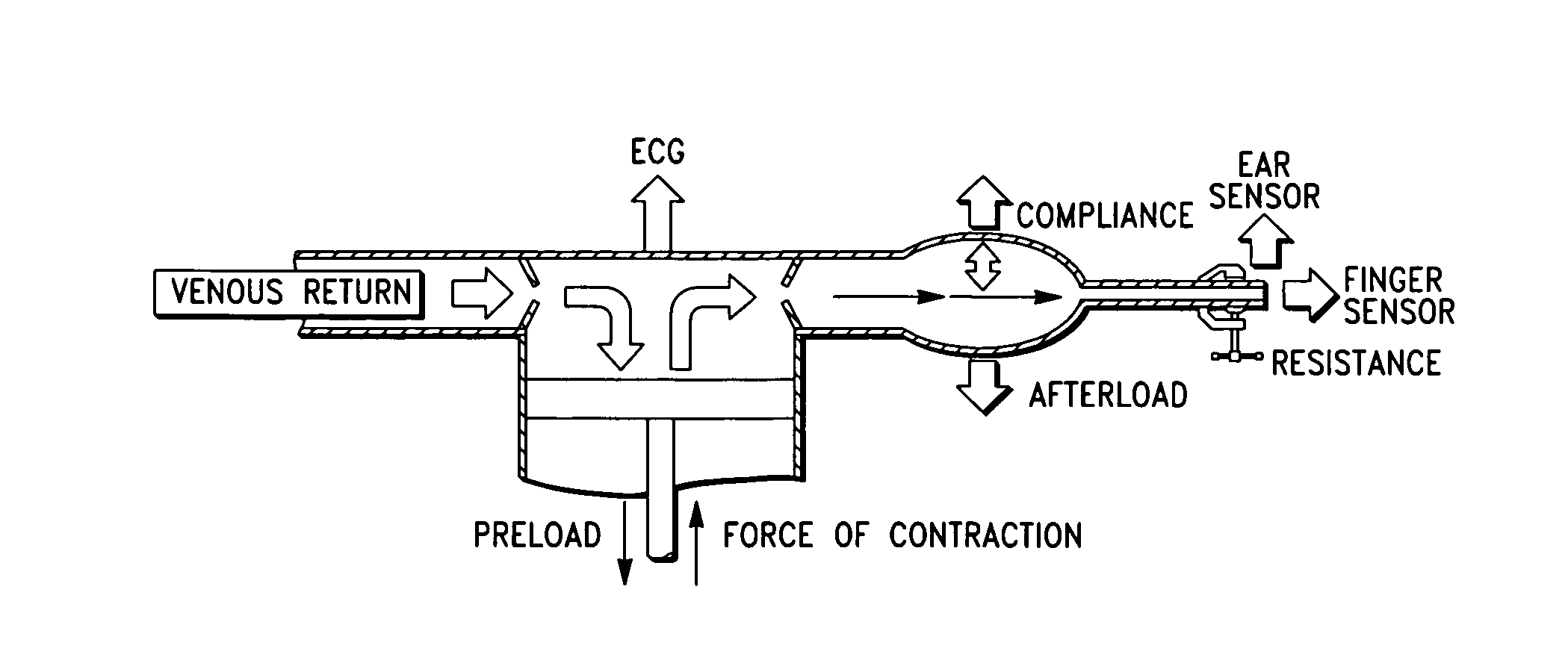
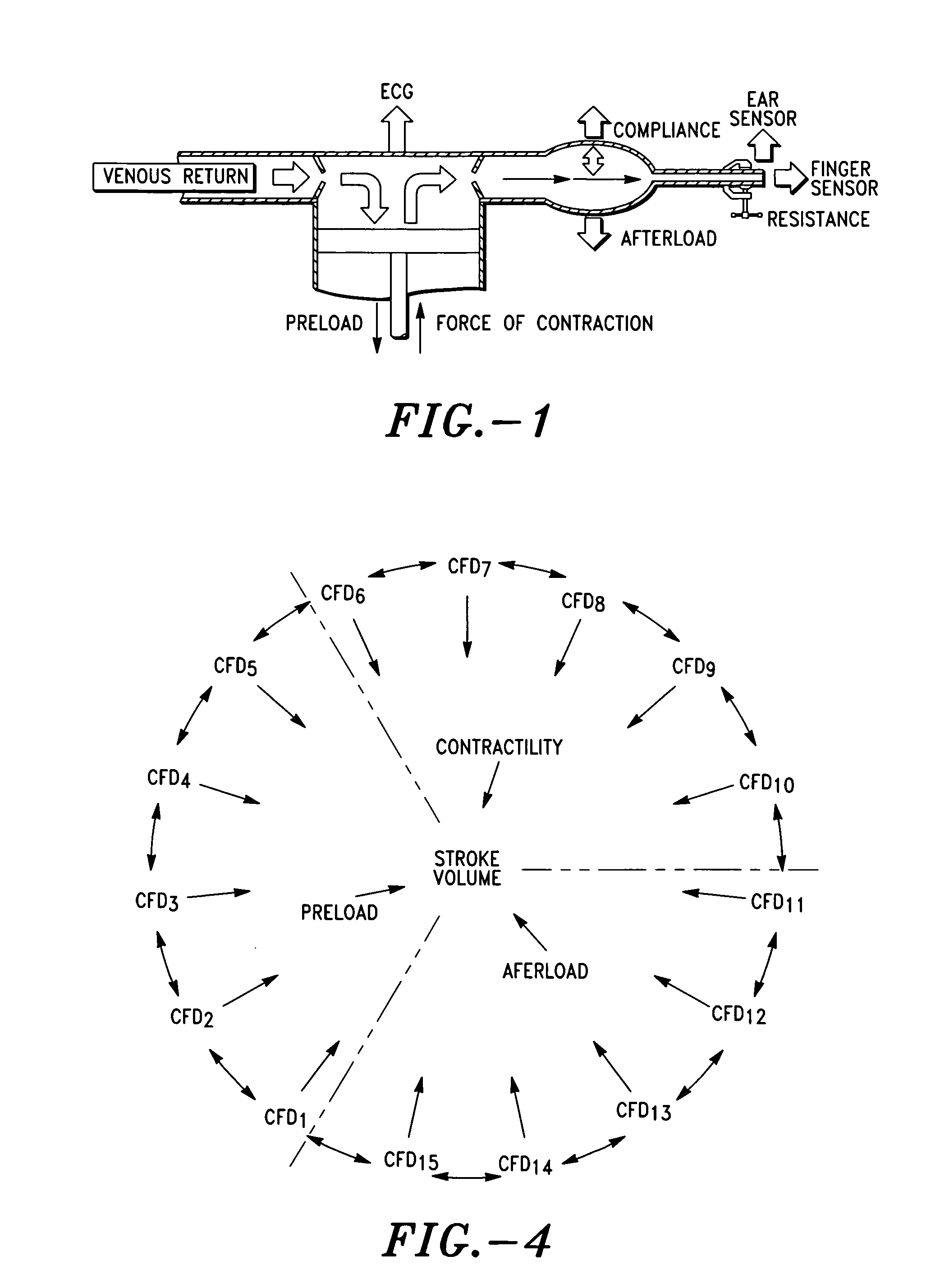
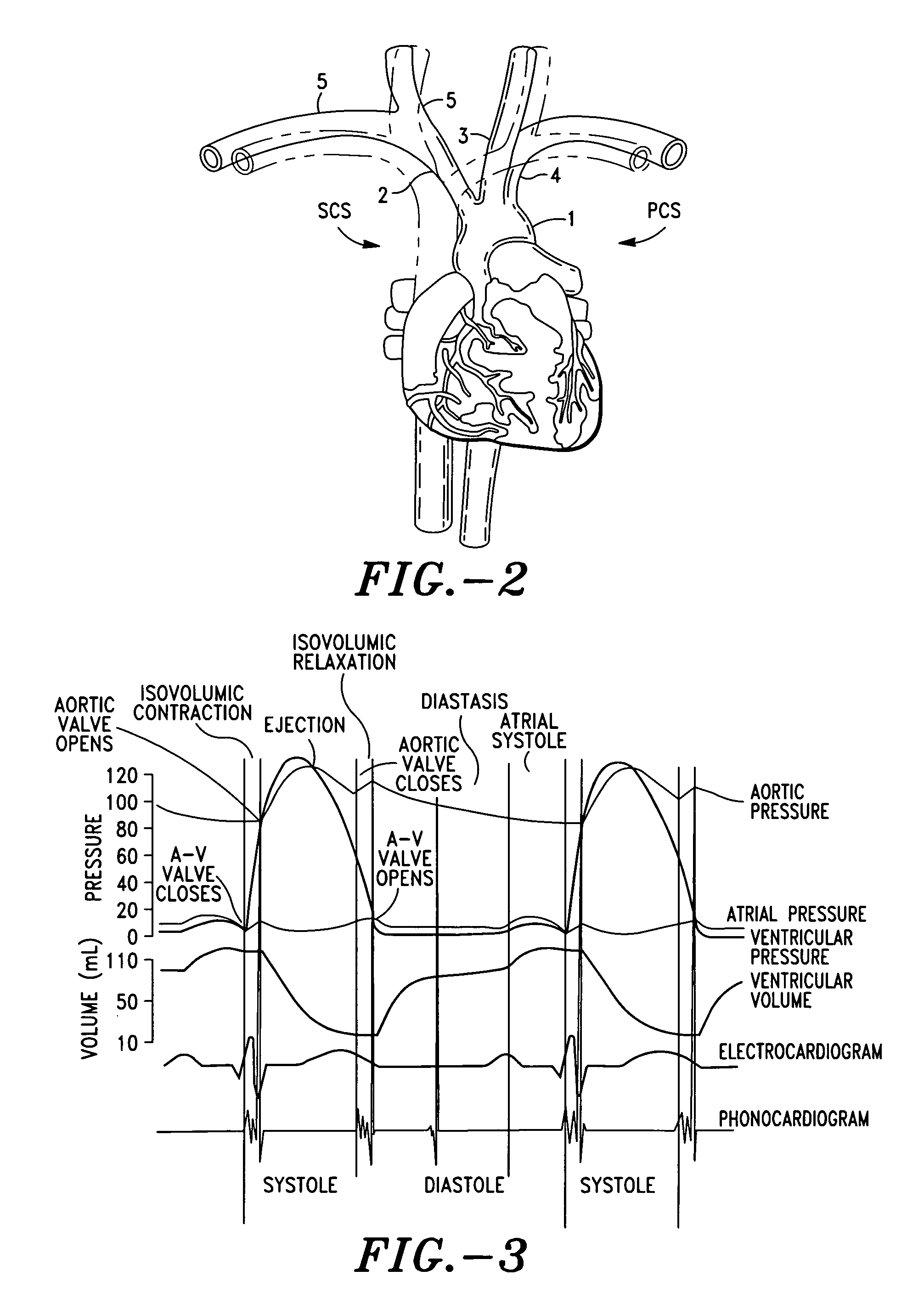
Method and system for determining cardiac performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0200]Referring now to Equation 7, there is shown a general empirical relationship of the invention that can be employed to derive an accurate estimation of cardiac stroke index (SI), i.e.
SI=α*LVET / PEP*((1−β)*(dv / dte,s) / (dv / dtf,s)*((dv / dte,s) / (dv / dte,d))) Eq. 7
where:[0201]LVET=left ventricular ejection time;[0202]PEP=pre-ejection period;[0203]α and β=variable constants that are measurement system-specific;[0204]dv / dte,s=the maximal systolic upslope of the plethysmogram signal obtained at the ear;[0205]dv / dtf,s=the maximal systolic upslope of the plethysmogram signal obtained at the finger; and[0206]dv / dte,d=the maximal diastolic down slope of the plethysmogram signal obtained at the ear.
[0207]In this example, the Stroke Index (SI) is determined (via Equation 7) by the product of three terms or determinants: (i) the ratio of ejection time from onset at the max change of systolic upslope to the max change of rate of slope in the diastolic down-slope divided by pre-ejection period, (i...
example 2
[0216]A primary, uncorrected estimate of strength of contraction is obtained from the systolic upstroke interval as the difference of amplitudes between 75% and 25% divided by the maximal systolic amplitude; the derived strength of contraction serving as variable (dv / dte,s) in Eq. 7, above.
example 3
[0217]An equivalent measure for strength of contraction as upstroke interval (as described in Example 1) is obtained by calculating the time difference of the QRS component to 75% of systolic upstroke and QRS component to 25% of systolic upstroke. This time measure of contraction is normalized by the ejection period (EP), as measured from onset of systolic upstroke, and defined as maximal rate of amplitude increase to the indication of dichrotic notch, as measured and defined as the maximal rate of amplitude decrease on the diastolic side; the derived strength of contraction similarly serving as variable (dv / dte,s) in Eq. 7, above.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com