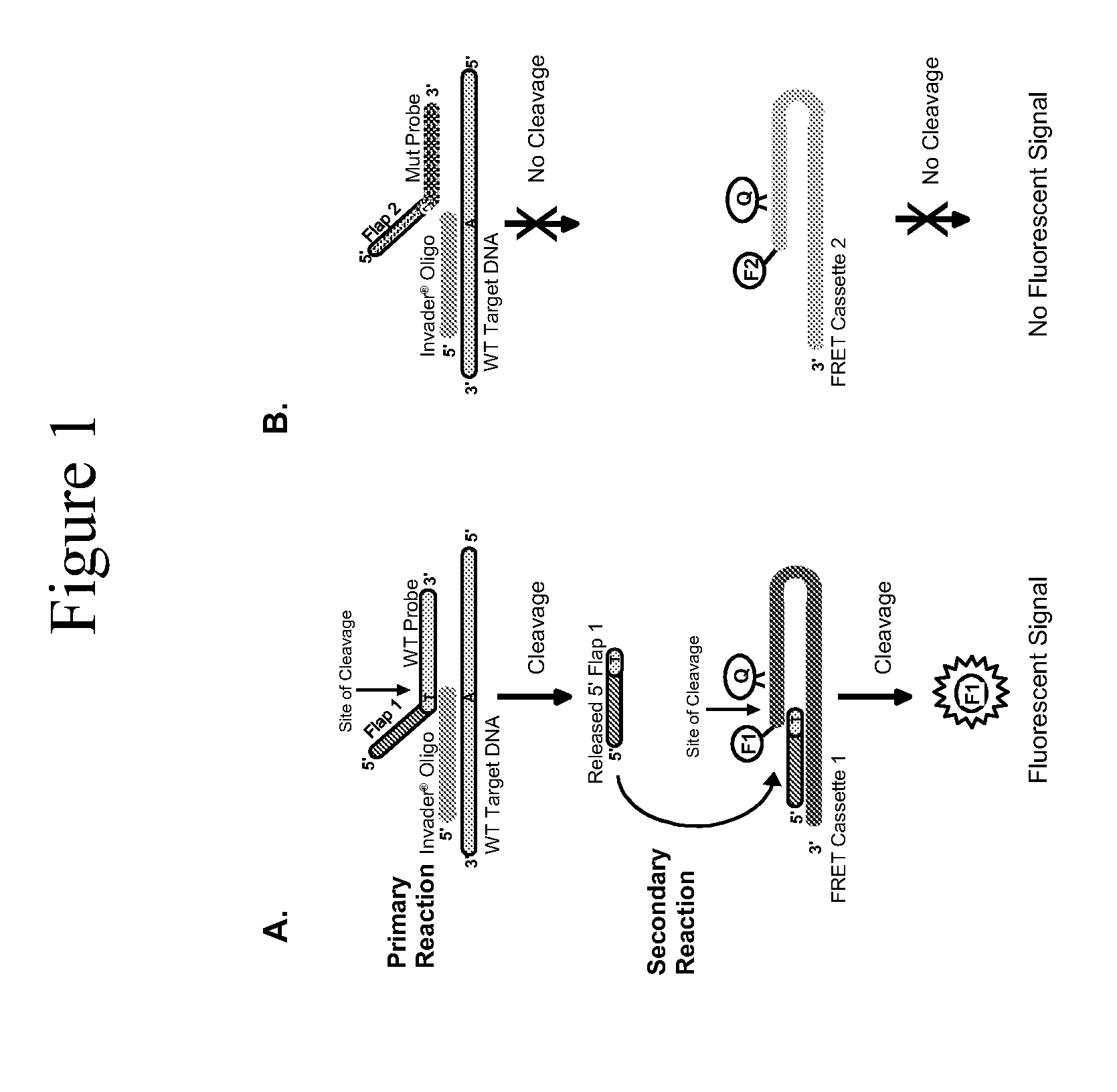
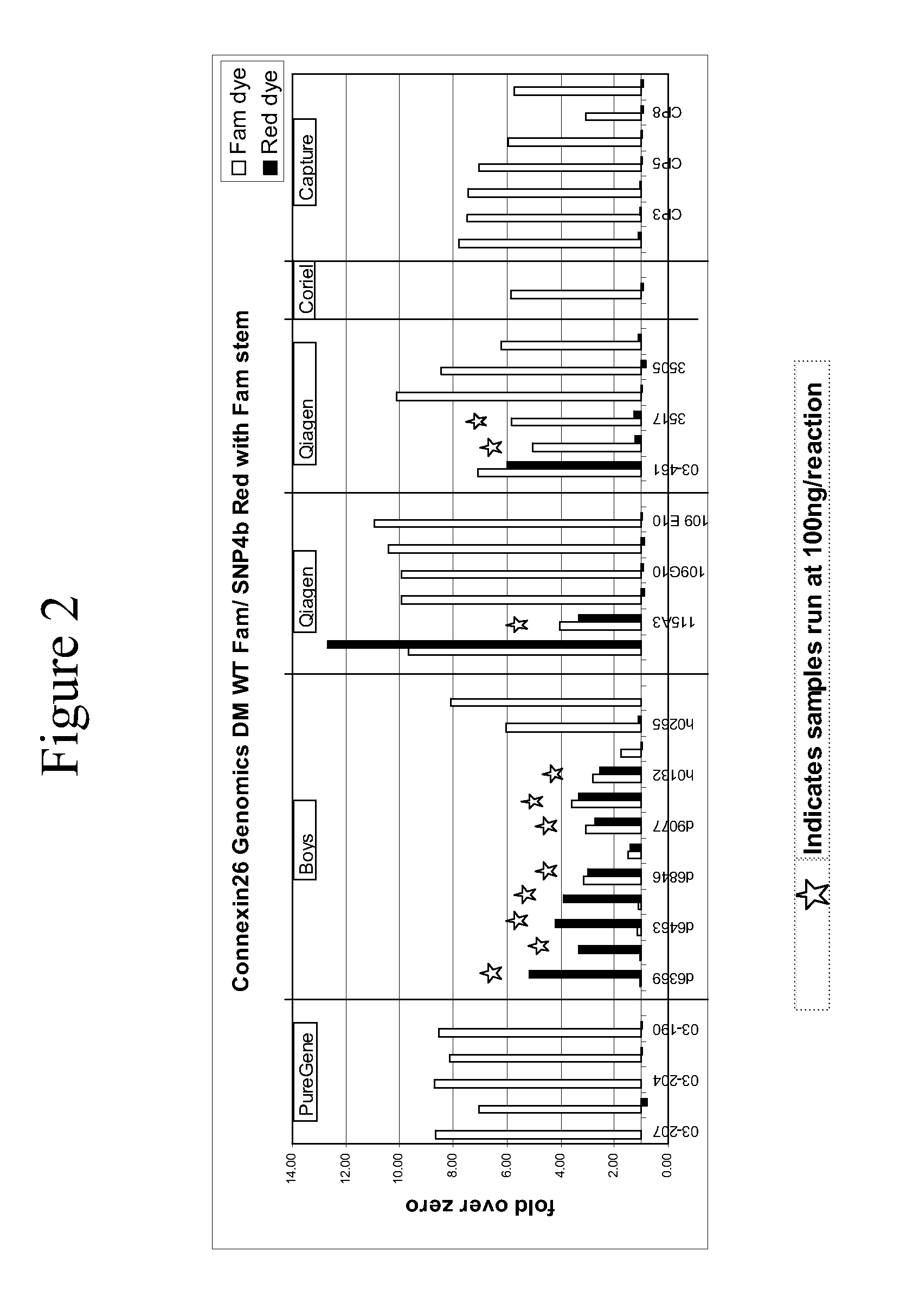
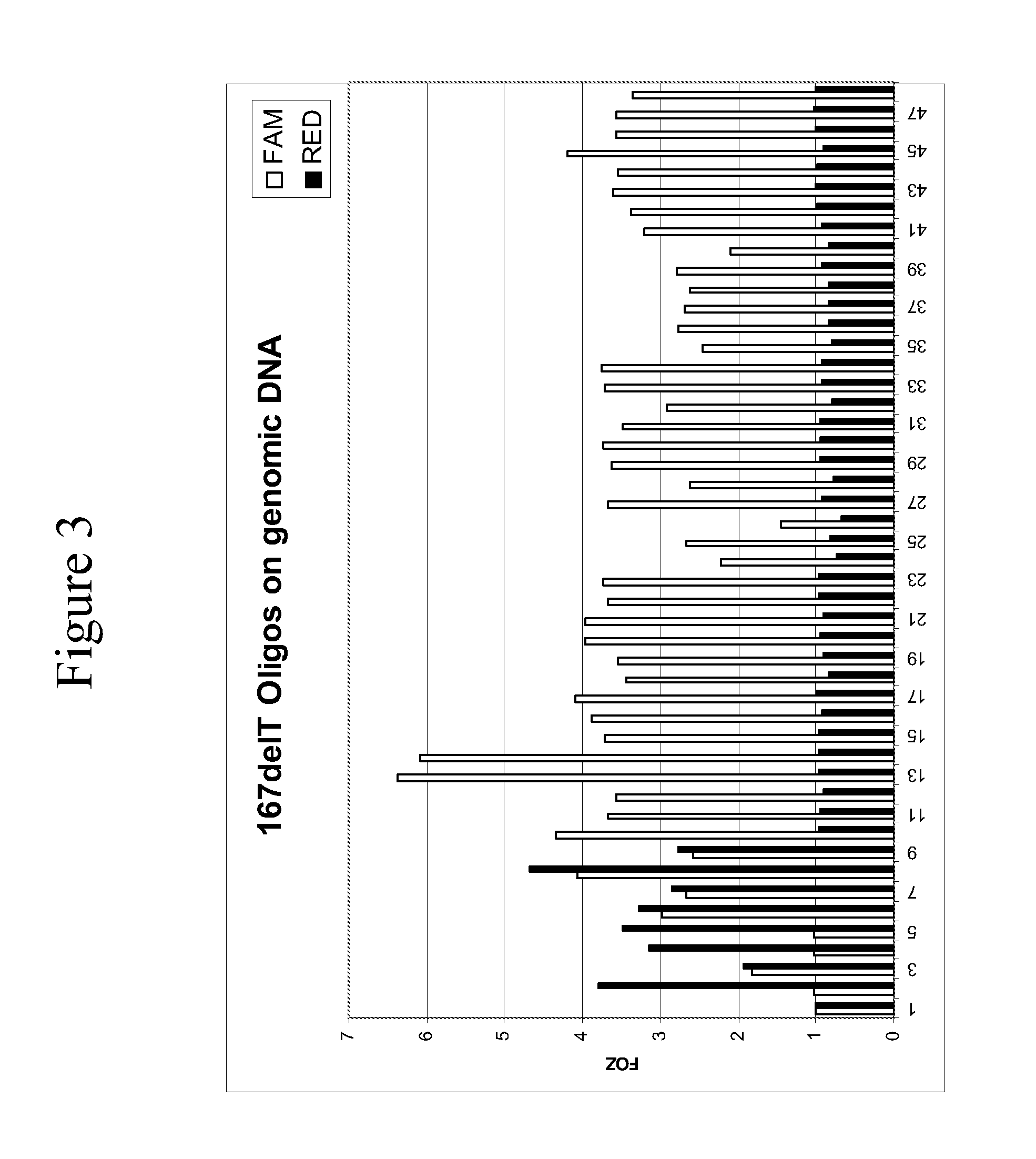
Connexin allele detection assays
a technology of allele detection and congenital hearing loss, applied in the field of congenital hearing loss mutation detection and characterization methods, can solve the problem that the method does not distinguish between true heterozygotes and compound heterozygotes, and achieve the effect of enhancing the raman effect or plasmon resonan
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Detection of the 30ΔG Mutation in Connexin 26 (GJB2)
[0162]This example describes detection of the 30ΔG, also referred to as the “35ΔG” mutation, as well as the corresponding wild type sequence, in genomic DNA isolated from blood samples using the INVADER assay. This example demonstrates that the INVADER