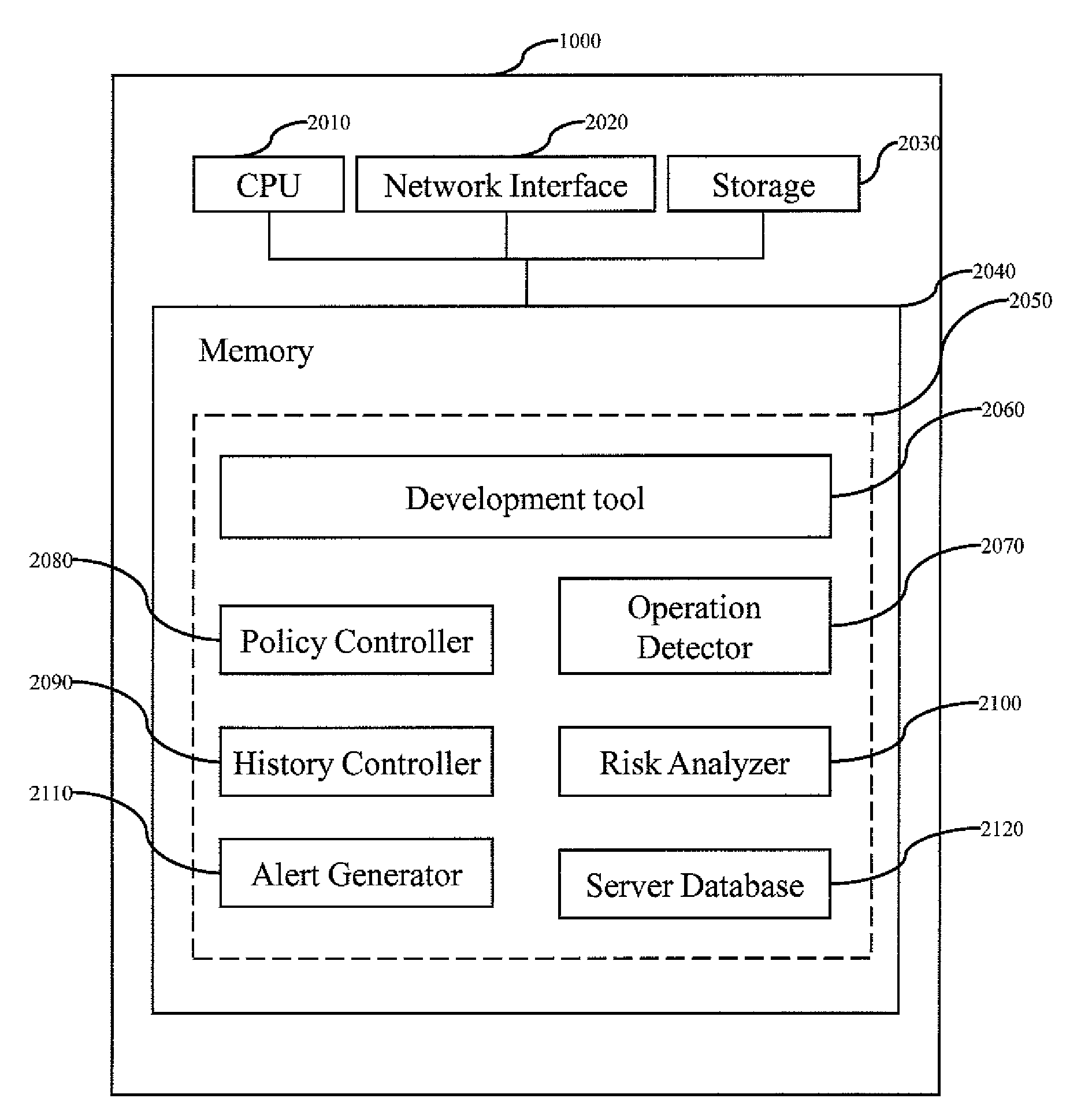
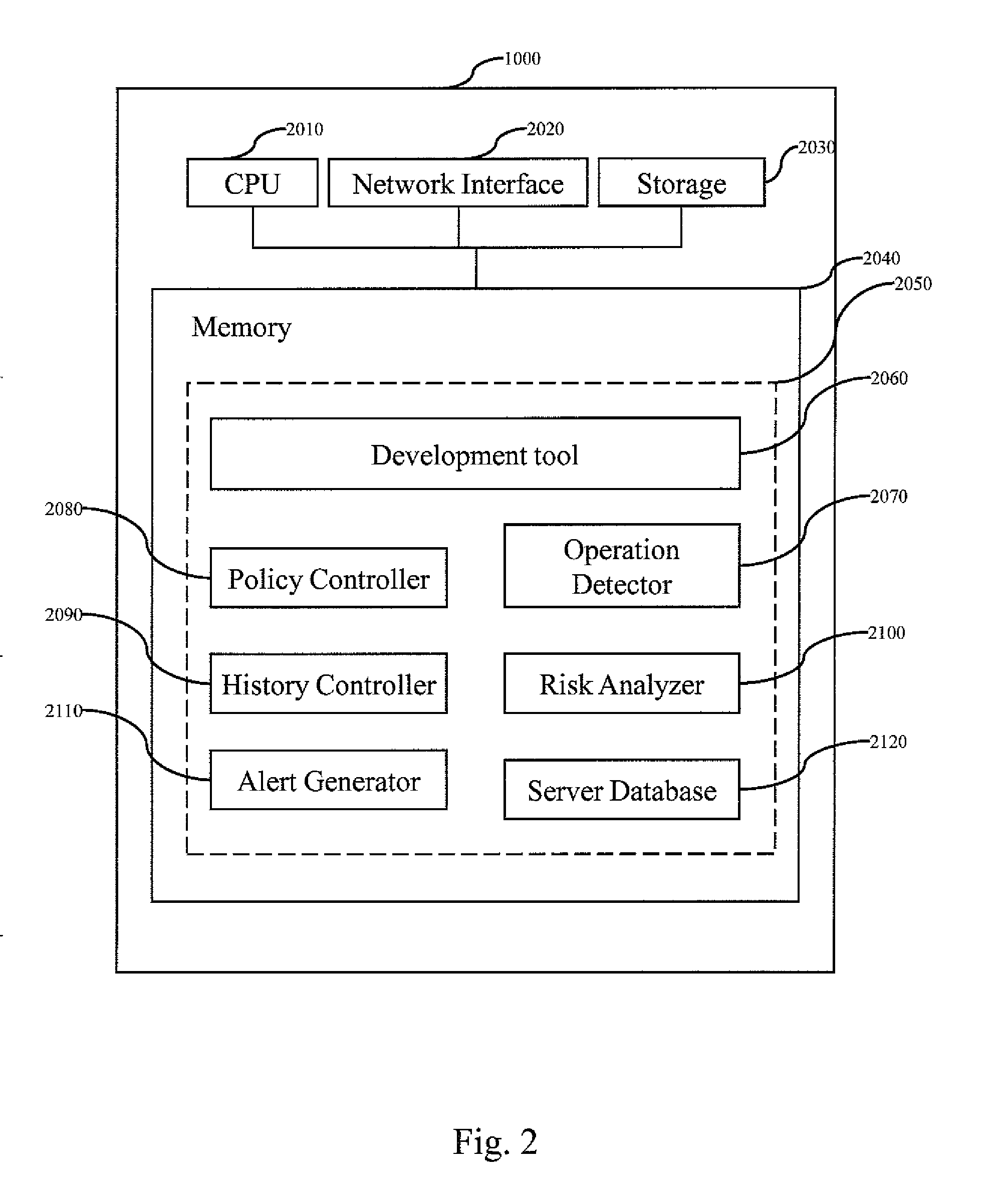
[0046]A source-related risk refers to any risk associated with source information. Source information refers to any information associated with source of an object, including content of the object, author / owner information of the object, a copyright or license term of the object, previous operations to the object, etc. Any improper operation on the source information may cause a source-related risk. For example, deletion of copyright information from open source code when used in software development is an improper operation and will result in a source-related risk (e.g., code pedigree). An object refers to hardware, software or service. The hardware includes, but is not limited to, a television, a radio, a computer, a watch, an air conditioner, a cellular phone, a pervasive digital device, etc. The software includes, but is not limited to, Microsoft® Windows®, FireFox, IBM® Informix®, etc. The service includes, but is not limited to, a child daycare service, gardening service, hous...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com