assay can readily discriminate homozygous wild type, heterozygous, and homozygous mutant genotypes at this locus. This example further demonstrates that various sample preparation procedures are compatible with detection using the Invader assay.
[0163]To determine the compatibility of the INVADER assay with different sample preparation methods, four sample preparation techniques were tested: Gentra Systems PUREGENE Kit, Gentra Systems GENERATION Products, QIAGEN QIAAMP Blood Kit from buffycoat or from whole blood.
[0164]Each kit was used according to the manufacturer's protocols using approximately 6 ml of blood or 200 μl of buffycoat.
[0165]In addition, 12 genomic ...
example 2
Detection of the 167ΔT Mutation in Connexin 26 (GJB2)
[0175]This example describes detection of the 167ΔT mutation, as well as the corresponding wild-type sequence, in genomic DNA isolated from blood samples using the INVADER assay. This example demonstrates that the INVADER assay can readily discriminate homozygous wild type, heterozygous, and homozygous mutant genotypes at this locus. This example further demonstrates that various sample preparation procedures are compatible with detection using the Invader assay.
[0176]To determine the compatibility of the INVADER assay with different sample preparation methods, two sample preparation techniques were tested: Gentra Systems PUREGENE Kit was used to purify genomic DNA from whole blood and QIAGEN QIAAMP Blood Kit from was used to purify genomic DNA from buffycoat.
[0177]Each kit was used according to the manufacturer's protocols using approximately 6 mls of blood or 200 μl of buffycoat.
ii. INVADER Assay Reagents an...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com